Osteosarcoma Sunburst Pattern
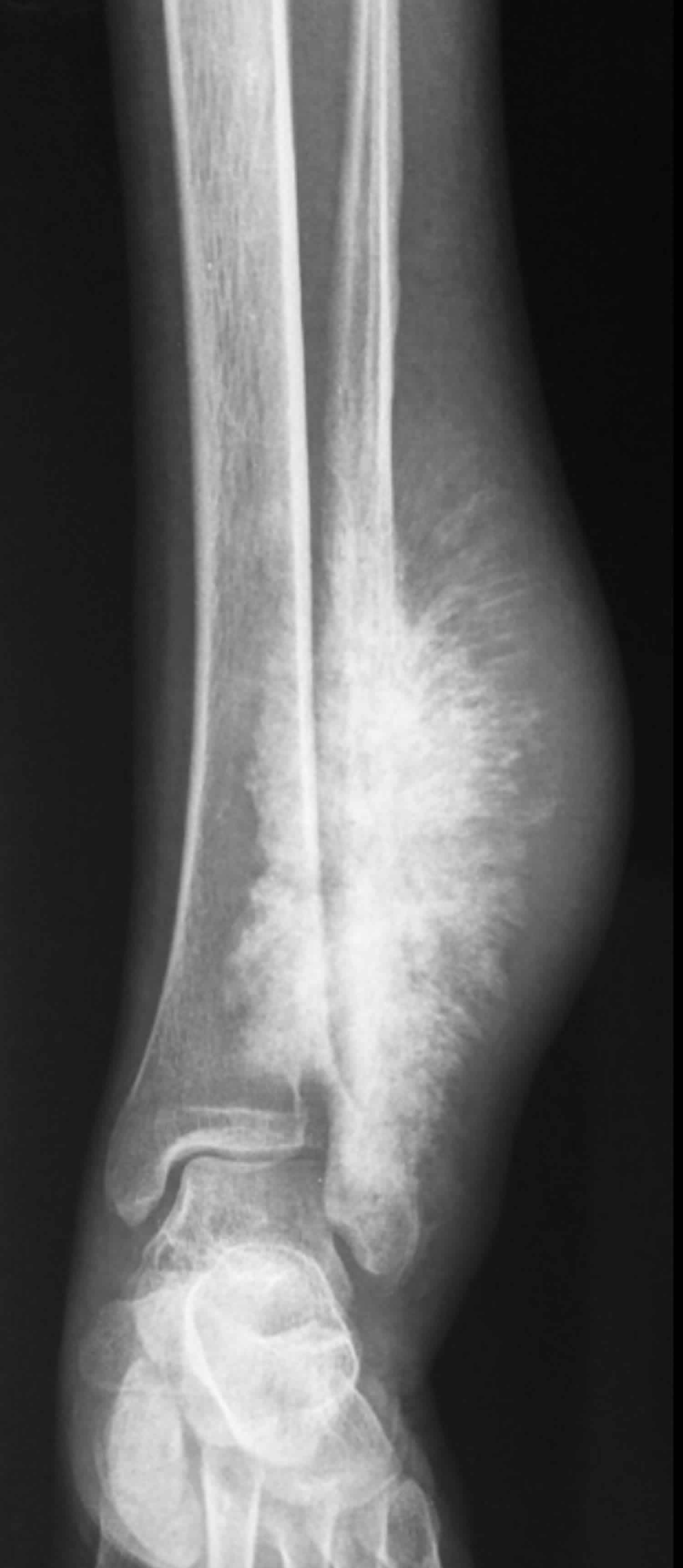
Osteosarcoma Sunburst Pattern - However, the sunburst pattern may also be seen in hemolytic anemias, thalassemia, and sickle cell anemia. Web reactive new bone formation may be seen under the periosteum forming a “codman angle,” or “codman’s triangle,” and invasion into adjacent soft tissues may produce a “sunburst” pattern of. The sunburst appearance occurs when the lesion grows too fast. (b) ultrasound of same patient in (a) showing cortical destruction and boney mass. A pathologic fracture may be seen through the abnormal bone. The codman triangle is another sign indicating an aggressive process. Summarize the pathophysiology of primary and secondary forms of osteosarcoma. Web the most common types of periosteal response encountered with osteosarcoma are the “sunburst” type and a codman triangle; Web osteosarcoma is usually sclerotic, involves the metaphysis, and has periosteal new bone formation (sunburst pattern), whereas ewing sarcoma is usually lytic, located in the diaphysis, and displays an onion skin effect. Web the radial sunburst pattern is a classic sign of osteosarcoma and affects mainly mineralized osteoid. Web sunburst type codman triangle lamellated (onion skin) reaction tumor matrix ossification / calcification soft tissue involvement low grade central osteosarcoma (radiographics 2010;30:1653, skeletal radiol 2004;33:373): Osteogenic sarcoma is the most common primary malignant bone tumor with an annual incidence of 900 cases in the united states. Web this pattern describes a lytic lesion with periosteal reaction and cortical disruption. Web reactive new bone formation may be seen under the periosteum forming a “codman angle,” or “codman’s triangle,” and invasion into adjacent soft tissues may produce a “sunburst” pattern of. Web the conventional plain radiograph is the best for probable diagnosis as it describes features like sun burst appearance, codman's triangle, new bone formation in soft tissues along with permeative. Web sunburst pattern due to new bone formation in soft tissue prognostic factors complete surgical resection with wide margins has been reported as the most significant prognostic factor Web in conventional osteosarcoma, the tumour invades the periosteum to give rise to the classic ‘sunburst appearance’, caused by many thin irregular spicules of new bone developing outwards from. It’s also important. Web in conventional osteosarcoma, the tumour invades the periosteum to give rise to the classic ‘sunburst appearance’, caused by many thin irregular spicules of new bone developing outwards from. Web the most common types of periosteal response encountered with osteosarcoma are the “sunburst” type and a codman triangle; Summarize the pathophysiology of primary and secondary forms of osteosarcoma. Adolescence and. Web the sunburst appearance occurs when the lesion grows too fast and the periosteum does not have enough time to lay down a new layer and instead the sharpey's fibers stretch out perpendicular to the bone. When a bone lesion grows too quickly, the membrane covering the affected bone’s outer surface (the periosteum) may not have enough time to lay. The codman triangle is another sign indicating an aggressive process. Web the radial sunburst pattern is a classic sign of osteosarcoma and affects mainly mineralized osteoid. Web sunburst type codman triangle lamellated (onion skin) reaction tumor matrix ossification / calcification soft tissue involvement low grade central osteosarcoma (radiographics 2010;30:1653, skeletal radiol 2004;33:373): Most commonly affecting the metaphysis of bone. Summarize. Identify the typical imaging findings associated with osteosarcoma. A pathologic fracture may be seen through the abnormal bone. The lamellated (onionskin) type of reaction is less frequently seen ( fig. In the past, computed tomography (ct) was an indispensable technique for evaluating these tumors ( fig. Web some osteosarcomas show a periosteal reaction manifesting as a sunburst pattern caused by. Web this article reviews the cause, clinical presentation, diagnostic methods, and management of osteosarcoma, the most common primary bone tumor and third most common cancer among children and adolescents. Web reactive new bone formation may be seen under the periosteum forming a “codman angle,” or “codman’s triangle,” and invasion into adjacent soft tissues may produce a “sunburst” pattern of. Web. Web reactive new bone formation may be seen under the periosteum forming a “codman angle,” or “codman’s triangle,” and invasion into adjacent soft tissues may produce a “sunburst” pattern of. Review the treatment considerations for patients with osteosarcoma. Identify the typical imaging findings associated with osteosarcoma. Web some osteosarcomas show a periosteal reaction manifesting as a sunburst pattern caused by. Adolescence and adults > 65 years of age. Web reactive new bone formation may be seen under the periosteum forming a “codman angle,” or “codman’s triangle,” and invasion into adjacent soft tissues may produce a “sunburst” pattern of. This activity reviews the role of the interprofessional team in history and physical examination, laboratory evaluation, and management. It is frequently associated. Web it’s important to distinguish a sunburst periosteal reaction from a sunburst (or honeycomb) trabeculation, which is a different type of finding indicating an intraosseous hemangioma. This activity reviews the role of the interprofessional team in history and physical examination, laboratory evaluation, and management. Web in conventional osteosarcoma, the tumour invades the periosteum to give rise to the classic ‘sunburst appearance’, caused by many thin irregular spicules of new bone developing outwards from. Web sunburst type codman triangle lamellated (onion skin) reaction tumor matrix ossification / calcification soft tissue involvement low grade central osteosarcoma (radiographics 2010;30:1653, skeletal radiol 2004;33:373): Web the conventional plain radiograph is the best for probable diagnosis as it describes features like sun burst appearance, codman's triangle, new bone formation in soft tissues along with permeative pattern of destruction of the bone and other characteristics for specific subtypes of osteosarcomas. Review the treatment considerations for patients with osteosarcoma. Osteogenic sarcoma is the most common primary malignant bone tumor with an annual incidence of 900 cases in the united states. Web sunburst pattern due to new bone formation in soft tissue prognostic factors complete surgical resection with wide margins has been reported as the most significant prognostic factor Formation of new bone in a sunburst pattern; It is frequently associated with osteosarcoma but can also occur with ewing sarcoma or osteoblastic metastases. It’s also important to distinguish both of these sunburst patterns from the sunburst sign of meningioma vascularity. When a bone lesion grows too quickly, the membrane covering the affected bone’s outer surface (the periosteum) may not have enough time to lay down a new layer. Summarize the pathophysiology of primary and secondary forms of osteosarcoma. Web the associated soft tissue mass can exhibit variable patterns of ossification, leading to the characteristic radial sunburst pattern often associated with osteosarcoma. 1, 2 early diagnosis and complete tumor resection are mandatory to improve the prognosis of jaw os. In the past, computed tomography (ct) was an indispensable technique for evaluating these tumors ( fig.OrthoInfo AAOS
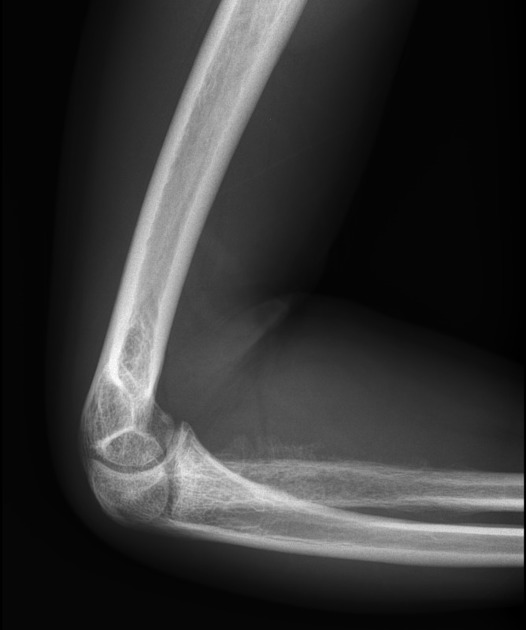
Sunburst appearance (bone) pacs
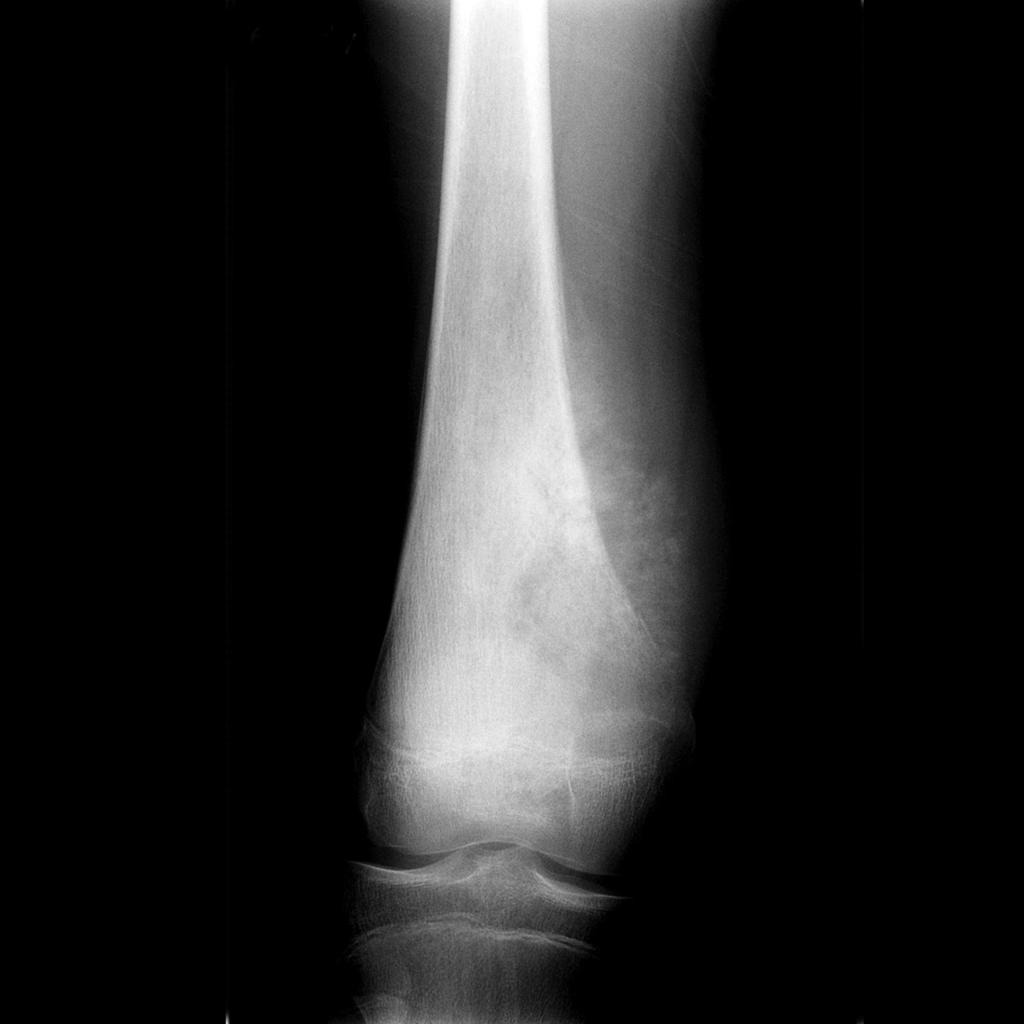
Sunray Appearance
Sunburst periosteal reaction Image
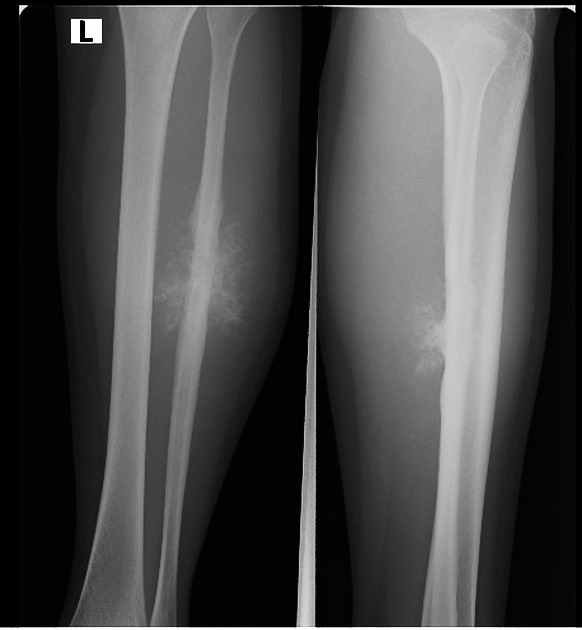
sunburst appearance pacs

Xray Sunburst
Typical 'sunburst' appearance as the tumor soft tissue as it

Malignant Bone Tumors Oncology Medbullets Step 1
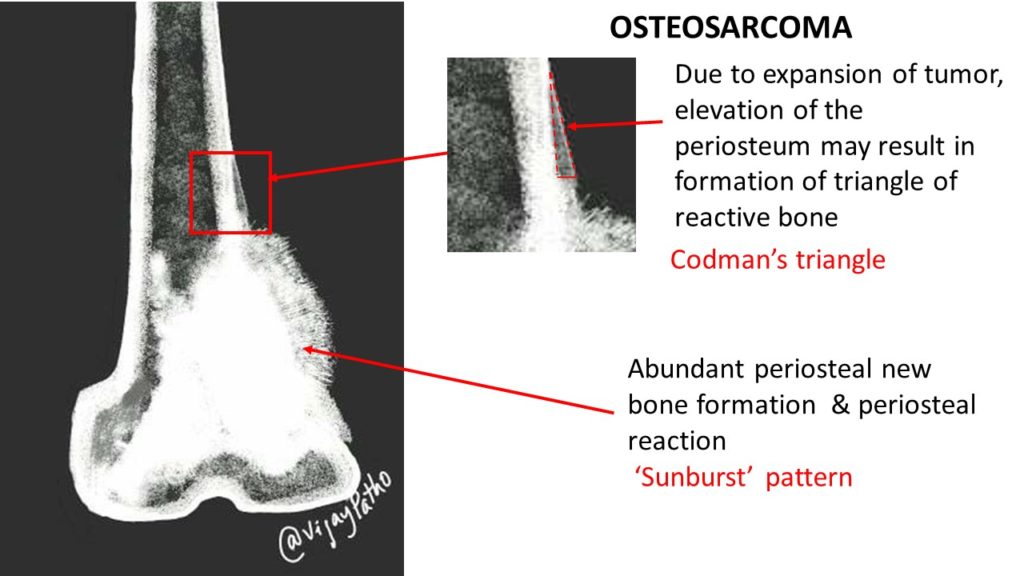
Pathological features Pathology Made Simple
Periosteal reaction & types of periosteal reaction
Web Radiologic Depiction Of A Sunburst Pattern Of New Bone Formation Is Characteristic.
Localized Widening Of The Periodontal Ligament Space Of 1 Or 2 Teeth In The Absence Of Dental Disease May Occur In An Early Stage Of Osteosarcoma.
Web This Article Reviews The Cause, Clinical Presentation, Diagnostic Methods, And Management Of Osteosarcoma, The Most Common Primary Bone Tumor And Third Most Common Cancer Among Children And Adolescents.
Malignant Bone Tumor Secondary To Overproduction Of Osteoid Cells By Malignant Cells.
Related Post:
