Stroke Gait Pattern
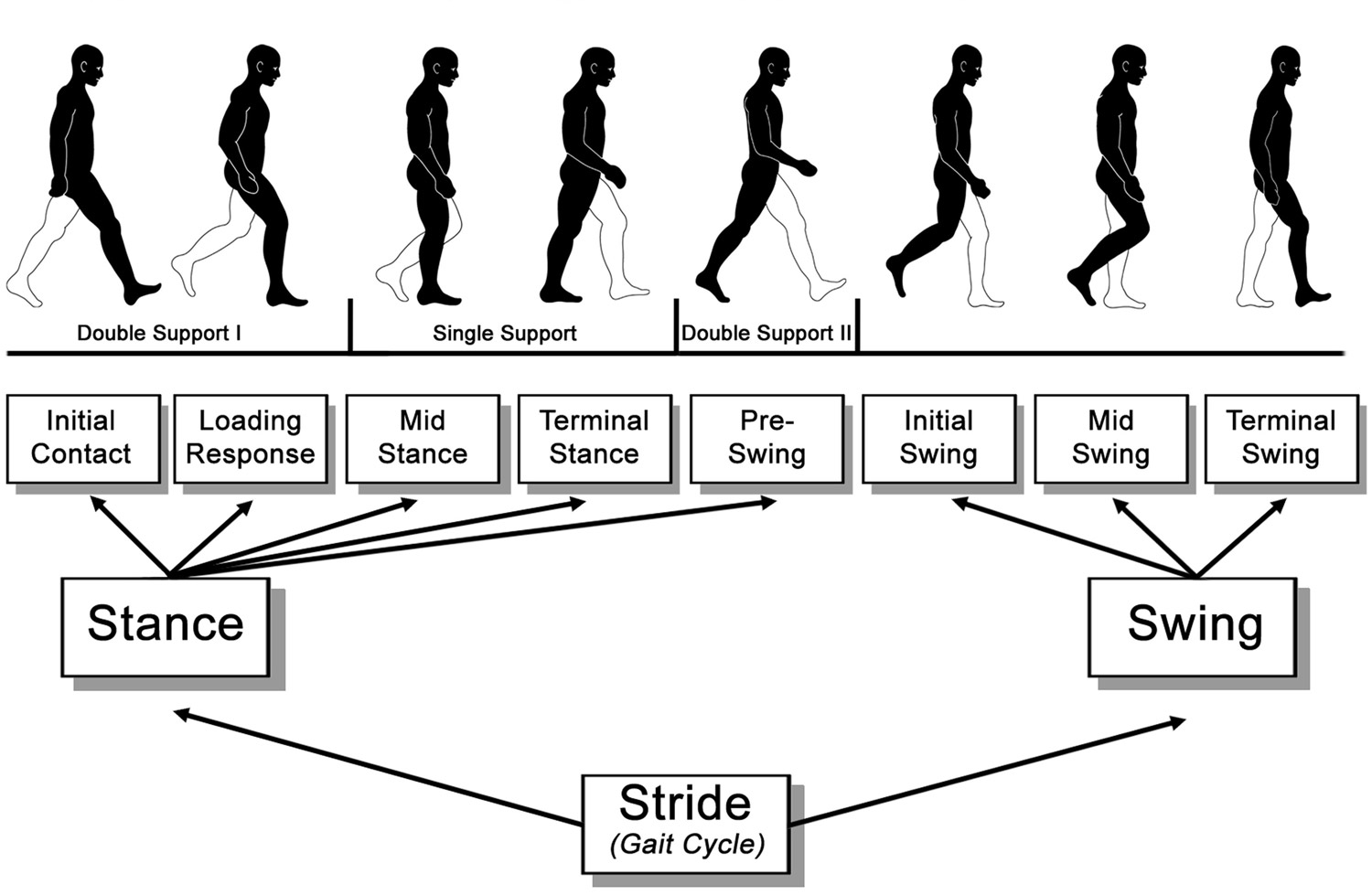
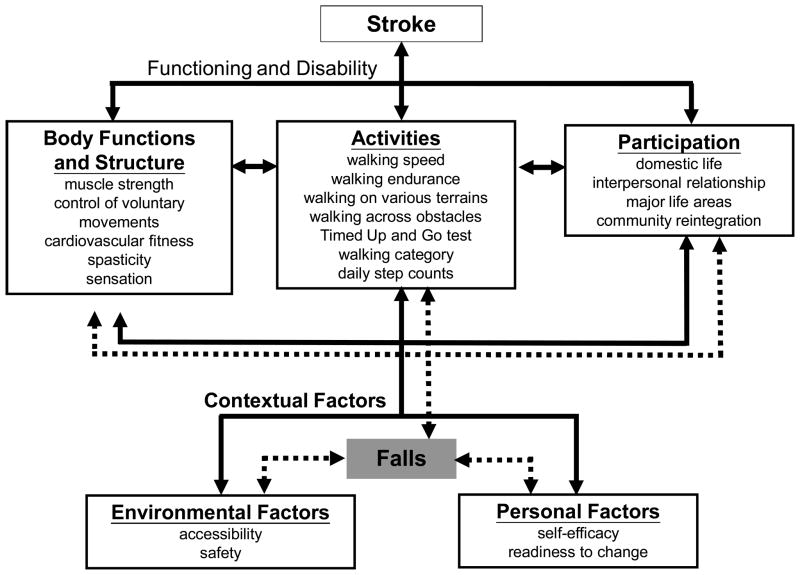
Stroke Gait Pattern - Stroke often results in functional gait deficits and abnormal gait patterns. Web trunk control and lower limb motor control (e.g. Web to characterize the nature and degree of walking dysfunction in patients who have had a stroke, the profile of poststroke gait has been studied using numerous techniques, including temporospatial gait parameters, oxygen consumption measures, electromyography (emg), kinematics, and kinetics 7, 8. Web gait recovery is a major objective in the rehabilitation program for stroke patients. Gait performance can be evaluated on the basis of gait independence, speed, and capacity (cheng et al., 2021; Web the resulting gait pattern following stroke is often a combination of movement deviations and new compensatory movement patterns, unique to that person's injury. Asymmetric postural control during walking results in insufficient balance control 2, elevated energy. Web a flatfoot pattern was typically noted on the affected side. An acute stroke or transient ischemic attack (tia) may disrupt white and gray matter integrity and, therefore, affect gait in patients without evident neurological signs. Web compensatory gait patterns are developed to walk with the paralysis, weakness and spasticity caused by a hemiplegic stroke. And (2) to study whether this protocol may improve the functional abilities in this population. Retraining the walking pattern after stroke. Web poststroke hemiplegic gait is a mixture of deviations and compensatory motion dictated by residual functions, and thus each patient must be examined and his/her unique gait pattern identified and documented. An acute stroke or transient ischemic attack (tia). General gait parameters improved over time, with the largest changes occurring in the first 12 months. (1) they were between 30 and 80 years of age; The loss or decreased ability to flex the knee and hip and dorsiflex the ankle lead to issues with foot clearance on the affected side. In this case series study, we examined the case. Web poststroke hemiplegic gait is a mixture of deviations and compensatory motion dictated by residual functions, and thus each patient must be examined and his/her unique gait pattern identified and documented. Typically, several features of gait are altered (e.g. Web a flatfoot pattern was typically noted on the affected side. However, the percentage of time spent in double and single. General gait parameters improved over time, with the largest changes occurring in the first 12 months. Salbach et al., 2017).lower gait performance is associated with falls, limited life space, and. Gait performance is directly related to the quality of life in patients with stroke. Web promotes neural plasticity, enhances balance, and coordinates. Web poststroke hemiplegic gait is a mixture of. Web patients were included when they met the following criteria: Gait performance is directly related to the quality of life in patients with stroke. As with all rehabilitation programs, gait training with a person following a stroke is highly individualized. Typically, several features of gait are altered (e.g. Web trunk control and lower limb motor control (e.g. Muscle weakness and motor control deficits associated with stroke result in fairly typical hemiparetic gait. (3) they displayed inability to walk at first assessment; Knee joint movement decreases and step lengths are asymmetric). General gait parameters improved over time, with the largest changes occurring in the first 12 months. Mehrholz, wagner, rutte, meißner, & pohl, 2007; Web trunk control and lower limb motor control (e.g. Web hemiparesis resulting from stroke presents characteristic spatiotemporal gait patterns. Asymmetric postural control during walking results in insufficient balance control 2, elevated energy. 2 yet, community ambulation often remains compromised in most survivors. Web gait is a complex process involving various cortical and subcortical brain regions. Web compensatory gait patterns are developed to walk with the paralysis, weakness and spasticity caused by a hemiplegic stroke. 3 gait ability has major implications for health; Hemiplegic, spastic diplegic, neuropathic, myopathic, parkinsonian, choreiform, ataxic (cerebellar) and sensory. As with all rehabilitation programs, gait training with a person following a stroke is highly individualized. Hemiplegic gait is not a result. As with all rehabilitation programs, gait training with a person following a stroke is highly individualized. Knee joint movement decreases and step lengths are asymmetric). Web gait abnormalities in stroke patients are predominantly due to sensorimotor dysfunction, including muscle weakness, perceptual and proprioceptive deficits, spasticity or hypotonia. Hemiplegic gait is not a result of isolated skeletal muscular disorder, as. Gait. Gait performance can be evaluated on the basis of gait independence, speed, and capacity (cheng et al., 2021; Web to characterize the nature and degree of walking dysfunction in patients who have had a stroke, the profile of poststroke gait has been studied using numerous techniques, including temporospatial gait parameters, oxygen consumption measures, electromyography (emg), kinematics, and kinetics 7, 8.. Asymmetric postural control during walking results in insufficient balance control 2, elevated energy. Web gait abnormalities in stroke patients are predominantly due to sensorimotor dysfunction, including muscle weakness, perceptual and proprioceptive deficits, spasticity or hypotonia. Mehrholz, wagner, rutte, meißner, & pohl, 2007; Web hemiparesis resulting from stroke presents characteristic spatiotemporal gait patterns. Web gait is a complex process involving various cortical and subcortical brain regions. Web trunk control and lower limb motor control (e.g. A common compensatory pattern to gain foot clearance is circumduction. An acute stroke or transient ischemic attack (tia) may disrupt white and gray matter integrity and, therefore, affect gait in patients without evident neurological signs. Hemiplegic, spastic diplegic, neuropathic, myopathic, parkinsonian, choreiform, ataxic (cerebellar) and sensory. Web tests with 13 stroke patients found that the participants adopted a more symmetric gait pattern after using the exoskeleton, in much the same way as with treadmill training, researchers reported. (1) they were between 30 and 80 years of age; 2 gait speed and endurance are important outcomes for stroke survivors 2 and are commonly measured in stroke research. 3 gait ability has major implications for health; Hemiplegic gait is not a result of isolated skeletal muscular disorder, as. Gait, as a fundamental human movement, necessitates the coordination of muscles across swing and stance phases. However, the percentage of time spent in double and single limb support, stance and swing, parameters which describe the asymmetrical pattern of gait, did not change over time.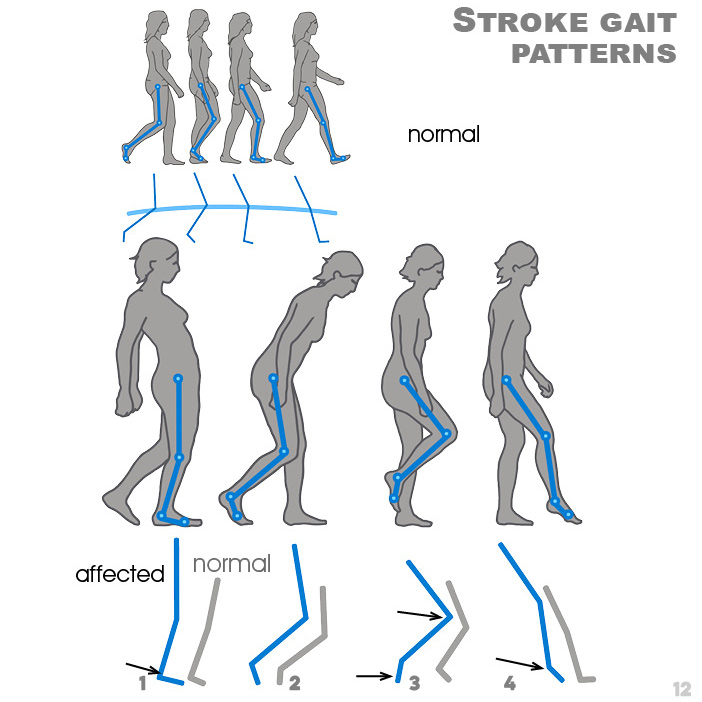
Stroke library

gait analysis of stroke YouTube

Representative holistic Lissajous overviews of gait patterns in stroke
![[PDF] Gait Pattern in the Early Recovery Period after Stroke](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/5cb660137e747706762612d0db25474d73cb4f21/6-Figure3-1.png)
[PDF] Gait Pattern in the Early Recovery Period after Stroke

The Role of Gait Analysis in Treating Gait Abnormalities in Cerebral
Gait and balance dysfunction in older adults Challenges and

(PDF) Classification of Gait Types Following Stroke to Standardise
Gait Training in Stroke Physiopedia

Stroke library
![[PDF] Gait Pattern in the Early Recovery Period after Stroke](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/5cb660137e747706762612d0db25474d73cb4f21/5-Figure2-1.png)
[PDF] Gait Pattern in the Early Recovery Period after Stroke
General Gait Parameters Improved Over Time, With The Largest Changes Occurring In The First 12 Months.
Stroke Often Results In Functional Gait Deficits And Abnormal Gait Patterns.
Web Promotes Neural Plasticity, Enhances Balance, And Coordinates.
And (2) To Study Whether This Protocol May Improve The Functional Abilities In This Population.
Related Post: