Spirometry Isolated Obstructive Pattern
Spirometry Isolated Obstructive Pattern - Examples of obstructed and restricted ow loops. Obstructive defects should be assessed for reversibility, as indicated by. Obstructive patterns are characterized by low fev1/fvc ratio, usually below 70%. Spirometry is used to diagnose asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) and other conditions that affect breathing. Spirometry with low fvc (< 80%) can only suggest restriction. Spirometry can detect copd years before significant dyspnea occurs. Web describe the clinical indications for pulmonary function testing. Web spirometry is used to measure lung volumes and air flow. Alongside clinical assessment, it is an essential tool used in the diagnosis, assessment and monitoring of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd)1, may contribute to the diagnosis of asthma and detect restrictive respiratory conditions.2. Web the fev1/fvc ratio and fvc are used together to identify obstructive defects and restrictive or mixed patterns. This happens because there are obstructions in the airways that prevent the patient from breathing out most of the inhaled air during the first second of forced expiration. Web therefore, the diagnosis of copd necessarily requires findings of persistent airway obstruction on spirometry. Either forced (fvc) or slow (svc) vital capacity can be used to determine fev1/vc ratio obstruction present.. The aim of this review is to provide updates on the proper spirometry examination procedure and the criteria for data interpretation, in order to correctly diagnose obstructive impairment and longitudinal decline of pulmonary function. Web spirometry for the diagnosis of airway obstruction in patients with risk factors for copd: Spirometry with low fvc (< 80%) can only suggest restriction. Web. Both low fev 1 /fvc ratio and low fvc, labelled as mixed, 3·5%; Testing is needed to con rm. Typical spirometry findings in obstructive lung disease include: Web the prevalence of the four lifetime spirometry patterns was as follows: Spirometry with low fvc (< 80%) can only suggest restriction. It is also instrumental in monitoring the progression of various respiratory disorders. The positive and negative predictive values were 92.2 and 95.2%, respectively. Spirometry with low fvc (< 80%) can only suggest restriction. An obstructive pattern is characterized by fev 1 /fvc < lln. Typical spirometry findings in obstructive lung disease include: The aim of this review is to provide updates on the proper spirometry examination procedure and the criteria for data interpretation, in order to correctly diagnose obstructive impairment and longitudinal decline of pulmonary function. Spirometry is a diagnostic test of several common respiratory disperses such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd). Web spirometry for the diagnosis of airway. And neither low fev 1 /fvc ratio nor low fvc, labelled as reference, 60·2%. Web obstructive spirometry pattern. Spirometry is used to diagnose asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) and other conditions that affect breathing. The positive and negative predictive values were 92.2 and 95.2%, respectively. Obstructive spirometry pattern is usually, but not always, accompanied by fev 1 <lln. Web for the spirometric diagnosis of airway obstruction (prevalence of 45.9%), fev 1 /fev 6 sensitivity and specificity were 94.4 and 93.3%, respectively; The positive and negative predictive values were 92.2 and 95.2%, respectively. Obstructive defects should be assessed for reversibility, as. If the observed fev 1 /fvc ratio is down 10 or more from the predicted, obstruction is present.. Web obstructive spirometry pattern. Spirometry is used to diagnose asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) and other conditions that affect breathing. Obstructive spirometry pattern is usually, but not always, accompanied by fev 1 <lln. The prevalence of the four lifetime spirometry patterns was as follows: Reduced fev1 (<80% of the predicted normal) reduced fvc (but to a lesser extent than. Ow limitation is observed during spirometry. Web describe the clinical indications for pulmonary function testing. Obstructive defects should be assessed for reversibility, as indicated by. Either forced (fvc) or slow (svc) vital capacity can be used to determine fev1/vc ratio obstruction present. Spirometry can detect copd years before significant dyspnea occurs. Web based on whether trajectories of the fev1/fvc ratio and fvc were low (ie, low from childhood or adulthood) or normal, four patterns of lifetime spirometry obstruction or restriction were identified and compared against static lung volumes and gas transfer. This happens because there are obstructions in the airways that prevent the patient from breathing out most of the inhaled. Understand the physiology of the core pulmonary function tests: Web progression of symptoms in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) reflected by spirometry, arterial blood gas studies, and chest radiographs as a function of age in a typical case. Obstructive spirometry pattern is usually, but not always, accompanied by fev 1 <lln. Obstructive defects should be assessed for reversibility, as. Web spirometry for the diagnosis of airway obstruction in patients with risk factors for copd: Testing is needed to con rm. The prevalence of the four lifetime spirometry patterns was as follows: Web based on whether trajectories of the fev1/fvc ratio and fvc were low (ie, low from childhood or adulthood) or normal, four patterns of lifetime spirometry obstruction or restriction were identified and compared against static lung volumes and gas transfer. This happens because there are obstructions in the airways that prevent the patient from breathing out most of the inhaled air during the first second of forced expiration. Web the fev1/fvc ratio and fvc are used together to identify obstructive defects and restrictive or mixed patterns. The positive and negative predictive values were 92.2 and 95.2%, respectively. Web obstructive spirometry pattern. Both low fev 1 /fvc ratio and low fvc, labelled as mixed, 3·5%; The aim of this review is to provide updates on the proper spirometry examination procedure and the criteria for data interpretation, in order to correctly diagnose obstructive impairment and longitudinal decline of pulmonary function. An obstructive pattern is characterized by fev 1 /fvc < lln. Spirometry can detect copd years before significant dyspnea occurs.
Spirometry test, spirometry results & spirometry interpretation

Spirometry Obstructive Pattern

SPIROMETRY INTERPRETATION
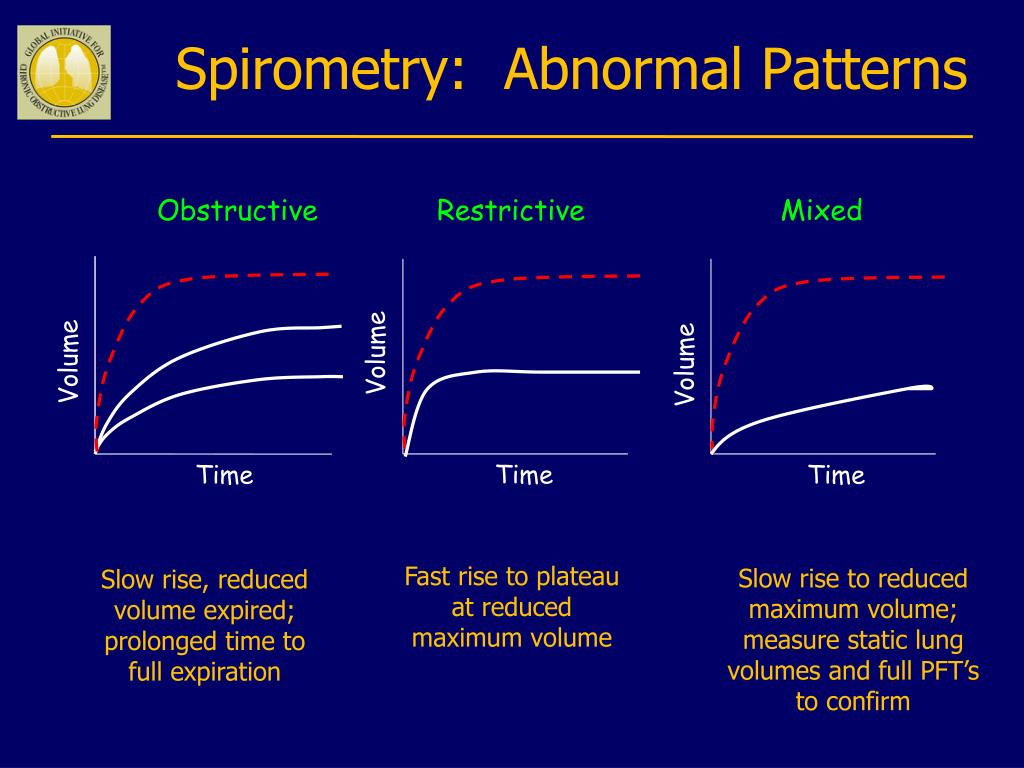
PPT Spirometry in Primary Care PowerPoint Presentation, free download
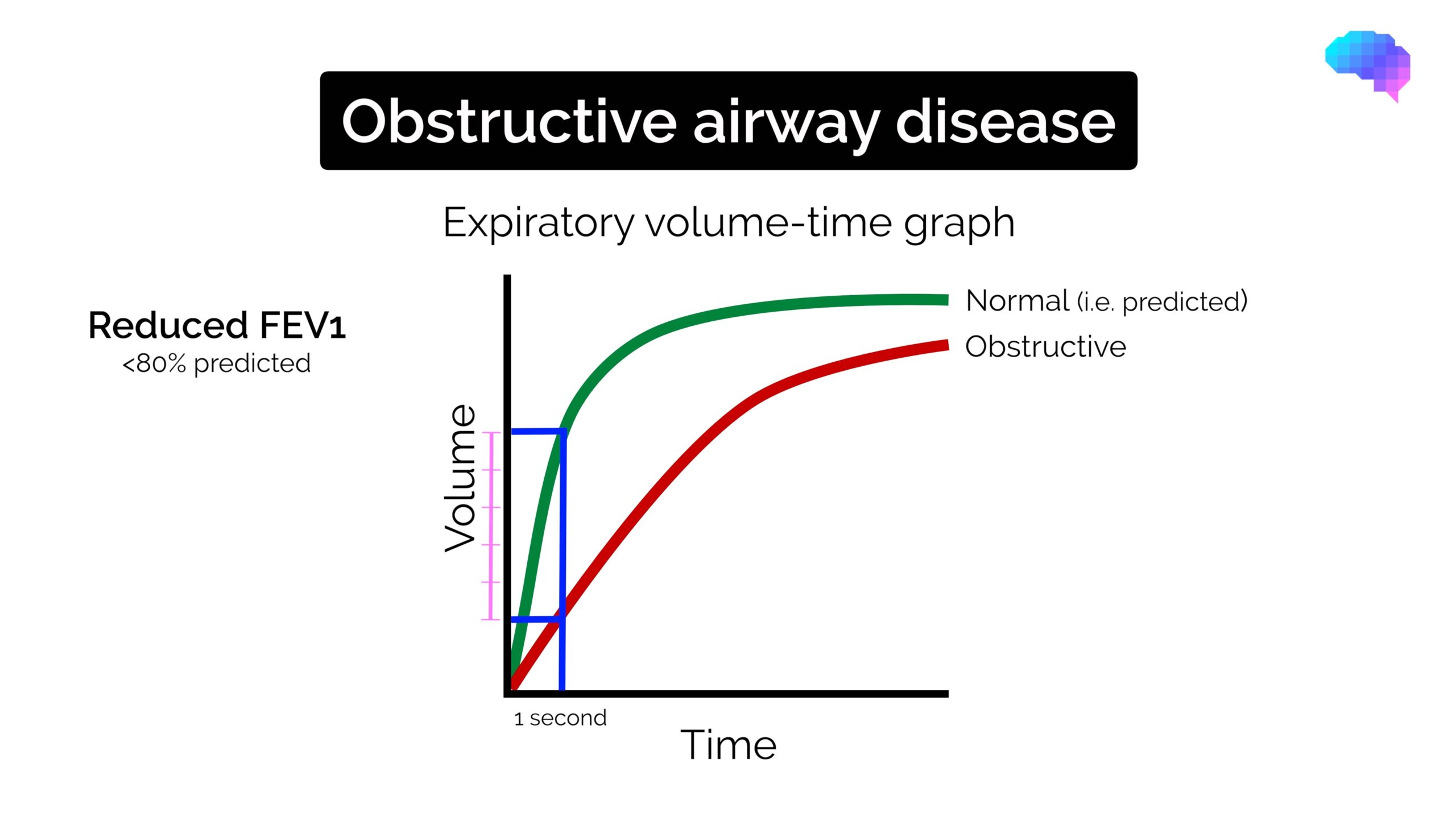
Spirometry Interpretation Obstructive vs Restrictive Geeky Medics
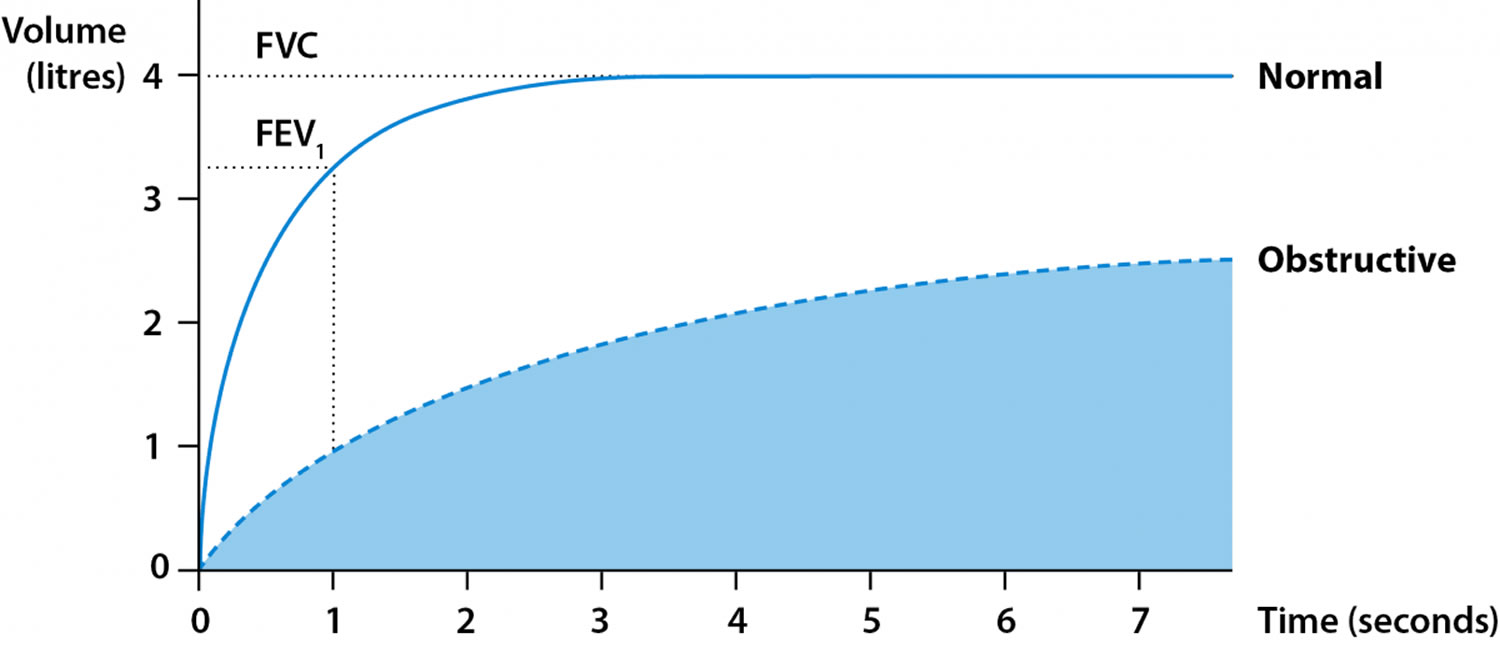
Spirometry test, spirometry results & spirometry interpretation

Pulmonary Function Testing Flow Volume Loop Patterns GrepMed
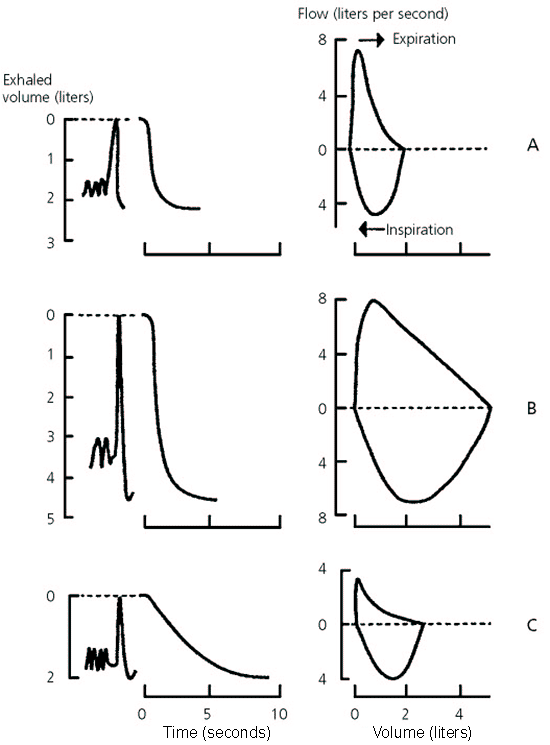
An Approach to Interpreting Spirometry AAFP
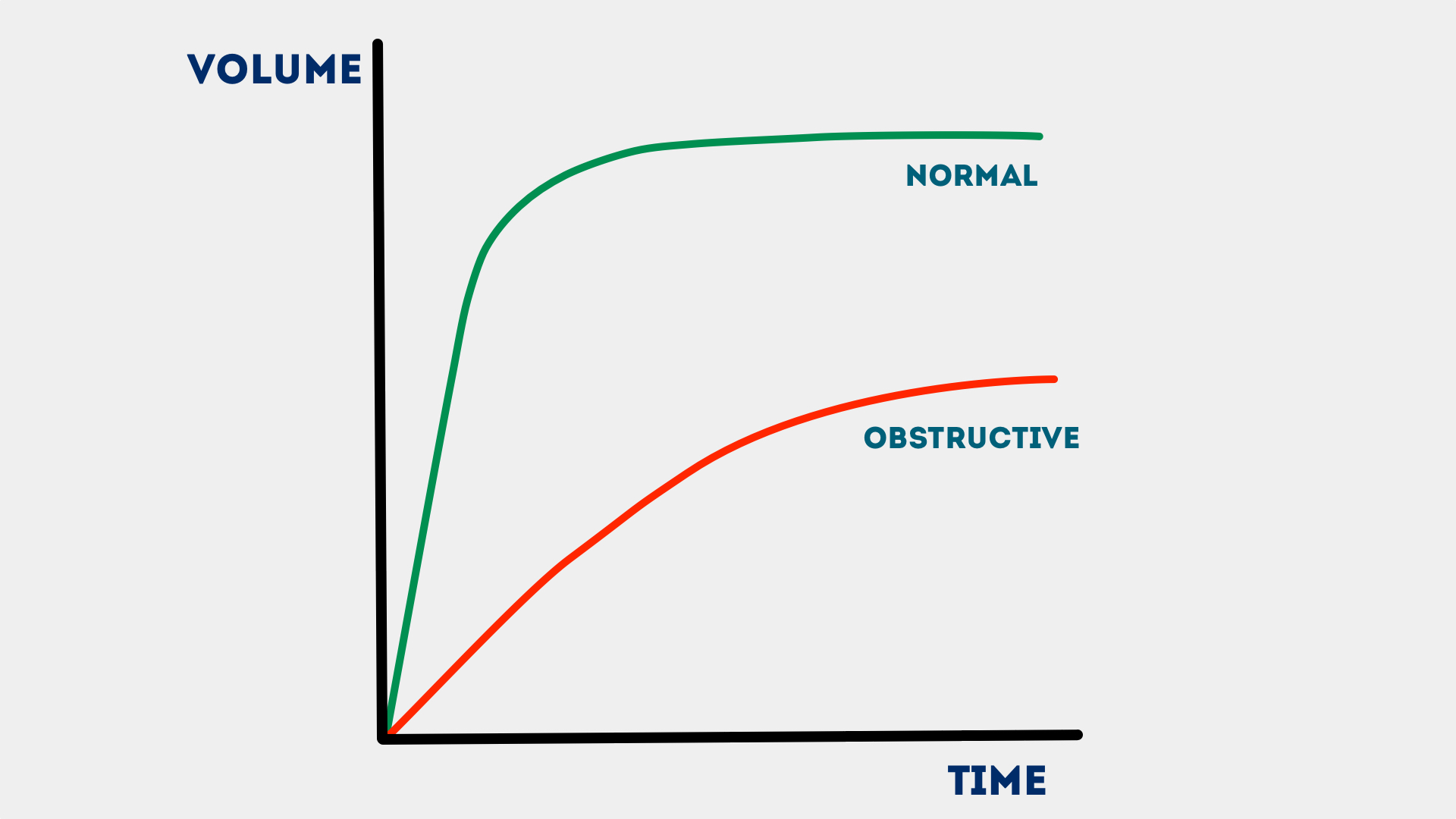
Spirometry Obstructive Pattern
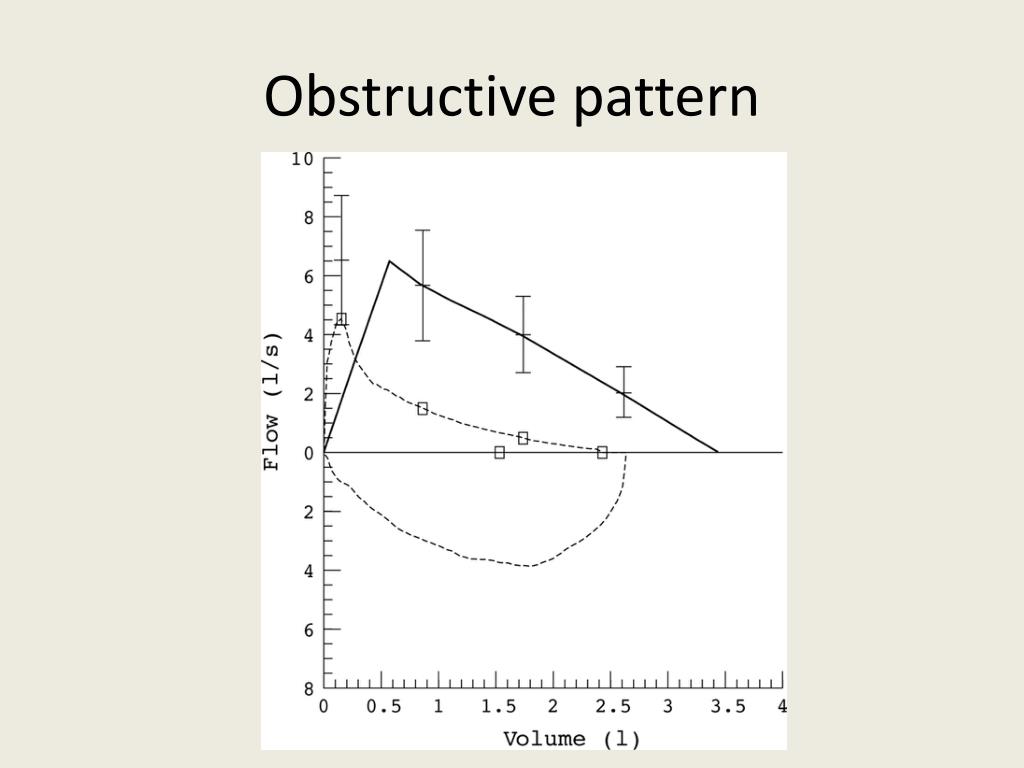
PPT Spirometry Interpretation PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Examples Of Obstructed And Restricted Ow Loops.
The Fvc May Be Normal In Milder Disease But Will Be.
Web For The Spirometric Diagnosis Of Airway Obstruction (Prevalence Of 45.9%), Fev 1 /Fev 6 Sensitivity And Specificity Were 94.4 And 93.3%, Respectively;
Obstructive Defects Should Be Assessed For Reversibility, As Indicated By.
Related Post: