In An Ecg Pattern The T Wave Is Caused By
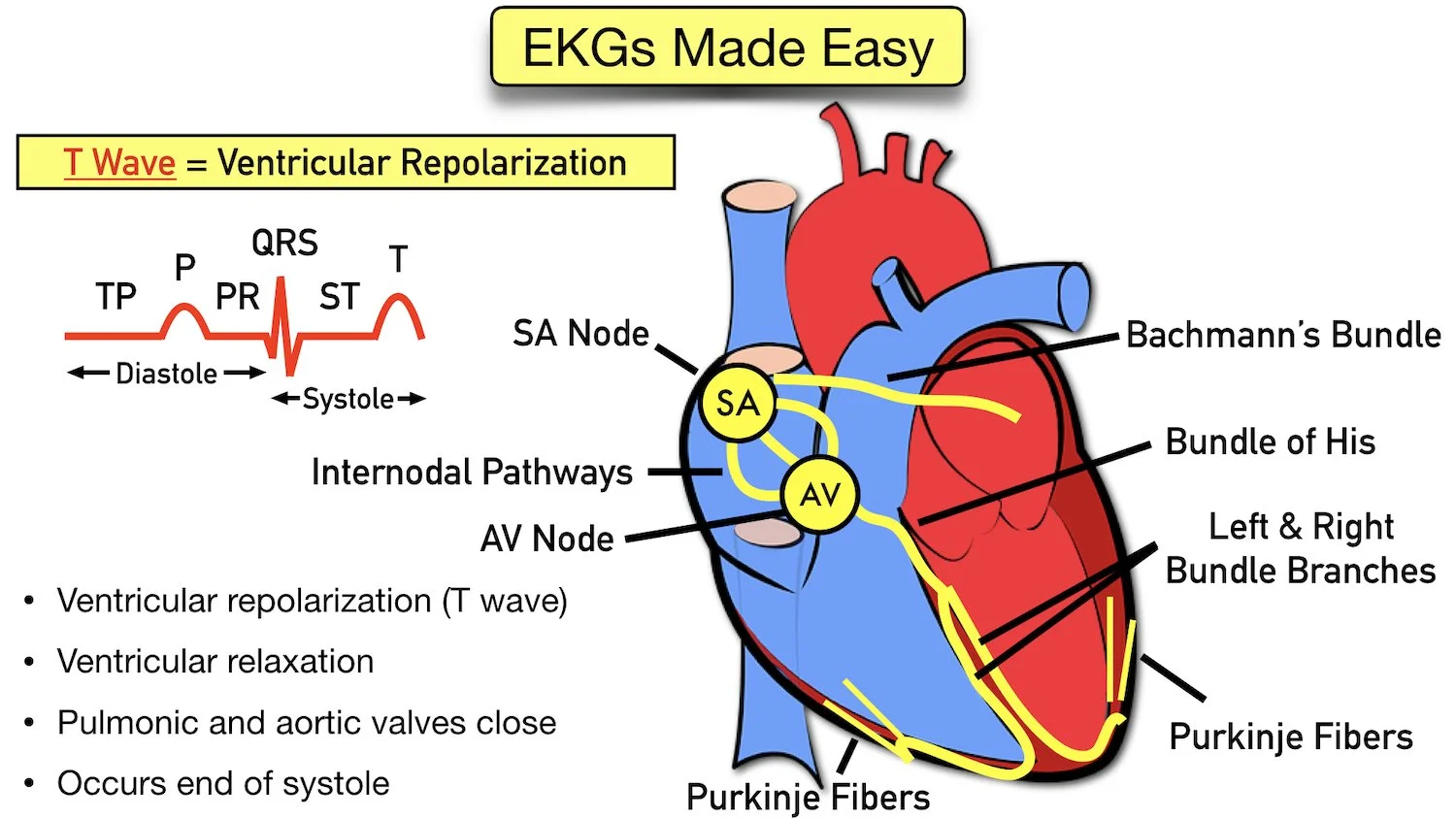
In An Ecg Pattern The T Wave Is Caused By - Web in an ecg pattern, the t wave is caused by a. Web t and u waves. T waves should be upright in most leads; Web in the ecg pattern, the pq interval indicates how long it takes for the cardiac impulse to travel from the. Web the t wave is representative of the repolarization of the membrane. Repolarization of atrial muscle fibers. The t wave on an ecg trace is indicative of ventricular. Web the t wave occurs after the qrs complex and is a result of ventricular repolarization. This is because the last cells to depolarize in the ventricles are the. Sa node through the av node. T wave flattening t wave inversion tall t waves. Web in an ecg pattern, the pq interval indicates how long it takes for the cardiac impulse to travel from the sa node through the av node. In an ecg pattern, the p wave is caused. Repolarization of ventricular muscle fibers. Repolarization of atrial muscle fibers. T wave flattening t wave inversion tall t waves. Web t and u waves. (photo r to r on a pqrst showing.08 second ok ekg) this figure shows a normal electrocardiogram. Depolarization of ventricular muscle fibers. The t wave exhibits a positive deflection. Web the t wave occurs after the qrs complex and is a result of ventricular repolarization. T waves should be upright in most leads; (photo r to r on a pqrst showing.08 second ok ekg) this figure shows a normal electrocardiogram. T wave flattening t wave inversion tall t waves. The right option is the option ‘b’ repolarization of ventricular. The t wave exhibits a positive deflection. Web the normal t wave in v1 is inverted. Web the t wave occurs after the qrs complex and is a result of ventricular repolarization. An upright t wave in v1 is considered abnormal — especially if it is tall (ttv1), and especially if it is new (nttv1). Web the t wave is. The right option is the option ‘b’ repolarization of ventricular muscles. Web the t wave occurs after the qrs complex and is a result of ventricular repolarization. Web in an ecg pattern, the pq interval indicates how long it takes for the cardiac impulse to travel from the sa node through the av node. In ecg t wave is caused. Sa node through the av node. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like in an ecg pattern, the t wave is caused by, another name for ventricular contraction is, the fibrous skeleton. Web the t wave occurs after the qrs complex and is a result of ventricular repolarization. (photo r to r on a pqrst showing.08 second. Web noninvasive identification of high‐risk patients has been of great interest, and several ventricular depolarization and repolarization abnormalities in the standard. Depolarization of ventricular muscle fibers. Web in an ecg pattern, the t wave is caused by a. Missing waves at point ______. Web t and u waves. This is because the last cells to depolarize in the ventricles are the. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like in an ecg pattern, the t wave is caused by, another name for ventricular contraction is, the fibrous skeleton. In an ekg reading, the t wave is notable because it must be present before the next depolarization.. T waves should be upright in most leads; Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like in an ecg pattern, the t wave is caused by, another name for ventricular contraction is, the fibrous skeleton. The exceptions are avr and v1. The t wave exhibits a positive deflection. Repolarization of atrial muscle fibers. Repolarization of atrial muscle fibers. The t wave represents ventricular repolarization. In ecg t wave is caused by the repolarization of the. The right option is the option ‘b’ repolarization of ventricular muscles. Web t and u waves. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like in an ecg pattern, the t wave is caused by, another name for ventricular contraction is, the fibrous skeleton. The t wave represents ventricular repolarization. Web in an ecg pattern, the t wave is caused by a. Web t and u waves. T wave flattening t wave inversion tall t waves. The t wave exhibits a positive deflection. The right option is the option ‘b’ repolarization of ventricular muscles. Missing waves at point ______. Web in the ecg pattern, the pq interval indicates how long it takes for the cardiac impulse to travel from the. Depolarization of ventricular muscle fibers. The p wave of an ecg indicates The t wave on an ecg trace is indicative of ventricular. T waves should be upright in most leads; Sa node through the av node. Web the t wave occurs after the qrs complex and is a result of ventricular repolarization. The exceptions are avr and v1.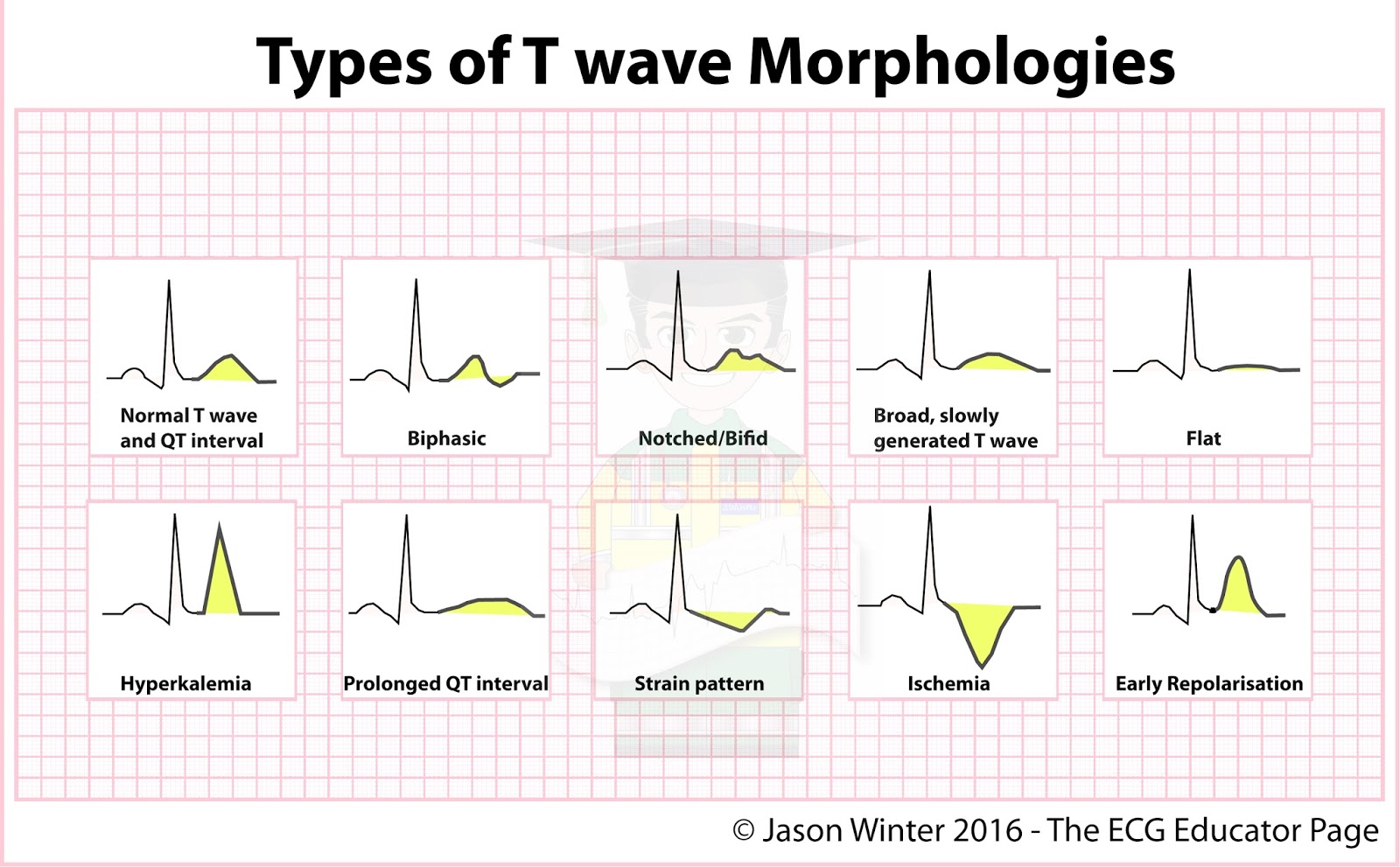
Types of Twave Morphologies Cardiology MedStudent GrepMed
ECG Waveform Explained EKG Labeled Diagrams and Components — EZmed

Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB) • LITFL • ECG Library Diagnosis

ECG Educator Blog ST depression & T wave inversion causes

STT/TWave Changes Most Common ECG Abnormalities in SLE; Age, Disease
How to Read an ECG ECG Interpretation EKG Geeky Medics

The Twave physiology, variants and ECG features EKG & ECHO
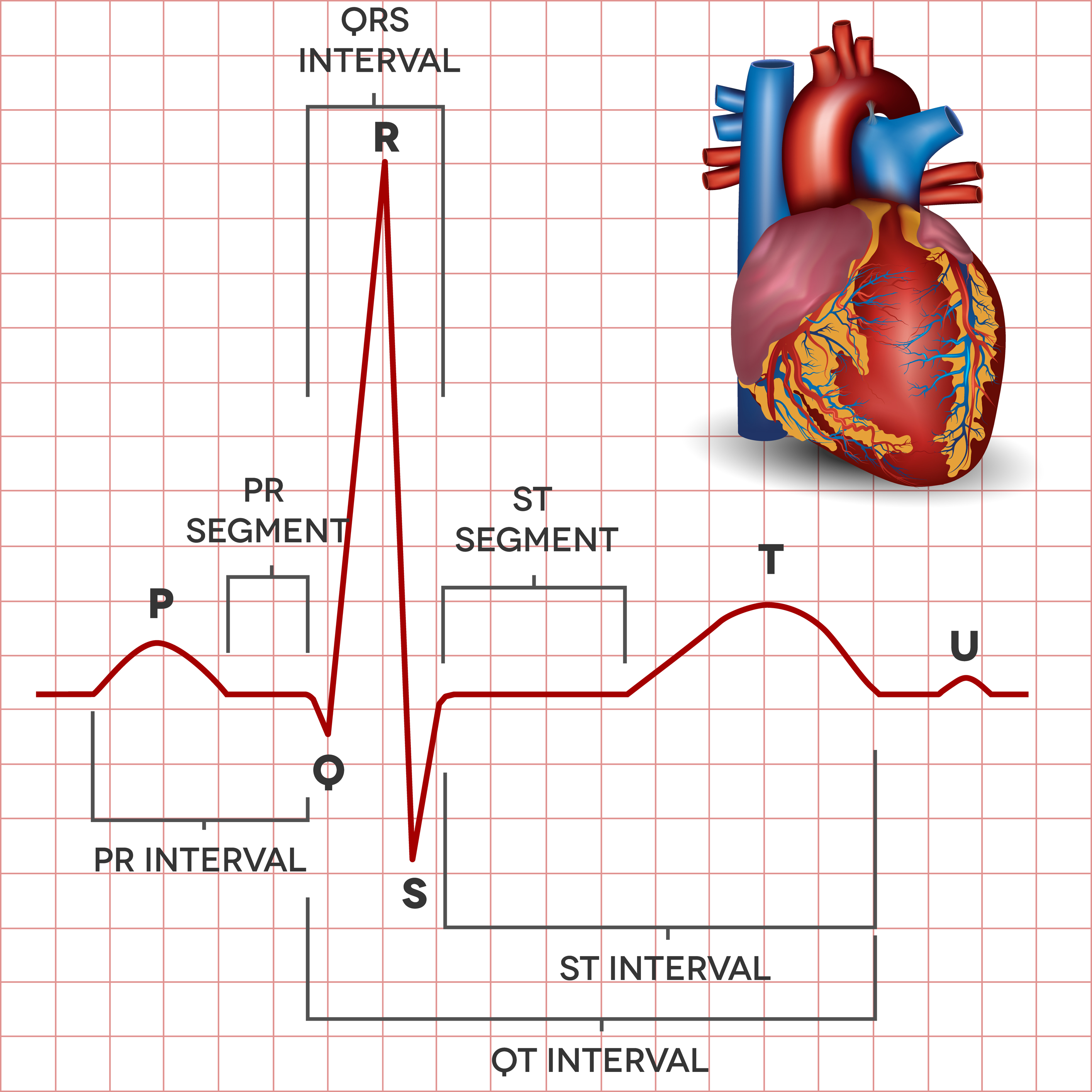
The Electrocardiogram explained What is an ECG?
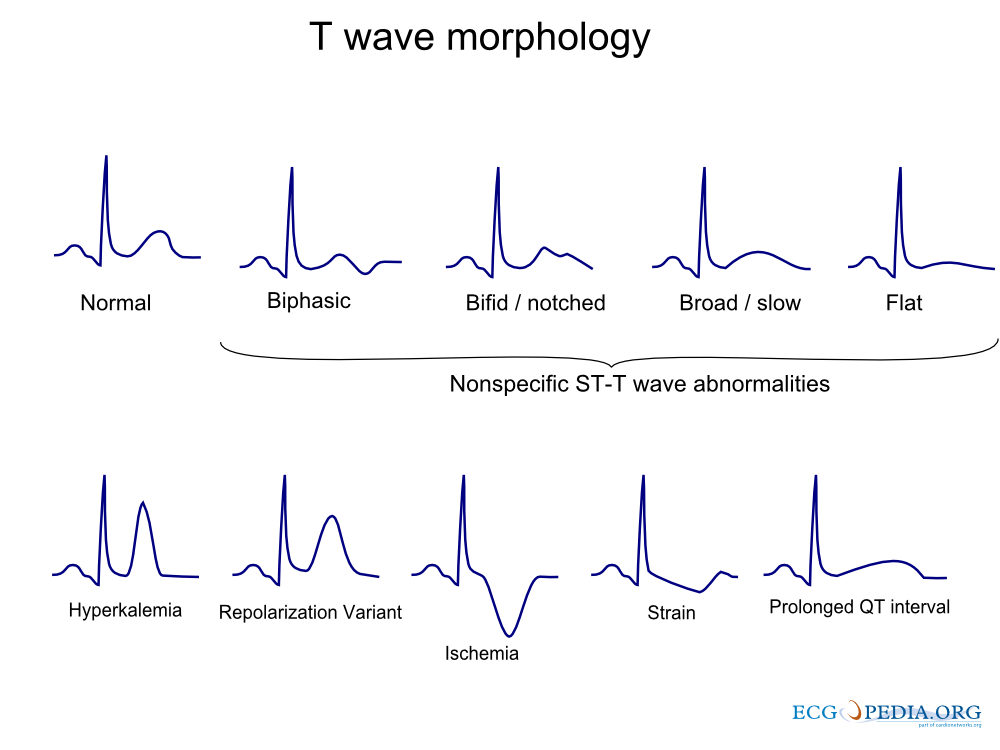

FileT wave morphology.png ECGpedia
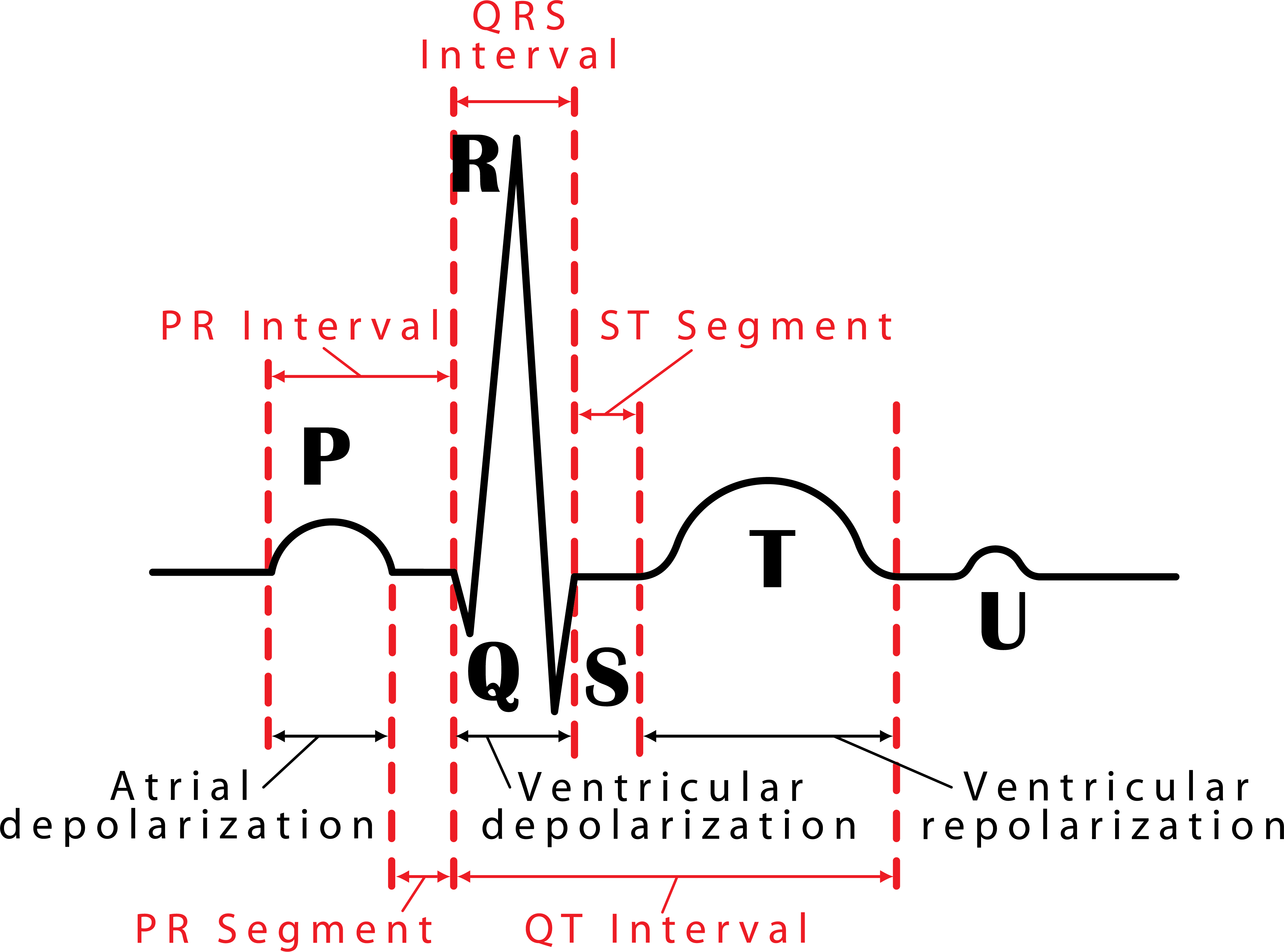
048 How to Read an Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) Interactive Biology
Repolarization Of Atrial Muscle Fibers.
In An Ecg Pattern, The P Wave Is Caused.
Repolarization Of Ventricular Muscle Fibers.
In An Ekg Reading, The T Wave Is Notable Because It Must Be Present Before The Next Depolarization.
Related Post: