Template Vs Non Template Strand
Template Vs Non Template Strand - Given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. Web on the other hand, the template strand serves as a blueprint in the process of transcription, where rna molecules are synthesized based on the dna template. What is the difference between the template and coding strand of dna? Web the rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand. Web the coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. What is the difference between a template and a complementary strand? The template contains anticodons, while coding involves codons. Rna polymerase reads the template strand to make mrna. Why is the coding strand not transcribed? Web template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. Given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. Write the similarities between the template and coding strand. Rna polymerase reads the template strand to make mrna. What is the difference between the template and coding strand of dna? After binding. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand ). Web t7 rna polymerase is a highly specific enzyme ( 6 ): They work together to ensure accurate synthesis of. After rna polymerase binds to the promoter, the dna strands unwind, and the polymerase initiates rna synthesis at the start point on the template strand. Web t7 rna polymerase is a highly specific enzyme ( 6 ): To understand dna replication, it is vital to recognize that the two strands have opposite orientations. The coding strand functions to determine the. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. Write the similarities between the template and coding strand. After rna polymerase binds to the promoter, the dna strands unwind, and the polymerase initiates rna synthesis at the start point on the template strand. They work together to ensure accurate synthesis of dna and the. Why is the coding strand not transcribed? The template contains anticodons, while coding involves codons. Rna polymerase reads the template strand to make mrna. In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the second function of dna (the first was replication) is to provide the information needed to construct the proteins necessary so that the cell can perform all of its functions. On. Write the similarities between the template and coding strand. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand ). Dna is the fundamental building block of an organism’s genetic information.. The template contains anticodons, while coding involves codons. What is the difference between a template and a complementary strand? Web the coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. They work together to ensure accurate synthesis of dna and the. Why is the coding strand not transcribed? It is also called the antisense strand. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Web the main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same sequence of nucleotides in the mrna except thymine. Web. The template strand goes in one direction, while the coding strand goes in the opposite direction. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand ). They work together to. The template strand goes in one direction, while the coding strand goes in the opposite direction. Web the coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. After rna polymerase binds to the promoter, the dna strands unwind, and the polymerase. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. Web the coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. The template contains anticodons, while coding involves codons. After binding to the promoter, repeated cycles of initiation and product release result in the accumulation of short abortive products. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand ). In most organisms, the strand of dna that serves as the. The coding strand does not read, but it has the same sequence as mrna. To do this, the dna is “read” or transcribed into an mrna molecule. Therefore, the two strands have complementary roles in both dna replication and gene expression. Web template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. Web in summary, the template strand is the dna strand that is used as a template for the synthesis of rna, whereas the coding strand is the complementary strand to the template strand that contains the same sequence as the rna product. Web the main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same sequence of nucleotides in the mrna except thymine. This way, both strands work together, ensuring the right information is transferred from dna to rna. Dna is the fundamental building block of an organism’s genetic information. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. Why is the coding strand not transcribed?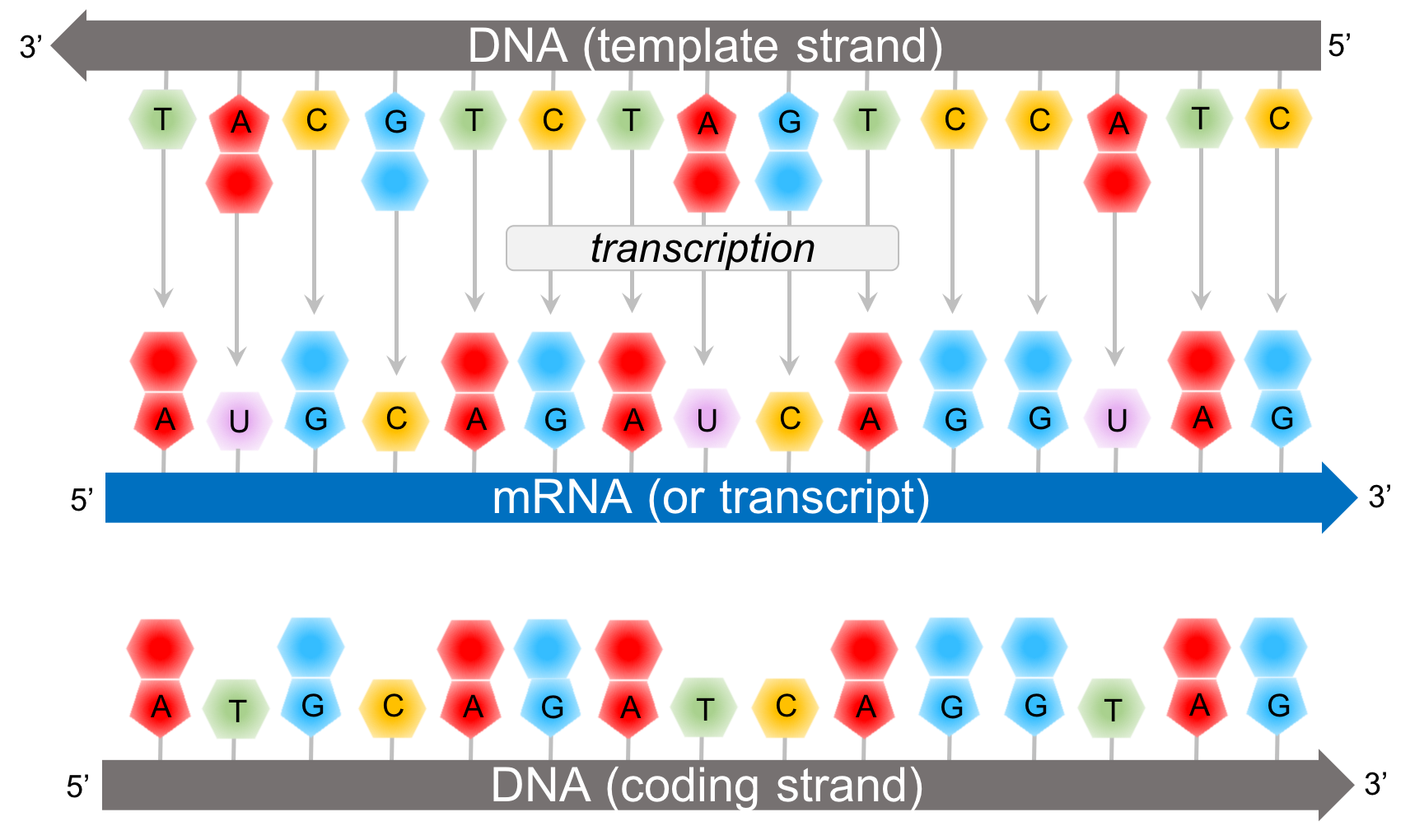
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer

Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Definition

Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Differences

Information Flow and Levels of Regulation Medical 1st Ed
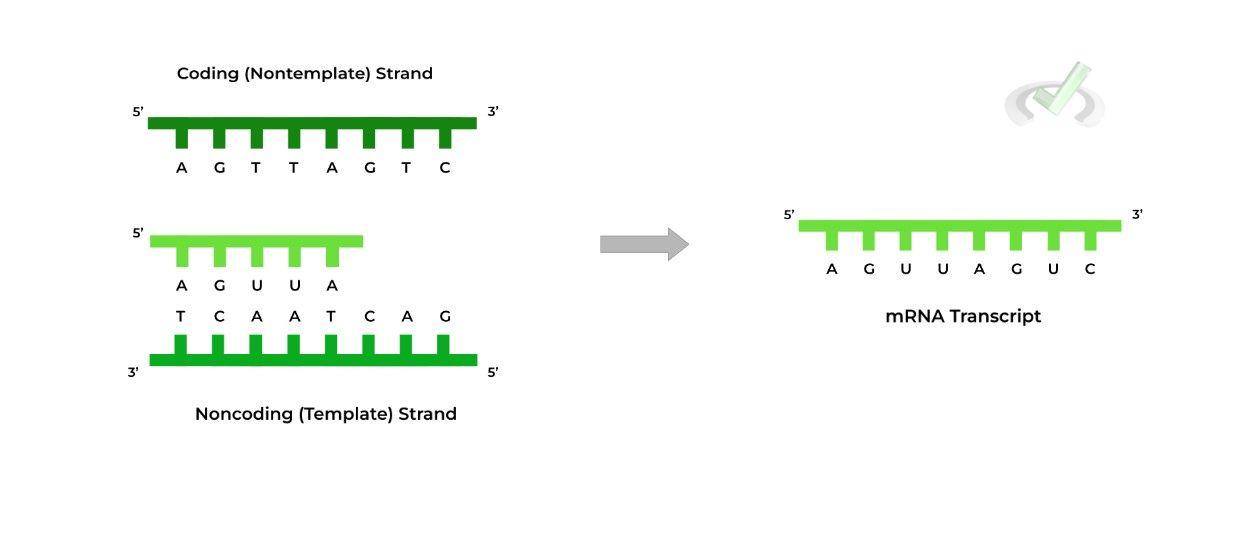
RNA Transcription Fundamentals and Key Terms on the MCAT MCAT Mastery

Template Vs Nontemplate Strand
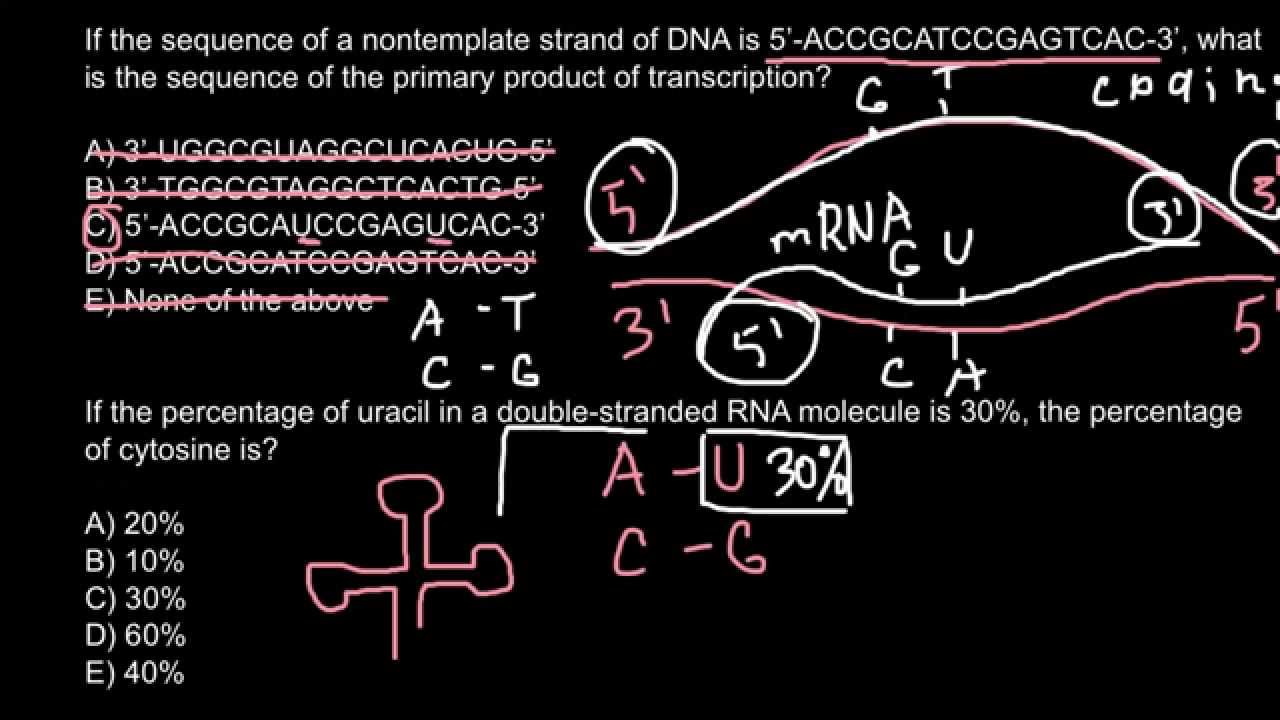
How to differ DNA strands coding and noncoding, template and

Gene Expression Transcription Agriculture, and Biotechnology

DNA Transcription Steps and Mechanism • Microbe Online

Template Strand Vs Coding Strand Understanding The Difference GRAPHICOLD
In Both Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes, The Second Function Of Dna (The First Was Replication) Is To Provide The Information Needed To Construct The Proteins Necessary So That The Cell Can Perform All Of Its Functions.
Web The Coding Strand Determines The Correct Nucleotide Sequence Of Mrna.
To Understand Dna Replication, It Is Vital To Recognize That The Two Strands Have Opposite Orientations.
It Is Complementary To The Coding Strand And Has A Sequence That Is Identical To The Rna Transcript, Except For The Substitution Of Thymine With Uracil In Rna.
Related Post: