The Coriolis Effect Causes Winds To Move In A Pattern
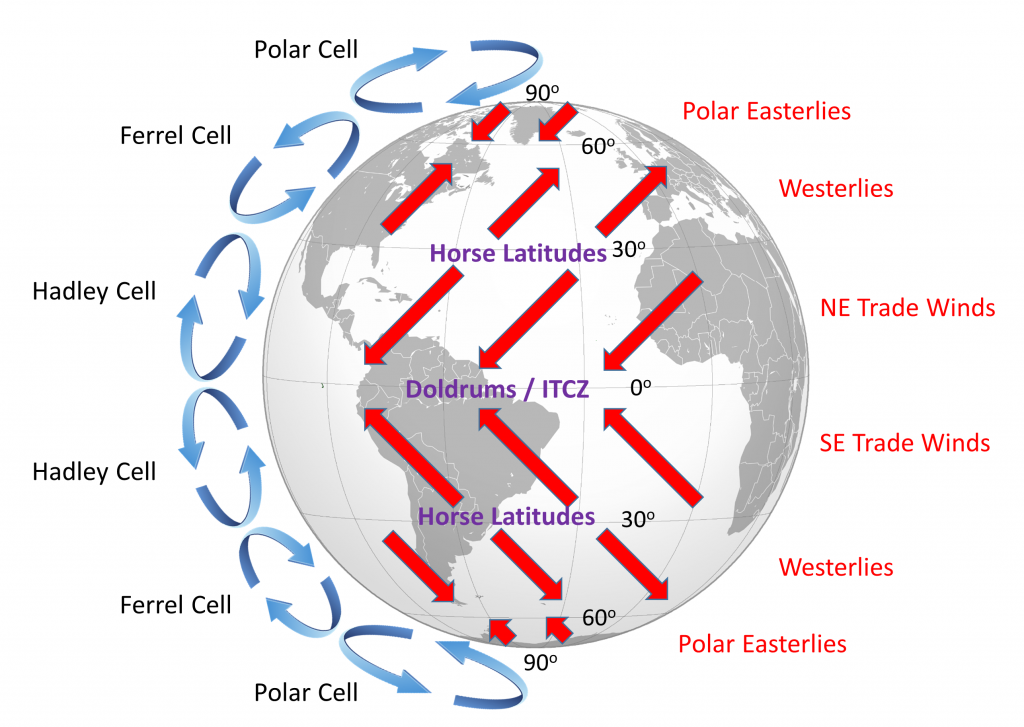
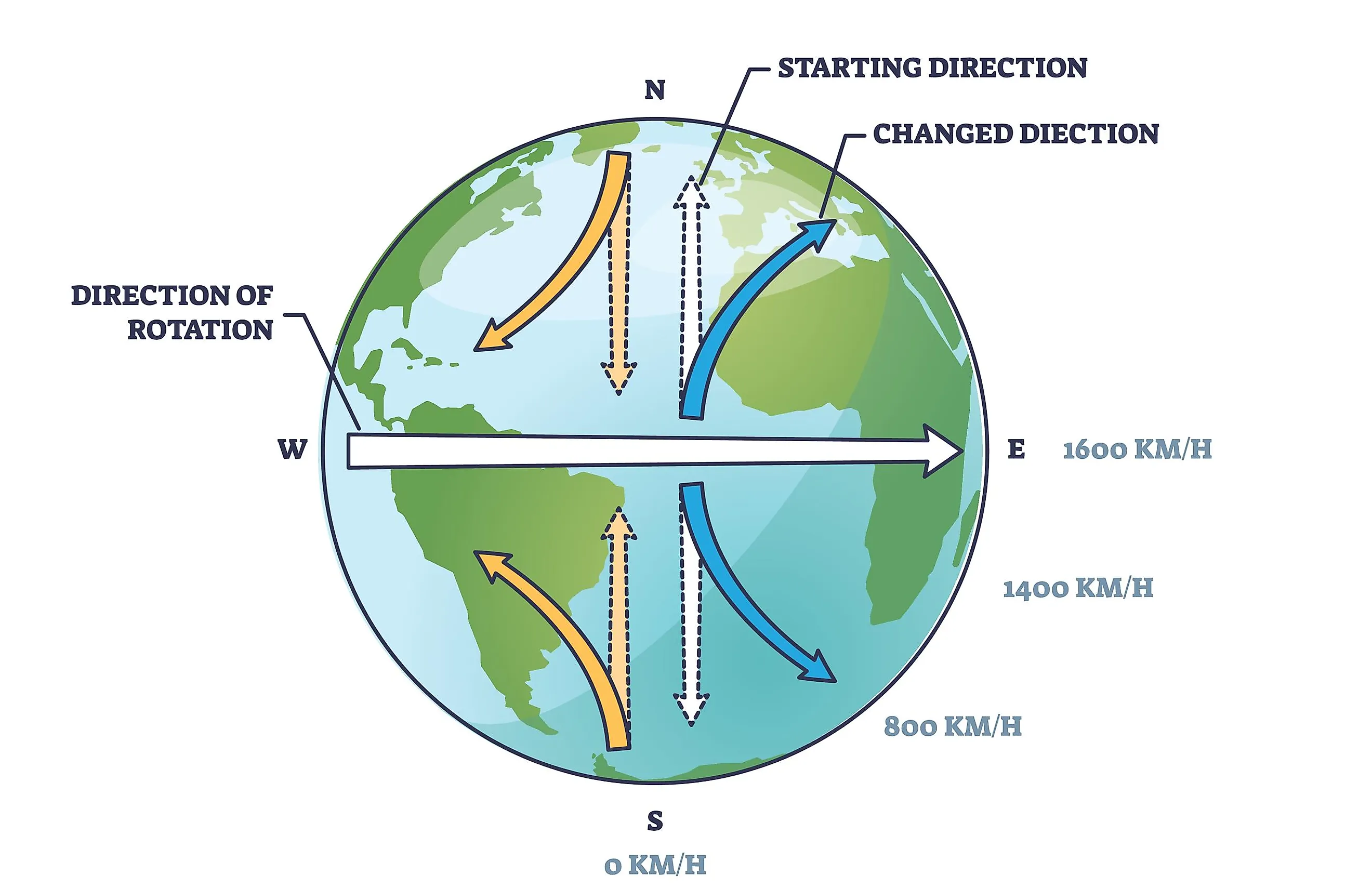
The Coriolis Effect Causes Winds To Move In A Pattern - Web updated on january 22, 2020. Winds and ocean currents are in constant motion. Web this curving has to do with the rotation of earth and is called the coriolis effect. As prevailing winds blow across the ocean, they create surface currents in the water. Web what is the coriolis effect? The coriolis effect is named after gustave coriolis, the. As these prevailing winds blow across the surface of the land and water, they also pushed against. It is spinning from west to east. The coriolis effect causes winds and currents to form circular patterns. The earth's rotation means that we experience an apparent force known as the coriolis force. The coriolis effect describes how objects that are not connected to the. Web because the earth rotates on its axis, circulating air is deflected toward the right in the northern hemisphere and toward the left in the southern hemisphere. The coriolis effect (also known as the coriolis force) refers to the apparent deflection of objects (such as airplanes, wind, missiles,. As prevailing winds blow across the ocean, they create surface currents in the water. Winds and ocean currents are in constant motion. Web the coriolis effect deflects the path of the winds to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. The coriolis effect is named after gustave coriolis, the. It is spinning from. In the atmosphere, large masses of air are set into motion by differences in temperature and. This is left to right on a map. Web this curving has to do with the rotation of earth and is called the coriolis effect. Earth is constantly rotating, or spinning. Web in physics, the coriolis force is an inertial (or fictitious) force that. This movement does not follow a straight line but. Web the coriolis effect plays a critical role in weather patterns. It is spinning from west to east. Web updated on january 22, 2020. Coriolis does not force anything to happen! This movement does not follow a straight line but. This deflects the direction of the wind to the right in the. Web this curving has to do with the rotation of earth and is called the coriolis effect. As prevailing winds blow across the ocean, they create surface currents in the water. This is left to right on a map. When an object is moved off its course, we say it has been deflected. Web outside storm systems, the impact of the coriolis effect helps define regular wind patterns around the globe. Web because the earth rotates on its axis, circulating air is deflected toward the right in the northern hemisphere and toward the left in the southern hemisphere. Web. In the atmosphere, large masses of air are set into motion by differences in temperature and. Winds and ocean currents are in constant motion. Web the coriolis effect plays a critical role in weather patterns. Adding this deflection leads to. When an object is moved off its course, we say it has been deflected. This is called the coriolis effect. Web the actual paths of winds—and of ocean currents, which are pushed by wind—are partly a result of the coriolis effect. The earth's rotation means that we experience an apparent force known as the coriolis force. Web because the earth rotates on its axis, circulating air is deflected toward the right in the northern. The coriolis effect describes how objects that are not connected to the. The coriolis effect is not a force, even though that's what it is sometimes called. Web the coriolis effect is caused by the planet 's rotation. In the northern hemisphere, these warm air currents are deflected to. Web the global pattern of prevailing winds is caused by the. The coriolis effect causes winds and currents to form circular patterns. Coriolis does not force anything to happen! Web because the earth rotates on its axis, circulating air is deflected toward the right in the northern hemisphere and toward the left in the southern hemisphere. Web in physics, the coriolis force is an inertial (or fictitious) force that acts on. Web because the earth rotates on its axis, circulating air is deflected toward the right in the northern hemisphere and toward the left in the southern hemisphere. Earth is constantly rotating, or spinning. It is spinning from west to east. As warm air rises near the equator, for instance, it flows toward the poles. Web the coriolis effect plays a critical role in weather patterns. The coriolis effect describes how objects that are not connected to the. Web ‘coriolis effect’ or coriolis force can be defined simply as deflection of wind. As prevailing winds blow across the ocean, they create surface currents in the water. The coriolis effect (also known as the coriolis force) refers to the apparent deflection of objects (such as airplanes, wind, missiles, and ocean. The direction that they spin depend on the hemisphere that they are in. The coriolis effect is not a force, even though that's what it is sometimes called. The earth's rotation means that we experience an apparent force known as the coriolis force. This movement does not follow a straight line but. This deflects the direction of the wind to the right in the. Web the coriolis effect is caused by the planet 's rotation. As these prevailing winds blow across the surface of the land and water, they also pushed against.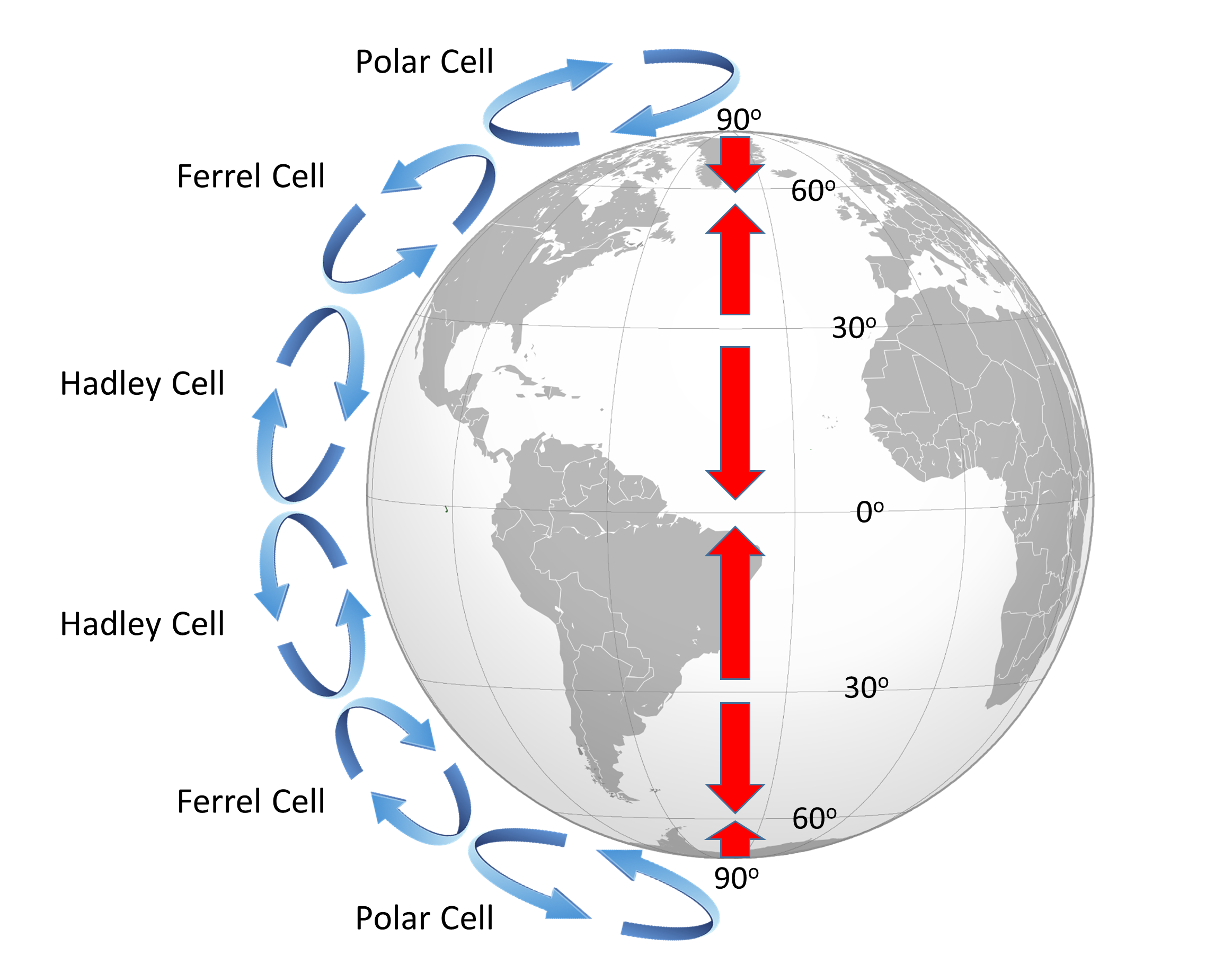
8.2 Winds and the Coriolis Effect Introduction to Oceanography
Global winds, satellitebased diagram. The rotation of this Earth globe
10.2 Winds and the Coriolis Effect Geosciences LibreTexts
What is the Coriolis Effect? WorldAtlas

What is the Coriolis force Windy.app

what is the coriolis effect
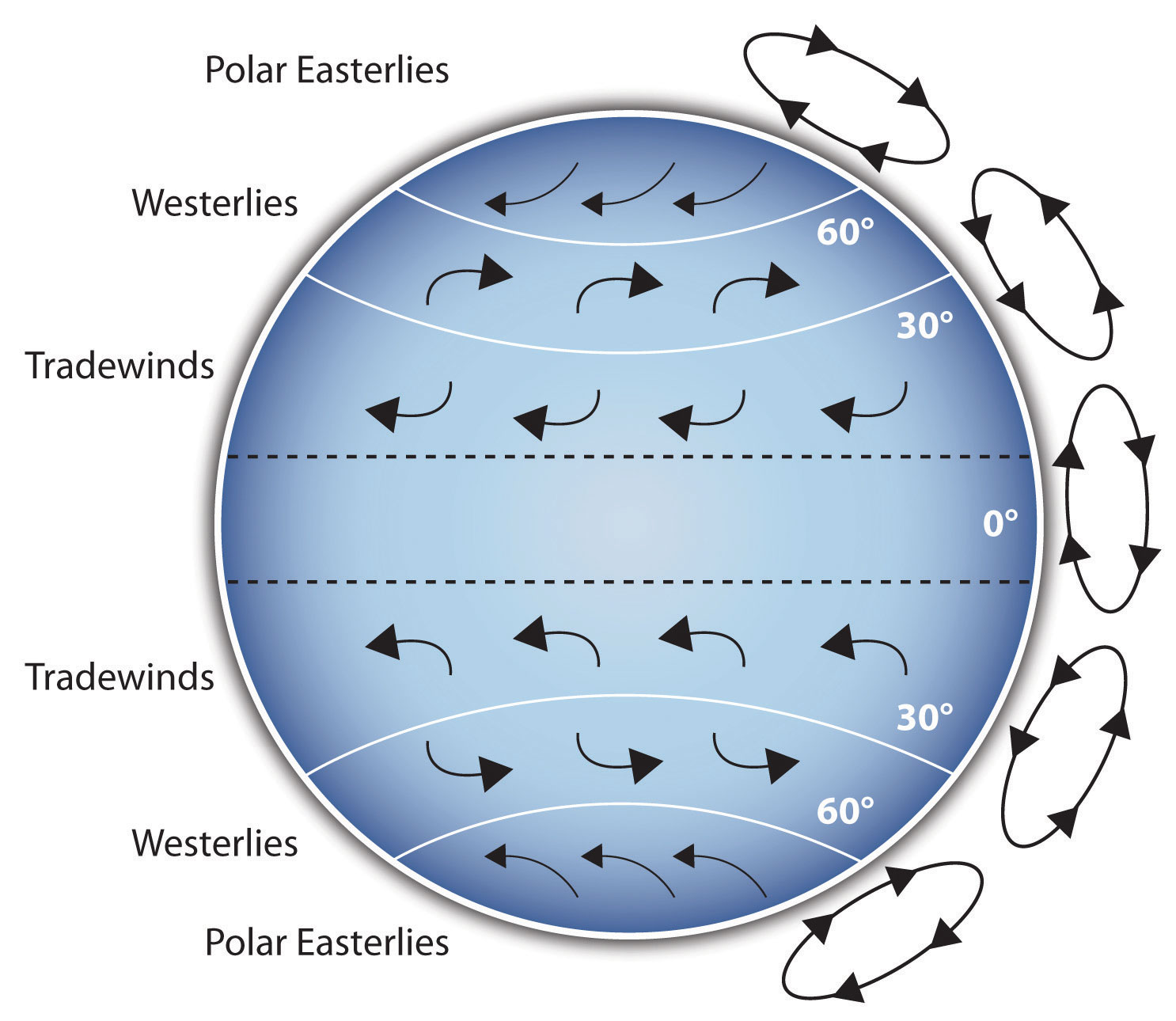
The Coriolis effect (video) Clouds Khan Academy

Deflection Of Winds, Oceanic Currents & Coriolis Theory Free UPSC
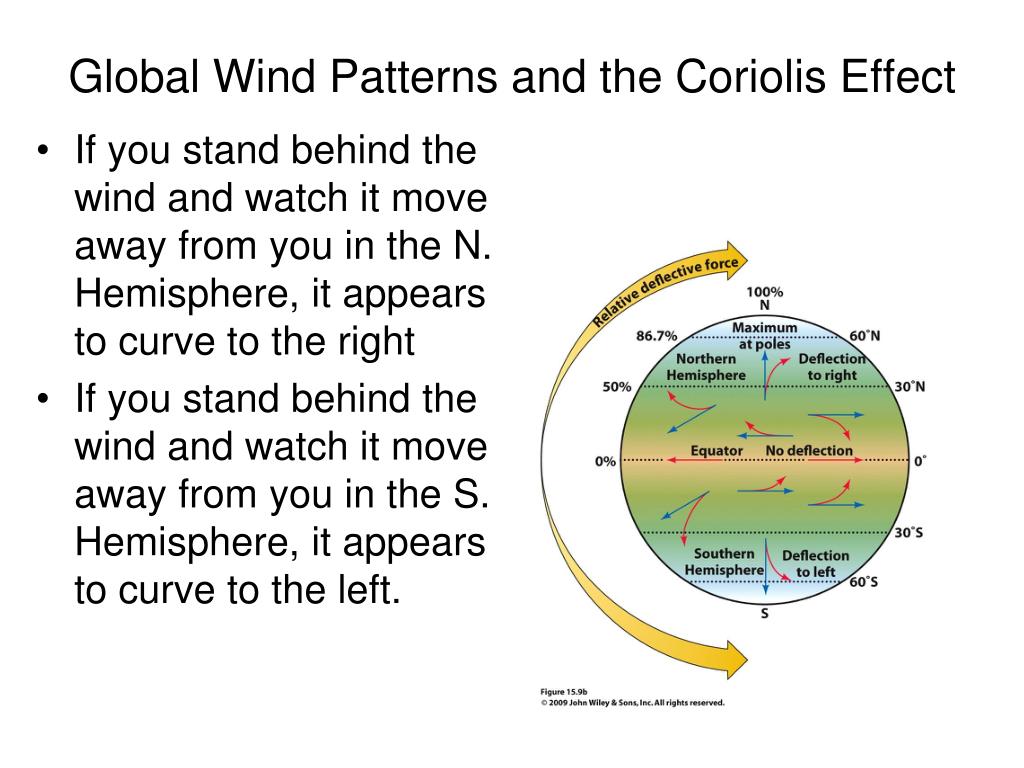
PPT Ch15 Global Circulation and Weather PowerPoint Presentation ID
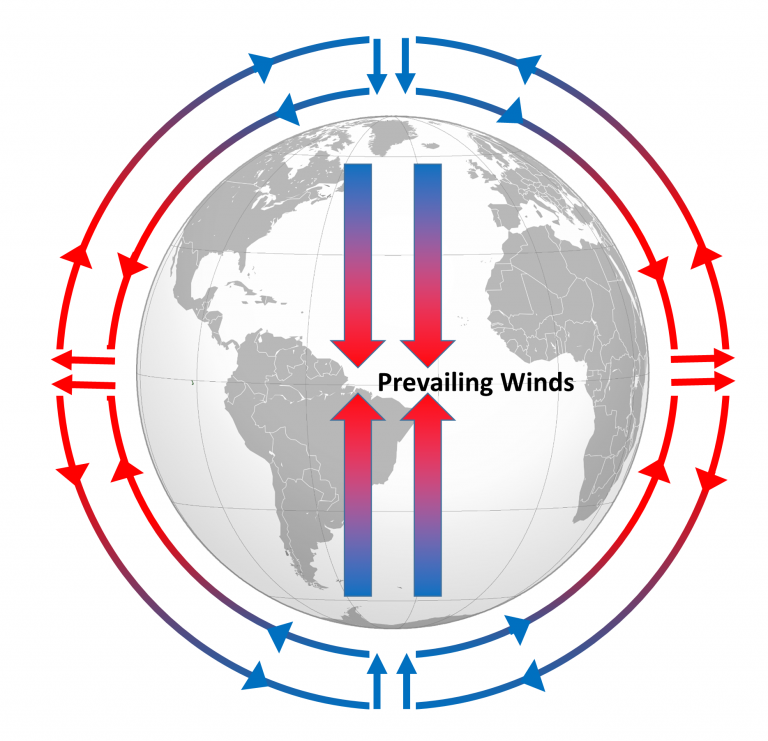
8.2 Winds and the Coriolis Effect Introduction to Oceanography
Web Outside Storm Systems, The Impact Of The Coriolis Effect Helps Define Regular Wind Patterns Around The Globe.
Web In Physics, The Coriolis Force Is An Inertial (Or Fictitious) Force That Acts On Objects In Motion Within A Frame Of Reference That Rotates With Respect To An Inertial Frame.
Winds And Ocean Currents Are In Constant Motion.
By About 30° Of Latitude (North And South) The Air Begins.
Related Post: