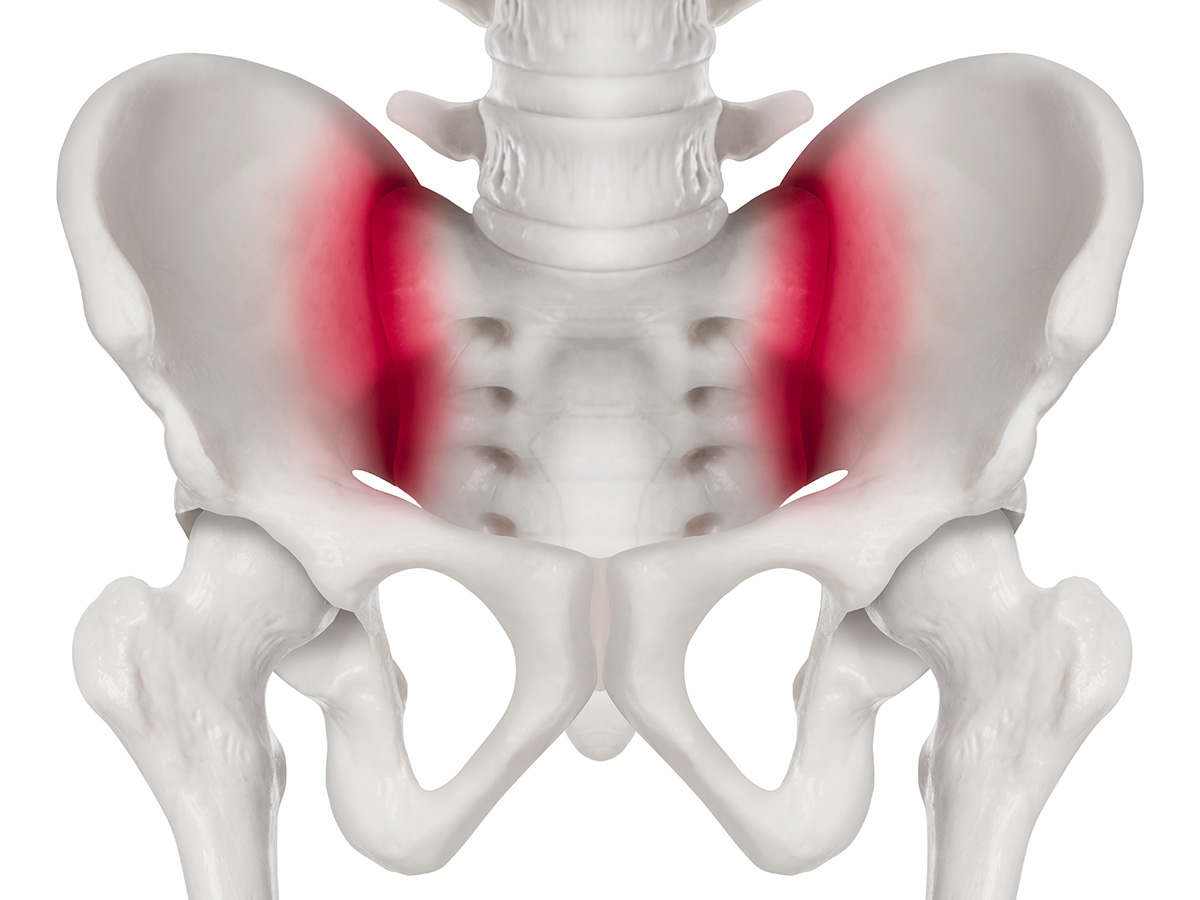
Si Joint Referred Pain Pattern
Si Joint Referred Pain Pattern - Pointing the finger to this area is the fortin finger test. Adjacent structures, such as the piriformis muscle,. The variable patterns of pain referral observed may arise for several reasons, including the joint's complex innervation, sclerotomal pain referral, irritation of adjacent structures, and varying. Referral patterns are important to understand in accurately diagnosing and treating sacroiliac joint dysfunction. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction describes pain due to abnormal movement (too much or too little) or misalignment of the si joint. Web sacroiliac joint pain can radiate to other areas of the body, making it challenging to pinpoint the exact source of the pain. Mechanical issues within the spine are commonplace, often stemming from everyday wear and tear or injuries. Pain arising from the si joint accounts for up to 25% of cases of lower back pain. Thus, it appears that it is precisely the combination of pain in the fortin area with exclusion of pain in the tuber area that argues for the presence of si joint pain. Web referred pain from the sacroiliac joint mainly dis tributes to the. Web referred pain from the sacroiliac joint mainly dis tributes to the. Web typically, referred pain is described as dull, aching, gnawing, annoying, drilling, or pressing ( 1, 55 ). Once present, referred pain tends to become fixed in a particular region, depending on the referral pattern ( 1, 55 ). The variable patterns of pain referral observed may arise. Pain arising from the si joint accounts for up to 25% of cases of lower back pain. Referral patterns are important to understand in accurately diagnosing and treating sacroiliac joint dysfunction. Mechanical issues within the spine are commonplace, often stemming from everyday wear and tear or injuries. Pain referral from the sacroiliac joint does not appear to be limited to. Pain referral from the sacroiliac joint does not appear to be limited to the lumbar region and buttock. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction describes pain due to abnormal movement (too much or too little) or misalignment of the si joint. Web patients with isolated si joint dysfunction often localize their pain inferior and medial to the psis. The range of. Web this information is then compared with presenting features of primary musculoskeletal disorders that have similar patterns of presentation. Web the primary pain patterns involve the neck, shoulders, low back, sacroiliac (si) joints and lateral hip with referred pain to the cervical/upper limb region, lumbar region, gluteal region, trochanteric, lateral thigh, posterior thigh and groin. If numbness and tingling or. Relationship between pain referral patterns a nd the source of chronic low back pain. Web the primary pain patterns involve the neck, shoulders, low back, sacroiliac (si) joints and lateral hip with referred pain to the cervical/upper limb region, lumbar region, gluteal region, trochanteric, lateral thigh, posterior thigh and groin. The range of motion in the sij is small, less. The variable patterns of pain referral observed may arise for several reasons, including the. Once present, referred pain tends to become fixed in a particular region, depending on the referral pattern ( 1, 55 ). Referral patterns are important to understand in accurately diagnosing and treating sacroiliac joint dysfunction. One common referral pattern is pain or discomfort in one or. Web the evidence favoring the perspective that mechanical sij dysfunctions are related to the experience of back and referred pain is less than convincing, despite the volume of papers published on the subject 12, 13. Mechanical issues within the spine are commonplace, often stemming from everyday wear and tear or injuries. Sacroiliitis can cause pain and stiffness in the buttocks. Web sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a term used to describe the pain of the sacroiliac joint (si joint). The pain is typically described as a nearly constant dull ache with episodic stabbing pain. Pointing the finger to this area is the fortin finger test. Once present, referred pain tends to become fixed in a particular region, depending on the referral. Standing or sitting for a long time or climbing stairs can. Web however, the specific areas of innervation of these nerves remain up for debate, which may account for the varying patterns in referred pain of the si joint. Web characterized by minor pathology causing abnormal motion and resultant pain. Sacroiliac pain can be aggravated with prolonged sitting or standing,. Pain patterns of the chest, back, shoulder, scapula, pelvis, hip, groin, and sacroiliac (si) joint are the most common sites of referred pain from a systemic disease process. Web sacroiliac joint pain is most commonly felt in the low back and buttock but can also be referred into the thigh and leg. Adjacent structures, such as the piriformis muscle,. The. These joints can become sources of pain due to factors like arthritis, back injuries, or mechanical stress. Web the primary pain patterns involve the neck, shoulders, low back, sacroiliac (si) joints and lateral hip with referred pain to the cervical/upper limb region, lumbar region, gluteal region, trochanteric, lateral thigh, posterior thigh and groin. Web pain referral from the sacroiliac joint does not appear to be limited to the lumbar region and buttock. Pain referral from the sacroiliac joint does not appear to be limited to the lumbar region and buttock. Web the evidence favoring the perspective that mechanical sij dysfunctions are related to the experience of back and referred pain is less than convincing, despite the volume of papers published on the subject 12, 13. One common referral pattern is pain or discomfort in one or both buttocks. Web typically, referred pain is described as dull, aching, gnawing, annoying, drilling, or pressing ( 1, 55 ). ( 31 ) conducted a prevalence study in 54 patients with unilateral lbp using a series of blocks done with different la based on international spinal injection society guidelines ( 32 ). Once present, referred pain tends to become fixed in a particular region, depending on the referral pattern ( 1, 55 ). Web sacroiliac joint pain can radiate to other areas of the body, making it challenging to pinpoint the exact source of the pain. Referral patterns are important to understand in accurately diagnosing and treating sacroiliac joint dysfunction. The variable patterns of pain referral observed may arise for several reasons, including the joint's complex innervation, sclerotomal pain referral, irritation of adjacent structures, and varying. Web sacroiliac joint pain is most commonly felt in the low back and buttock but can also be referred into the thigh and leg. Relationship between pain referral patterns a nd the source of chronic low back pain. If numbness and tingling or weakness is present, an alternative diagnosis should be considered. Sacroiliac pain can be aggravated with prolonged sitting or standing, standing on one leg, stair climbing, going from sit to.
Causes and Effects of Sacroiliac Joint Pain? Expert Guide Oklahoma

SI Joint Pain The Complete Injury Guide Vive Health
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction Dr Yu Chao Lee

SI Joint Pain Symptoms & Treatment Options Florida Surgery Consultants
Sacroiliac joint pain London Neurosurgery Partnership Spine

The Causes of SI Joint Pain and Dysfunction Somatic Movement Center
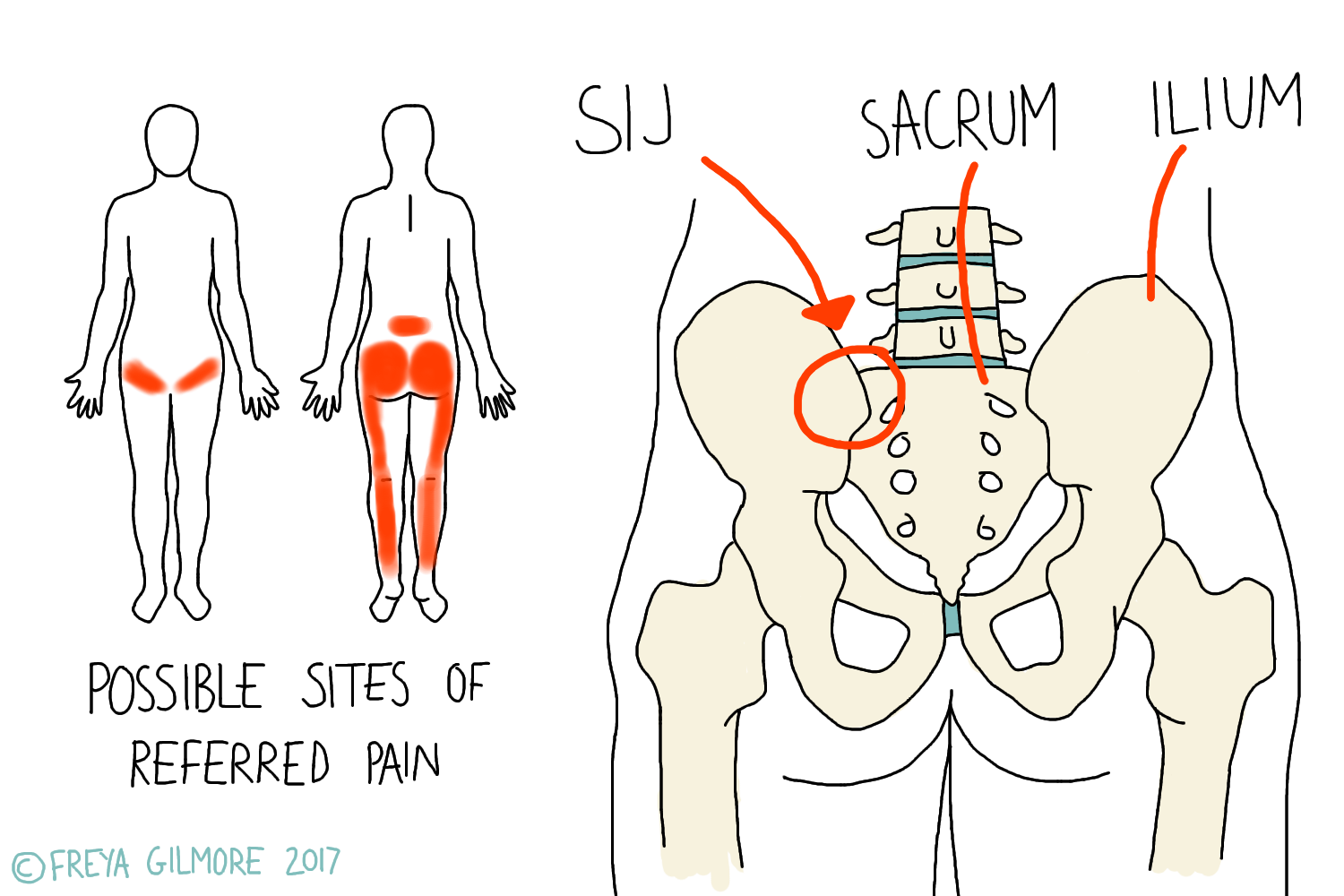
The Sacroiliac Joint (SIJ) Beth Forrest Osteopathy

Sacroiliac (SI) Joint Pain EVERYTHING YOU SHOULD KNOW YouTube

Pain referral from the sacroiliac joint. Van der Wurff et al., 2006 [33

Sacroiliac Joint Pain Explainer ChiroUp EvidenceBased Chiropractic
Web Referred Pain From The Sacroiliac Joint Mainly Dis Tributes To The.
Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome Is A Significant Source Of Pain In 15% To 30% Of People With Mechanical Low Back Pain.
The Variable Patterns Of Pain Referral Observed May Arise For Several Reasons, Including The.
Adjacent Structures, Such As The Piriformis Muscle,.
Related Post: