Template Strand In Dna
Template Strand In Dna - Dna is the hereditary material, passing traits from parents to offspring. Web synthesis of the rna strand takes place in the 5′ to 3′ direction, antiparallel to the template strand. Rna polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the nucleotides that are encoded in the template strand in order to form the primary rna transcript. Web in conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized. It involves copying a gene's dna sequence to make an rna molecule. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web only one of the two dna strands serves as a template for transcription. After rna polymerase binds to the promoter, the dna strands unwind, and the polymerase initiates rna synthesis at the start point on the template strand. The genetic instructions for various cellular processes of living organisms are carried in the dna molecule. Web dsrna generation mechanisms during ivt. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. Web synthesis of the rna strand takes place. Dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. Rna polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the nucleotides that are encoded in the template strand in order to form the primary rna transcript. Web the dna template is used by rna polymerase to produce a strand of rna with a nucleotide sequence that is the same as the coding strand for. For example, when dna polymerase meets an adenosine nucleotide on the template strand, it adds a thymidine to the 3′ end of the newly synthesized strand, and then moves to the next nucleotide on the template. The bodies of the two ukrainian soldiers lay motionless in a field for months. Web synthesis of the rna strand takes place in the. Web each strand of dna acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. The promoter is the sequence of dna that encodes the information about where to begin transcription for each gene. Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new and one old strand. In this view, the 5' end of the rna strand. Web only one of the two dna strands serves as a template for transcription. This strand is called the template strand.the rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand.however, there is one important difference: During transcription, the enzyme rna polymerase (green) uses dna as a. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with. The bases of the new strand and the template form complementary pairs held together by hydrogen bonds. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach. Web only one of the two dna strands serves as a template for transcription. The interaction of pol32 with. Transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a. The bases of the new strand and the template form complementary pairs held together by hydrogen bonds. Web the. For example, when dna polymerase meets an adenosine nucleotide on the template strand, it adds a thymidine to the 3′ end of the newly synthesized strand, and then moves to the next nucleotide on the template. The addition of nucleotides occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding. Web the template strand, on the other hand, has a sequence of nucleotides that is complementary to the sequence on the coding strand. Dna is the hereditary material, passing traits from parents to offspring. Web the dna double helix then unwinds, and rna synthesis begins at the start point on the template strand of dna. During elongation, the new rna. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with. The bodies of the two ukrainian soldiers lay motionless in a field for months. Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new and one old strand. Web the diagram shows a template dna strand paired up with. This strand is called the template strand.the rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand.however, there is one important difference: Web dsrna generation mechanisms during ivt. Web in conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized. The soldiers’ relatives identified their bodies from. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Dna has a double helix structure meaning, it consists of two long polynucleotide chains that are. Depending on the promoter, either strand of dna can be used as the template strand. Web the template strand, on the other hand, has a sequence of nucleotides that is complementary to the sequence on the coding strand. Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or. For example, when dna polymerase meets an adenosine nucleotide on the template strand, it adds a thymidine to the 3′ end of the newly synthesized strand, and then moves to the next nucleotide on the template. During elongation, the new rna strand becomes longer and longer as the dna template is transcribed. Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new and one old strand. Dna is the hereditary material, passing traits from parents to offspring. In such cases, wither the molecule moves down towards the strand in the direction of 3’. When transcription is completed, the rna is released, and the dna helix reforms. The bases of the new strand and the template form complementary pairs held together by hydrogen bonds.
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
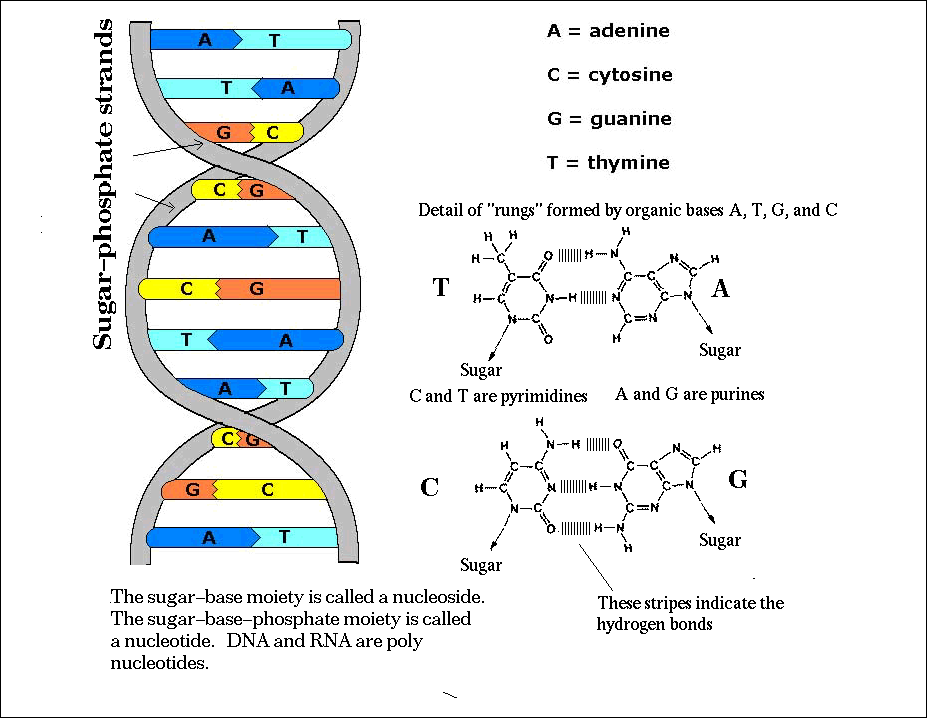
dna strand diagram

Template Strand Of Dna

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

DNA Structure & DNA Replication Biology Online Tutorial
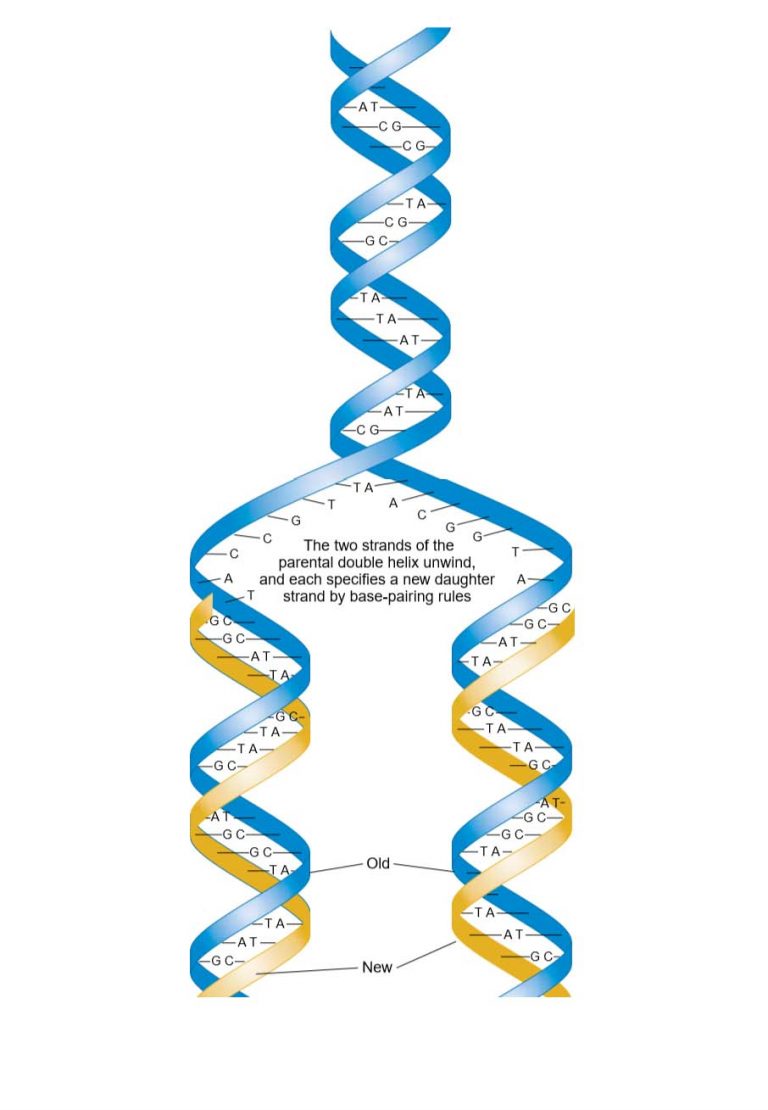
DNA Replication Study Solutions
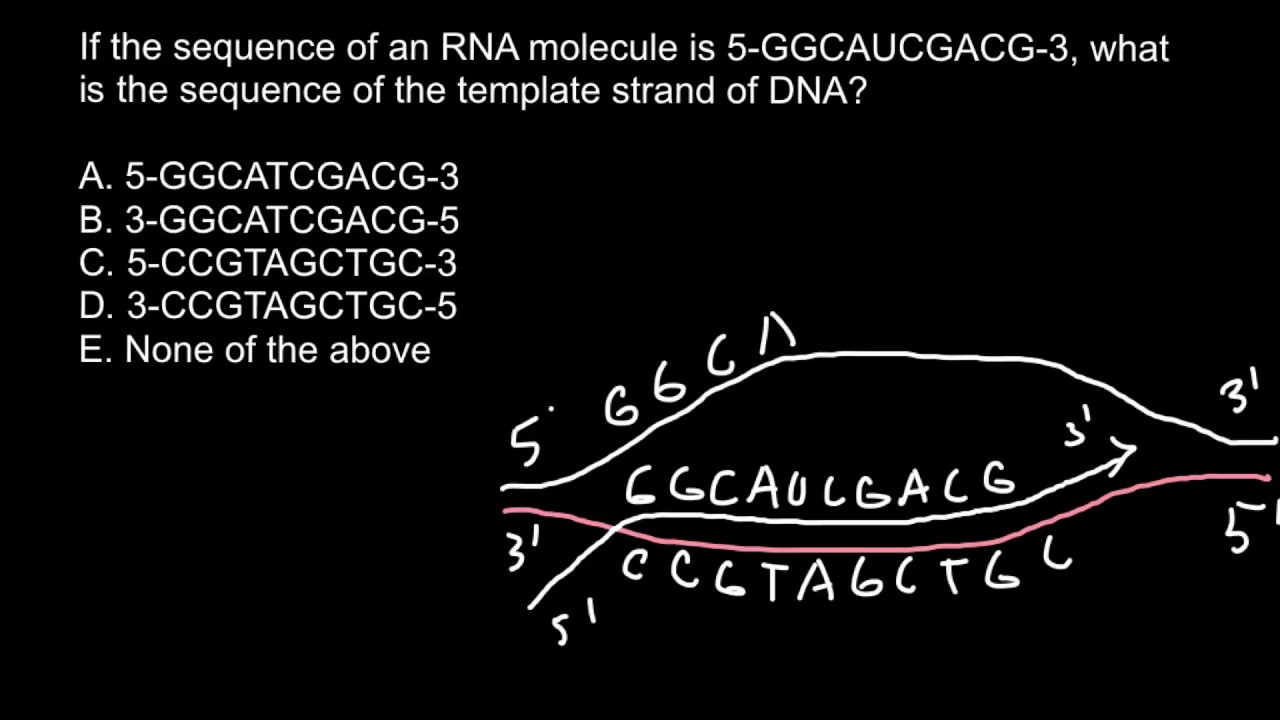
How to find sequence of the template strand of DNA YouTube
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
The Genetic Instructions For Various Cellular Processes Of Living Organisms Are Carried In The Dna Molecule.
These Enzymes Unzip Dna Molecules By Breaking The Hydrogen Bonds That Hold The Two Strands Together.
The Addition Of Nucleotides Occurs In The 5’ To 3’ Direction.
Web The Diagram Shows A Template Dna Strand Paired Up With A New Dna Strand That Is Currently Being Synthesized.
Related Post: