Template In Dna
Template In Dna - What is dna made of? Web in addition, when proteins are being made, the double helix unwinds to allow a single strand of dna to serve as a template. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. This strand is called the template strand. Web dsrna generation mechanisms during ivt. Rna purification protocol was described in rna preparation. Web either dna strand can be a template. The rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand. What is dna template strand? Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new and one old strand. Major types of cellular rna. What is dna template strand? It is complementary to the coding strand of dna for the target gene. Web coding strand vs. Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new and one old strand. This strand is called the template strand. Web as discussed in chapter 3, dna replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. Hydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together (. Web coding strand vs. Dna is the information. The four dna nucleotides (datp, dttp, dctp, dgtp) the template dna to be sequenced. Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a template). New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the. Aquaticus lives in hot springs and hydrothermal vents. So, the coding strand and template strand are the two complementary strands forming the double helix structure of dna, and they play crucial roles in processes like transcription and translation, which are essential for protein synthesis. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. Each of these chains. Web each strand of dna acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. This template strand is then transcribed into mrna, which is a molecule that conveys vital instructions to the. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription. Web dna template translation is the process of using an mrna molecule as a template to produce a protein. Dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a template). Web transcription always proceeds from one of the. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among. Web as discussed in chapter 3, dna replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. What is dna made of? This strand is called. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. This template strand is then transcribed into mrna, which is a molecule that conveys vital instructions to the. It is complementary to the coding strand of dna for the target gene. Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to produce rna. The nontemplate. Web coding strand vs. This strand is called the template strand. Web as discussed in chapter 3, dna replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna. Web either dna strand can be a template. Each strand in the double helix acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. These enzymes utilize energy from atp to move on dna, destabilize the hydrogen bonds between bases, and separate the two strands of the double helix. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed. The nontemplate strand is referred. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. The four dna nucleotides (datp, dttp, dctp, dgtp) the template dna to be sequenced. Web a dna molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotide subunits. These enzymes utilize energy from atp to move on dna, destabilize the hydrogen bonds between bases, and separate the two strands of the double helix. Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a template). This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Major types of cellular rna. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. What is dna made of? Hydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together (. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. Web dsrna generation mechanisms during ivt. Web during dna replication, the template is generated by enzymes known as helicases. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively.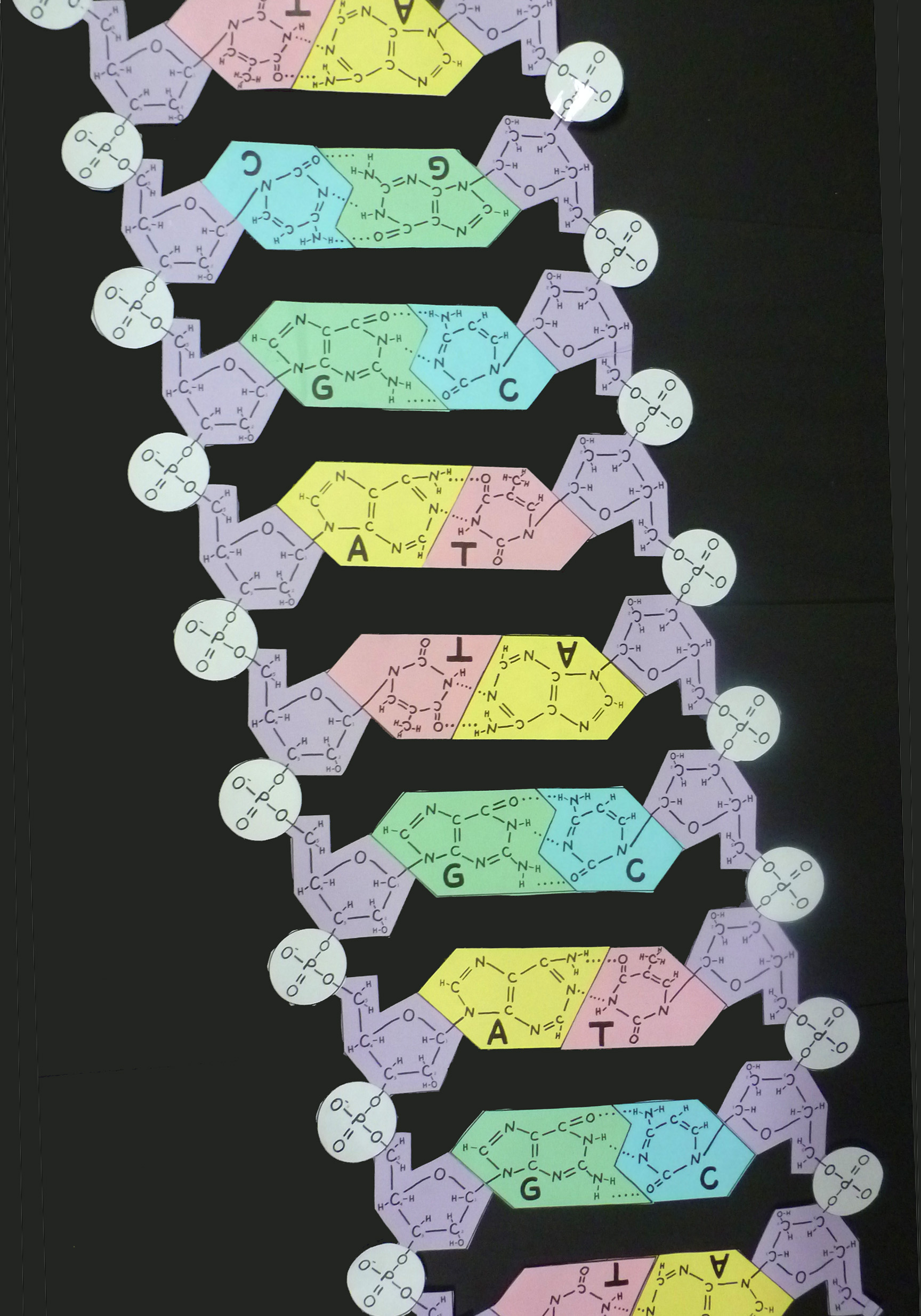
DNA PAPER MODEL to cut and assemble Ellen McHenry's Basement
DNA infographic template Simple Infographic Maker Tool by Easelly

DNA Structure & DNA Replication Biology Online Tutorial

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

Dna Template Sequence
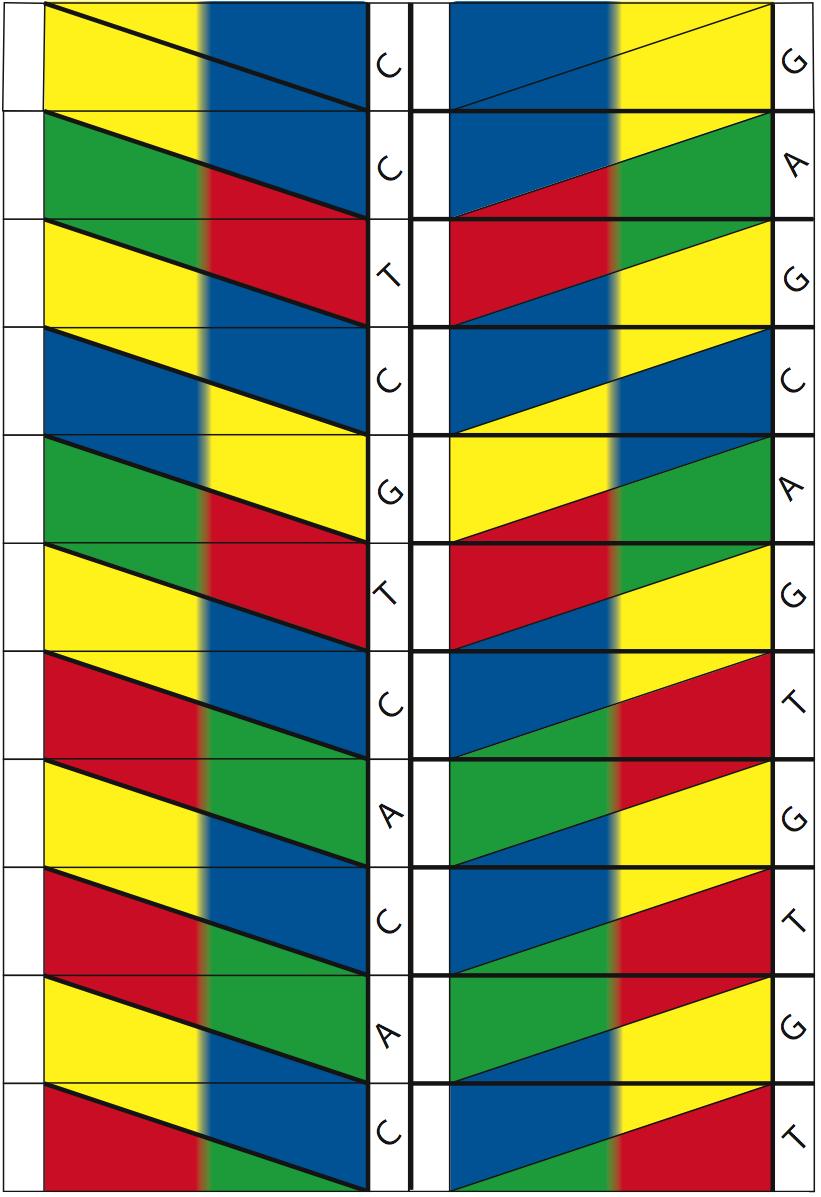
Printable Paper Dna Model Template Free Printable Paper

Dna Template Sequence
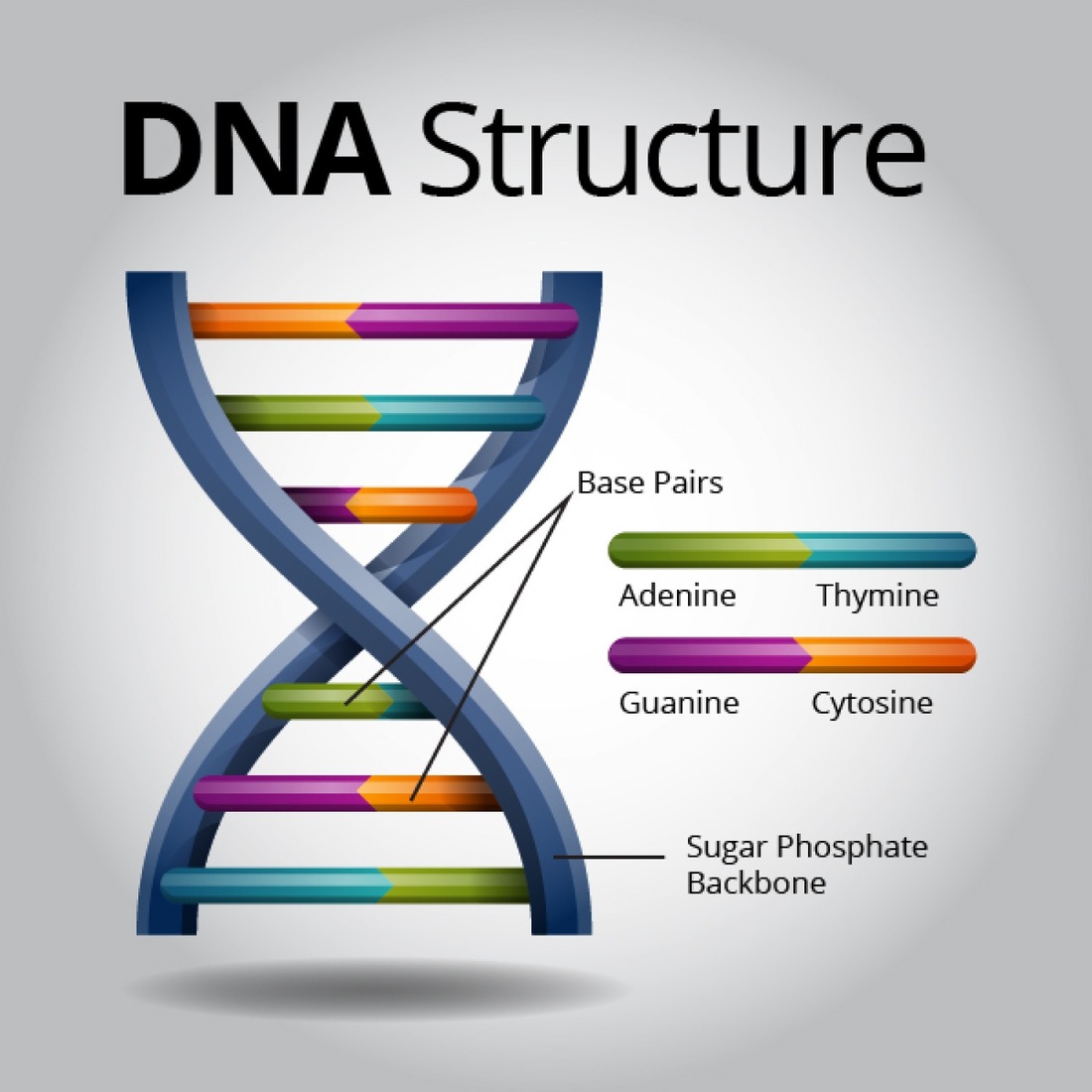
DNA AP Biology Portfolio
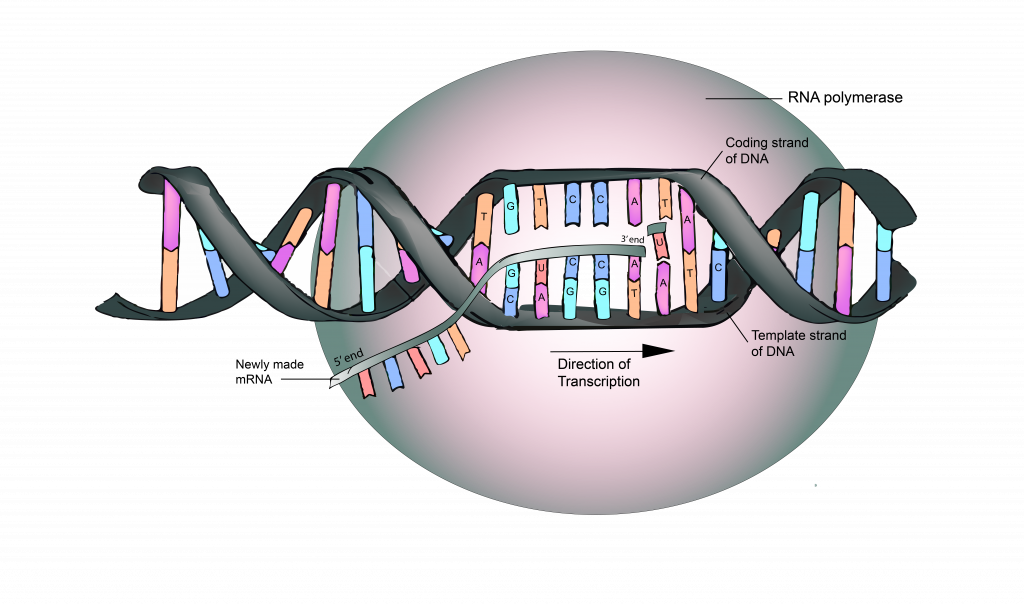
5.4 RNA is Transcribed from a DNA Template The Evolution and Biology

Template In Dna
Web As Discussed In Chapter 3, Dna Replication Is A Semiconservative Process In Which Each Parental Strand Serves As A Template For The Synthesis Of A New Complementary Daughter Strand.
This Strand Is Called The Template Strand.
Each New Double Strand Consists Of One Parental Strand And One New Daughter Strand.
Web In Addition, When Proteins Are Being Made, The Double Helix Unwinds To Allow A Single Strand Of Dna To Serve As A Template.
Related Post: