Thoracic Facet Joint Pain Referral Patterns
Thoracic Facet Joint Pain Referral Patterns - Web pain patterns from thoracic facet joints should be differentiated from those of the costotransverse joints. Web thoracic facet pain pattern. Web the differential diagnosis of thoracic pain is usually challenging, including visceral conditions (e.g. Web pain patterns were located superficial to the injected joint, with only the right t2 injections showing referred pain 2 segments cranially and caudally. Web with appropriate investigations, using controlled diagnostic medial branch blocks, thoracic facet joints have been established as sources of mid back pain, upper. Web pain patterns were located superficial to the injected joint, with only the right t2 injections showing referred pain 2 segments cranially and caudally. Unfortunately, there is a significant overlap between some of the thoracic facet joints. Diagnostic blocks (for example, medial branch. Coronary, aortic, or esophageal diseases), or various. Facetogenic pain, also known as zygapophysial joint pain, is a frequent cause of mechanical spine pain. Web referred pain is a common but less understood symptom that originates from somatic tissues. Srinivas chiravuri, md director, pain medicine fellowship director, neuromodulation assistant professor university of michigan health system ann arbor, mi chad m. Established pain patterns for the thoracic facet joints: Arthritic changes in the facets may cause a feeling of grinding or grating in the joints. Web thoracic facet joints have distinct referral patterns, as seen in the figure below. Web with appropriate investigations, using controlled diagnostic medial branch blocks, thoracic facet joints have been established as sources of mid back pain, upper. Established pain patterns for the thoracic facet joints: Web pain patterns from thoracic facet joints should be differentiated from those of the costotransverse. Web thoracic facet joint pain paterns. Established pain patterns for the thoracic facet joints: Web referred pain is a common but less understood symptom that originates from somatic tissues. Facet joint syndrome is most commonly found in the neck (cervical region) and lower back (lumbar) and is caused by natural wear and tear on the joints (facets) over time. Facetogenic. Web typical referral patterns for pain emanating from specific facet joints have been identified and mapped for the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar zygapophyseal joints. Facet mediated pain does not usually radiate below the. Facetogenic pain, also known as zygapophysial joint pain, is a frequent cause of mechanical spine pain. Web salient characteristics of facet pain include pain on extension, either. Web pain patterns from thoracic facet joints should be differentiated from those of the costotransverse joints. Facet joint syndrome is most commonly found in the neck (cervical region) and lower back (lumbar) and is caused by natural wear and tear on the joints (facets) over time. Causes of facet joint syndrome. Causes parasagittal cervicothoracic and thoracic pain. Web for example,. Established pain patterns for the thoracic facet joints: Web the differential diagnosis of thoracic pain is usually challenging, including visceral conditions (e.g. Srinivas chiravuri, md director, pain medicine fellowship director, neuromodulation assistant professor university of michigan health system ann arbor, mi chad m. Web typical referral patterns for pain emanating from specific facet joints have been identified and mapped for. Web the differential diagnosis of thoracic pain is usually challenging, including visceral conditions (e.g. Web thoracic facet syndrome is a type of osteoarthritis that, with the deterioration of the cartilage lining on the joint, can lead to joint inflammation and limited mobility. Arthritic changes in the facets may cause a feeling of grinding or grating in the joints upon movement.. Coronary, aortic, or esophageal diseases), or various. Arthritic changes in the facets may cause a feeling of grinding or grating in the joints upon movement. Web typical referral patterns for pain emanating from specific facet joints have been identified and mapped for the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar zygapophyseal joints. Facet mediated pain does not usually radiate below the. Web for. Unfortunately, there is a significant overlap between some of the thoracic facet joints. Web thoracic facet syndrome is a type of osteoarthritis that, with the deterioration of the cartilage lining on the joint, can lead to joint inflammation and limited mobility. Web pain patterns were located superficial to the injected joint, with only the right t2 injections showing referred pain. Facet mediated pain does not usually radiate below the. The costotransverse joint pain is a deep, dull aching, and. Web pain patterns were located superficial to the injected joint, with only the right t2 injections showing referred pain 2 segments cranially and caudally. Web pain patterns from thoracic facet joints should be differentiated from those of the costotransverse joints. Web. Web thoracic facet joints have distinct referral patterns, as seen in the figure below. Facetogenic pain, also known as zygapophysial joint pain, is a frequent cause of mechanical spine pain. Unfortunately, there is significant overlap between the thoracic referral patterns which. Coronary, aortic, or esophageal diseases), or various. Srinivas chiravuri, md director, pain medicine fellowship director, neuromodulation assistant professor university of michigan health system ann arbor, mi chad m. Arthritic changes in the facets may cause a feeling of grinding or grating in the joints upon movement. Established pain patterns for the thoracic facet joints: A comprehensive recognition of referred pain is important for. Causes of facet joint syndrome. Web pain patterns were located superficial to the injected joint, with only the right t2 injections showing referred pain 2 segments cranially and caudally. Web pain patterns from thoracic facet joints should be differentiated from those of the costotransverse joints. Web the differential diagnosis of thoracic pain is usually challenging, including visceral conditions (e.g. Web clinical facet joint syndrome is defined as a unilateral or bilateral back pain radiating to one or both buttocks, sides of the groin, and thighs, and stopping above the. Web thoracic facet pain pattern. Web salient characteristics of facet pain include pain on extension, either with or without combined rotation movements. Web medical history, referred pain patterns, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging studies (standard radiographs, magnetic resonance imaging,.
Facet Joint Pain
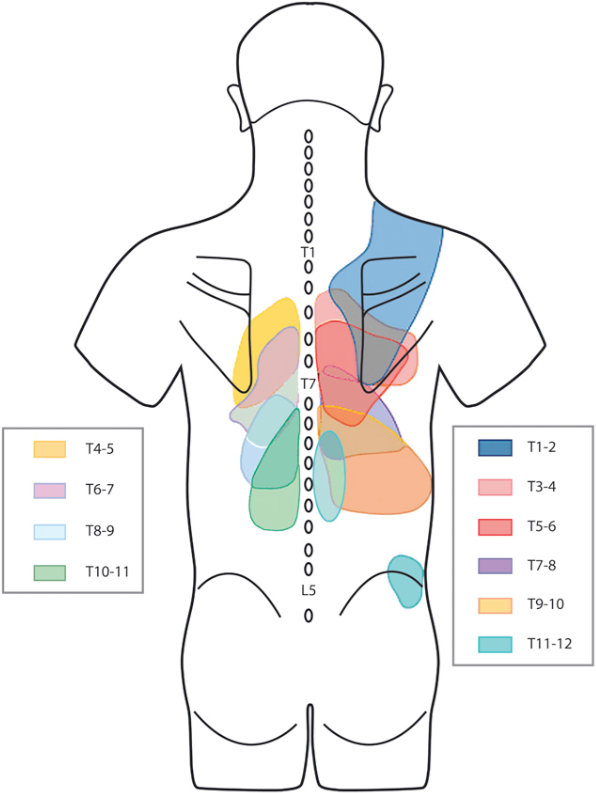
Details for Thoracic Facet Referral Pain Patterns and Related Queries

Facet Referral Patterns Bead Pattern (Free)
Facet Joint Pain
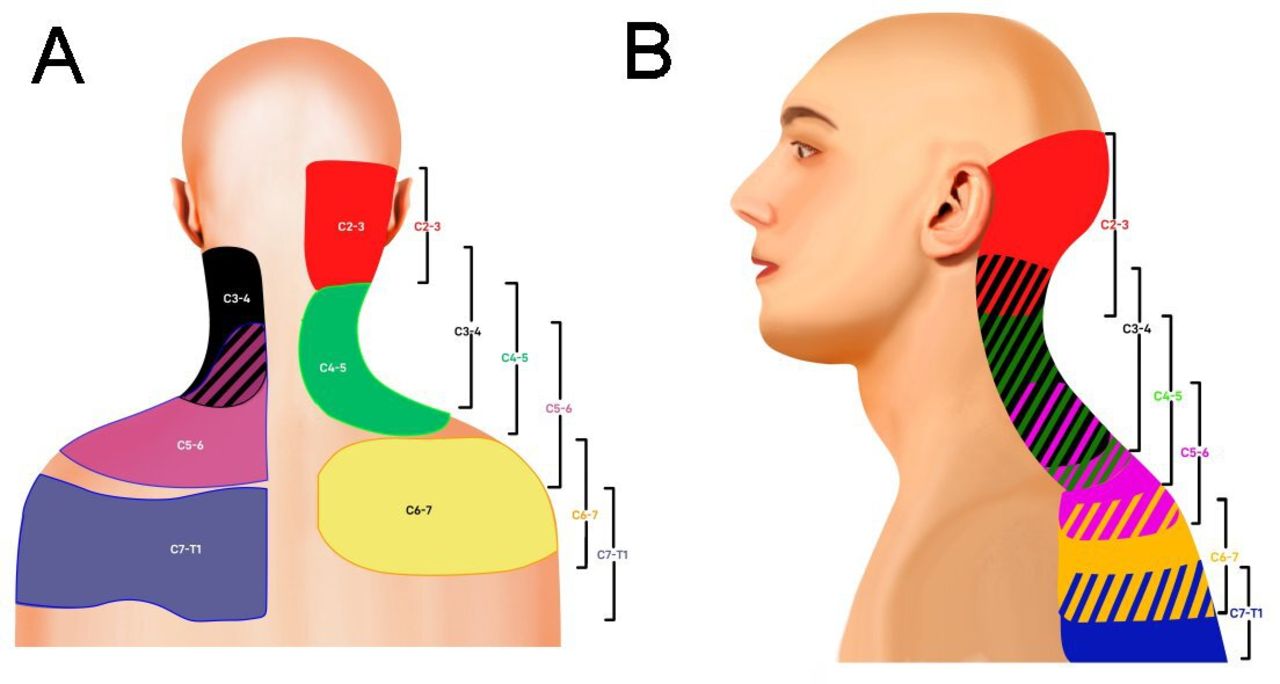
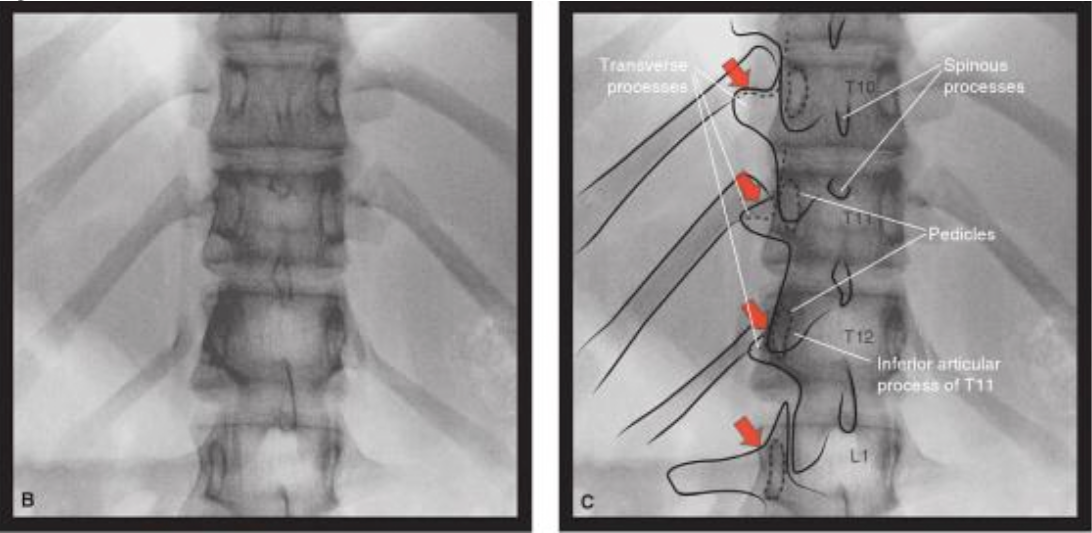
Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine

Evidence based pain referral patterns Download Scientific Diagram

Facet Pain Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment Clinical Tree

Illustration of distribution pattern related to facet joint pain
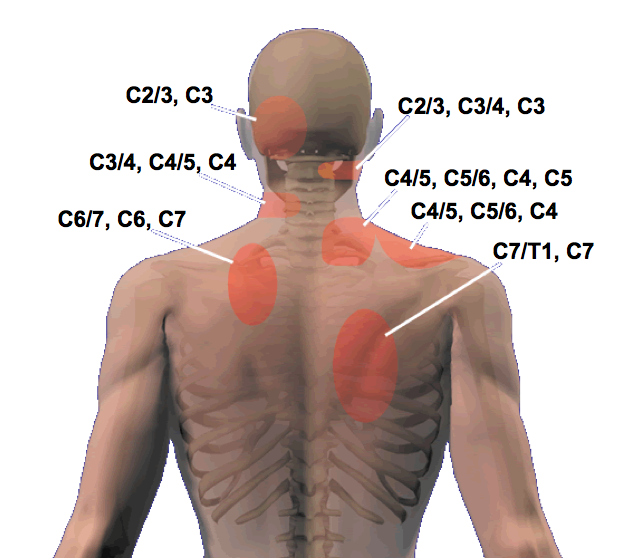
Cloward sign & Cervical Referral Patterns Modern Manual Therapy Blog

Radiation pattern of thoracic facet pain. (illustration Rogier Trompert
Web For Example, Pain From Injury Of The T3/4 Facet Is Felt Along The Inside Border Of The Scapula.
Web Thoracic Facet Syndrome Is A Type Of Osteoarthritis That, With The Deterioration Of The Cartilage Lining On The Joint, Can Lead To Joint Inflammation And Limited Mobility.
Web Thoracic Facet Joint Pain Paterns.
Web Pain Patterns Were Located Superficial To The Injected Joint, With Only The Right T2 Injections Showing Referred Pain 2 Segments Cranially And Caudally.
Related Post: