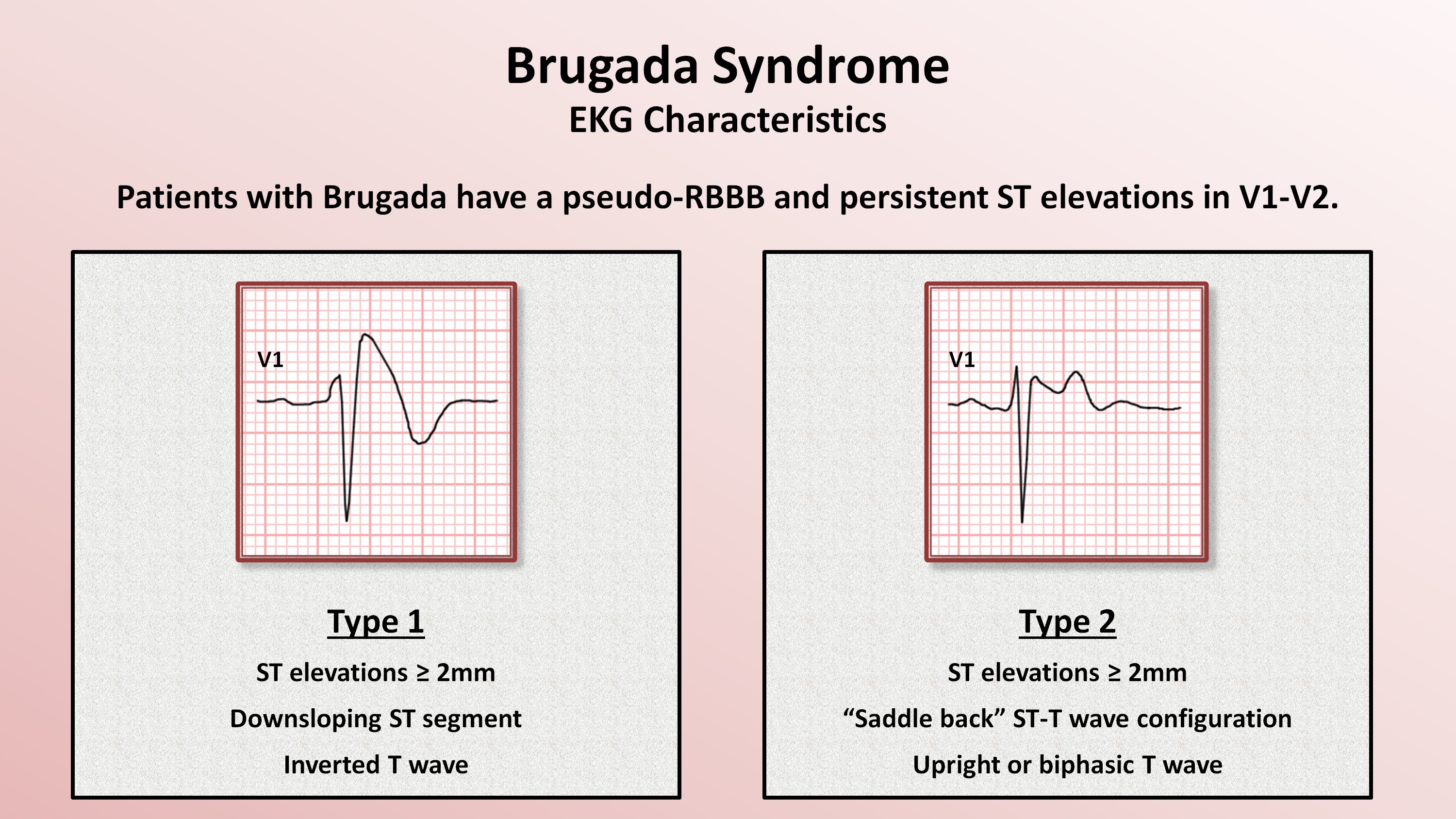
Type 1 Brugada Pattern
Type 1 Brugada Pattern - Furthermore, the proband’s genetic testing was performed using his banked cord blood, which identified the same variant. To diagnose brugada syndrome, a health care provider will perform a physical exam and listen to the heart with a stethoscope. Type 2 pattern is characterized by a. Web the brugada syndrome may present with three different ecg patterns, referred to as type 1, type 2, and type 2 brugada syndrome ecg. People with brugada syndrome have an increased risk of irregular heart rhythms beginning in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). Once diagnosed, there are important changes to lifestyle and medical management that can greatly reduce the risk of serious arrhythmias. Recognized risk factors are spontaneous type 1 ecg and syncope of presumed arrhythmic origin. It's rarely diagnosed in young children because the symptoms are often unnoticed. (see also overview of arrhythmias and overview of channelopathies.) 2 there are 3 types of brugada patterns. It's rarely diagnosed in young children because the symptoms are often unnoticed. Web the type 1 brugada ecg pattern has prominent st elevation in v1 and v2 (sometimes involving v3) that causes the qrs complex in these leads to resemble right bundle branch block. Web the brugada syndrome may present with three different ecg patterns, referred to as type 1,. A heterozygous scn5a p.r893c variant was found by genetic testing in the proband’s father and sister. Web the term brugada syndrome (brs) was first coined for this new arrhythmogenic entity in 1996 [ 3] and in 1997, [ 4] it was recognized as the same entity of sudden nocturnal death syndrome described by guazon et al. The most typical, and. A type 2 pattern raises the suspicion of bs, but the diagnosis depends on the emergence of a type 1 pattern with a drug challenge. Web ecg pattern in brugada syndrome. Patients have abnormal findings on the surface electrocardiogram (ecg) but do not usually have any apparent cardiac structural abnormalities. Web the type 1 pattern is diagnostic of bs whether. A type 2 pattern raises the suspicion of bs, but the diagnosis depends on the emergence of a type 1 pattern with a drug challenge. Brugada syndrome is an inherited channelopathy causing an increased risk of ventricular tachycardia (vt) and ventricular fibrillation (vf) leading to syncope and sudden death. A heterozygous scn5a p.r893c variant was found by genetic testing in. Web three different ecg patterns have been described in brugada syndrome patients: Web ecg pattern in brugada syndrome. Recognized risk factors are spontaneous type 1 ecg and syncope of presumed arrhythmic origin. Web brugada syndrome usually is diagnosed in adults and, sometimes, in adolescents. Web their father showed a spontaneous type 1 brugada electrocardiogram pattern. Patients have abnormal findings on the surface electrocardiogram (ecg) but do not usually have any apparent cardiac structural abnormalities. 1 the diagnosis is based on a particular ecg pattern described by the brugada brothers in 1992. Type 2 pattern is characterized by a. Web the type 1 pattern is diagnostic of bs whether occurring spontaneously or with an intravenous drug. Brugada syndrome is an inherited channelopathy causing an increased risk of ventricular tachycardia (vt) and ventricular fibrillation (vf) leading to syncope and sudden death. To diagnose brugada syndrome, a health care provider will perform a physical exam and listen to the heart with a stethoscope. Web brugada syndrome usually is diagnosed in adults and, sometimes, in adolescents. Web brugada syndrome. Web the brugada syndrome may present with three different ecg patterns, referred to as type 1, type 2, and type 2 brugada syndrome ecg. Web three different ecg patterns have been described in brugada syndrome patients: Prevalence of type 1 brugada electrocardiographic pattern evaluated by twelve‐lead twenty‐four‐hour holter monitoring. It's rarely diagnosed in young children because the symptoms are often. Type 2 and 3 may lead to suspicion, but provocation testing is required for diagnosis. Web 33 cerrato n, giustetto c, gribaudo e, richiardi e, barbonaglia l, scrocco c, zema d, gaita f. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.10.007 crossref medline google scholar Web the type 1 pattern is diagnostic of bs whether occurring spontaneously or with an intravenous drug challenge using a class i. Web the brugada ecg pattern may be caused by a different mechanism in patients with structural abnormalities (eg, excitation failure) than in patients without structural abnormalities (eg, loss of action potential dome). Brugada syndrome poses significant challenges in terms of risk stratification and management, particularly for asymptomatic patients who comprise the majority of individuals exhibiting brugada ecg pattern (brecg). Furthermore,. Web type 1 brugada ecg pattern. A heterozygous scn5a p.r893c variant was found by genetic testing in the proband’s father and sister. Web the type 1 pattern is diagnostic of bs whether occurring spontaneously or with an intravenous drug challenge using a class i antiarrhythmic drug. Web their father showed a spontaneous type 1 brugada electrocardiogram pattern. 1, 2 patients are at risk for sudden cardiac death (scd) due to ventricular fibrillation (vf). Web brugada syndrome usually is diagnosed in adults and, sometimes, in adolescents. People with brugada syndrome have an increased risk of irregular heart rhythms beginning in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). Web 33 cerrato n, giustetto c, gribaudo e, richiardi e, barbonaglia l, scrocco c, zema d, gaita f. Brugada syndrome poses significant challenges in terms of risk stratification and management, particularly for asymptomatic patients who comprise the majority of individuals exhibiting brugada ecg pattern (brecg). 10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.10.007 crossref medline google scholar Web the term brugada syndrome (brs) was first coined for this new arrhythmogenic entity in 1996 [ 3] and in 1997, [ 4] it was recognized as the same entity of sudden nocturnal death syndrome described by guazon et al. (see also overview of arrhythmias and overview of channelopathies.) A type 2 pattern raises the suspicion of bs, but the diagnosis depends on the emergence of a type 1 pattern with a drug challenge. The most typical, and diagnostic, is type 1 brugada syndrome. Web ecg pattern in brugada syndrome. Recognized risk factors are spontaneous type 1 ecg and syncope of presumed arrhythmic origin.
Syndrome de Brugada type 1 ecardiogram
Brugada Syndrome
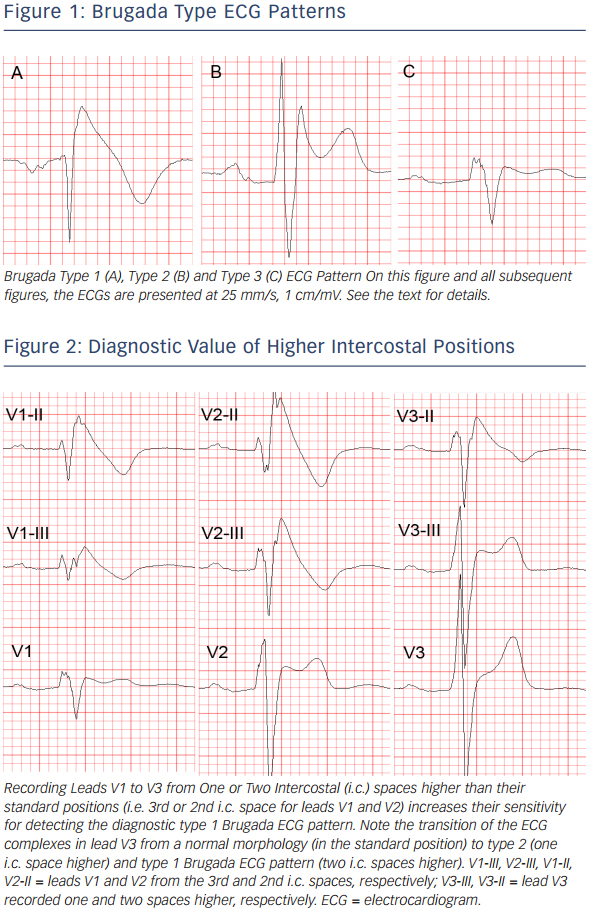
Figure 1 Brugada Type ECG Patterns Radcliffe Vascular

Brugada Syndrome Causes, ECG, Symptoms, Treatment
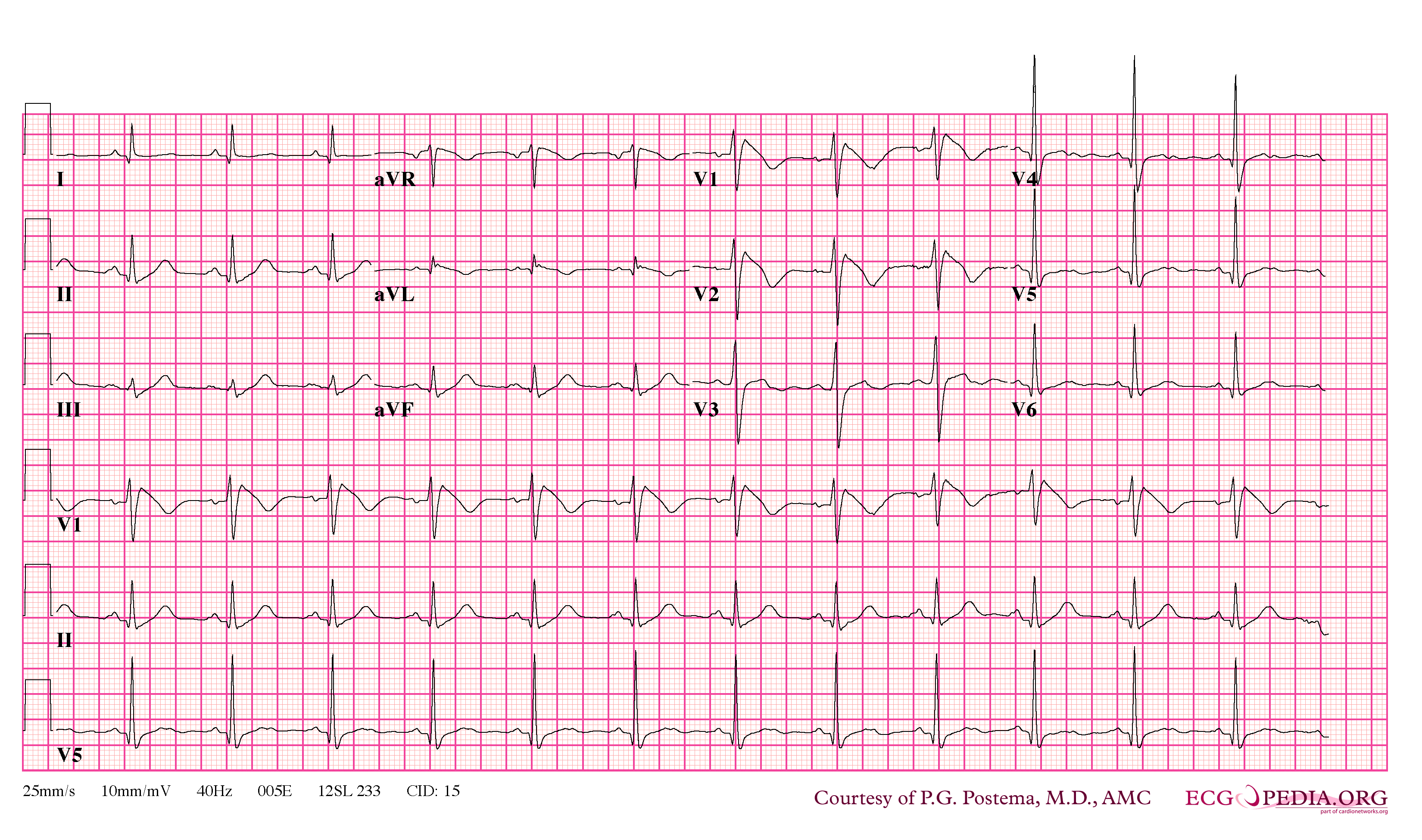
FileBrugada syndrome type1 example4.png ECGpedia

BrugadaSyndrom EKG, klinische Merkmale und Management EKG & ECHO

Brugada Syndrome Circulation Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology
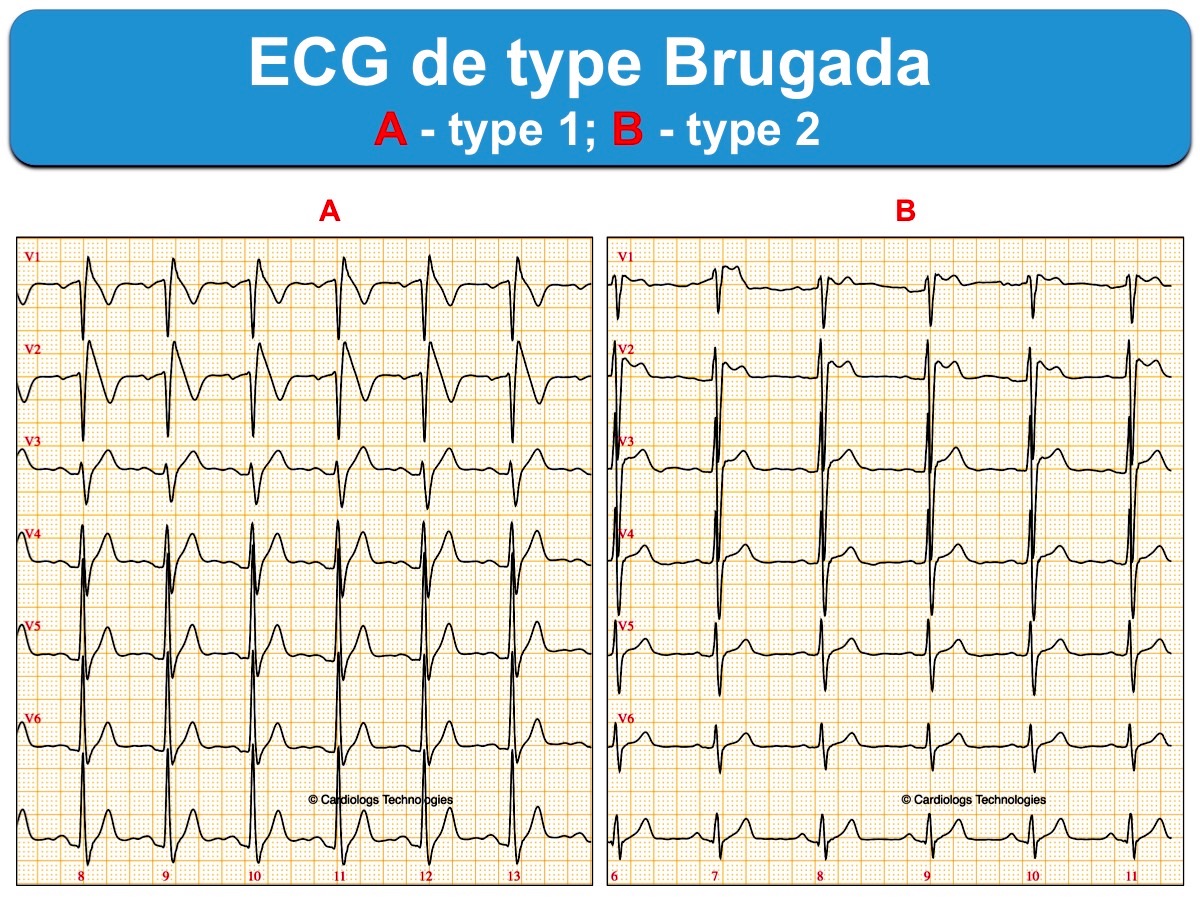
Type 1 Brugada Ecg

Type 1 Brugada ECG unmasked by intracoronary contrast media Heart

ECG Brugada type 1 ou 2 ecardiogram
Rarely, Implantable Defibrillators Can Help Reduce The Risk Of Sudden Death.
Web Brugada Syndrome Is A Genetic Disorder That Can Cause A Dangerous Irregular Heartbeat, Especially During Sleep Or At Rest.
1 The Diagnosis Is Based On A Particular Ecg Pattern Described By The Brugada Brothers In 1992.
Furthermore, The Proband’s Genetic Testing Was Performed Using His Banked Cord Blood, Which Identified The Same Variant.
Related Post: