Homogeneous Ana Pattern
Homogeneous Ana Pattern - Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus. Medically reviewed by scott zashin, md. Patterns that are reported include, homogeneous, speckled, centromere, and others. It’s the most common type of staining pattern. How the test is performed. What does a positive ana blood. The entire nucleus is stained with ana. An ana test detects antinuclear antibodies (ana) in your blood. Updated on october 14, 2022. Web an ana test is used to help diagnose autoimmune disorders, including: This is the most common type of lupus, a chronic disease affecting multiple parts of the body, including the joints, blood vessels, kidneys, and brain. A homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus. In contrast, antinuclear antibodies often attack your body's own tissues — specifically targeting each cell's nucleus. Patterns that. Web the pattern of the ana test can give information about the type of autoimmune disease present and the appropriate treatment program. Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. The entire nucleus is stained with ana. Medically reviewed by scott zashin, md. Understanding the ana blood test (antinuclear antibody test) by carol eustice. Web the pattern of the ana test can give information about the type of autoimmune disease present and the appropriate treatment program. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies. A homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus.. Web an ana test is used to help diagnose autoimmune disorders, including: Homogenous staining can result from antibodies to dna and histones. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. An ana test detects antinuclear antibodies (ana) in your blood. A titer (a measure of how much ana is in the blood) and a pattern (where the. Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus. A homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus. This is the most common type of lupus, a chronic disease affecting multiple parts of the body, including the joints, blood vessels, kidneys, and brain. Titres are reported in ratios, most. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Homogenous staining can result from antibodies to dna and histones. A homogenous pattern can mean any autoimmune disease but more specifically, lupus or sjögren’s syndrome. A titer (a measure of how much ana is in the blood) and a pattern (where the ana was detected in the. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana. What does a positive ana blood. Homogenous staining can result from antibodies to dna and histones. How the test is performed. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. The significance of ana pattern. What does a positive ana blood. An ana test detects antinuclear antibodies (ana) in your blood. Patterns that are reported include, homogeneous, speckled, centromere, and others. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. The entire nucleus is stained with ana. Homogenous staining can result from antibodies to dna and histones. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. How the test is performed. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. The significance of ana pattern. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. This is the most common type of lupus, a chronic disease affecting multiple parts of the body, including the joints, blood vessels,. Understanding the ana blood test (antinuclear antibody test) by carol eustice. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies. Web ana test results are most often reported in 2 parts: An ana test detects antinuclear antibodies (ana) in your blood. Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus. This is the most common type of lupus, a chronic disease affecting multiple parts of the body, including the joints, blood vessels, kidneys, and brain. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana. Homogenous staining can result from antibodies to dna and histones. Web an ana test is used to help diagnose autoimmune disorders, including: A titer (a measure of how much ana is in the blood) and a pattern (where the ana was detected in the cells). The significance of ana pattern. Web the pattern of the ana test can give information about the type of autoimmune disease present and the appropriate treatment program. The entire nucleus is stained with ana. A homogenous pattern can mean any autoimmune disease but more specifically, lupus or sjögren’s syndrome. A homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus. Medically reviewed by scott zashin, md.
ANA Patterns
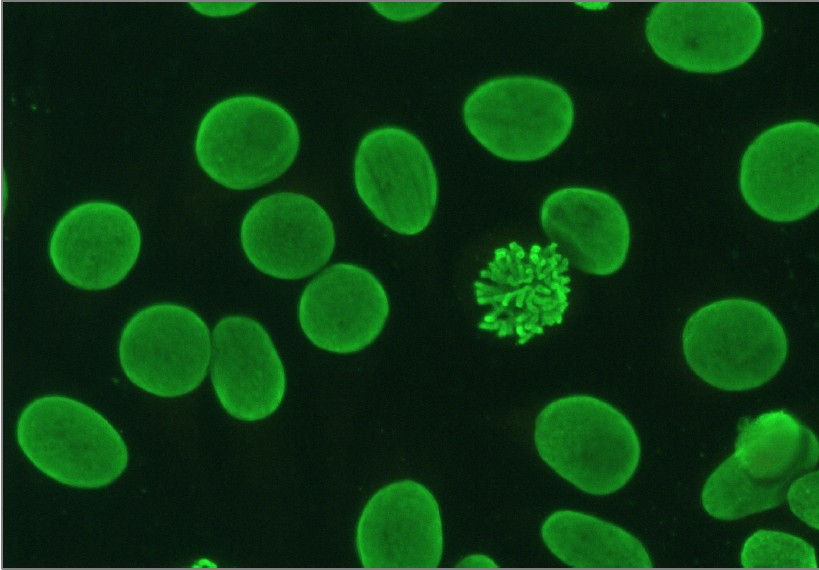
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) homogeneous pattern positive control

6. IFA pattern Homogeneous ANA pattern YouTube
.jpg)
ANA Mixed pattern University of Birmingham

Common ANA patterns by IIF a, negative sample; b, homogeneous; c
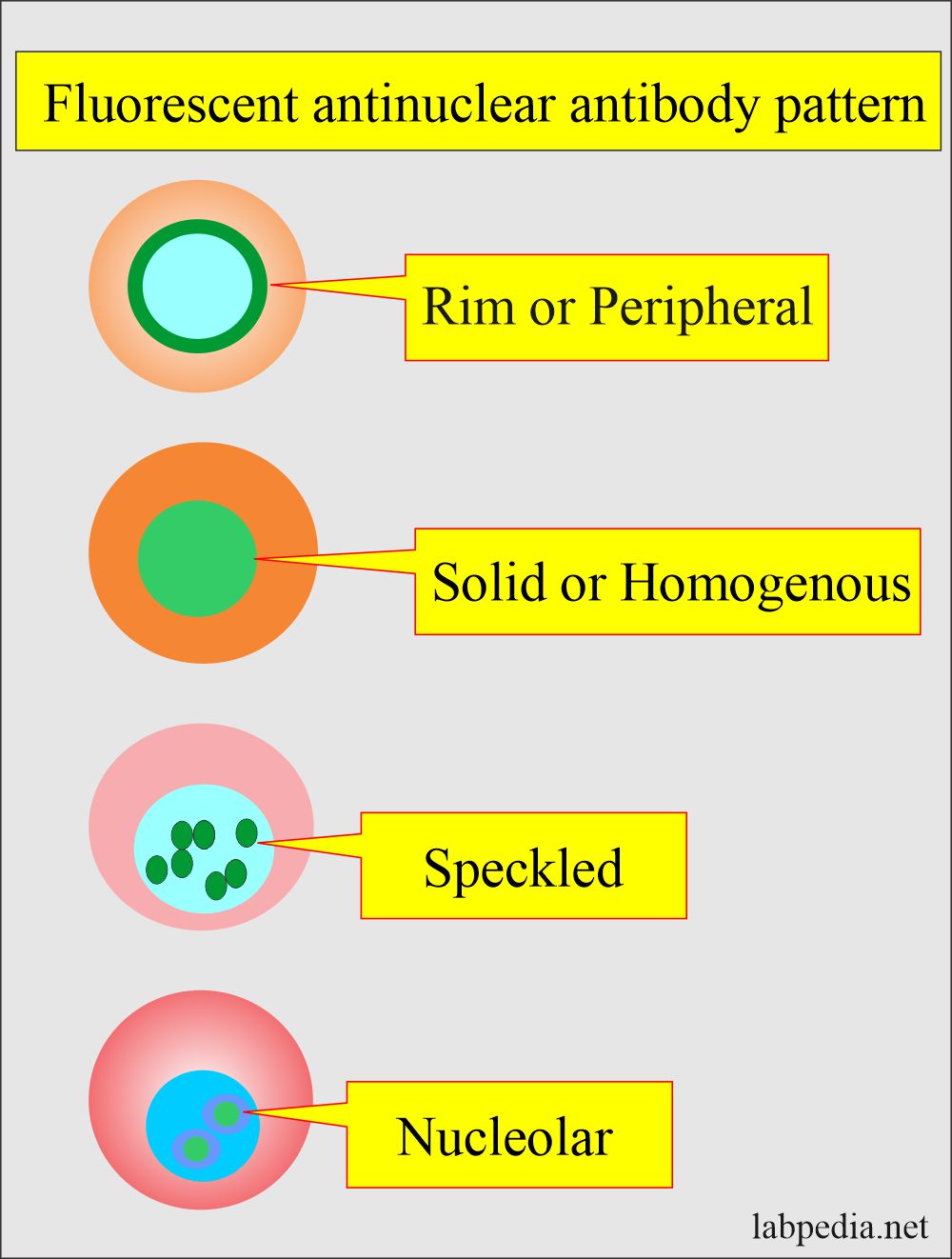
Antinuclear Factor (ANF), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) and Its
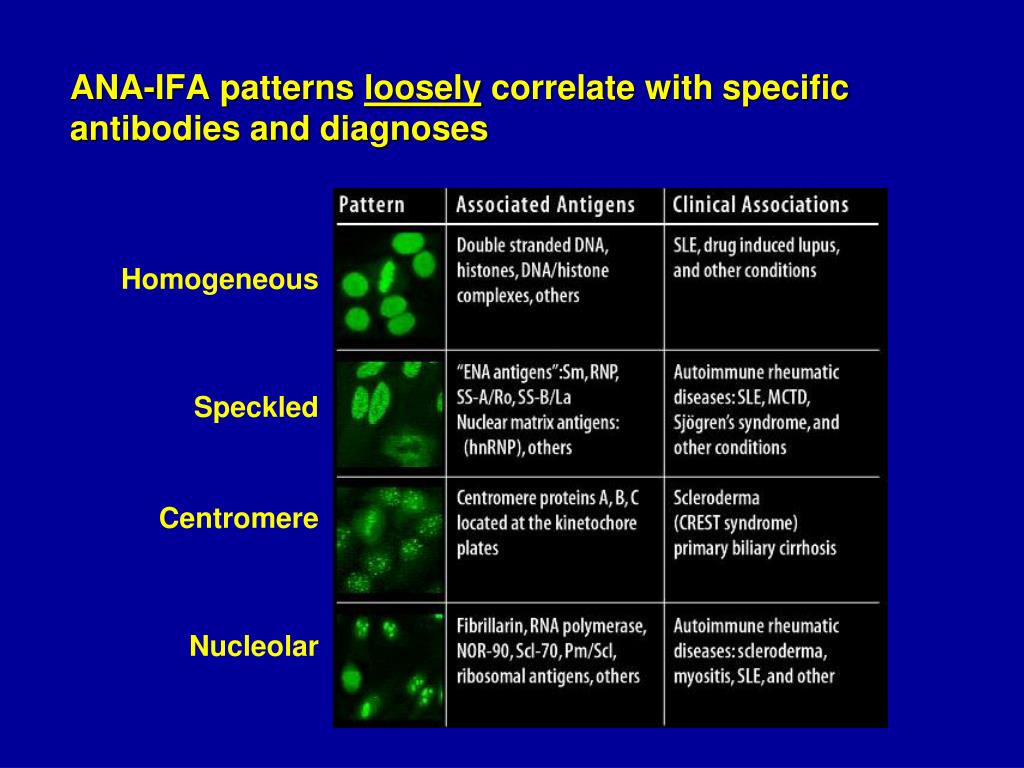
Homogeneous Ana Pattern Pagswa

DFS70 antibodies biomarkers for the exclusion of ANAassociated
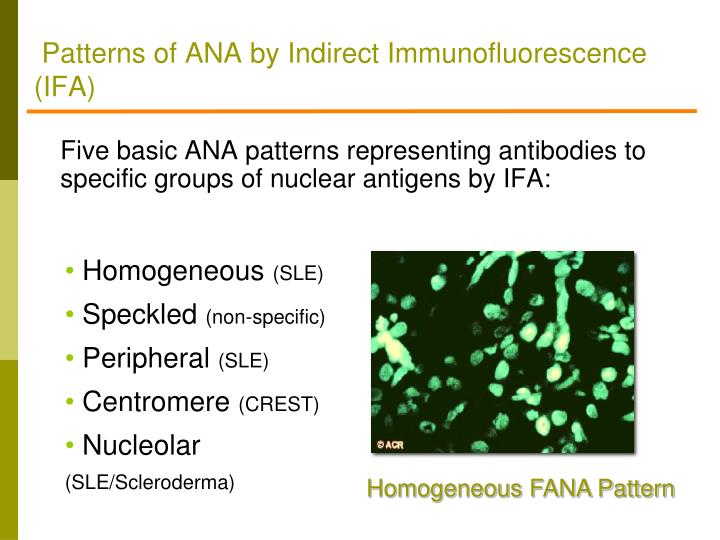
PPT Rheumatology Update Pearls for Primary Care PowerPoint
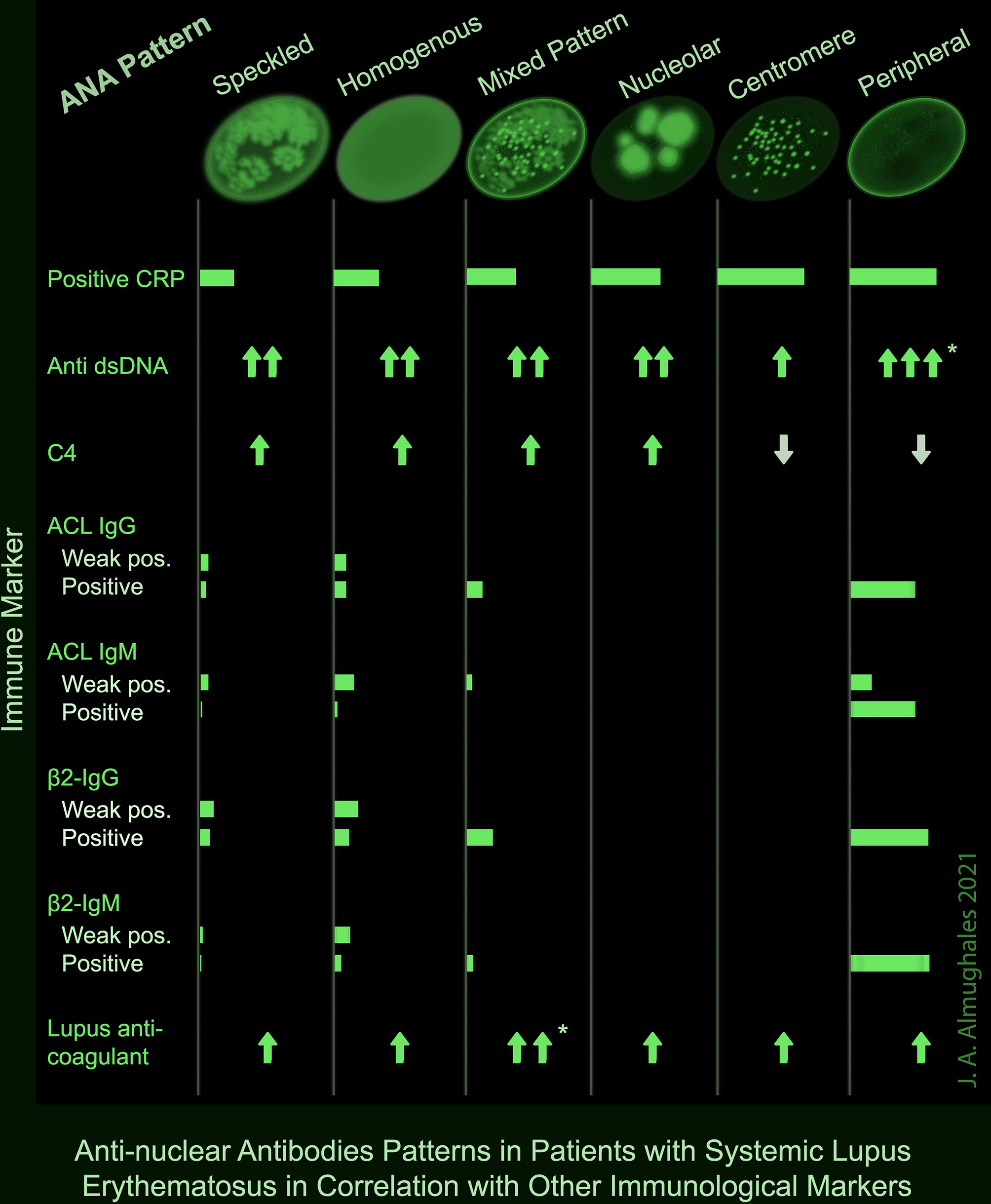
Frontiers AntiNuclear Antibodies Patterns in Patients With Systemic
This Is The Most Common Pattern And Can Be Seen With Any Autoimmune Disease.
It’s The Most Common Type Of Staining Pattern.
Patterns That Are Reported Include, Homogeneous, Speckled, Centromere, And Others.
Web A Homogeneous/Peripheral Pattern Reflects Antibodies To Histone/Dsdna/Chromatin, Whereas Many Other Specificities Found In Systemic Rheumatic Diseases Show Speckled Patterns Of Various Sizes And Densities (Fine Speckled, Large Speckled, Etc.).
Related Post: