Sporotrichoid Pattern
Sporotrichoid Pattern - Web sporotrichosis (also known as “rose gardener’s disease”) is an infection caused by a fungus called sporothrix. Web sporotrichosis is a fungal infection known for its distinct pattern of infectious skin nodules. Web a sporotrichoid pattern, or nodular lymphangitis, describes a distinctive clinical presentation in which inflammatory nodules spread linearly along the path of lymphatic drainage. Pulmonary and hematogenous involvement is uncommon. Web these may be restricted to one site (fixed pattern). Subsequent lesions arise proximally, that is, further up the arm, in an irregular, roughly linear, distribution. This form is typical of sporotrichosis but a similar clinical pattern can occur with other neglected tropical diseases such as cutaneous. Less commonly infection is caused by sporothrix brasiliensis, sporothrix globosa, sporothrix pallida, or sporothrix mexicana [ 1 ]. The lymphocutaneous route is the most common presentation of sporotrichosis and is sometimes described as sporotrichoid spread.it occurs following the implantation of spores in a wound. The lesions of sporotrichosis may present in 3 different patterns. Web sporotrichoid lymphocutaneous infection is an uncommon syndrome that is often misdiagnosed and improperly treated. Each lesion is an inflamed, irregular, firm nodule, which may. Web cutaneous, ulcerating, painless nodule on the hand and a classic sporotrichoid lymphangitic pattern spreading proximally up the arm. Web the sporotrichoid disease begins at a site of distal inoculation and leads to the development. Web a man in his 20s with well controlled crohn’s disease on infliximab (treated for four years) presented with a two year history of painful, crusted, and ulcerated nodules in a sporotrichoid (lymphangitic) distribution on the dorsum of his left hand and distal arm (fig 1). The classic pattern is described as “sporotrichoid” after the infection. The lymphocutaneous route is. The agent of choice is itraconazole [ 2 ]. Web sporotrichosis (also known as “rose gardener’s disease”) is an infection caused by a fungus called sporothrix. While working on a marsh prior to symptom onset, he noticed a splinter in his left. The lymphocutaneous route is the most common presentation of sporotrichosis and is sometimes described as sporotrichoid spread.it occurs. The lesions of sporotrichosis may present in 3 different patterns. By recognizing the distinct pattern of nodular lymphangitis and focusing on the diverse but limited etiologies, the physician can obtain the appropriate histologic and. Web sporotrichosis (also known as “rose gardener’s disease”) is an infection caused by a fungus called sporothrix. Web sporotrichosis is a cutaneous infection caused by the. Web cutaneous, ulcerating, painless nodule on the hand and a classic sporotrichoid lymphangitic pattern spreading proximally up the arm. Web nodular lymphangitis, also known as sporotrichoid lymphocutaneous infections, is characterized by suppurative inflammatory nodules along the lymphatic vessels. Web a sporotrichoid pattern describes a clinical presentation in which inflammatory nodules spread along the path of lymphatic drainage, being reported in. Sporotrichosis is caused by the acquisition of sporothrix schenckii, a dimorphic, saprophytic, and geophilic fungus. Biopsy of each lesion revealed a keratoacanthoma. Web cutaneous and lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis. Web nodular lymphangitis, also known as sporotrichoid lymphocutaneous infections, is characterized by suppurative inflammatory nodules along the lymphatic vessels. Web sporotrichosis is a cutaneous infection caused by the saprophytic mold sporothrix schenckii. This form is typical of sporotrichosis but a similar clinical pattern can occur with other neglected tropical diseases such as cutaneous. Web radiological patterns include cavitary disease, tracheobronchial lymph nodes enlargement, and nodular lesions. Pulmonary and hematogenous involvement is uncommon. While working on a marsh prior to symptom onset, he noticed a splinter in his left. Lesions usually appear on. Human infections typically occur several weeks after exposure of wounded skin to. Since most manifestations are subacute to chronic and localized, oral antifungal agents are usually preferred. Web sporotrichosis is a fungal infection known for its distinct pattern of infectious skin nodules. The lymphocutaneous route is the most common presentation of sporotrichosis and is sometimes described as sporotrichoid spread.it occurs. Web radiological patterns include cavitary disease, tracheobronchial lymph nodes enlargement, and nodular lesions. Web sporotrichosis is a fungal infection known for its distinct pattern of infectious skin nodules. Subsequent lesions arise proximally, that is, further up the arm, in an irregular, roughly linear, distribution. Human infections typically occur several weeks after exposure of wounded skin to. Web sporotrichosis is a. Acute infection is generally caused by streptococcal or staphylococcal bacteria. This form is typical of sporotrichosis but a similar clinical pattern can occur with other neglected tropical diseases such as cutaneous. Biopsy of each lesion revealed a keratoacanthoma. Web cutaneous, ulcerating, painless nodule on the hand and a classic sporotrichoid lymphangitic pattern spreading proximally up the arm. The lesions of. Web a sporotrichoid pattern describes a clinical presentation in which inflammatory nodules spread along the path of lymphatic drainage, being reported in association with several infectious, neoplastic, and inflammatory skin conditions. Human infections typically occur several weeks after exposure of wounded skin to. The classic pattern is described as “sporotrichoid” after the infection. Less commonly infection is caused by sporothrix brasiliensis, sporothrix globosa, sporothrix pallida, or sporothrix mexicana [ 1 ]. Web a man in his 20s with well controlled crohn’s disease on infliximab (treated for four years) presented with a two year history of painful, crusted, and ulcerated nodules in a sporotrichoid (lymphangitic) distribution on the dorsum of his left hand and distal arm (fig 1). The agent of choice is itraconazole [ 2 ]. Alternatively, the nodules may be arranged in lines along the course of lymphatic vessels (lymphocutaneous pattern), known as sporotrichoid spread. 1, 2 people get sporotrichosis by coming in contact with the fungal spores in the environment. Each lesion is an inflamed, irregular, firm nodule, which may. Web sporotrichoid‐lymphocutaneous‐pattern is classically seen in sporotrichosis, though also present in other infections like atypical mycobacteriosis and leishmaniasis. Although this fungal infection has been reported in semiarid environments, it is most typically. This manifestation is classic of sporotrichosis, however, other infections such as nocardiosis, atypical mycobacteriosis, leishmaniasis, among others, can also express. Web radiological patterns include cavitary disease, tracheobronchial lymph nodes enlargement, and nodular lesions. By recognizing the distinct pattern of nodular lymphangitis and focusing on the diverse but limited etiologies, the physician can obtain the appropriate histologic and. Since most manifestations are subacute to chronic and localized, oral antifungal agents are usually preferred. Treatment is with itraconazole or amphotericin b.
Figure 1 from A case of cutaneous nodules in a sporotrichoid pattern
Cureus Sporotrichoid Keratoacanthomas Case Report and Review of

Epidemiological, Clinical, and Histopathological Characteristics of
Sporotrichoid Pattern of Mycobacterium chelonaeabscessus Infection

Nodular lymphangitis Causes of Sporotrichoid Lesions GrepMed

Diagnosis of Mycobacterium marinum Infection with Sporotrichoid Pattern

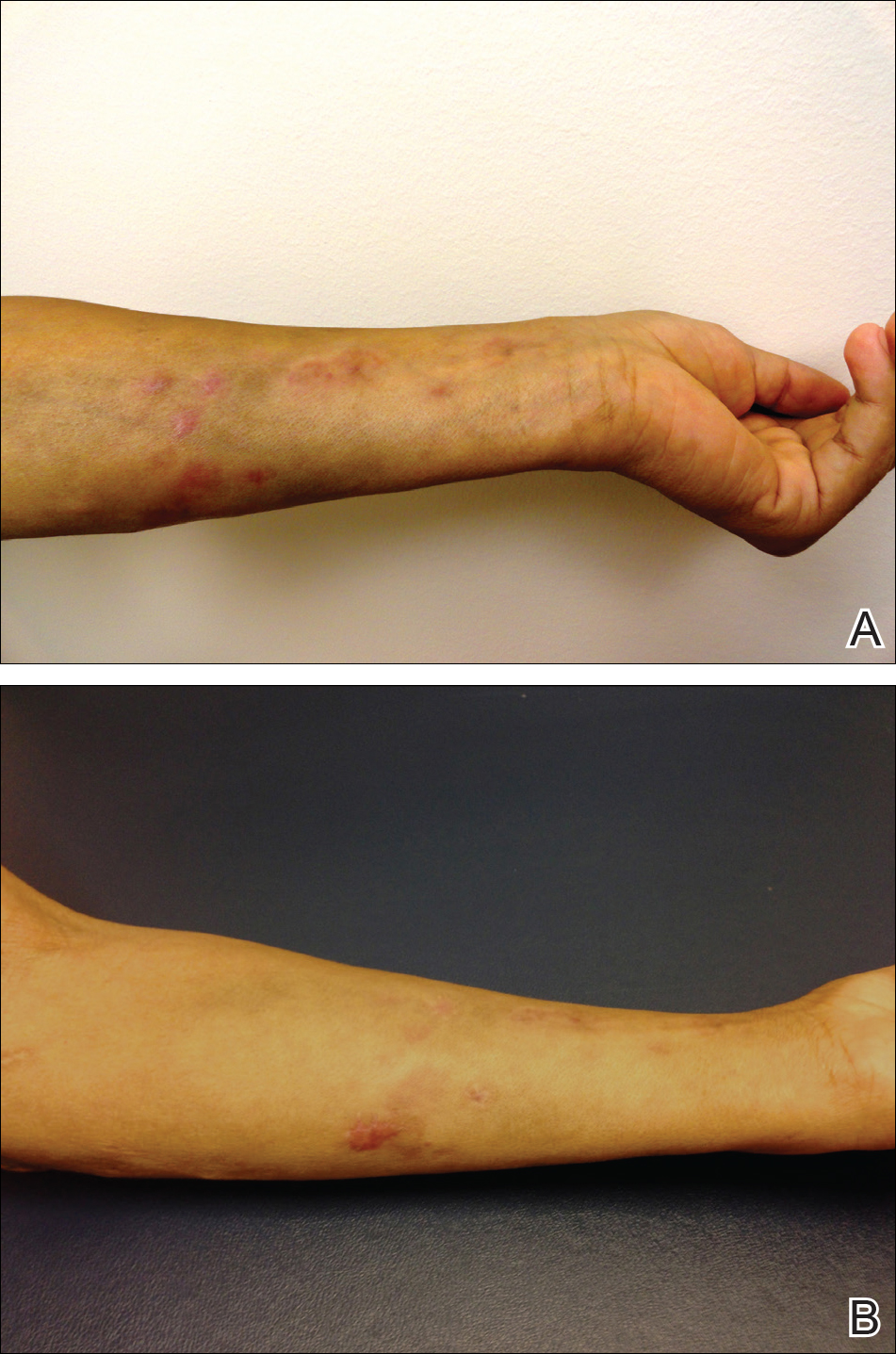
(a) Subcutaneous nodules over the left upper limb in a sporotrichoid
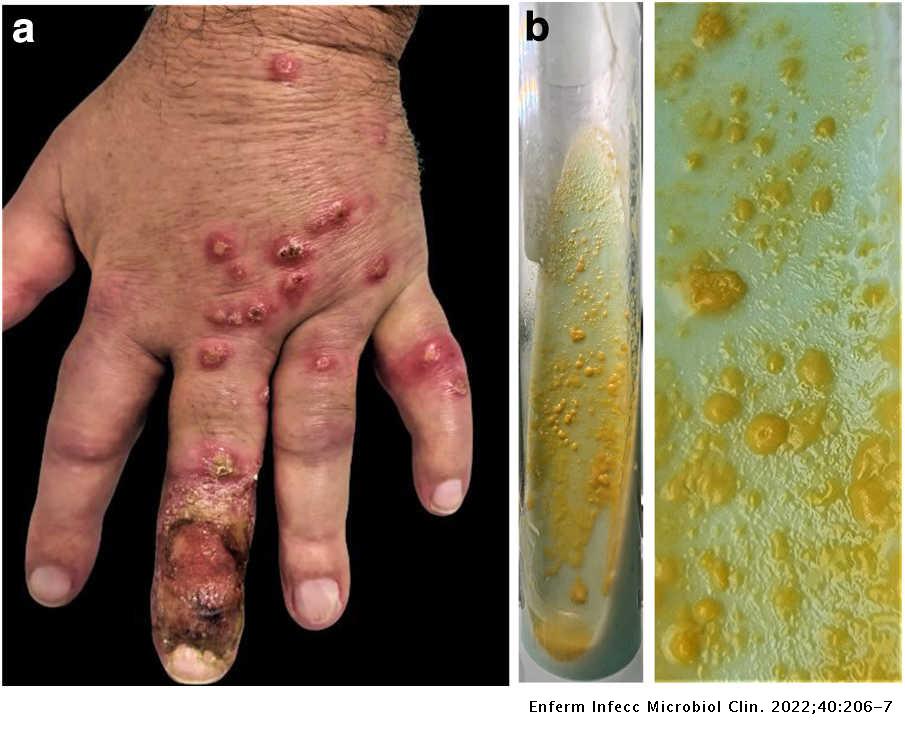
Cutaneous papules in a sporotrichoid pattern on the hand Enfermedades

(a) Clinical appearance of the left arm subcutaneous nodules with

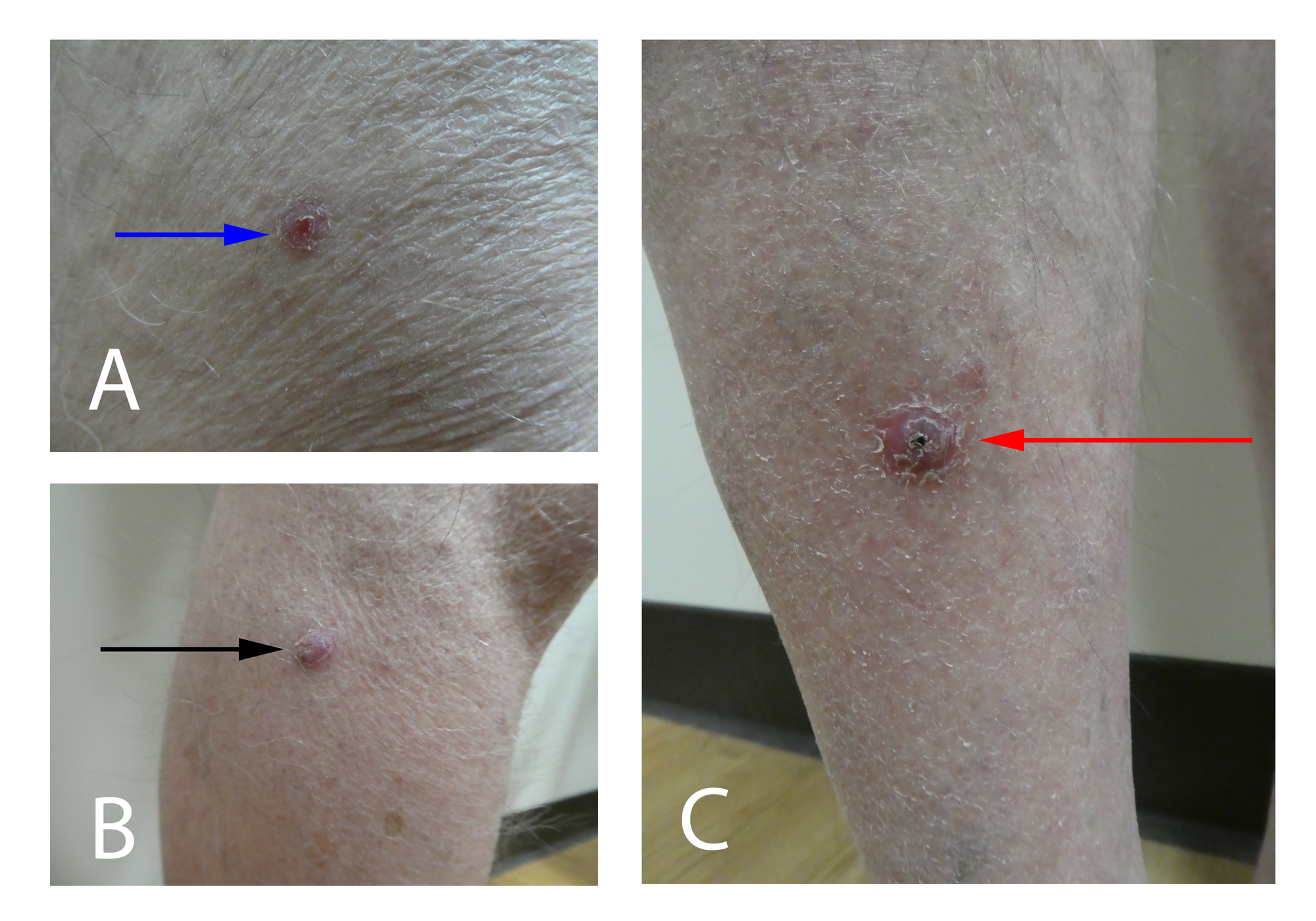
Acute Onset of Leg Nodules in a Sporotrichoid Pattern—Quiz Case
Web Infection With Sporotrichoid Pattern.
The Lesions Of Sporotrichosis May Present In 3 Different Patterns.
Infection Usually Involves Cutaneous And.
This Manifestation Is Classic Of Sporotrichosis, However, Other Infections Such As Nocardiosis, Atypical Mycobacteriosis, Leishmaniasis, Among Others, Can Also Express.
Related Post: