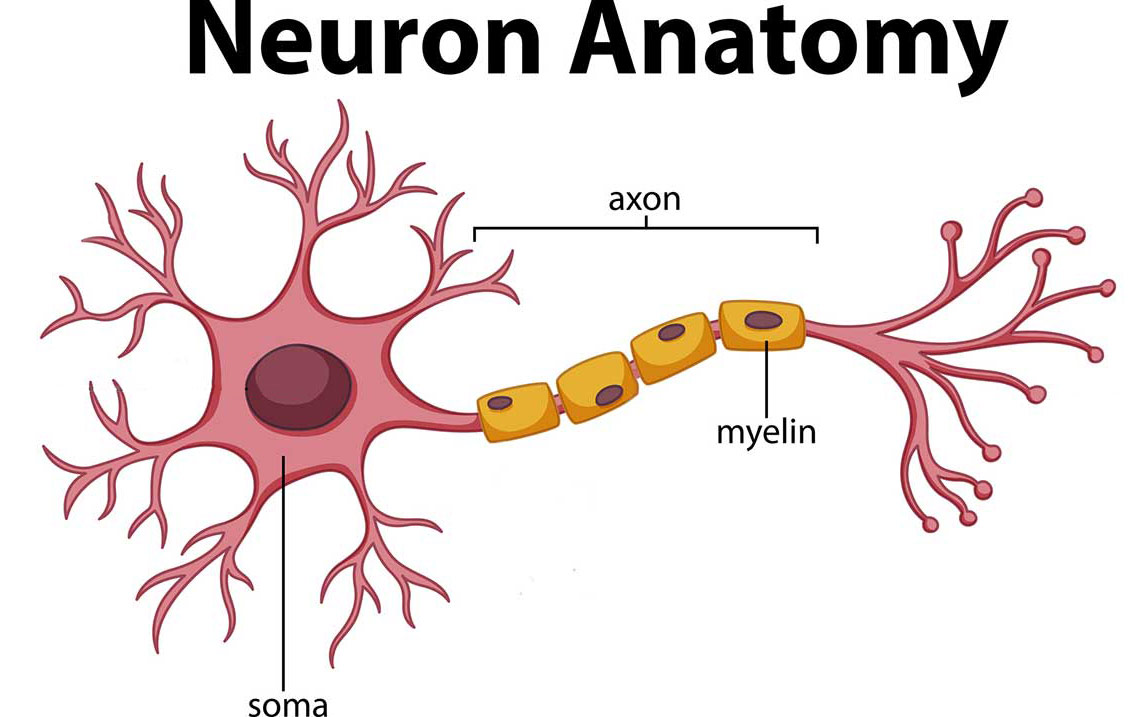
Drawing Of Nerve Cell
Drawing Of Nerve Cell - Large mitral cells lining the middle layer (black) are arranged such that their dendrites reach toward the glomeruli, where they form synapses with the axons extending from the. Web they are composed of groups of individual specialized cells called neurons (or nerve cells), which transmit motor and sensory information back and forth between the pns and central nervous system (cns). Web our hands comprise most of the nerve endings of our bodies as well as the highest numbers of muscles. While neurons have a lot in common with other types of cells, they’re. Web essentially, nerve cells, also known as a neurons, are the active component of the nervous system. Web the nerve fiber bundles enter spheres of cell bodies called glomeruli in the middle layer (b), which consists of gray matter (nerve cell bodies and dendrites). Every neuron consists of a body (soma) and a number of processes (neurites). Explore the structure of neurons, their types, and functions. Web this video introduces the structure and structural types of neurons. They stretch from your hips all the way down to your toes! Neurotransmitter can also be mopped up by nearby glial cells—not shown in the diagram below. A nerve signal passes from the dendrite to the cell body to the axon. Neurons are responsible for the processing and transmission of nerve signals throughout the body. However, the clinical outcomes remain unsatisfactory. They are adapted to carry electrical impulses from one place to. The nerve cell body contains the cellular organelles and is where neural impulses ( action potentials) are generated. Web neurons and nerves neurons are unique for many reasons. These include nerve cells (or neurons) and glial cells (or glia ). A neuron is also known as the nerve cell. They carry an electrical message or impulse when stimulated. Web nerve cells (aka neurons) are the basic functional units of the nervous system, and the adult human brain is thought to contain around 86 billion of them.the role of a nerve cell is to receive information from cells and transmit this information to other cells. A nerve cell structure is divided into dendrites, cell body (soma), and axon. The. These functions reflect in the. A nerve cell (neuron) consists of a large cell body and nerve fibers—one elongated extension (axon) for sending impulses and usually many branches (dendrites) for receiving impulses. These include nerve cells (or neurons) and glial cells (or glia ). Large mitral cells lining the middle layer (black) are arranged such that their dendrites reach toward. Neurons communicate with each other as well as with other cells through electric signals (nerve impulses), which in turn allows effector organs to respond to the appropriate stimuli. Web this video introduces the structure and structural types of neurons. There are three different types of nerve cells in the human body and, together,. Neurons are composed of three main parts:. The cell body, dendrites, and axon. A nerve signal passes from the dendrite to the cell body to the axon. Web the nerve cell or neuron is the fundamental structural and functional unit of the nervous system. This is very uncommon for cells, which are usually very short. Web neurons and nerves neurons are unique for many reasons. Web this induces electrical currents that stimulate nerve cells in specific areas of the brain. Large mitral cells lining the middle layer (black) are arranged such that their dendrites reach toward the glomeruli, where they form synapses with the axons extending from the. Web the neuron (or nerve cell) is the functional unit of both the central nervous system (cns). A neuron is a specialized cell, primarily involved in transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals. Despite the specific molecular, morphological, and functional features of any particular nerve cell type, the basic structure of neurons resembles that of other cells. Web nerve cells are also called neurons close neurons nerve cells. Receiving signals, integrating these signals and transmitting the signals. Web anatomy of a neuron. Web our hands comprise most of the nerve endings of our bodies as well as the highest numbers of muscles. Within a nervous system, a neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network. Web this video will be very useful to students. Web this induces electrical currents that stimulate nerve cells in specific areas of the brain. Uncover the roles of dendrites, axons, and the soma. In ocd, it is delivered to other parts of the brain’s prefrontal cortex associated with repetitive actions. Neurons are composed of three main parts: Web typical structure of a nerve cell. A nerve cell (neuron) consists of a large cell body and nerve fibers—one elongated extension (axon) for sending impulses and usually many branches (dendrites) for receiving impulses. Neurons, or nerve cell, are the main structural and functional units of the nervous system. These include nerve cells (or neurons) and glial cells (or glia ). Web repair strategies for injured peripheral nerve have achieved great progresses in recent years. Despite the specific molecular, morphological, and functional features of any particular nerve cell type, the basic structure of neurons resembles that of other cells. Nerve cells may be described as receivers and transmitters of. Web anatomy of a neuron. Uncover the roles of dendrites, axons, and the soma. Web neurons or nerve cells are the basic building blocks or units of the nervous system. Learn about the axon hillock, axon terminals, and the myelin sheath. A neuron is also known as the nerve cell. Neurons communicate with each other as well as with other cells through electric signals (nerve impulses), which in turn allows effector organs to respond to the appropriate stimuli. While neurons have a lot in common with other types of cells, they’re. Discover the different structural types of neurons: A group of neurons forms a nerve. There are three different types of nerve cells in the human body and, together,.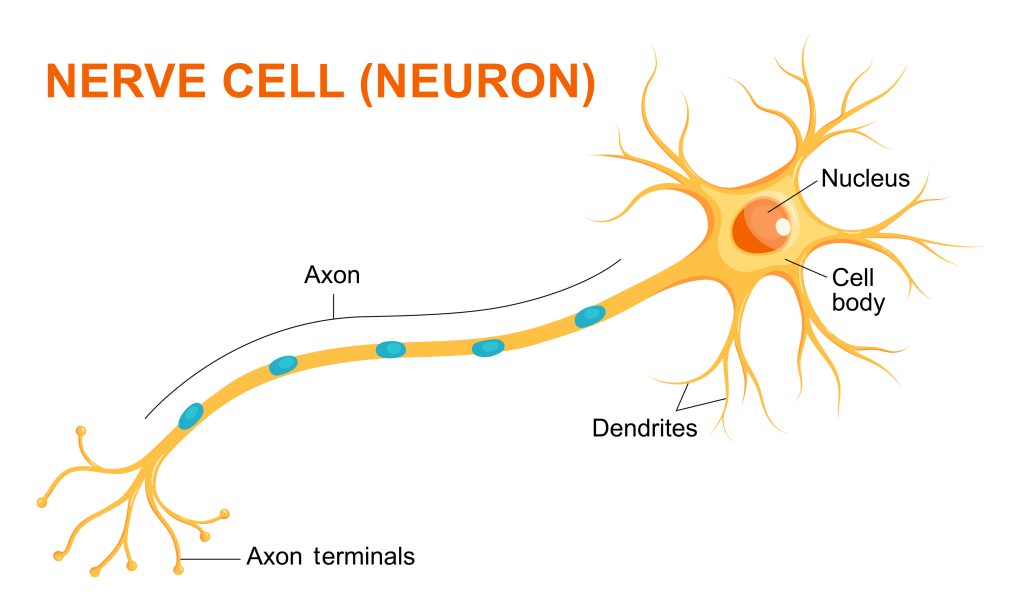
Science Snippet Get to Know Your Nerve Cells! Biomedical Beat Blog

What Is a Neuron? Diagrams, Types, Function, and More

Human Nerve Cell Labeled Diagram From the Ground
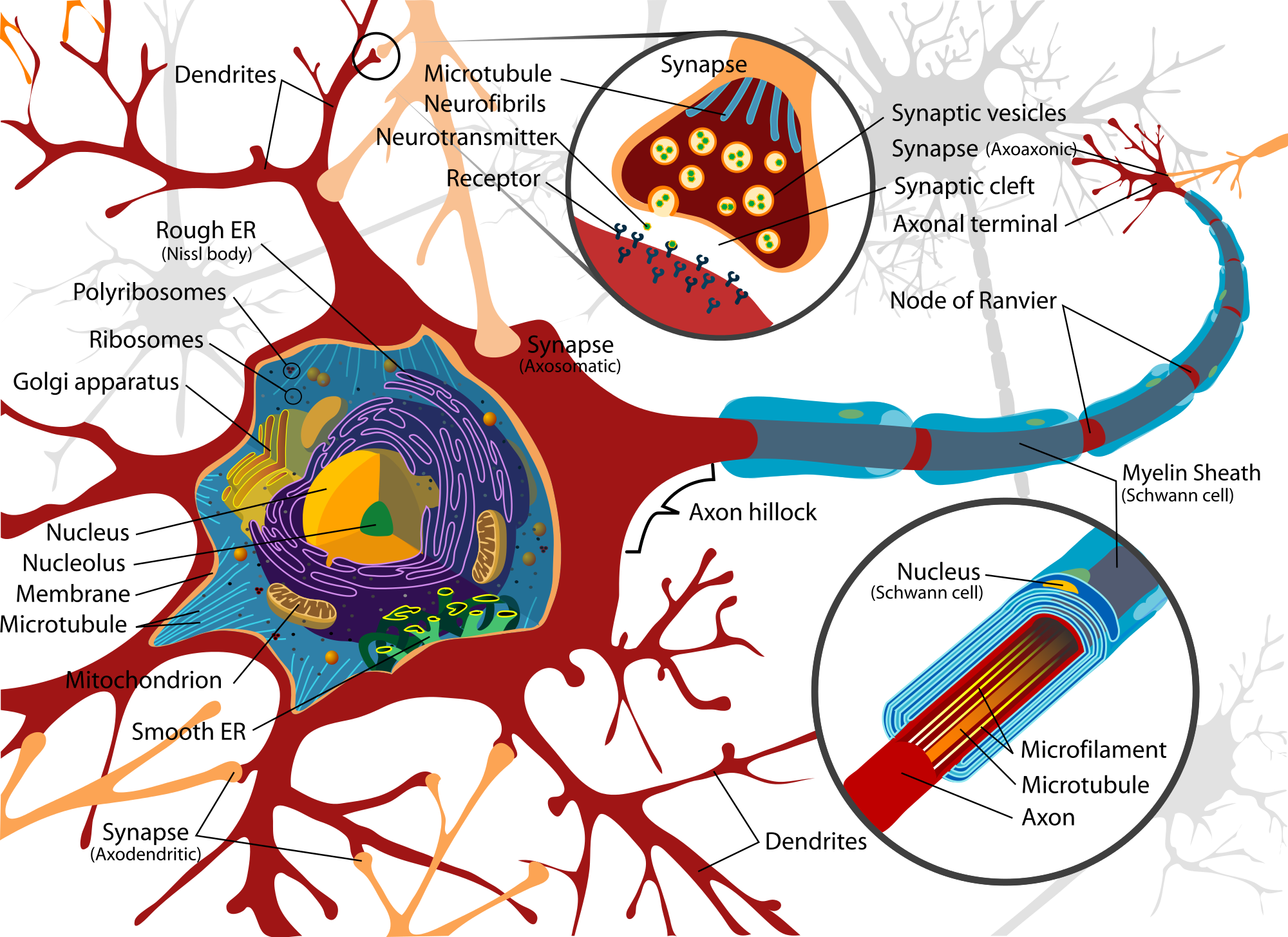
Nerve Cell Diagram Labeled ClipArt Best
Brain Anatomy and How the Brain Works Johns Hopkins Medicine
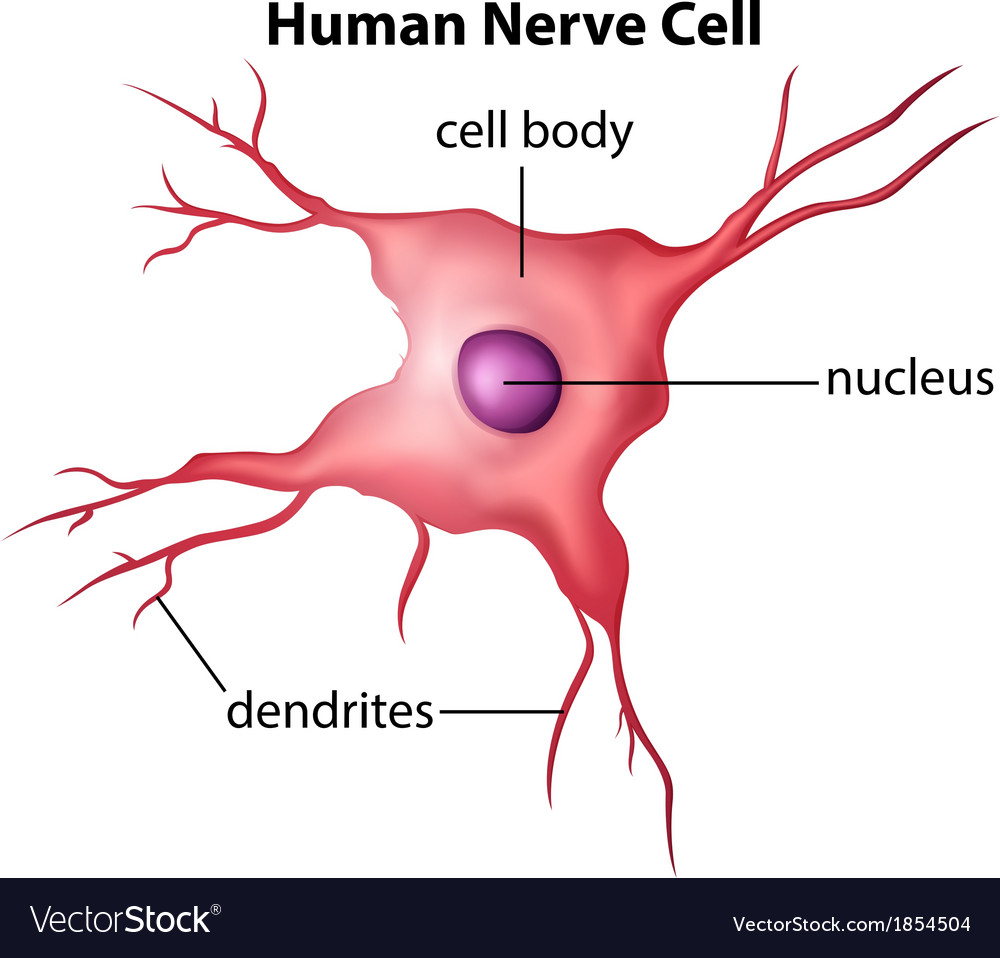
Human nerve cell Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock
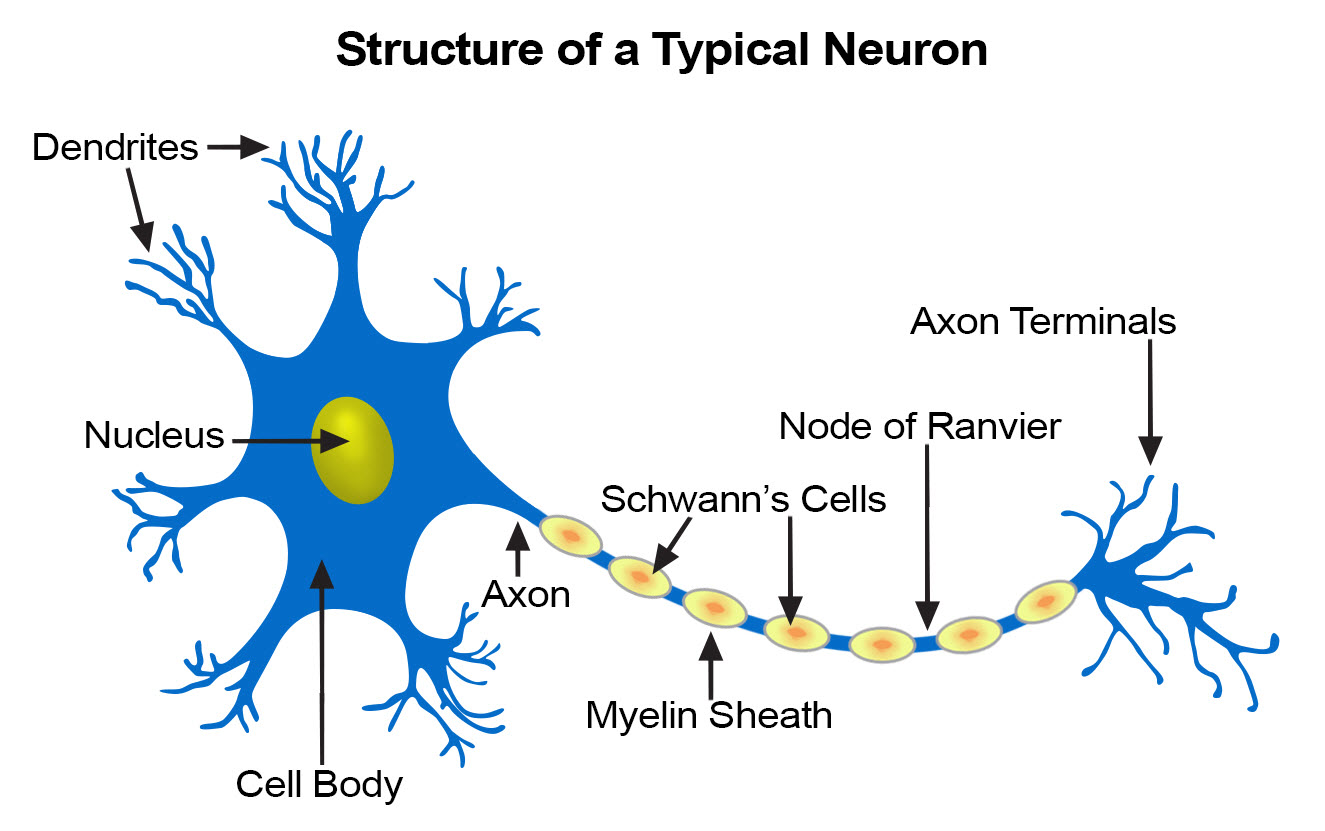
Nerve Tissue SEER Training
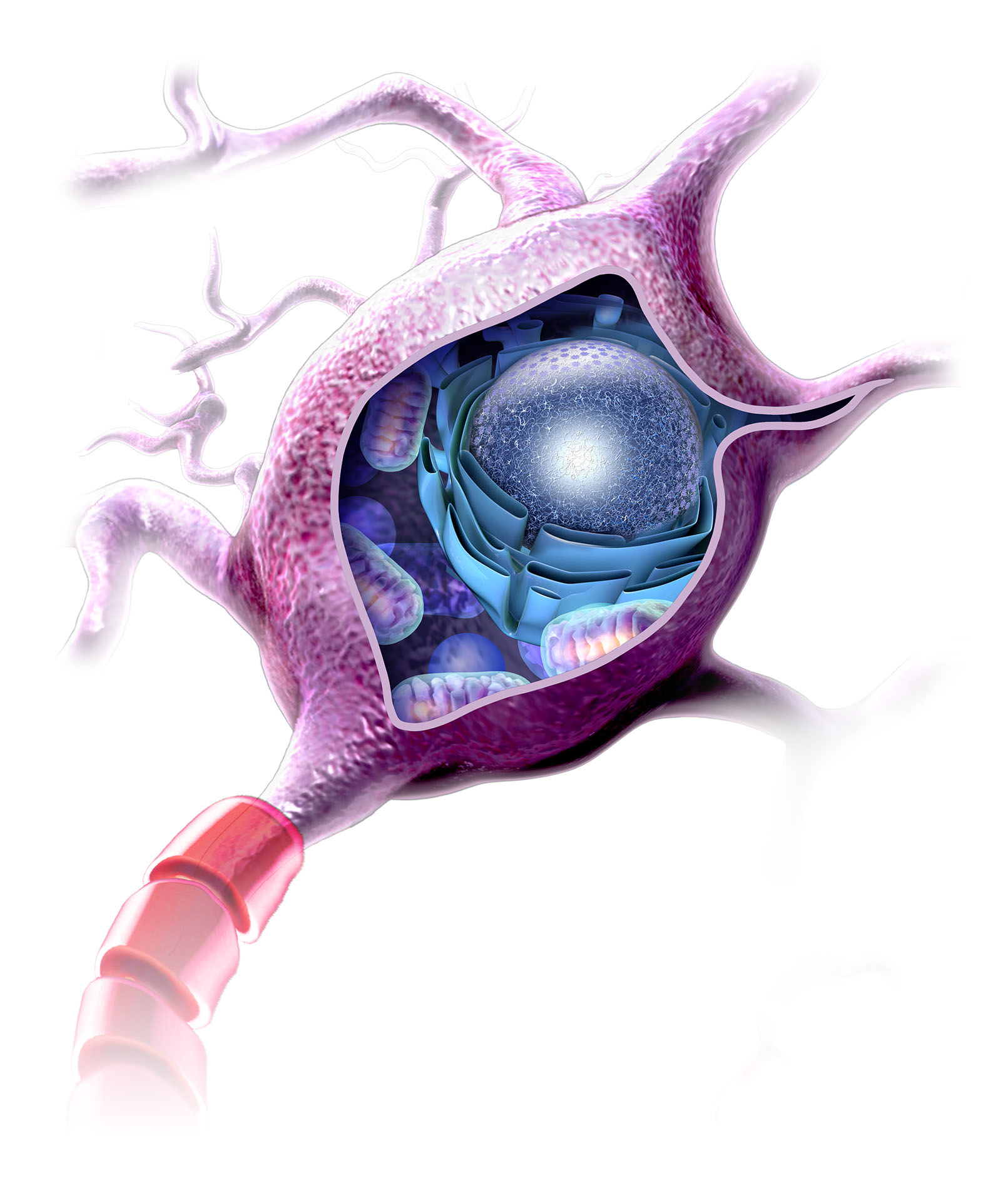
Nerve Cell Internal Structure Portfolio SayoStudio
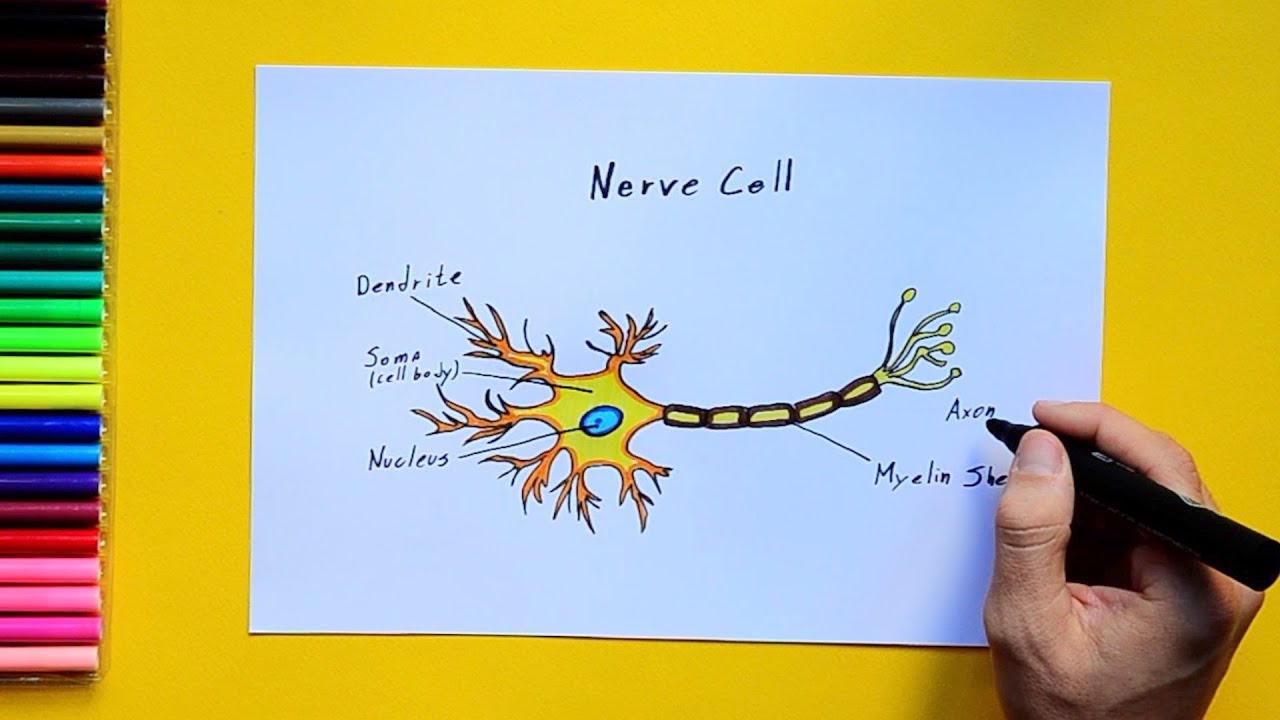
How to draw a nerve cell labeled science diagrams YouTube
Nervous System The Partnership in Education
They Are Highly Specialized Cells That Act As Information Processing And Transmitting Units Of The Brain.
The Impulses From The Axon Cross A Synapse (The Junction Between Two Nerve Cells) To The Dendrite Of Another Cell.
Web An Easy Guide To Neuron Anatomy With Diagrams.
Web Like The Heart, Lungs, And Stomach, The Nervous System Is Made Up Of Specialized Cells.
Related Post: