Rotor Wear Patterns
Rotor Wear Patterns - The wobble can be changed in two ways. As brake rotors are used, grooves, ridges and other. As a result, front rotors contain ventilation fins that aid in cooling and circulate airflow. Caliper slide not functioning correctly. More rapid inner pad wear can be caused by a seized caliper guide pin or slides. This heat, combined with normal wear, can warp and distort rotors. Web inspect the old pads for uneven wear patterns. Web inner pad wear. • pads seized in slides. Dtv is differences in rotor thickness at various contact points from uneven wear. In layman’s terms, it is a wobble in the rotor. Once the pads are off, remove the rotor. All paragon performance rotors come standard in straight slots. Web brake rotor wear patterns refer to the condition of the brake rotors on a vehicle and how they have been worn down over time due to the friction and heat generated when. Web sliding pin cleaning and lubrication: This audible warning serves as a clear indication that your brake pads need attention. Web on some vehicles, you can see the brake pads through the holes in the wheel by shining a flashlight at the calipers. The outboard brake pad shows increased wear when compared to the inboard pad. Rotor looks to have. Major damage, excessive wear or glazing on the brake pads. Caliper slide not functioning correctly. This print is located on the outer surface and is presented something like “min. The brake pad box will have a guide to reference when inspecting for uneven wear. Caliper or caliper piston hanging up; Excessive dtv can cause brake judder or pulsation. Today's vehicles use friction braking systems, producing heat. Major damage, excessive wear or glazing on the brake pads. More rapid inner pad wear can be caused by a seized caliper guide pin or slides. Second, a rotor can be shimmed with a plate between the rotor and flange that changes the runout. When the pads wear down to a certain point, these indicators come into contact with the rotors, creating a distinct squealing or scraping noise. Lower initial bite compared to c6 / cc24 / z16 / z24 face patterns. Once the pads are off, remove the rotor. First, the rotor can be machined to match the same plane. Web inner pad. Uneven rotor wear may manifest through various signs, including a pulsating or vibrating brake pedal,. This lip is created as the brake pads normally don't contact all of the rotor surface and therefore leaves an outer lip when the rotors are worn down. Grooves in the surface of the friction material. Dtv is differences in rotor thickness at various contact. Cracked lining or chipped corners on the friction material. Uneven wear on your brake pads is. • service caliper guide pins and bushings. • caliper guide pins and bushings seized. Vehicle may pull to one side. Web brake rotor wear patterns refer to the condition of the brake rotors on a vehicle and how they have been worn down over time due to the friction and heat generated when brakes are applied. Friction material has changed greatly over the last 15 years in the aftermarket with ceramic brake pads being the. In layman’s terms, it is. Web reduced braking efficiency, irregular, wear, noise and judder. As a result, front rotors contain ventilation fins that aid in cooling and circulate airflow. Grooves in the surface of the friction material. First, the rotor can be machined to match the same plane. Rotor inspection is easiest with the wheel removed because the minimum thickness standard is etched quite small. Over time, the rotor can wear down due to constant. Brake rotors are generally made of cast iron, which is highly durable but subject to wear over time. Uneven rotor wear and caliper issues Web reading rotor wear patterns and rotor failures. In layman’s terms, it is a wobble in the rotor. Web a mechanic can measure the thickness of the rotors and check for wear patterns, warping, and other issues that might necessitate replacement. Rotor inspection is easiest with the wheel removed because the minimum thickness standard is etched quite small on the rotor. • pads seized in slides. Friction material has changed greatly over the last 15 years in the aftermarket with ceramic brake pads being the. This print is located on the outer surface and is presented something like “min. Over time, the rotor can wear down due to constant. Web reading rotor wear patterns and rotor failures. The brake pad box will have a guide to reference when inspecting for uneven wear. Grooves in the surface of the friction material. In layman’s terms, it is a wobble in the rotor. Web these indicators are small metal tabs or grooves embedded within the brake pads. Excessive dtv can cause brake judder or pulsation. Caliper slide not functioning correctly. The wobble can be changed in two ways. Major damage, excessive wear or glazing on the brake pads. Uneven wear on your brake pads is.
A brake pad that has word unevenly on a brake rotor as evident by the

Brake Rotor Wear Patterns FREE PATTERNS

Brake Rotors Choosing the Right Pattern Auto Parts Central
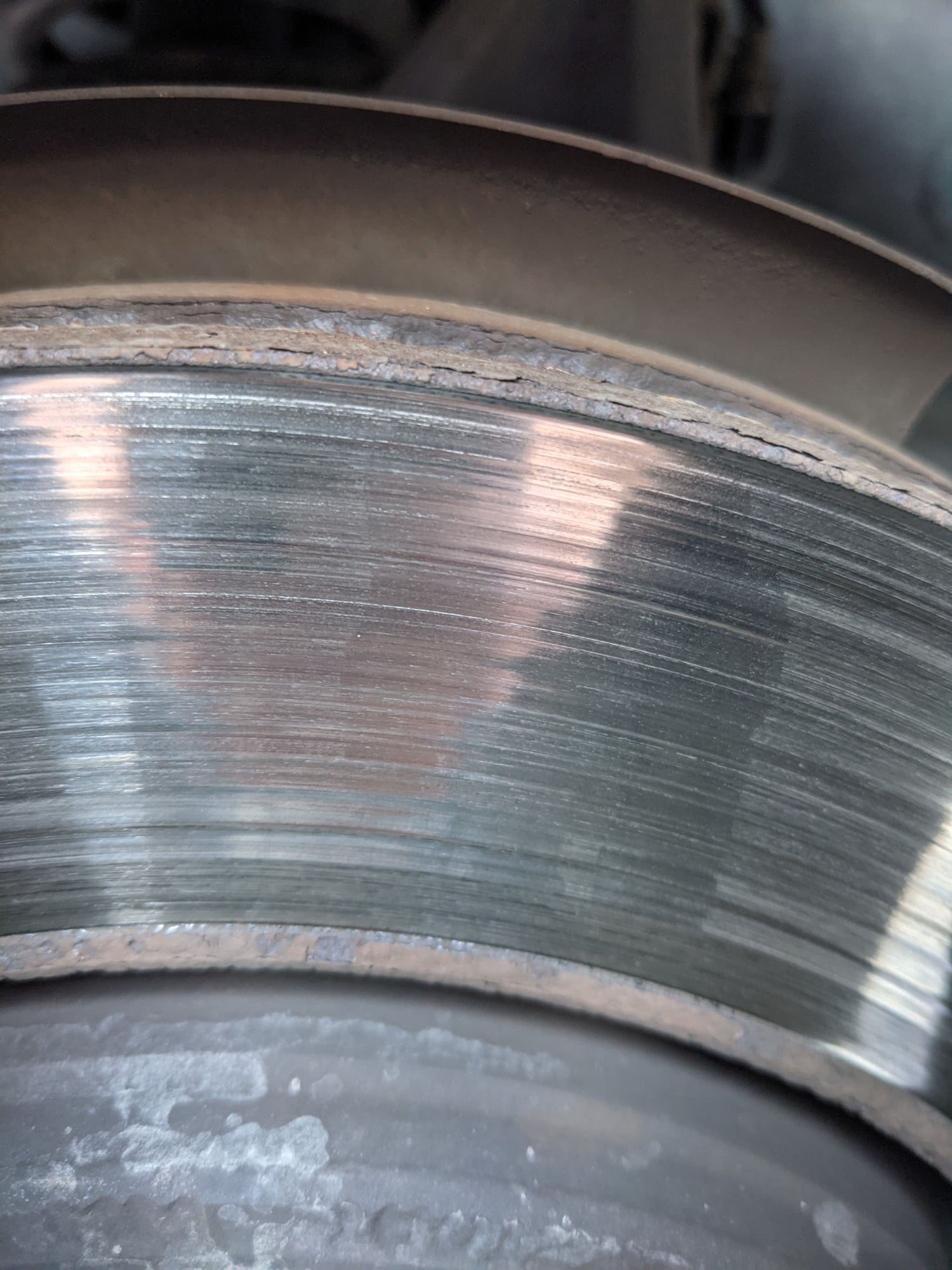

Strange Wear Pattern on Brake Rotor Ford F150 Forum Community of

Brake Rotor Wear Patterns FREE PATTERNS
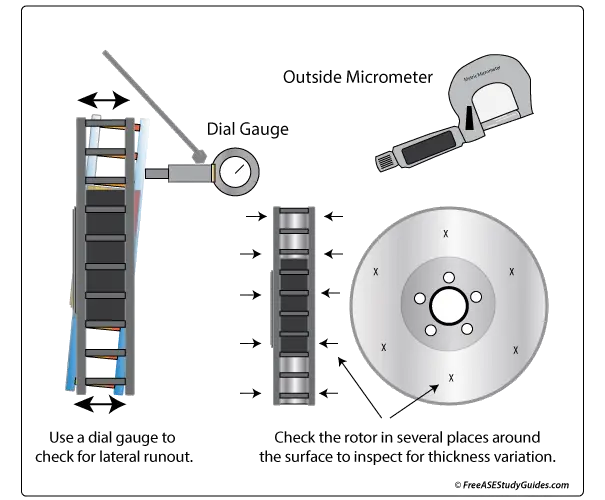
Brake Rotor Wear Patterns

Brake Rotor Wear Patterns FREE PATTERNS

Brake Rotor Wear Patterns FREE PATTERNS

Brake Rotor Wear Patterns FREE PATTERNS
ACDelco Techconnect • Reading Rotor Wear Patterns and Rotor Failures Blog
Second, A Rotor Can Be Shimmed With A Plate Between The Rotor And Flange That Changes The Runout.
This Is Interpreted As “Minimum Thickness Of 1.5Mm”.
When The Pads Wear Down To A Certain Point, These Indicators Come Into Contact With The Rotors, Creating A Distinct Squealing Or Scraping Noise.
First, The Rotor Can Be Machined To Match The Same Plane.
Related Post: