Spatial Patterns Ap Human Geography
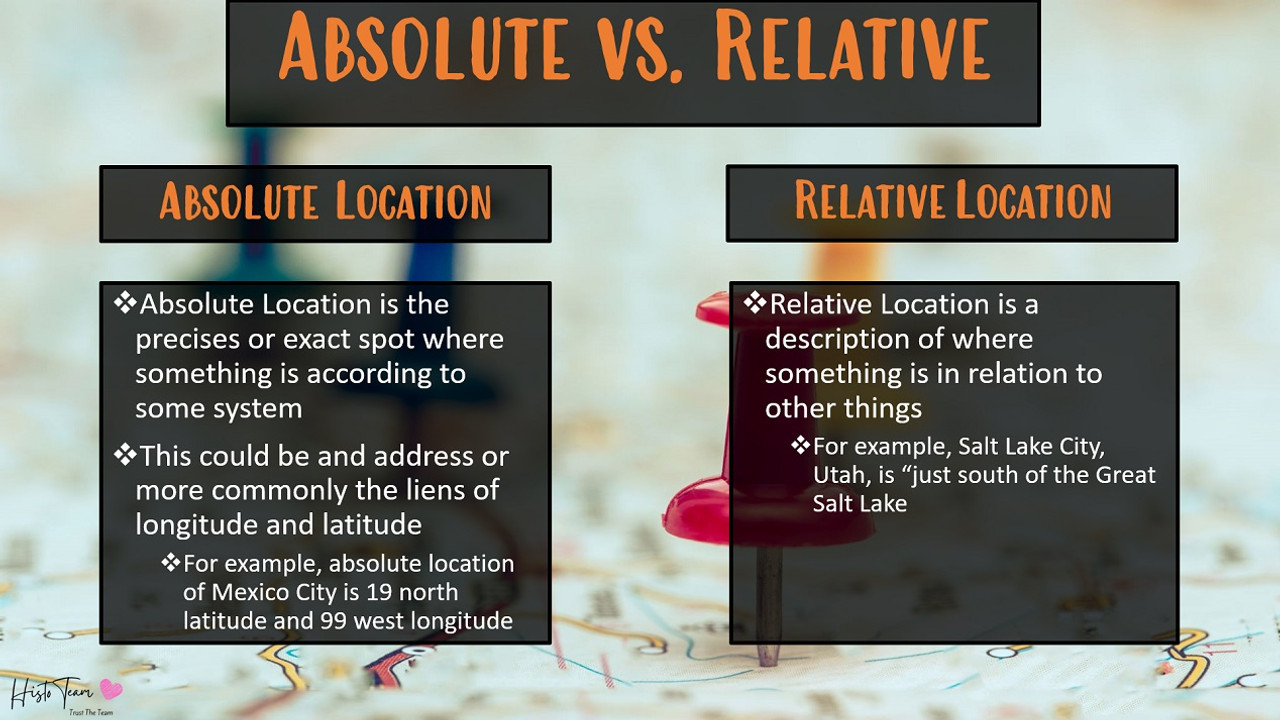
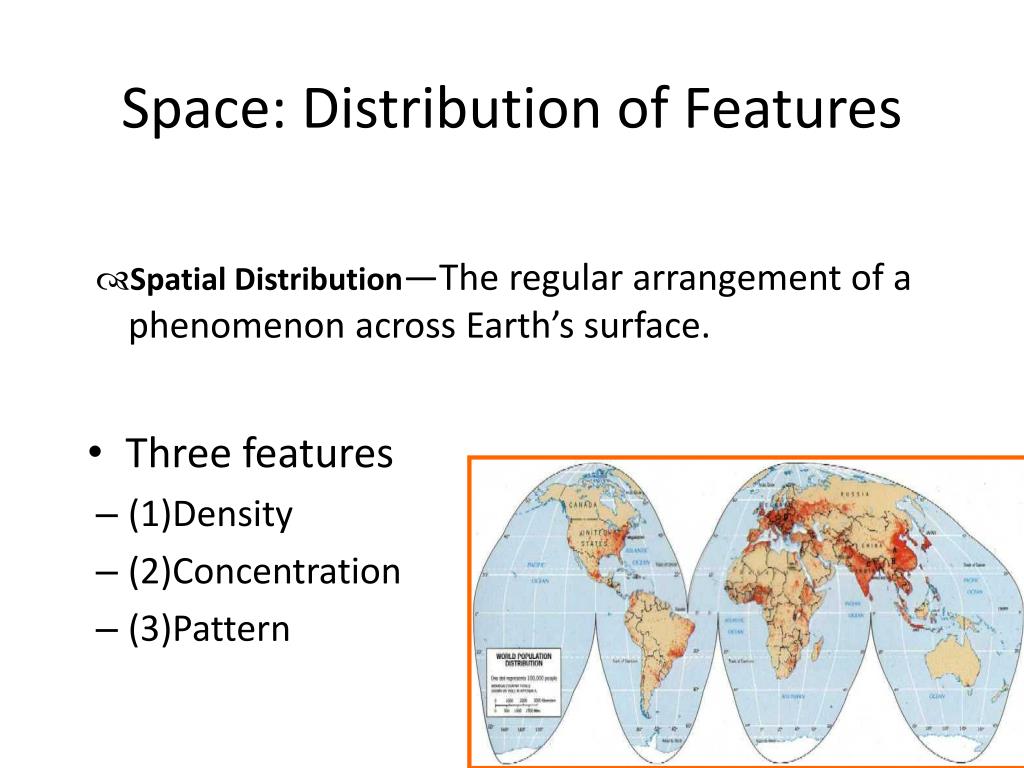
Spatial Patterns Ap Human Geography - Who was von thünen and why is he important to ap® human geography? Spiral across topics and units. It aligns closely to the college board course and exam description® to improve student performance on the ap® exam. Web the ap human geography exam will test your understanding of the geographic concepts covered in the course units, as well as your ability to analyze maps, geospatial data, infographics, and more. Objects that form a group. Nucleated settlements, which are characterized by a higher population density and a more concentrated grouping of structures; How to use this lesson plan. The geometric arrangement of objects in an area (how things are placed). Web some common types of rural settlement patterns include dispersed settlements, which are characterized by a low population density and a scattered distribution of homes and other structures; Describe one way that humans have altered the environmental sustainability of agricultural lands. During the exam, students are challenged to think critically and apply their knowledge to solve problems. Access to markets has been, and still is, a huge problem for farmers all over the world. Web examples of spatial patterns shown on maps include. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like *learning objective*, absolute location, relative location and more. Web. Web ap® human geography 2021 scoring guidelines question 3: Characterize and analyze changing interactions among different places. Web examples of spatial patterns shown on maps include. Web course & exam pages. Web consider maps and spatial data. Define the concept of carrying capacity. Web ap® human geography 2021 scoring guidelines question 3: Web consider maps and spatial data. Seeing patterns and trends in data and in visual sources such as maps and drawing conclusions from them. Show a strong understanding of how the world looks from a spatial perspective. Click the card to flip 👆. Show a strong understanding of how the world looks from a spatial perspective. How to use this lesson plan. The clusters are mostly located along the. Study of people and places. Web course & exam pages. Web some common types of rural settlement patterns include dispersed settlements, which are characterized by a low population density and a scattered distribution of homes and other structures; 1 point accept one of the following: Seeing patterns and trends in data and in visual sources such as maps and drawing conclusions from them. Web ap®. Students cultivate their understanding of human geography through data and geographic analyses as they explore topics like patterns and spatial organization, human impacts and interactions with their environment, and spatial processes and societal changes. Define the concept of carrying capacity. Web the ap human geography exam will test your understanding of the geographic concepts covered in the course units, as. Define the concept of carrying capacity. Assign the personal progress checks—either as homework or in class—for each unit. Show a strong understanding of how the world looks from a spatial perspective. Characterize and analyze changing interactions among different places. The way things are laid out and organized on the surface of the earth. Here are 10 suggestions to help students develop as geographers and spatial thinkers. The program fully meets the 2019 college board framework for ap® human geography. Web the purpose of ap human geography is to introduce students to the systematic study of patterns and processes that have shaped human understanding, use, and alteration of earth's surface. It aligns closely to. Click the card to flip 👆. During the exam, students are challenged to think critically and apply their knowledge to solve problems. A spatial perspective is designed specifically for high school ap® students. Objects that form a group. Web this ap® human geography study guide will help you understand how his theory is used to explain agricultural land use and. Seeing patterns and trends in data and in visual sources such as maps and drawing conclusions from them. Web the ap human geography exam will test your understanding of the geographic concepts covered in the course units, as well as your ability to analyze maps, geospatial data, infographics, and more. Students employ spatial concepts and landscape analysis to examine human. Web the purpose of ap human geography is to introduce students to the systematic study of patterns and processes that have shaped human understanding, use, and alteration of earth's surface. A spatial perspective is designed specifically for high school ap® students. During the exam, students are challenged to think critically and apply their knowledge to solve problems. 1 point accept one of the following: Absolute and relative location and distance, direction, elevation, dispersal, and clustering. Students employ spatial concepts and landscape analysis to examine human social organization and its environmental consequences. Web spatial thinking is the ability to understand and reason about relationships between objects in space. Define the concept of carrying capacity. Seeing patterns and trends in data and in visual sources such as maps and drawing conclusions from them. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like *learning objective*, absolute location, relative location and more. Assign the personal progress checks—either as homework or in class—for each unit. Click the card to flip 👆. Web a spatial perspective allows for a focus on the ways phenomena are related to one another in particular places, which in turn allows for the examination of human organization and its environmental consequences. Students cultivate their understanding of human geography through data and geographic analyses as they explore topics like patterns and spatial organization, human impacts and interactions with their environment, and spatial processes and societal changes. Web students must be able to think spatially and understand how various factors interact to shape human behavior and the physical landscape. Web thinking through maps and in, about, and with space are all productive habits of mind for ap human geography students.
Spatial Fix Definition Ap Human Geography DEFNITO
Spatial Concepts in AP Human Geography PowerPoint Lesson
Module 1.5 Field Work and Geospatial Data AP Human Geography

Examples Of Spatial Patterns In Geography
PPT AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY EXAM REVIEW PowerPoint Presentation, free

2022 Live Review 3 AP Human Geography Spatial Relationships with

National Geographic Human Geography a Spatial Perspective AP® Edition

survey patterns ap human geography sensitivecondal

Spatial Association & Sense of Place [AP Human Geography Unit 1 Topic 4

PPT Patterns in Human Geography PowerPoint Presentation, free
The Way Things Are Laid Out And Organized On The Surface Of The Earth.
Spiral Across Topics And Units.
Web Examples Of Spatial Patterns Shown On Maps Include.
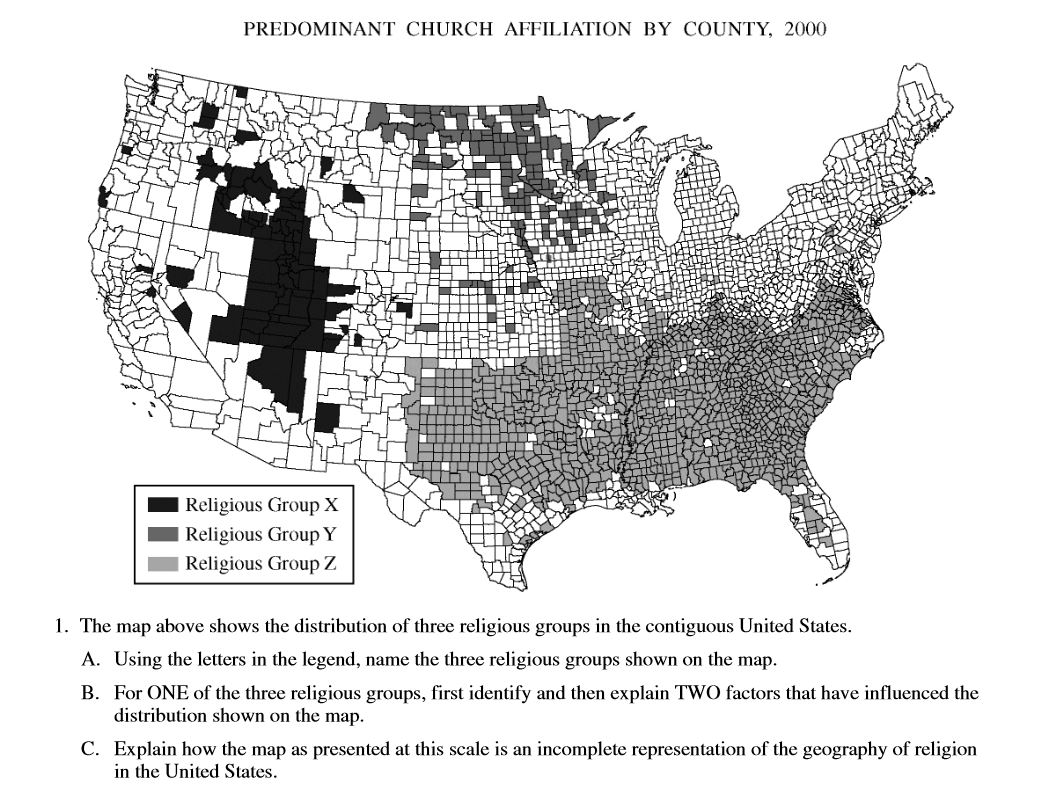
Each Map Is Unique In The Information It Shows, And No Map Is Perfect.
Related Post: