Si Joint Referral Pattern
Si Joint Referral Pattern - Similar content being viewed by others. If numbness and tingling or weakness is present, an alternative diagnosis should be considered. It is usually caused by abnormal motion (i.e. Low back pain / physiopathology. Web sacroiliac joint pain is most commonly felt in the low back and buttock but can also be referred into the thigh and leg. The clinical presentation of sij pathologies is variable and challenging in imaging visualization. One common referral pattern is pain or discomfort in one or both buttocks. Among these other patterns included pain down the posterior/lateral thigh (50%), pain distal to the knee (28%), and pain in the foot (14%). Web sij dysfunction generally refers to aberrant position or movement of sij structures that may or may not result in pain. The prevalence of sij pain has been reported to be up to 75 % [ 1 ]. The ilium, ischium, and pubic bone. Symptoms that suggest that the sacroiliac joint (sij), as opposed to pathology of the lumbar spine or hip, may be a source of pain include pain with position changes, such as standing from a seated position or sitting on a hard surface. Each innominate is formed by the fusion of the three bones of. Web localized pain is not always a reliable presentation, as a 2000 study reported 18 different pain referral patterns from the si joint. Web sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a degenerative condition of the sacroiliac joint resulting in lower back pain. The l5 nerve ventral ramus and lumbosacral trunk pass anteriorly and the s1 nerve ventral ramus passes inferiorly to the. Web pain referral patterns as well as therapeutic injections help diagnose si joint dysfunction. Web sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a term used to describe the pain of the sacroiliac joint (si joint). Low back pain / physiopathology. Pain is the main symptom of si joint dysfunction. Similar content being viewed by others. Web sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a term used to describe the pain of the sacroiliac joint (si joint). This paper aims to clarify the difference between these clinical concepts and present current available evidence regarding diagnosis and. One common referral pattern is pain or discomfort in one or both buttocks. The ilium, ischium, and pubic bone. Large diarthrodial join t. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction describes pain due to abnormal movement (too much or too little) or misalignment of the si joint. Large diarthrodial join t [1] made up of the sacrum and the two innominates of the pelvis. Several sacral ligaments and pelvic muscles support the sij. Radiation to the groin or fortin area also suggest sacroiliac joint as. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction describes pain due to abnormal movement (too much or too little) or misalignment of the si joint. This paper aims to clarify the difference between these clinical concepts and present current available evidence regarding diagnosis and. Web the sacroiliac joint (sij) is a common pain generator for individuals with low back pain (lbp). Web localized. Web sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a term used to describe the pain of the sacroiliac joint (si joint). The ilium, ischium, and pubic bone. Web the variable patterns of pain referral observed may arise for several reasons, including the joint's complex innervation, sclerotomal pain referral, irritation of adjacent structures, and varying locations of injury with the sacroiliac joint. The clinical. Several sacral ligaments and pelvic muscles support the sij. It is usually caused by abnormal motion (i.e. The prevalence of sij pain has been reported to be up to 75 % [ 1 ]. This pain may worsen with prolonged sitting or standing and can resemble symptoms of sciatica. Web pain referral patterns as well as therapeutic injections help diagnose. If numbness and tingling or weakness is present, an alternative diagnosis should be considered. These joints sit where the lower spine and pelvis meet. The ilium, ischium, and pubic bone. Low back pain / physiopathology. Large diarthrodial join t [1] made up of the sacrum and the two innominates of the pelvis. The clinical presentation of sij pathologies is variable and challenging in imaging visualization. Pain is the main symptom of si joint dysfunction. These joints sit where the lower spine and pelvis meet. Large diarthrodial join t [1] made up of the sacrum and the two innominates of the pelvis. Each innominate is formed by the fusion of the three bones. Web pain referral patterns as well as therapeutic injections help diagnose si joint dysfunction. One common referral pattern is pain or discomfort in one or both buttocks. Web sacroiliac joint pain is most commonly felt in the low back and buttock but can also be referred into the thigh and leg. The ilium, ischium, and pubic bone. Web the sij complex is part of the kinetic chain connecting the spine and lower extremities, and may be a primary or secondary pain generator depending on the clinical scenario and should be examined routinely in the evaluation of back or leg complaints. Diagnosis is made clinically with pain just inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine that is made worse with hip flexion, abduction, and external rotation. Pain is the main symptom of si joint dysfunction. Low back pain / etiology. Several sacral ligaments and pelvic muscles support the sij. Web although referred si joint pain patterns may be complex, understanding the role of the si joint in the contribution to low back pain will allow for effective treatment options and improved patient outcomes. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction describes pain due to abnormal movement (too much or too little) or misalignment of the si joint. Recent studies have demonstrated that historical and physical examination findings and radiological imaging are insufficient to diagnose si joint pain. Each innominate is formed by the fusion of the three bones of the pelvis: Sacroiliac joint syndrome is a significant source of pain in 15% to 30% of people with mechanical low back pain. This paper aims to clarify the difference between these clinical concepts and present current available evidence regarding diagnosis and. Web the variable patterns of pain referral observed may arise for several reasons, including the joint's complex innervation, sclerotomal pain referral, irritation of adjacent structures, and varying locations of injury with the sacroiliac joint.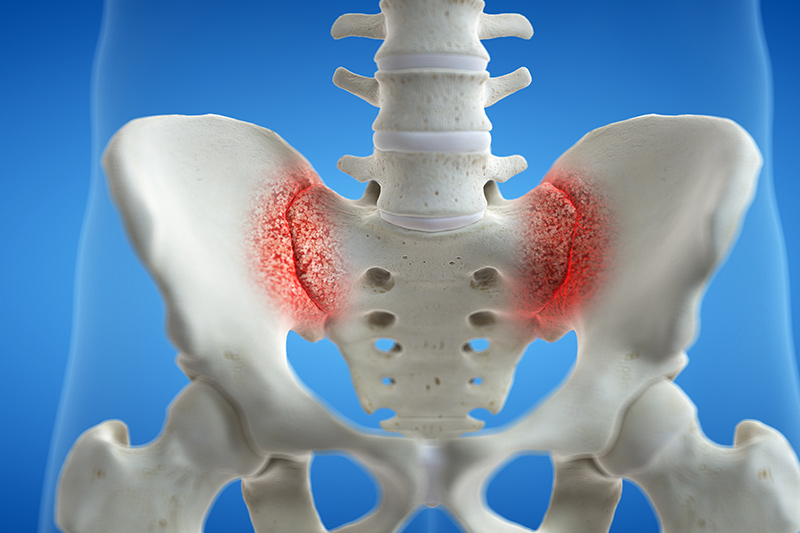
Sacroilliac (SI) Joint Pain The Orthopedic Pain Institute, Beverly

SI Joint Pain The Complete Injury Guide Vive Health
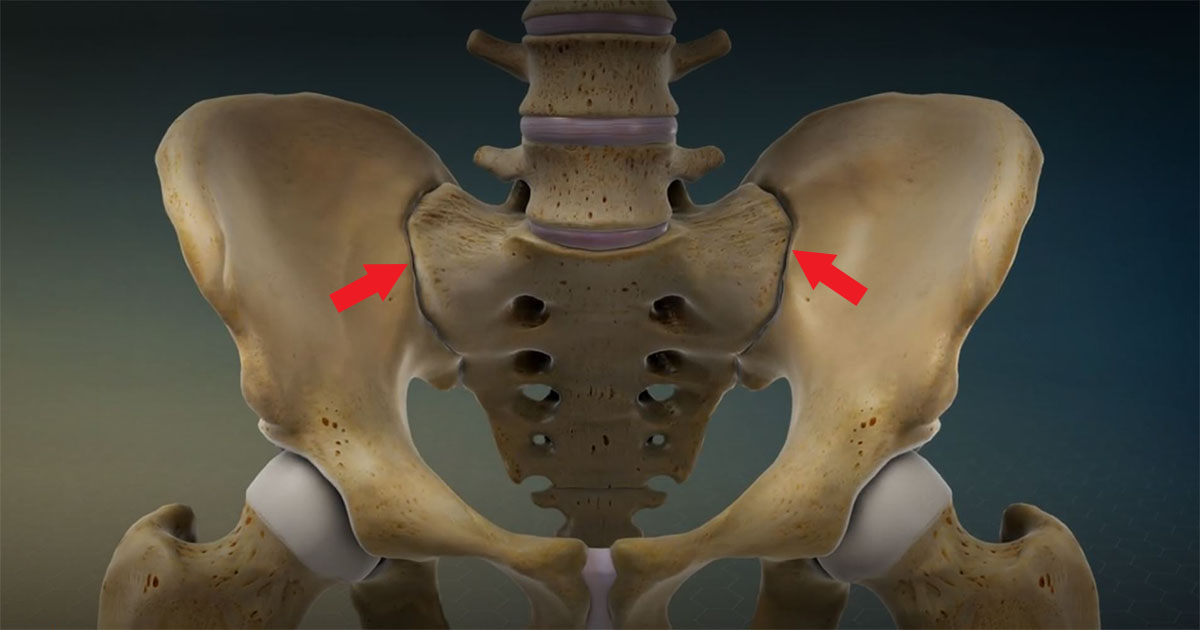
Sacroiliac Joint Diagram

The Referral Patterns of the Sacroiliac Joint, Facet Joints, and

Pain referral from the sacroiliac joint. Van der Wurff et al., 2006 [33

The SI Joint....from A PT Perspective CHARM
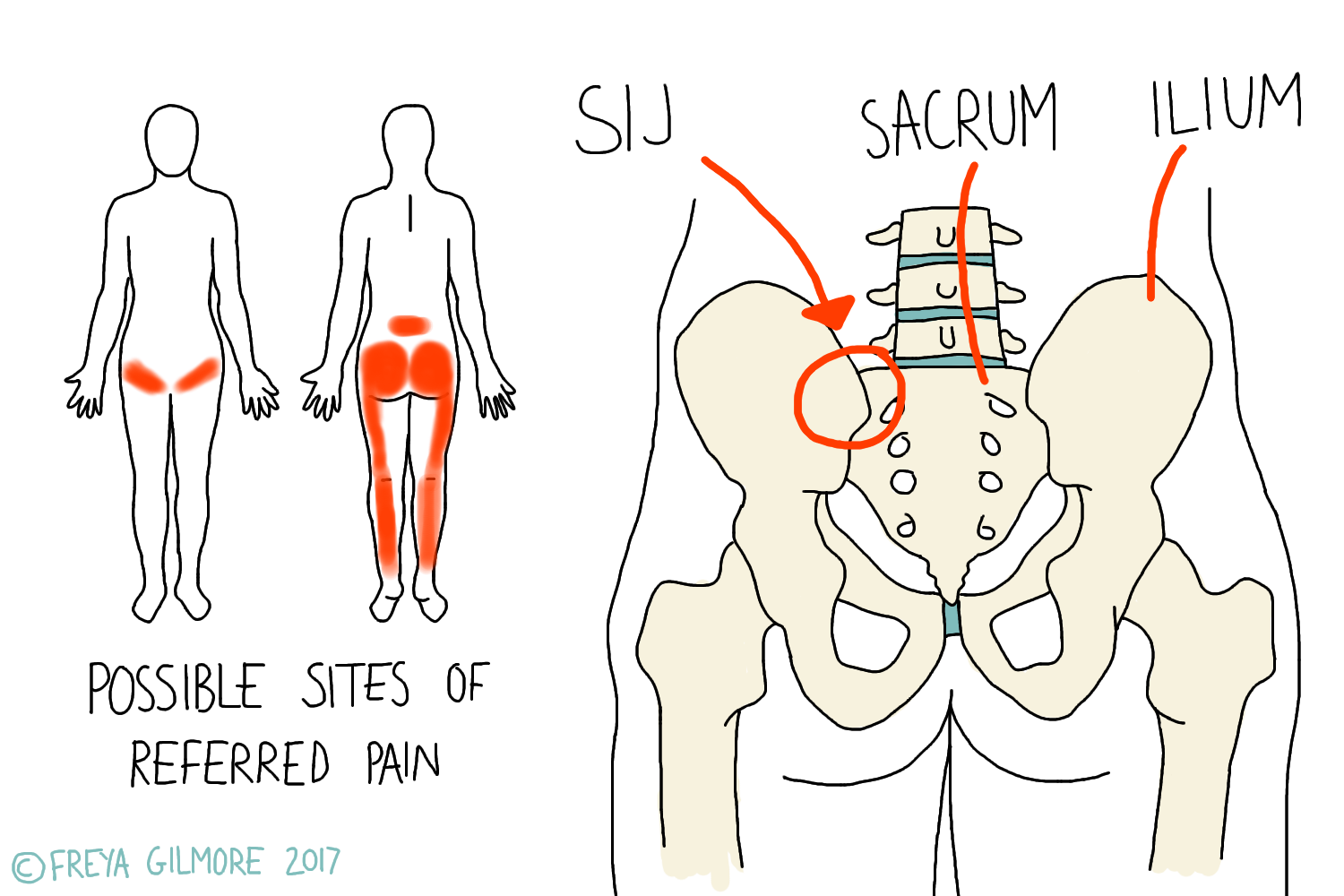
The Sacroiliac Joint (SIJ) Beth Forrest Osteopathy

Lumbar Spine Facet Joint Referral Patterns Bead Pattern (Free)
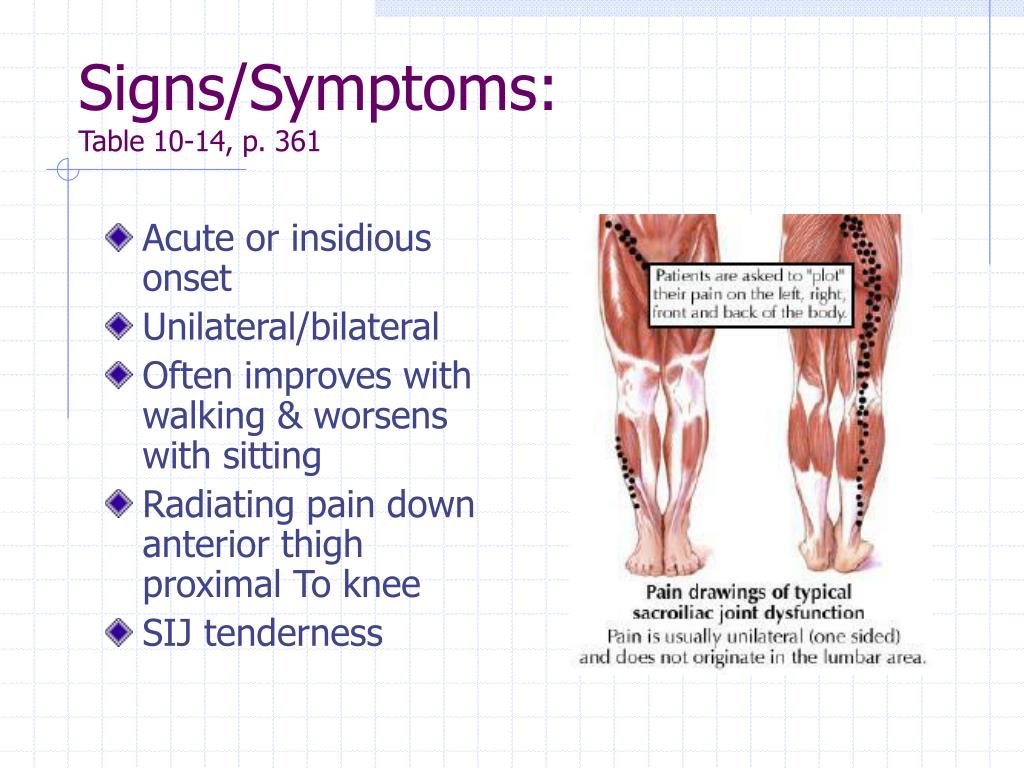
PPT Sacroiliac Dysfunction PowerPoint Presentation, free download

The Referral Patterns of the Sacroiliac Joint, Facet Joints, and
Low Back Pain Has Many Different Causes, Including Issues Related To The Sacroiliac (Si) Joints.
The Prevalence Of Sij Pain Has Been Reported To Be Up To 75 % [ 1 ].
Web Sij Dysfunction Generally Refers To Aberrant Position Or Movement Of Sij Structures That May Or May Not Result In Pain.
The Clinical Presentation Of Sij Pathologies Is Variable And Challenging In Imaging Visualization.
Related Post: