Stroke Spasticity Pattern
Stroke Spasticity Pattern - Web background and purpose: It is considered a “positive” umn sign since it represents. In chronic stroke when motor. These alterations limit the use of arm in. It occurs when a muscle involuntarily contracts when you move and commonly. About 25 to 43% of survivors will have spasticity in the first year. Symptoms include painful, stiff, rigid muscles, involuntary contractions or. Spasticity can have an impact on. Web a high number of patients with stroke develop upper extremity spasticity, causing abnormal postures and patterns. Web spasticity is a common complication of stroke, but is only one of the many consequences of the umn syndrome. It’s more common in younger stroke survivors. Web spasticity and weakness (spastic paresis) are the primary motor impairments after stroke and impose significant challenges for treatment and patient care. Web it is estimated that 19% of stroke patients develop spasticity during the first three months after the acute event ( sommerfield 2004 ), and it has been found that. Four. Web it is estimated that 19% of stroke patients develop spasticity during the first three months after the acute event ( sommerfield 2004 ), and it has been found that. Web a high number of patients with stroke develop upper extremity spasticity, causing abnormal postures and patterns. It occurs when a muscle involuntarily contracts when you move and commonly. Web. About 25 to 43% of survivors will have spasticity in the first year. Web a stroke is a brain injury. Web spasticity and weakness (spastic paresis) are the primary motor impairments after stroke and impose significant challenges for treatment and patient care. The most important factor for pss management is its early initiation, so that early recognition of pss is. It’s also more common when the stroke is. Web chronic stroke survivors with spastic hemiplegia have various clinical presentations of ankle and foot muscle spasticity patterns. It’s more common in younger stroke survivors. Four common ankle and foot. Web a high number of patients with stroke develop upper extremity spasticity, causing abnormal postures and patterns. Web it is estimated that 19% of stroke patients develop spasticity during the first three months after the acute event ( sommerfield 2004 ), and it has been found that. Spasticity can have an impact on. Other features include, but are not. The most important factor for pss management is its early initiation, so that early recognition of pss is. Web about 25 to 43% of survivors will have spasticity in the first year after their stroke. It occurs in anywhere from 19%. It’s more common in younger stroke survivors. Symptoms include painful, stiff, rigid muscles, involuntary contractions or. It occurs when a muscle involuntarily contracts when you move and commonly. Web they are mechanical consequences of interactions between spasticity and weakness of surrounding muscles during walking. Spasticity can have an impact on. Web a high number of patients with stroke develop upper extremity spasticity, causing abnormal postures and patterns. Web it is estimated that 19% of stroke patients develop spasticity during the first three months after the acute event (. Web it is estimated that 19% of stroke patients develop spasticity during the first three months after the acute event ( sommerfield 2004 ), and it has been found that. Web spasticity is a common complication of stroke, but is only one of the many consequences of the umn syndrome. Web spasticity is an important milestone in the course of. Web they are mechanical consequences of interactions between spasticity and weakness of surrounding muscles during walking. Four common ankle and foot. Web spasticity following stroke is often associated with pain, soft tissue stiffness, and joint contracture, and may lead to abnormal limb posture, decreased quality of life,. Web about 25 to 43% of survivors will have spasticity in the first. The most important factor for pss management is its early initiation, so that early recognition of pss is required in clinical practice. It emerges and disappears as the recovery progresses. Web spastic hemiparesis (spasticity and weakness on one side of the body) is the hallmark motor impairment after a stroke. When the injured area of the brain controls muscle tone,. Chronic stroke survivors with spastic hemiplegia have various clinical presentations of ankle and foot muscle spasticity patterns. These alterations limit the use of arm in. It is considered a “positive” umn sign since it represents. Spasticity can have an impact on. It’s more common in younger stroke survivors. The most important factor for pss management is its early initiation, so that early recognition of pss is required in clinical practice. Web about 25 to 43% of survivors will have spasticity in the first year after their stroke. Other features include, but are not. It occurs when a muscle involuntarily contracts when you move and commonly. It occurs in anywhere from 19%. Web a stroke is a brain injury. Web chronic stroke survivors with spastic hemiplegia have various clinical presentations of ankle and foot muscle spasticity patterns. Web a high number of patients with stroke develop upper extremity spasticity, causing abnormal postures and patterns. In chronic stroke when motor. Web spasticity is a common complication of stroke, but is only one of the many consequences of the umn syndrome. When the injured area of the brain controls muscle tone, spasticity may occur.
Spasticity and Stroke

Post Stroke Spasticity What is the best treatment Orlando Neuro Therapy
Frontiers New insights into the pathophysiology of poststroke

Post Stroke Spasticity What is the best treatment Orlando Neuro Therapy
Spasticity Causes, Symptoms and Treatments

Prevalence of Spasticity and Postural Patterns in the Upper Extremity
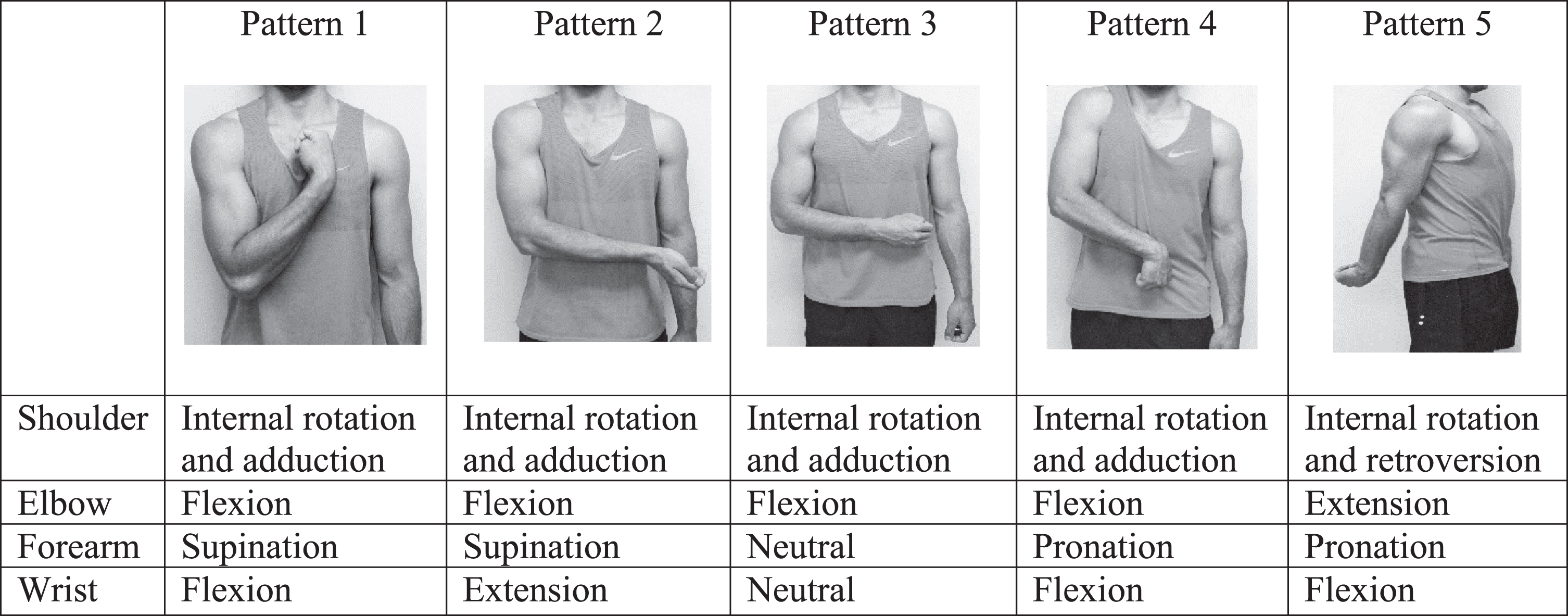
Association between postural patterns of spastic upper extremity and
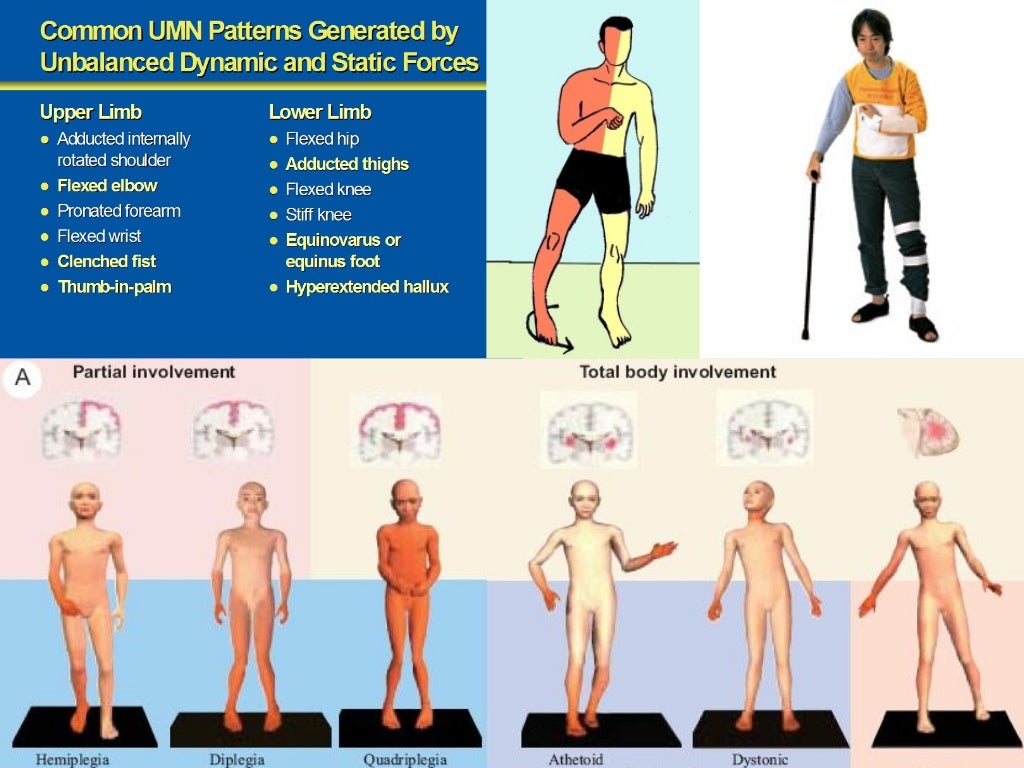
Spasticity in Rehabilitation

Post Stroke Spasticity What is the best treatment Orlando Neuro Therapy

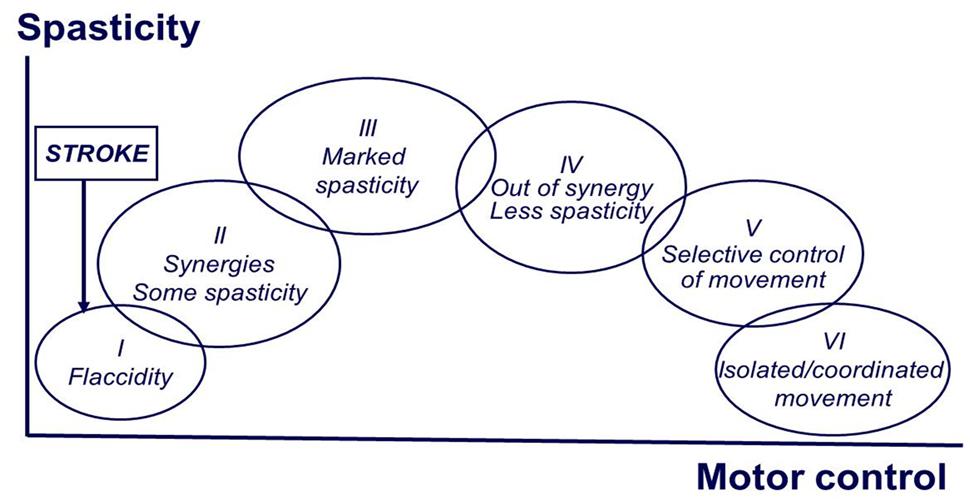
Understanding the Brunnstrom Stages of Stroke Recovery
Web Spastic Hemiparesis (Spasticity And Weakness On One Side Of The Body) Is The Hallmark Motor Impairment After A Stroke.
Web Spasticity And Weakness (Spastic Paresis) Are The Primary Motor Impairments After Stroke And Impose Significant Challenges For Treatment And Patient Care.
Web Spasticity Is Part Of The Positive Signs Among Other Motor Symptoms Which Occur After Lesions In The Descending Corticospinal System Such As Spastic Dystonia (Muscle.
Symptoms Include Painful, Stiff, Rigid Muscles, Involuntary Contractions Or.
Related Post:
