What Causes The Repeating Pattern Of The Moons Appearance
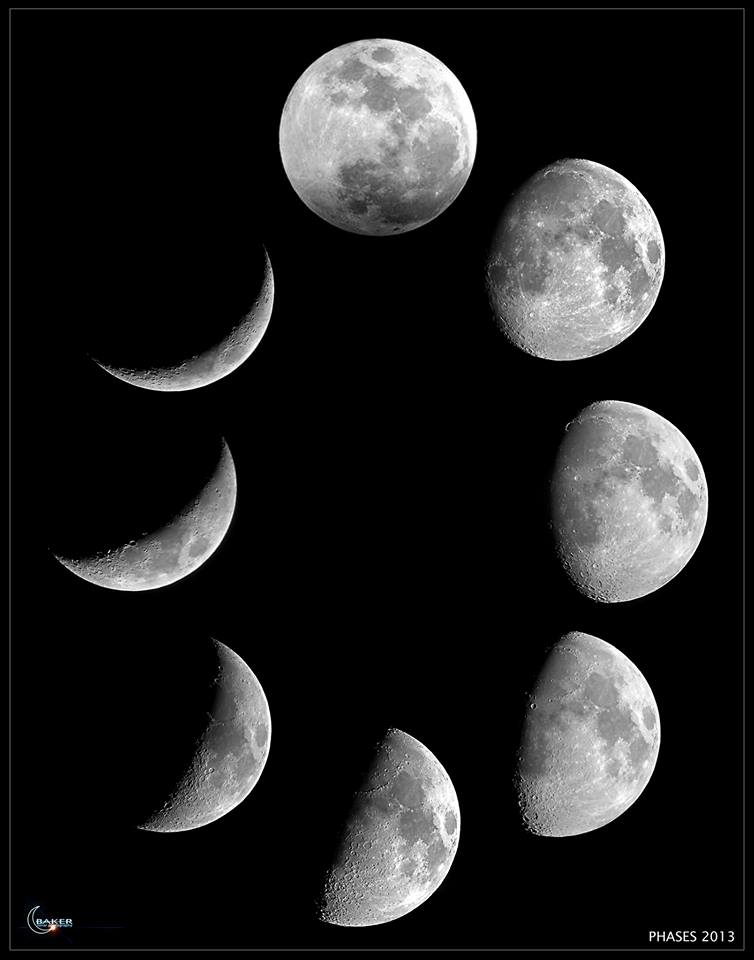
What Causes The Repeating Pattern Of The Moons Appearance - Web the differences in the moon’s appearance from one night to the next are due to changing illumination by the sun, not to its own rotation. Web a guide to the phases of the moon, and why its appearance changes night after night from crescent to gibbous and back again. Web the repeating pattern of the moon's appearance, known as lunar phases, is caused by the relative positions of the earth, moon, and sun. Web the moon's phases represent its changing appearance as seen from earth, a cycle that repeats approximately every 29.5 days. One starting point is for children to choose a card and try to find the match on the banner. The moon’s sidereal period—that is, the period of its revolution about earth measured with respect to the stars—is a little over 27 days: They use this evidence to record and make predictions about the moon’s appearance in the sky. By galileo, these 1610 lunar maps are some of the first published to rely on telescope views. Figure l1.1 shows the pattern that the appearance of the moon follows. Place the opened paper the long way on top of the lap board. You sometimes hear the back side of the moon (the side we never see) called the “dark side.” The relative positions of these celestial bodies determine the amount of sunlight reaching different parts of the moon, resulting in the observed phases. You sometimes hear the back side of the moon (the side we never see) called the “dark side.” Place. Web some of the patterns students noticed were that the moon appeared to get bigger and then smaller across the month, that the moon appeared to “grow” toward a full moon and then “shrink” and not be visible, and that the shapes of the moon in the second half of the month appeared to be the reverse of what was. There are a total of eight lunar phases. The moon’s sidereal period—that is, the period of its revolution about earth measured with respect to the stars—is a little over 27 days: You sometimes hear the back side of the moon (the side we never see) called the “dark side.” Web the phases of the moon and their role in solar. You sometimes hear the back side of the moon (the side we never see) called the “dark side.” Web as the bright parts of the moon appear to change shape during the month, each stage of the change is called a phase, and each phase carries its own name. The center ring shows the moon as it revolves around the. New moon, first quarter, full moon, and finally last quarter. Web the differences in the moon’s appearance from one night to the next are due to changing illumination by the sun, not to its own rotation. By galileo, these 1610 lunar maps are some of the first published to rely on telescope views. Observing the moon’s changing appearance and experiencing.. Web the differences in the moon’s appearance from one night to the next are due to changing illumination by the sun, not to its own rotation. New moon, first quarter, full moon, and finally last quarter. Web the differences in the moon’s appearance from one night to the next are due to changing illumination by the sun, not to its. New moon, first quarter, full moon, and finally last quarter. The phases of the moon are caused by the changing positions of the moon, earth, and the sun. Demonstrate how they should fold the sheet of paper, so that when it is unfolded, there are eight equal boxes. They use this evidence to record and make predictions about the moon’s. Demonstrate how they should fold the sheet of paper, so that when it is unfolded, there are eight equal boxes. Web some of the patterns students noticed were that the moon appeared to get bigger and then smaller across the month, that the moon appeared to “grow” toward a full moon and then “shrink” and not be visible, and that. Because the moon reflects its light from the sun, only the part of the moon that faces the sun is visible. New moon, first quarter, full moon, and finally last quarter. Web these different shapes are called the phases of the moon, and they change with a regular pattern over a period of about 30 days. Place the opened paper. Web by focusing their attention on the different shapes of the moon, you are helping them move beyond just looking at the moon in ways that will help them start noticing a pattern in their observations — the moon’s appearance changes in a cyclical pattern. Web the repeated pattern in appearance is caused by the position of the moon in. Web the repeated pattern in appearance is caused by the position of the moon in regard to the earth and sun. Web the moon’s revolution and rotation. They use this evidence to record and make predictions about the moon’s appearance in the sky. Observing the moon’s changing appearance and experiencing. Web the moon's phases represent its changing appearance as seen from earth, a cycle that repeats approximately every 29.5 days. Web the phases of the moon and their role in solar eclipses showcase the intricate relationships between earth, the moon, and the sun. The sidereal month is 27.3217 days to be exact. Web these different shapes are called the phases of the moon, and they change with a regular pattern over a period of about 30 days. By galileo, these 1610 lunar maps are some of the first published to rely on telescope views. Because the moon reflects its light from the sun, only the part of the moon that faces the sun is visible. Web by focusing their attention on the different shapes of the moon, you are helping them move beyond just looking at the moon in ways that will help them start noticing a pattern in their observations — the moon’s appearance changes in a cyclical pattern. This chart shows why this happens. The moon’s sidereal period—that is, the period of its revolution about earth measured with respect to the stars—is a little over 27 days: You sometimes hear the back side of the moon (the side we never see) called the “dark side.” The time interval in which the phases repeat—say, from full to full—is the solar month, 29.5306 days.the difference results. The center ring shows the moon as it revolves around the earth, as seen from above the north pole.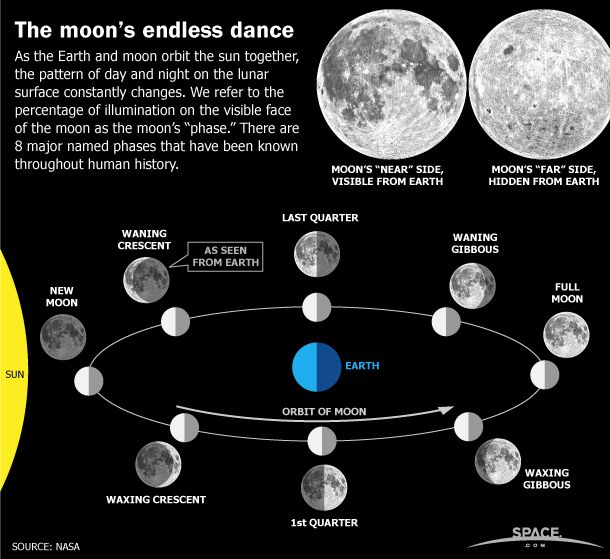
Earth's Moon Phases, Monthly Lunar Cycles (Infographic) Space
![The Phases of the Moon for Kids [Characteristics & Eclipses] HowForKids](https://howforkids.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Moons-Revolution-and-Rotation-1.jpg)
The Phases of the Moon for Kids [Characteristics & Eclipses] HowForKids

Understanding moon phases Moon Phases EarthSky

Lunar¡¯s Phases Astronomy for kids solar Eclipses. What Causes Phases

Moon Phases The Pattern Collective

Lunar Motions Lunar Orbit, Months, Eclipses Scholars Online Astronomy
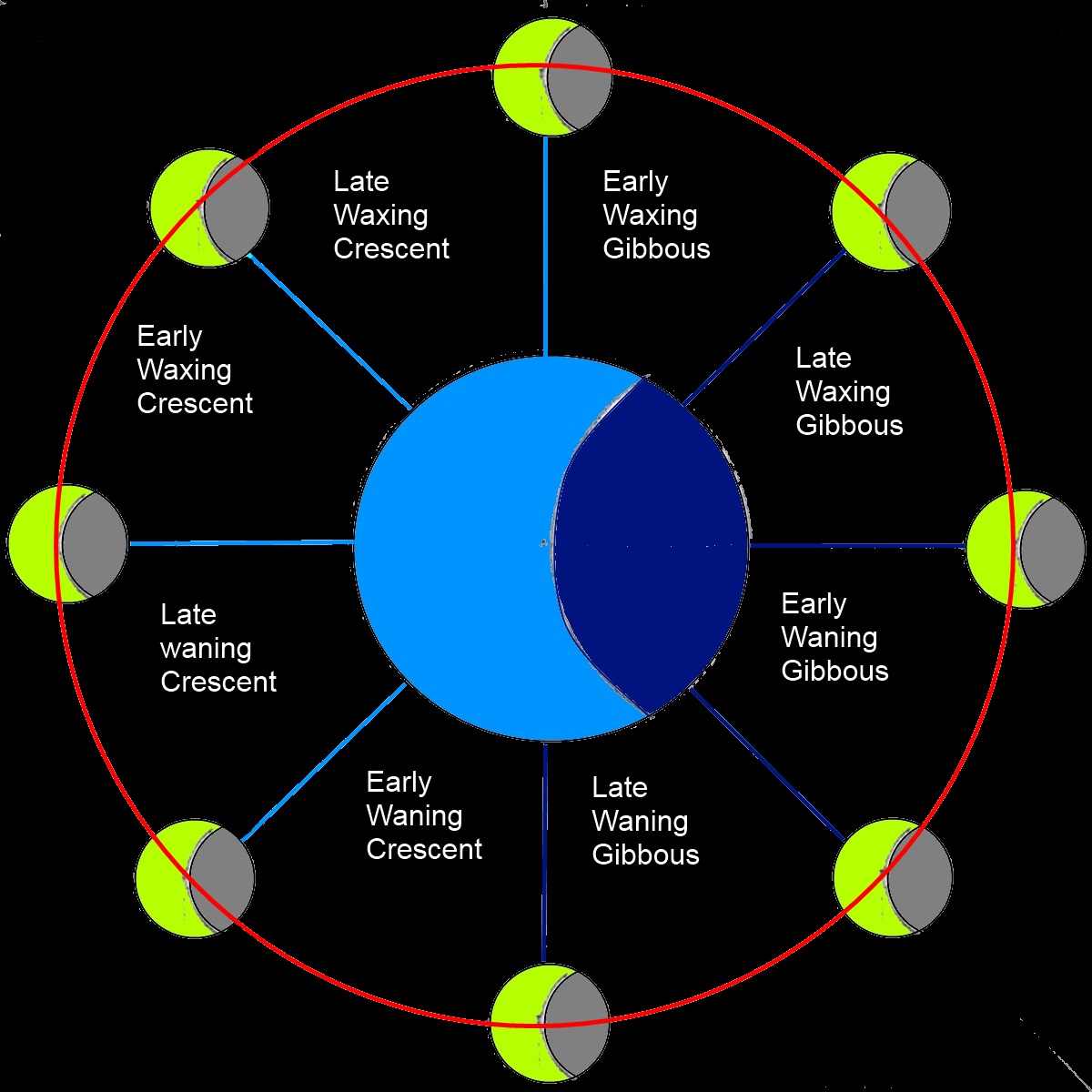
The Lunar Phases and How to Use Them Part 1
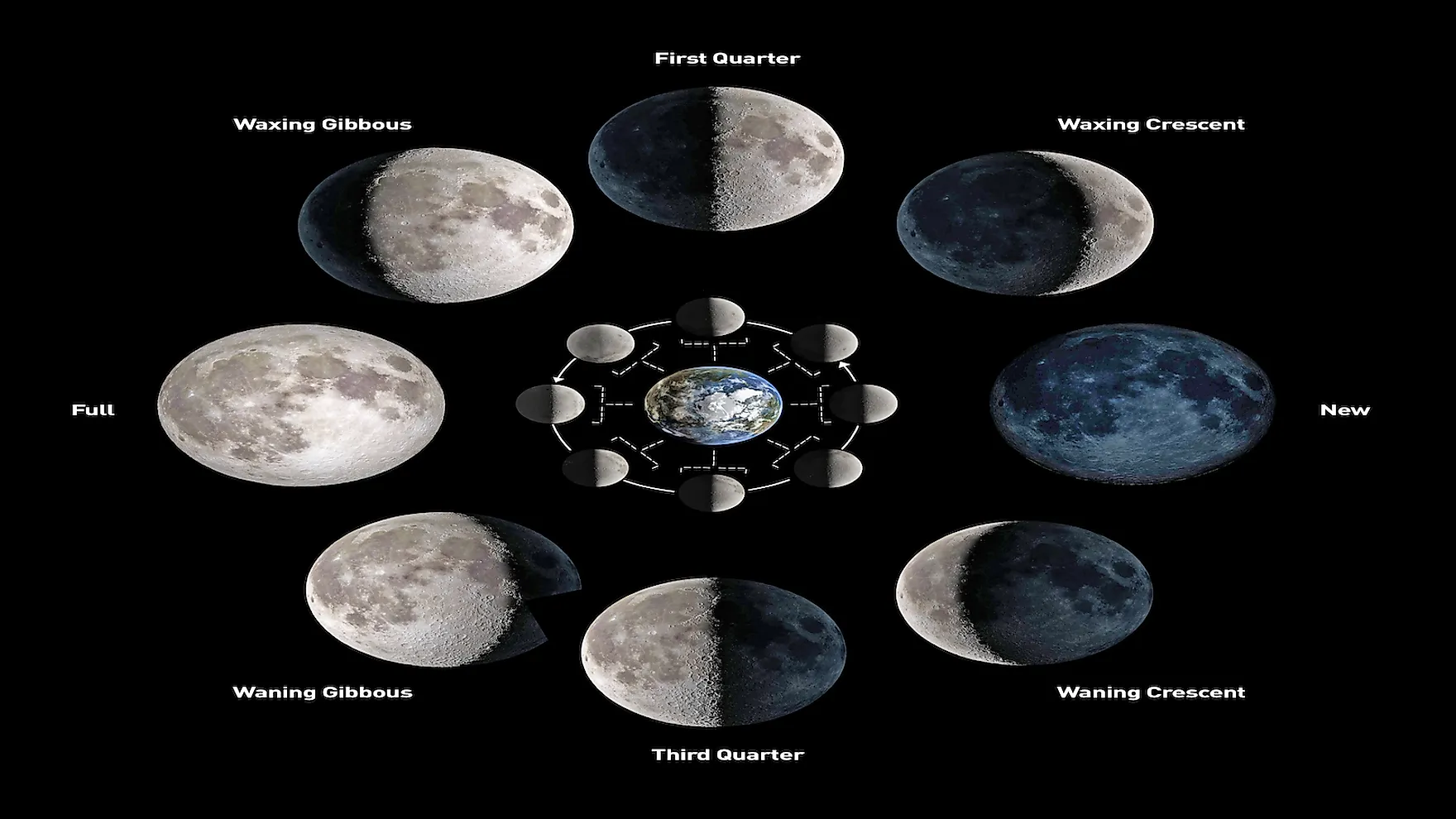
What Are The Different Phases Of The Moon? WorldAtlas

PPT Phases of the Moon PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
The orbits of Jupiter's moons The Society
Web As The Bright Parts Of The Moon Appear To Change Shape During The Month, Each Stage Of The Change Is Called A Phase, And Each Phase Carries Its Own Name.
Web People Can Use The Appearance Of The Moon To Mark The Passage Of Time Because The Moon’s Appearance Changes In A Predictable Pattern Over A Period Of 29.5 Days.
You Sometimes Hear The Back Side Of The Moon (The Side We Never See) Called The “Dark Side.”
Place The Stool In The Center Of Their Circle.
Related Post: