Triplet Splitting Pattern
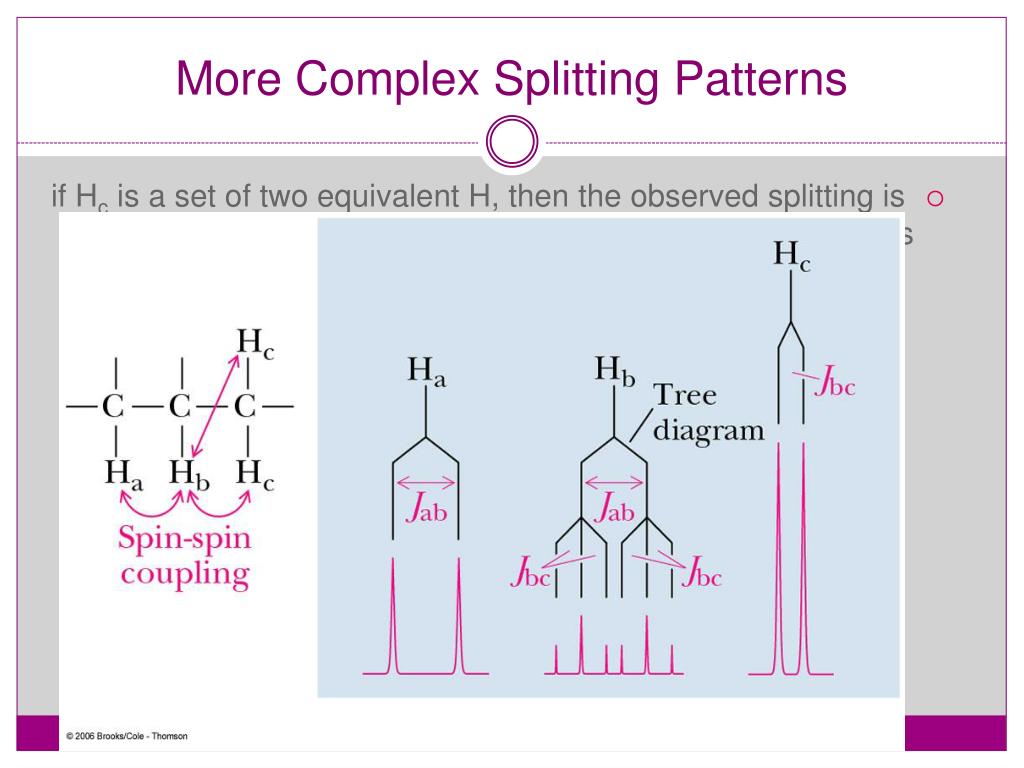
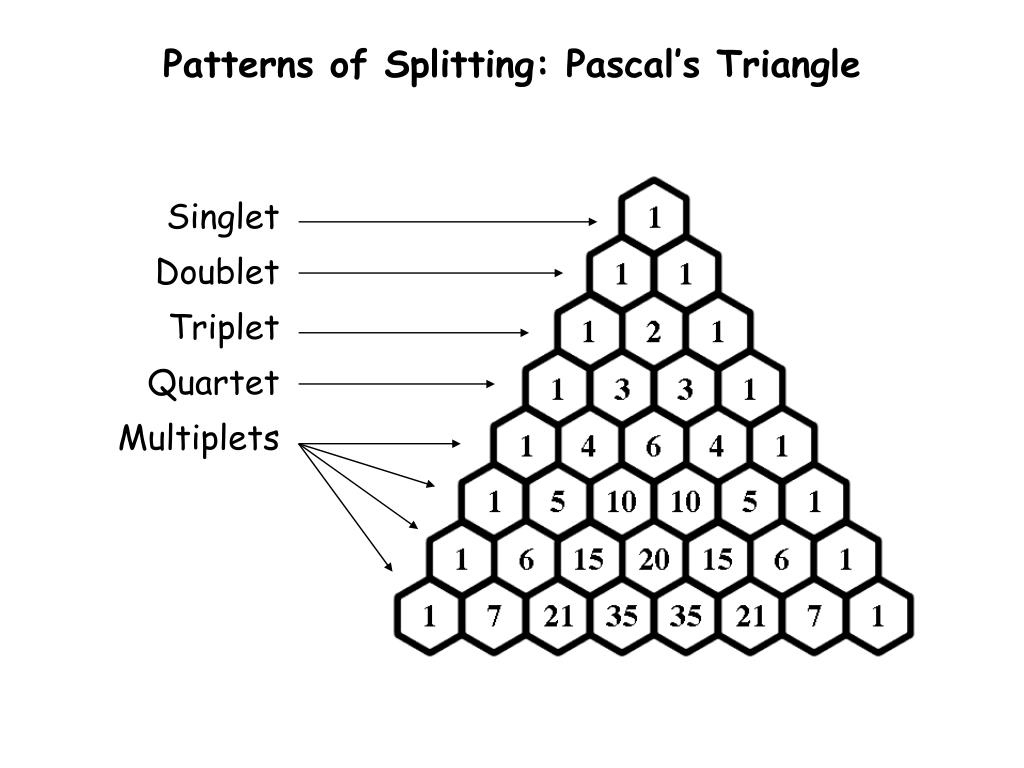
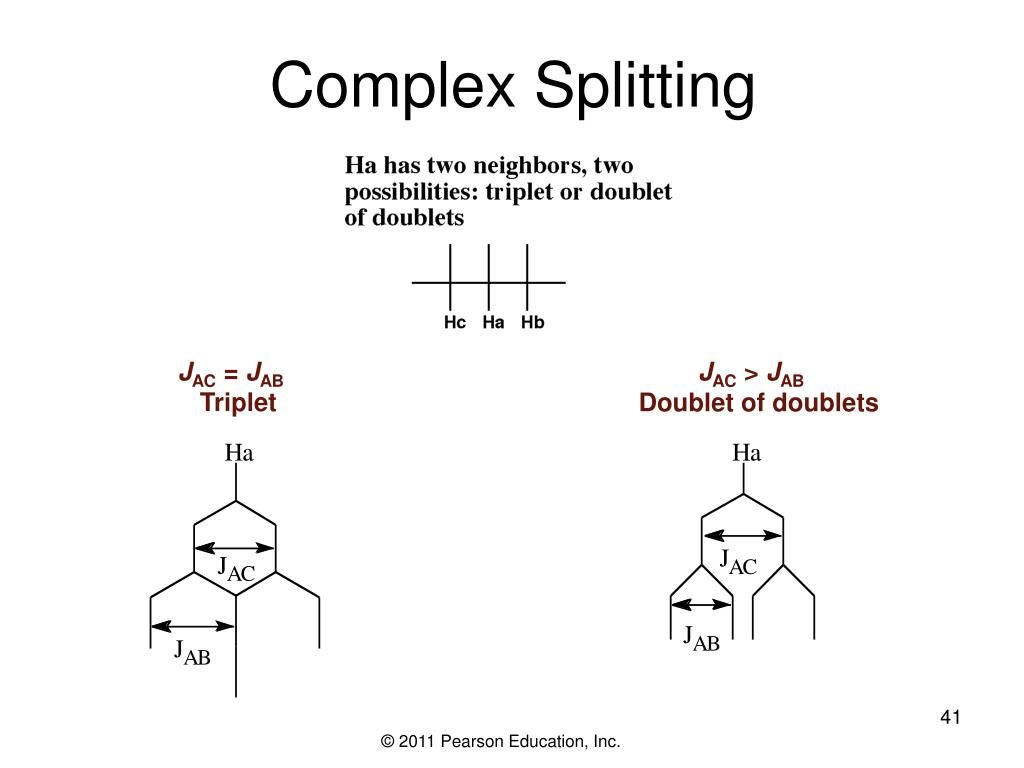
Triplet Splitting Pattern - Want to join the conversation? Web by now, you probably have recognized the pattern which is usually referred to as the n + 1 rule: Another effect that can complicate a spectrum is the “closeness” of signals. This means that h a would be a triplet as would h c. Let’s first see how the doublet originates. Also, when multiplets are well separated, they form patterns. Web one adjacent proton splits an nmr signal into a doublet and two adjacent protons split the signal into a triplet. 40k views 10 years ago nmr spectrocsopy. It explains how to use the n+1 rule to determine. Thus the two h b hydrogens in ethyl acetate split the h c signal into a triplet, and the three h c hydrogens split the h b signal into a quartet. However, the hydrogen on c 2 “sees” two different sets of neighbouring hydrogens, and would therefore produce a triplet of triplets. Also, when multiplets are well separated, they form patterns. Web to interpret the nmr information, let’s look at each absorption individually. Web by now, you probably have recognized the pattern which is usually referred to as the n +. Ha and hb are nonequivalent protons so they split each other’s nmr signals. Web two hydrogens on the adjacent atoms will split the resonance into three peaks with an area in the ratio of 1:2:1, a triplet. Let’s first see how the doublet originates. Web the hydrogens at c 1 and c 3 would each be triplets because of coupling. Ha and hb are nonequivalent protons so they split each other’s nmr signals. The aldehyde proton signal at c1 ( red ) appears in the normal downfield position at 9.69 δ and is split into a doublet with j = 6 hz by the adjacent proton at c2. Web the hydrogens at c 1 and c 3 would each be. Thus the two h b hydrogens in ethyl acetate split the h c signal into a triplet, and the three h c hydrogens split the h b signal into a quartet. Web introduction to nmr splitting patterns. It explains how to use the n+1 rule to determine. It demonstrates how the magnetic fields of protons can interact, leading to splitting. Web coupling to first nucleus (n=1, triplet) coupling to second nucleus (n=2, quintet) coupling to third nucleus (n=3, septet) coupling to fourth nucleus (n=4, nonet) etc. However, h b has two sets of neighboring protons (h a and h c). Web the five aromatic proton signals (black in figure 13.14) overlap into a complex pattern with a large peak at. Web to interpret the nmr information, let’s look at each absorption individually. Web by now, you probably have recognized the pattern which is usually referred to as the n + 1 rule: It explains how to use the n+1 rule to determine. Thus the two h b hydrogens in ethyl acetate split the h c signal into a triplet, and. Web one adjacent proton splits an nmr signal into a doublet and two adjacent protons split the signal into a triplet. Let’s first see how the doublet originates. The peaks split like so: The aldehyde proton signal at c1 ( red ) appears in the normal downfield position at 9.69 δ and is split into a doublet with j =. Web the five aromatic proton signals (black in figure 13.14) overlap into a complex pattern with a large peak at 7.42 δ and a broad absorption at 7.57 δ. Web the hydrogens at c 1 and c 3 would each be triplets because of coupling to the two hydrogens on c 2. Web by now, you probably have recognized the. However, the hydrogen on c 2 “sees” two different sets of neighbouring hydrogens, and would therefore produce a triplet of triplets. However, h b has two sets of neighboring protons (h a and h c). It explains how to use the n+1 rule to determine. Thus the two h b hydrogens in ethyl acetate split the h c signal into. This tutorial looks at singlet, doublet, triplet and quartet. Web remember, splitting occurs primarily between hydrogens that are separated by three bonds. Thus the two h b hydrogens in ethyl acetate split the h c signal into a triplet, and the three h c hydrogens split the h b signal into a quartet. Web by now, you probably have recognized. Web learn how to predict the splitting pattern when a proton has two different kinds of neighboring protons by using a splitting tree. Thus the two h b hydrogens in ethyl acetate split the h c signal into a triplet, and the three h c hydrogens split the h b signal into a quartet. Web two hydrogens on the adjacent atoms will split the resonance into three peaks with an area in the ratio of 1:2:1, a triplet. Web by now, you probably have recognized the pattern which is usually referred to as the n + 1 rule: Thus the two h b hydrogens in ethyl acetate split the h c signal into a triplet, and the three h c hydrogens split the h b signal into a quartet. Want to join the conversation? Also, when multiplets are well separated, they form patterns. The aldehyde proton signal at c1 ( red ) appears in the normal downfield position at 9.69 δ and is split into a doublet with j = 6 hz by the adjacent proton at c2. The peaks split like so: Web the five aromatic proton signals (black in figure 13.14) overlap into a complex pattern with a large peak at 7.42 δ and a broad absorption at 7.57 δ. Web by now, you probably have recognized the pattern which is usually referred to as the n + 1 rule: Web this organic chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into spin spin splitting / coupling as it relates to proton nmr spectroscopy. This tutorial looks at singlet, doublet, triplet and quartet. Web the hydrogens at c 1 and c 3 would each be triplets because of coupling to the two hydrogens on c 2. Let’s first see how the doublet originates. However, h b has two sets of neighboring protons (h a and h c).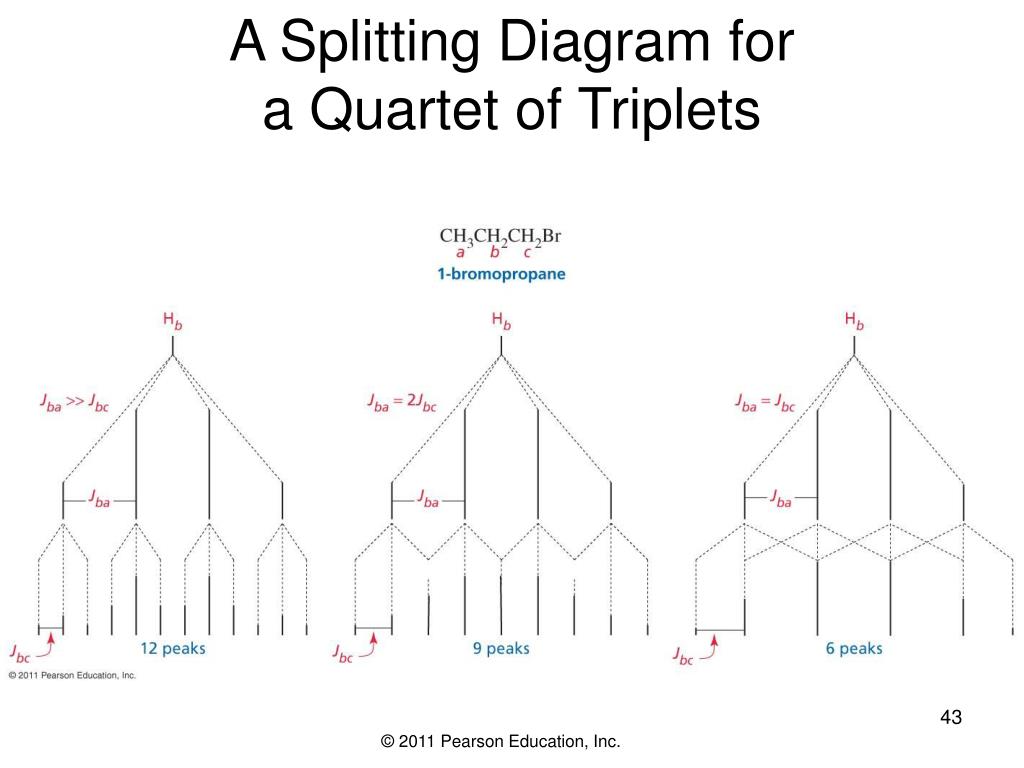
PPT Chapter 14 NMR Spectroscopy PowerPoint Presentation, free

H NMR Splitting Patterns

The pseudotriplet splitting pattern in the 1 H NMR spectrum of

Splitting and Multiplicity (N+1 rule) in NMR Spectroscopy Chemistry Steps
PPT Organic Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1414842
PPT Nuclear Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy PowerPoint

Bass Drum Splitting Exercise Triplet Split Patterns Rudimental

Splitting and Multiplicity (N+1 rule) in NMR Spectroscopy Chemistry Steps
PPT Chapter 14 NMR Spectroscopy PowerPoint Presentation, free

Singlettriplet splitting in the 3 ˜ d state of HeH +. The quantity
This Means That H A Would Be A Triplet As Would H C.
It Should Also Be Noted That The Approach Taken In This Guide Is Based On Pattern Recognition And Is
Web Remember, Splitting Occurs Primarily Between Hydrogens That Are Separated By Three Bonds.
Another Effect That Can Complicate A Spectrum Is The “Closeness” Of Signals.
Related Post: