Interference Pattern Equation
Interference Pattern Equation - Each line can be described as a relatively. Web to find the angle of diffraction, take the inverse sine of the ratio of the wavelength to the distance between the slits. Suppose we are given two waves, ψψ 11(xt, ) = 0sin(k 1x±+ω 1t φ 1), ψ22(,xt)=ψ0sin(k2x±ω2t+φ2) (14.1.1) the resulting wave is simply ψ(,xt)=±ψ10 sin(kx1. Destructive interference happens when two. Web these conditions can be expressed as equations: Web we have sinθ = z/ (l 2 + z 2) ½ and λ = zd/ (m (l 2 + z 2) ½ ), where z is the distance from the center of the interference pattern to the mth bright line in the pattern. Web the formula for the sum of two waves can be derived as follows: Difference between diffraction grating and double slits. Web the equations for double slit interference imply that a series of bright and dark lines are formed. The two special cases of superposition that produce the simplest results are pure constructive interference and pure destructive interference. (constructive interference) δ l = m λ , for m = 0 , ± 1 , ± 2 , ± 3. Displacement y = (order m x wavelength x distance d )/ ( slit separation. Web we have sinθ = z/ (l 2 + z 2) ½ and λ = zd/ (m (l 2 + z 2) ½ ), where. Web to find the angle of diffraction, take the inverse sine of the ratio of the wavelength to the distance between the slits. For vertical slits, the light spreads out horizontally on either side of the incident. Destructive interference happens when two. Web the equations for double slit interference imply that a series of bright and dark lines are formed.. For vertical slits, the light spreads out horizontally on either side of the incident. Difference between diffraction grating and double slits. Web the equations for double slit interference imply that a series of bright and dark lines are formed. For vertical slits, the light spreads out horizontally on either side of the incident beam into. Hyperphysics ***** light and vision. For vertical slits, the light spreads out horizontally on either side of the incident. Web these conditions can be expressed as equations: Δ l = m λ , for m = 0 , ± 1 , ± 2 , ± 3. If l >> z then (l. Suppose we are given two waves, ψψ 11(xt, ) = 0sin(k 1x±+ω 1t. Displacement y = (order m x wavelength x distance d )/ ( slit separation. Suppose we are given two waves, ψψ 11(xt, ) = 0sin(k 1x±+ω 1t φ 1), ψ22(,xt)=ψ0sin(k2x±ω2t+φ2) (14.1.1) the resulting wave is simply ψ(,xt)=±ψ10 sin(kx1. Constructive interference happens when two waves overlap in such a way that they combine to create a larger wave. Δ l =. Δ l = m λ , for m = 0 , ± 1 , ± 2 , ± 3. This can be expressed in terms of the intensities of the individual waves as. (constructive interference) δ l = m λ , for m = 0 , ± 1 , ± 2 , ± 3. Web to find the angle of. Displacement y = (order m x wavelength x distance d )/ ( slit separation. Destructive interference happens when two. If l >> z then (l. This can be expressed in terms of the intensities of the individual waves as. Web we have sinθ = z/ (l 2 + z 2) ½ and λ = zd/ (m (l 2 + z. For vertical slits, the light spreads out horizontally on either side of the incident. Displacement y = (order m x wavelength x distance d )/ ( slit separation. Web the intensity of the light at r is given by. Constructive interference happens when two waves overlap in such a way that they combine to create a larger wave. The two. Web in other words, the locations of the interference fringes are given by the equation d sin θ = m λ d sin θ = m λ, the same as when we considered the slits to be point sources, but the. Thus, the interference pattern maps out the difference in. Constructive interference happens when two waves overlap in such a. For vertical slits, the light spreads out horizontally on either side of the incident. Web the formula for the sum of two waves can be derived as follows: Web we have sinθ = z/ (l 2 + z 2) ½ and λ = zd/ (m (l 2 + z 2) ½ ), where z is the distance from the center. Web in other words, the locations of the interference fringes are given by the equation d sin θ = m λ d sin θ = m λ, the same as when we considered the slits to be point sources, but the. Δ l = m λ , for m = 0 , ± 1 , ± 2 , ± 3. (constructive interference) δ l = m λ , for m = 0 , ± 1 , ± 2 , ± 3. This can be expressed in terms of the intensities of the individual waves as. Web the intensity of the light at r is given by. Destructive interference happens when two. Web the formula for the sum of two waves can be derived as follows: Each line can be described as a relatively. Web these conditions can be expressed as equations: Difference between diffraction grating and double slits. For vertical slits, the light spreads out horizontally on either side of the incident. Web to find the angle of diffraction, take the inverse sine of the ratio of the wavelength to the distance between the slits. If l >> z then (l. Suppose we are given two waves, ψψ 11(xt, ) = 0sin(k 1x±+ω 1t φ 1), ψ22(,xt)=ψ0sin(k2x±ω2t+φ2) (14.1.1) the resulting wave is simply ψ(,xt)=±ψ10 sin(kx1. The two special cases of superposition that produce the simplest results are pure constructive interference and pure destructive interference. Web double slit interference equation with w, s and d represented on a diagram the interference pattern on a screen will show as ‘fringes’ which are dark or bright bands.
ThinFilm Interference using Fresnel Equations YouTube
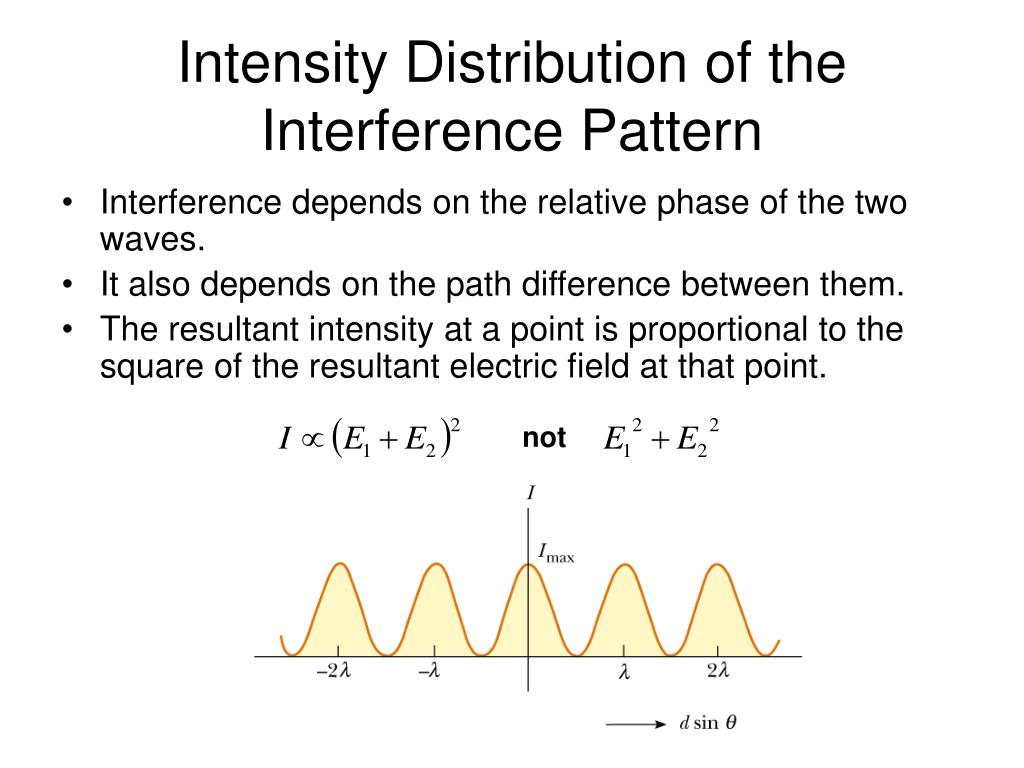
PPT Interference of Light Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free

Singleslit Diffraction Interference Pattern & Equations Video

PPT Interference Patterns PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID

PHYSICS Form 4 Form5 Interference equation
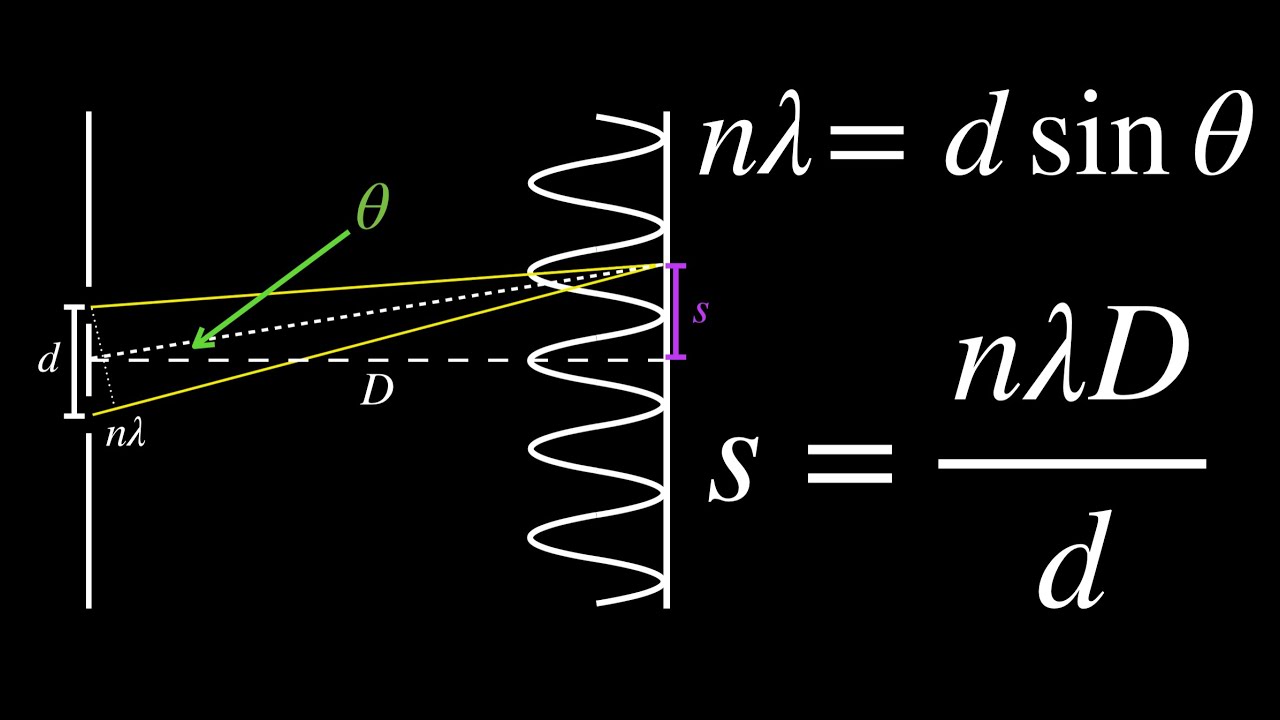
Deriving Young’s Double Slit Interference Formulas YouTube

PPT Interference Patterns PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
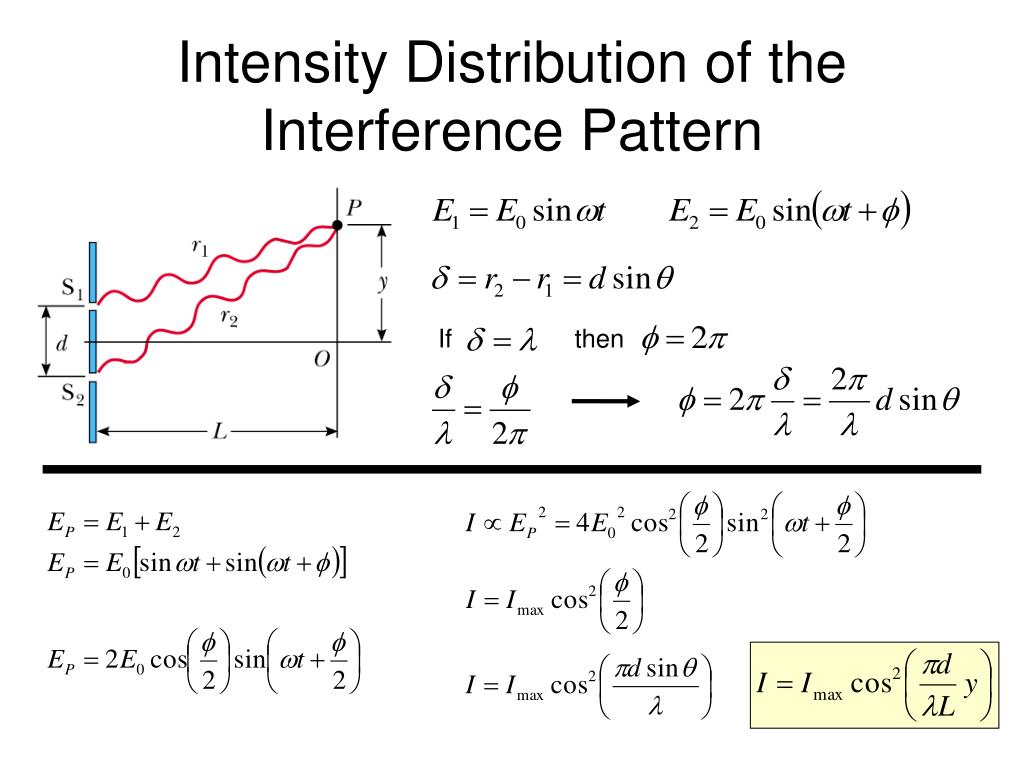
PPT Interference of Light Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free

Multipleslit Diffraction Interference Pattern & Equations Video

Doubleslit Diffraction Interference Pattern & Equations Video
Hyperphysics ***** Light And Vision.
Web We Have Sinθ = Z/ (L 2 + Z 2) ½ And Λ = Zd/ (M (L 2 + Z 2) ½ ), Where Z Is The Distance From The Center Of The Interference Pattern To The Mth Bright Line In The Pattern.
Web The Equations For Double Slit Interference Imply That A Series Of Bright And Dark Lines Are Formed.
Thus, The Interference Pattern Maps Out The Difference In.
Related Post: