Sunburst Pattern Of Osteosarcoma
Sunburst Pattern Of Osteosarcoma - Web the sunburst appearance occurs when the lesion grows too fast and the periosteum does not have enough time to lay down a new layer and instead the sharpey's fibers stretch out perpendicular to the bone. It is frequently associated with. Web intercrestal osteosarcoma may be a subtle relative of the expansion associated with the classic sunburst pattern. Web a radiograph of the distal thigh demonstrates a sunburst pattern and codman triangle. Web the conventional plain radiograph is the best for probable diagnosis as it describes features like sun burst appearance, codman's triangle, new bone formation in soft tissues along. Often an adolescent during a growth spurt. Web sunburst appearance periosteal reaction in a pathologically proven case of osteosarcoma. The sunburst appearance occurs when the lesion grows too fast. Web in conventional osteosarcoma, the tumour invades the periosteum to give rise to the classic ‘sunburst appearance’, caused by many thin irregular spicules of new bone. Web the preoperative diagnosis rate of dlos is low at 40% and 65% for core needle biopsy and incisional biopsy, respectively, making it a difficult tumor to diagnose. Web in conventional osteosarcoma, the tumour invades the periosteum to give rise to the classic 'sunburst appearance', caused by many thin irregular spicules of new. It is frequently associated with. Web sunburst type codman triangle lamellated (onion skin) reaction tumor matrix ossification / calcification soft tissue involvement low grade central. Web the associated soft tissue mass can exhibit variable patterns. Often an adolescent during a growth spurt. Web intercrestal osteosarcoma may be a subtle relative of the expansion associated with the classic sunburst pattern. Web some osteosarcomas show a periosteal reaction manifesting as a sunburst pattern caused by radiating mineralized tumor spicules or a triangular elevation of the. Web osteosarcoma is usually sclerotic, involves the metaphysis, and has periosteal new. Web sunburst appearance periosteal reaction in a pathologically proven case of osteosarcoma. Web the preoperative diagnosis rate of dlos is low at 40% and 65% for core needle biopsy and incisional biopsy, respectively, making it a difficult tumor to diagnose. Web radiologic depiction of a sunburst pattern of new bone formation is characteristic. Because malignant entities such as. Web some. Web in conventional osteosarcoma, the tumour invades the periosteum to give rise to the classic 'sunburst appearance', caused by many thin irregular spicules of new. Web reactive new bone formation may be seen under the periosteum forming a “codman angle,” or “codman’s triangle,” and invasion into adjacent soft tissues may produce a. Overproduction of osteoid and immature bone by malignant. Web sunburst appearance periosteal reaction in a pathologically proven case of osteosarcoma. Web some osteosarcomas show a periosteal reaction manifesting as a sunburst pattern caused by radiating mineralized tumor spicules or a triangular elevation of the. Web this article reviews the cause, clinical presentation, diagnostic methods, and management of osteosarcoma, the most common primary bone tumor and third most common.. Web the conventional plain radiograph is the best for probable diagnosis as it describes features like sun burst appearance, codman's triangle, new bone formation in soft tissues along. Web (a) osteosarcoma affecting the distal femur showing sun ray/sunburst pattern as indicated by the arrow (b) chondrosarcoma affecting the distal femur,. Often an adolescent during a growth spurt. Malignant bone tumor. Web reactive new bone formation may be seen under the periosteum forming a “codman angle,” or “codman’s triangle,” and invasion into adjacent soft tissues may produce a. Web a radiograph of the distal thigh demonstrates a sunburst pattern and codman triangle. Often an adolescent during a growth spurt. Web less frequently, examples of odontogenic myxomas with a “sunray” or “sunburst”. Web the associated soft tissue mass can exhibit variable patterns of ossification, leading to the characteristic radial sunburst pattern often associated with osteosarcoma. 1, 2 early diagnosis and complete tumor resection are mandatory to. Malignant bone tumor secondary to overproduction of osteoid. Overproduction of osteoid and immature bone by malignant osteoblasts. Web the conventional plain radiograph is the best for. Web the sunburst appearance occurs when the lesion grows too fast and the periosteum does not have enough time to lay down a new layer and instead the sharpey's fibers stretch out perpendicular to the bone. Overproduction of osteoid and immature bone by malignant osteoblasts. Web the associated soft tissue mass can exhibit variable patterns of ossification, leading to the. Web the preoperative diagnosis rate of dlos is low at 40% and 65% for core needle biopsy and incisional biopsy, respectively, making it a difficult tumor to diagnose. Web radiologic depiction of a sunburst pattern of new bone formation is characteristic. Web the associated soft tissue mass can exhibit variable patterns of ossification, leading to the characteristic radial sunburst pattern. The sunburst appearance occurs when the lesion grows too fast. Often an adolescent during a growth spurt. Web sunburst type codman triangle lamellated (onion skin) reaction tumor matrix ossification / calcification soft tissue involvement low grade central. Web less frequently, examples of odontogenic myxomas with a “sunray” or “sunburst” pattern have been reported. Web reactive new bone formation may be seen under the periosteum forming a “codman angle,” or “codman’s triangle,” and invasion into adjacent soft tissues may produce a. Web this article reviews the cause, clinical presentation, diagnostic methods, and management of osteosarcoma, the most common primary bone tumor and third most common. Web in conventional osteosarcoma, the tumour invades the periosteum to give rise to the classic 'sunburst appearance', caused by many thin irregular spicules of new. Web sunburst appearance periosteal reaction in a pathologically proven case of osteosarcoma. Overproduction of osteoid and immature bone by malignant osteoblasts. Meticulous attention to details is crucial. Web sunburst pattern due to new bone formation in soft tissue prognostic factors complete surgical resection with wide margins has been reported as the most significant. Web the sunburst appearance occurs when the lesion grows too fast and the periosteum does not have enough time to lay down a new layer and instead the sharpey's fibers stretch out perpendicular to the bone. Web a radiograph of the distal thigh demonstrates a sunburst pattern and codman triangle. Web (a) osteosarcoma affecting the distal femur showing sun ray/sunburst pattern as indicated by the arrow (b) chondrosarcoma affecting the distal femur,. Web osteosarcoma is usually sclerotic, involves the metaphysis, and has periosteal new bone formation (sunburst pattern), whereas ewing sarcoma is usually. Because malignant entities such as.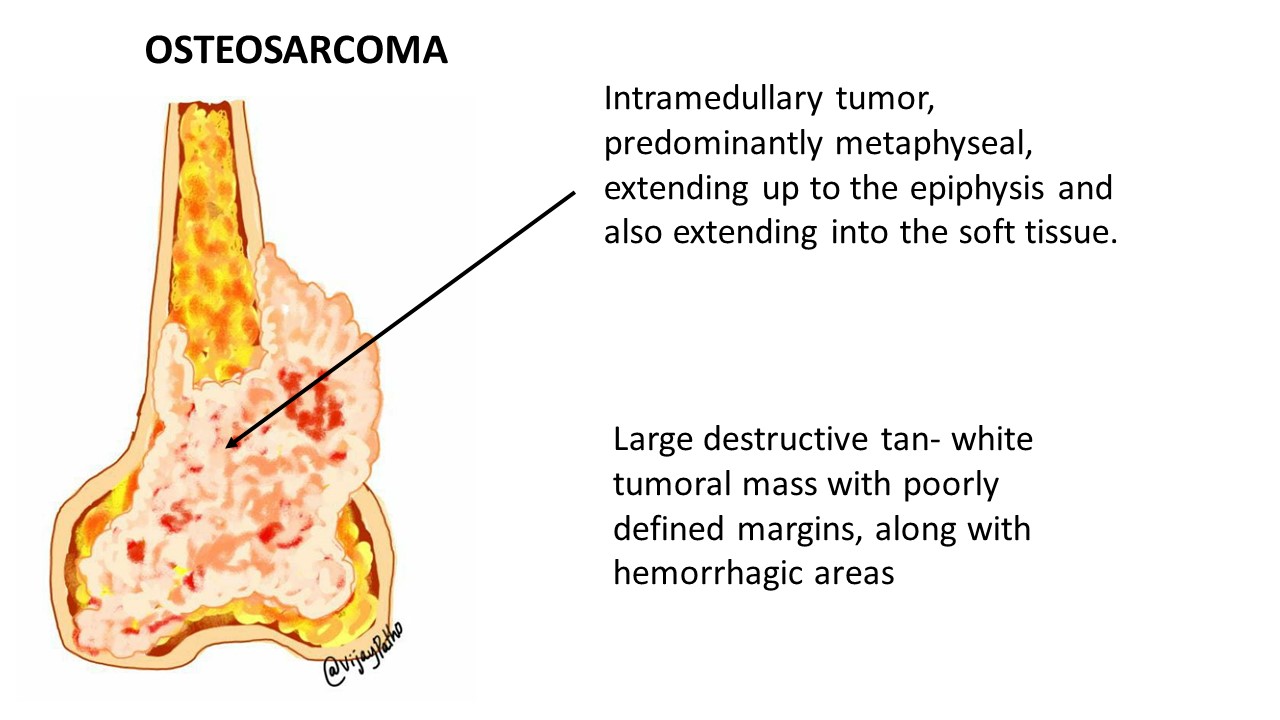
Pathological features Pathology Made Simple

Malignant Bone Tumors Oncology Medbullets Step 1
Sunburst appearance (bone) pacs
sunburst appearance pacs
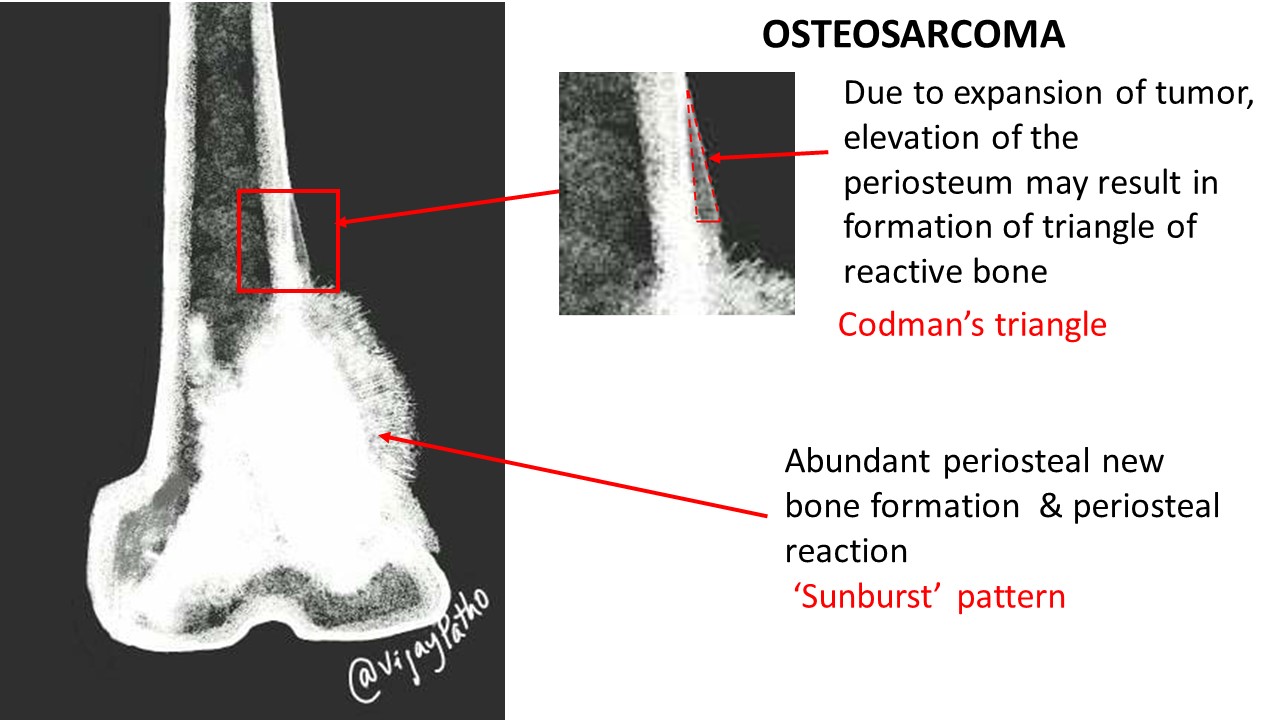
Pathological features Pathology Made Simple
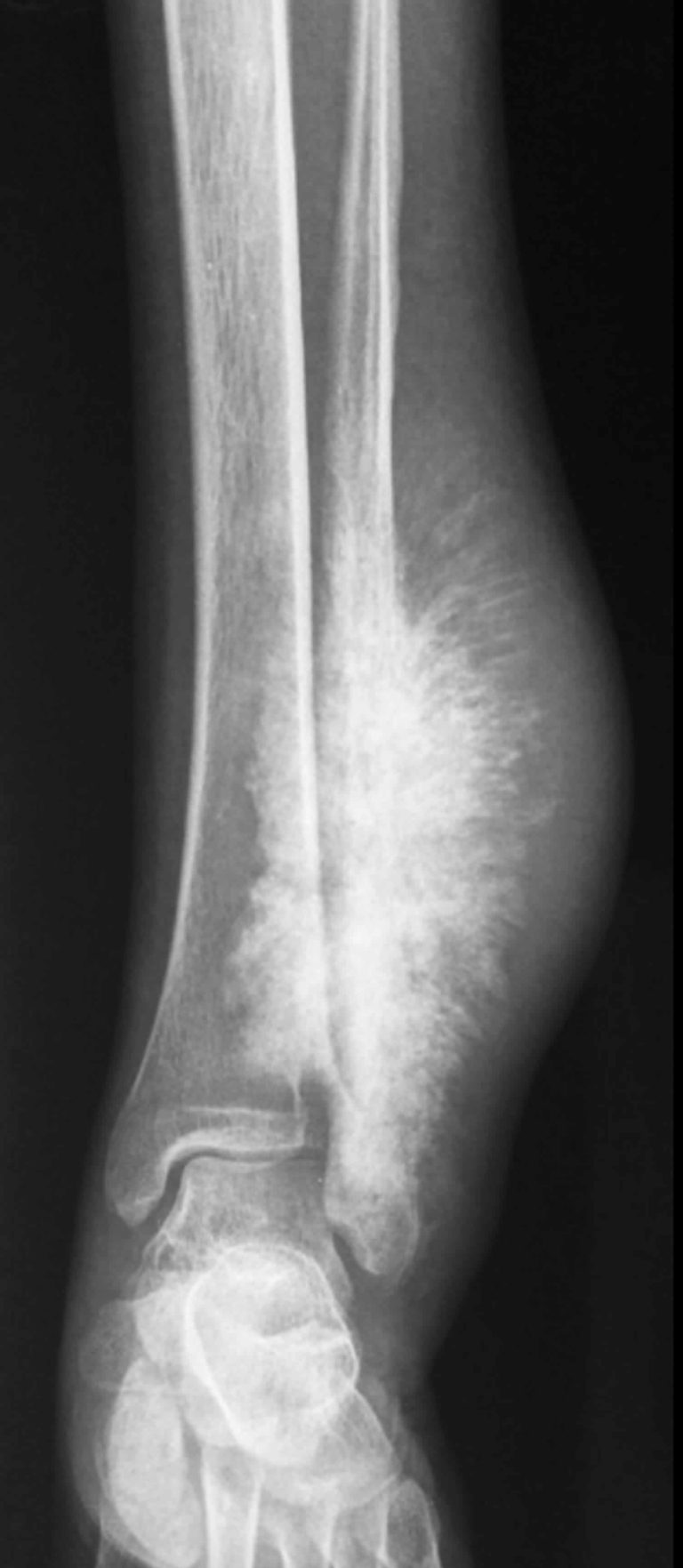
Periosteal reaction & types of periosteal reaction
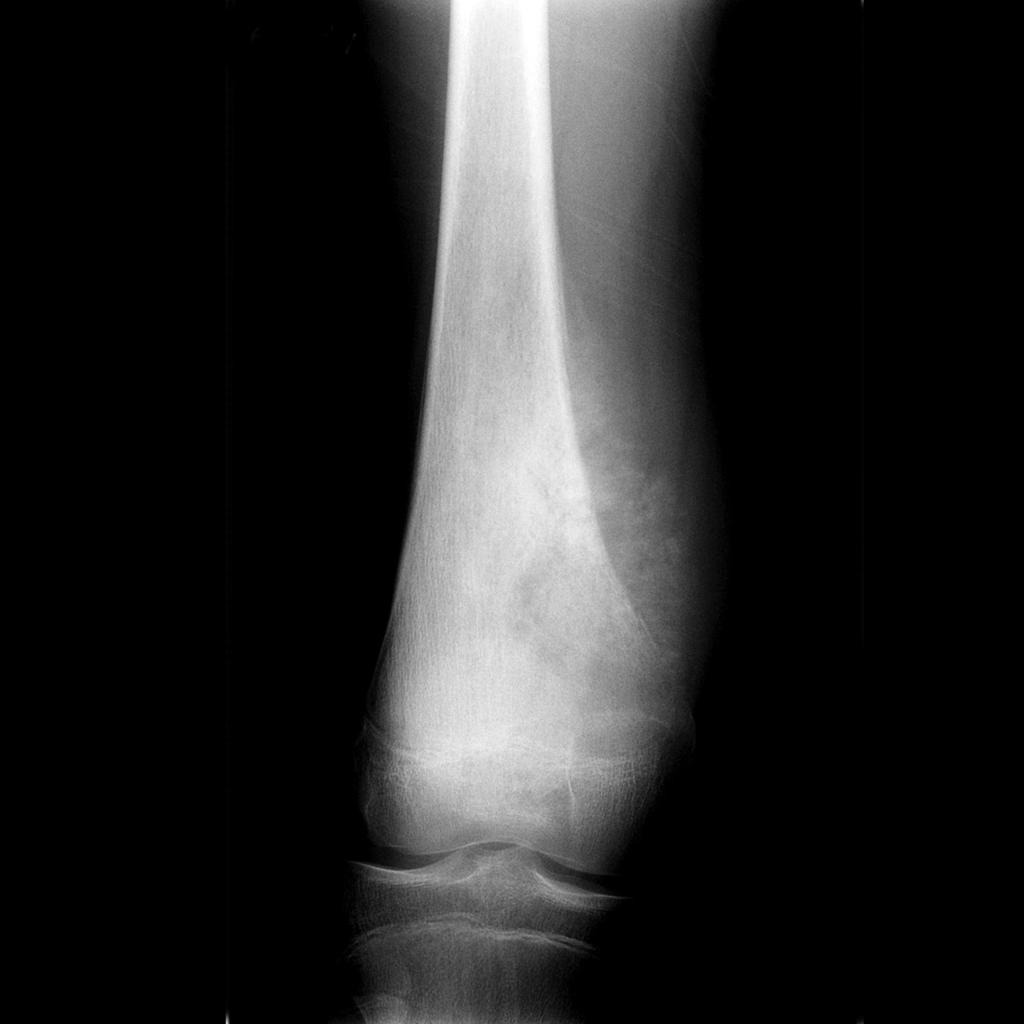
Sunray Appearance
OrthoInfo AAOS
Sunburst periosteal reaction Image
OrthoInfo AAOS
Web The Associated Soft Tissue Mass Can Exhibit Variable Patterns Of Ossification, Leading To The Characteristic Radial Sunburst Pattern Often Associated With Osteosarcoma.
It Is Frequently Associated With.
Web The Conventional Plain Radiograph Is The Best For Probable Diagnosis As It Describes Features Like Sun Burst Appearance, Codman's Triangle, New Bone Formation In Soft Tissues Along.
1, 2 Early Diagnosis And Complete Tumor Resection Are Mandatory To.
Related Post:
