Saw Tooth Pattern Ecg
Saw Tooth Pattern Ecg - Web on the surface electrocardiogram, the atrial flutter wave forms a “sawtooth” pattern in the inferior leads ( fig. I admitted him to the hospital and started a blood thinner and an intravenous drug to slow his heart rate. Three findings that distinguish atypical atrial flutter arrhythmia from typical atrial flutter: Web the ecg pattern may not reflect the mechanism. Ventricular rate depends on av conduction ratio (see below) This is the result of an ectopic atrial pacemaker or because of a rapid reentry pathway somewhere within the atria but outside of the sa node area. Web in typical flutter, ecg shows continuous and regular atrial activation with a sawtooth pattern, most obvious in leads ii, iii, and avf (see figure atrial flutter ). Web sawtooth pattern on ecg. By observing the inferior leads we can determine the direction of the stimulus and classify it further as counterclockwise atrial flutter or clockwise atrial flutter. Electrocardiographic approach to atrial flutter. Intracardiac mapping has shown what. Atrial flutter is the only diagnosis causing this baseline appearance, which is why it. Web afl makes a very distinct sawtooth pattern on an electrocardiogram (ecg), a test used to diagnose abnormal heart rhythms. Conducted with right bundle branch block.) carotid sinus massage can increase av block and better expose the typical flutter waves. The. Last reviewed 1 jan 2018. Ventricular rate depends on av conduction ratio (see below) After questioning him, it was clear that he had been having palpitations and near dizzy spells on and off for a couple of weeks. Web in typical flutter, ecg shows continuous and regular atrial activation with a sawtooth pattern, most obvious in leads ii, iii, and. Web ecg shows sawtooth pattern of atrial activity (rate 300 beats/min) stroke risk should be considered equivalent to that with atrial fibrillation. If atrial flutter is associated with a 2:1 block, p waves are difficult to recognise because of the superposition of the preceding t waves. By observing the inferior leads we can determine the direction of the stimulus and. (a) ecg fulfilling classical flutter criteria (rate and lack of isoelectric baseline) in a case of focal tachycardia originating in the right superior pulmonary vein. Ventricular rate depends on av conduction ratio (see below) Web on an ecg, atrial flutter resembles f waves with a sawtooth pattern. Last reviewed 1 jan 2018. Web afl makes a very distinct sawtooth pattern. Web ecg shows sawtooth pattern of atrial activity (rate 300 beats/min) stroke risk should be considered equivalent to that with atrial fibrillation. Atrial flutter is the only diagnosis causing this baseline appearance, which is why it. Web the ecg pattern may not reflect the mechanism. Web the electrocardiogram shows a saw tooth's pattern in inferior leads, with a slow downward. Web the ecg showed that he was in atrial flutter (afl). Web ecg shows sawtooth pattern of atrial activity (rate 300 beats/min) stroke risk should be considered equivalent to that with atrial fibrillation. Web sawtooth pattern on ecg. Web the electrocardiogram shows a saw tooth's pattern in inferior leads, with a slow downward slope followed by a fast upward slope. If atrial flutter is associated with a 2:1 block, p waves are difficult to recognise because of the superposition of the preceding t waves. The foci responsible for focal atrial tachycardia do not occur randomly throughout the atria but tend to cluster at characteristic anatomical locations. This pattern is composed of a two‐phased descent and a rapid ascent, with no. Web ecg strip (electrocardiogram, ekg) of sawtooth pattern of atrial flutter. Web atrial flutter produces a distinctive “sawtooth” pattern on an electrocardiogram (ekg or ecg), a test used to monitor the heart and diagnose heart rhythm disorders. This ectopic pacemaker usually originates somewhere in the lower atrium and closer to the av node, making a distinct wave pattern. Web the. (4,5) this saw tooth’s appearance could be easily regis. Note the irregular ventricular rate. Web the ecg showed that he was in atrial flutter (afl). The fl wave is predominantly negative in the inferior leads (sawtooth) and v6 while positive in v1. Last reviewed 1 jan 2018. Web in typical flutter, ecg shows continuous and regular atrial activation with a sawtooth pattern, most obvious in leads ii, iii, and avf (see figure atrial flutter ). This is the result of an ectopic atrial pacemaker or because of a rapid reentry pathway somewhere within the atria but outside of the sa node area. The downslope of the surface. Web on an ecg, atrial flutter resembles f waves with a sawtooth pattern. Three findings that distinguish atypical atrial flutter arrhythmia from typical atrial flutter: Web on the surface electrocardiogram, the atrial flutter wave forms a “sawtooth” pattern in the inferior leads ( fig. Catheter ablation is highly successful and is considered the definitive treatment for typical atrial. Last reviewed 1 jan 2018. This pattern is composed of a two‐phased descent and a rapid ascent, with no isoelectric interval. Web in typical flutter, ecg shows continuous and regular atrial activation with a sawtooth pattern, most obvious in leads ii, iii, and avf (see figure atrial flutter ). Web ecg shows sawtooth pattern of atrial activity (rate 300 beats/min) stroke risk should be considered equivalent to that with atrial fibrillation. Web sawtooth pattern in ecg atrial flutter (afl) may exist with or without underlying structural heart disease. The fl wave is predominantly negative in the inferior leads (sawtooth) and v6 while positive in v1. Web the ecg pattern may not reflect the mechanism. If atrial flutter is associated with a 2:1 block, p waves are difficult to recognise because of the superposition of the preceding t waves. Ventricular rate depends on av conduction ratio (see below) (4,5) this saw tooth’s appearance could be easily regis. I admitted him to the hospital and started a blood thinner and an intravenous drug to slow his heart rate. Web the electrocardiographic pattern of typical ccwid flutter waves is easily recognizable:
Atrial Flutter Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Ablation

Electrocardiogram showing typical atrial flutter with variable
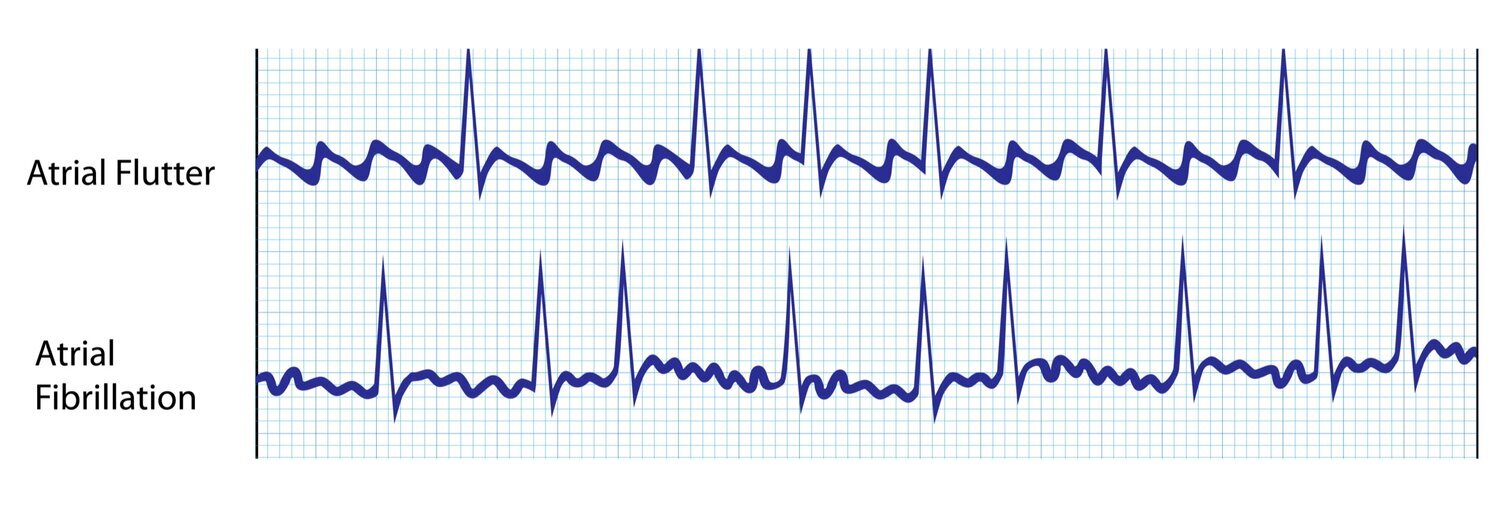
Atrial Flutter Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Dr. AFib
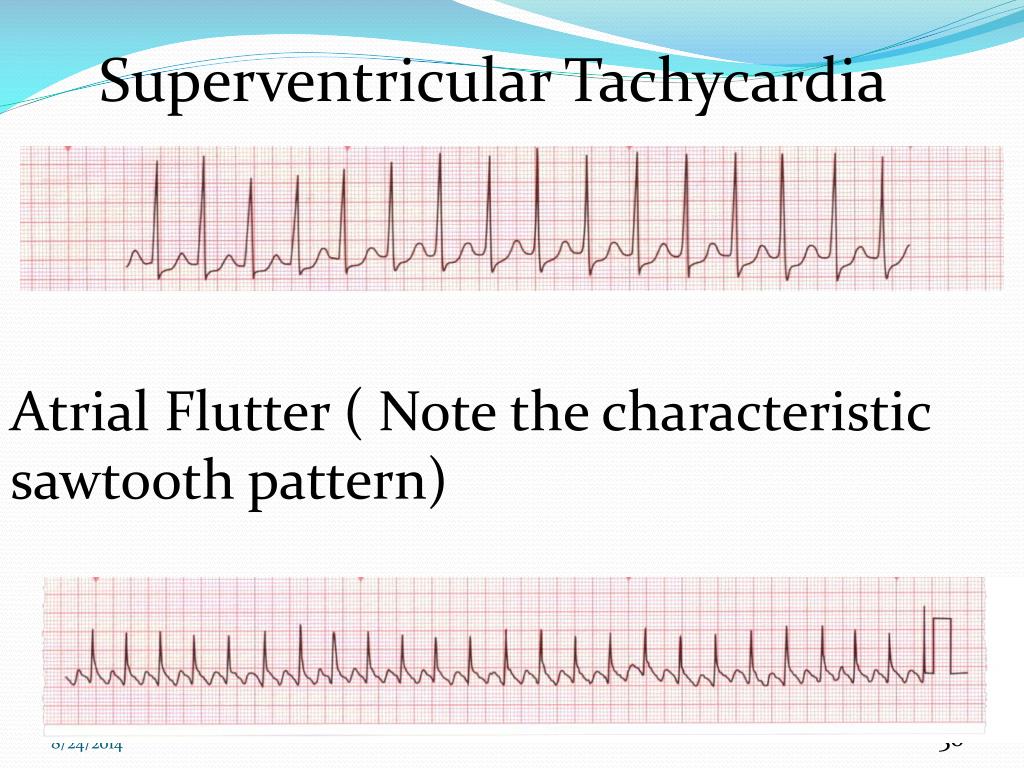
PPT ECG Basics Module 2( Arrhythmias level 1) PowerPoint Presentation

Electrocardiogram showing the ''sawtooth'' or ''picket fence'' pattern

Arrhythmias Originating in the Atria Cardiac Electrophysiology Clinics
![Atrial Flutter ECG Interpretation [With Examples] Manual of Medicine](https://manualofmedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Atrial-Flutter-with-Variable-AV-Block.png)
Atrial Flutter ECG Interpretation [With Examples] Manual of Medicine

Electrocardiogram showing the ''sawtooth'' or ''picket fence'' pattern
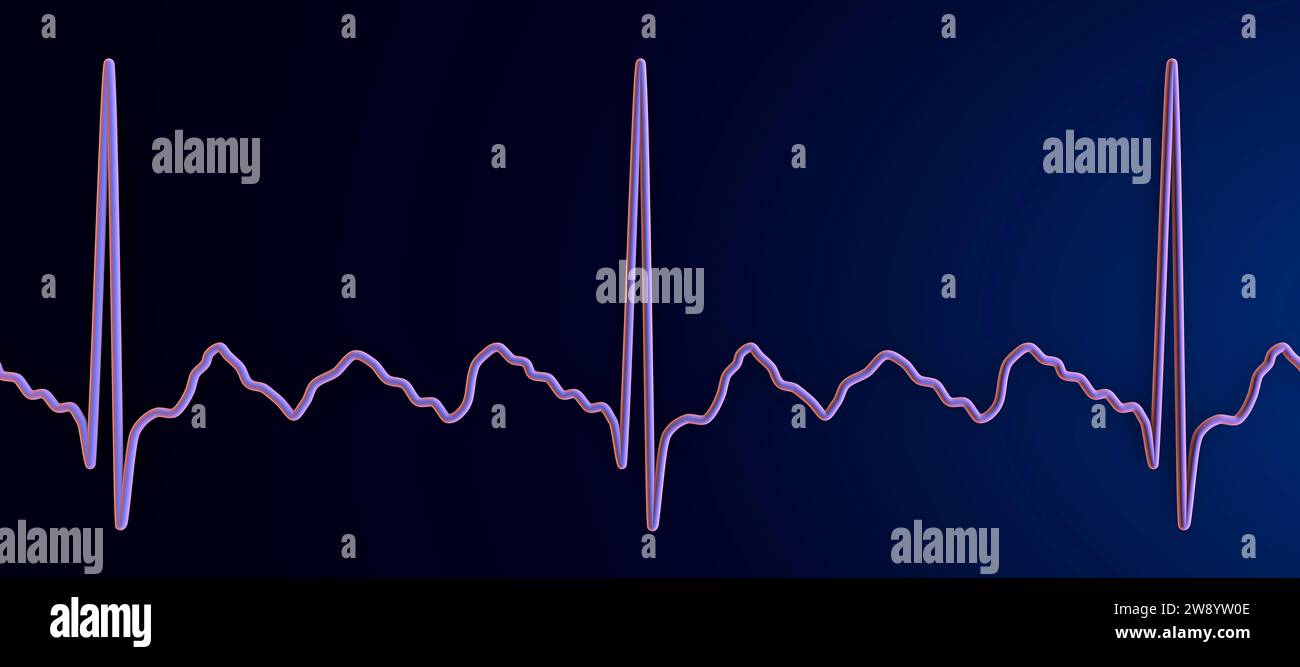
Illustration depicting an atrial flutter abnormal heart rhythm on an
![Atrial Flutter ECG Interpretation [With Examples] Manual of Medicine](https://manualofmedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Atrial-Flutter-with-2-1-AV-Block.png)
Atrial Flutter ECG Interpretation [With Examples] Manual of Medicine
Conducted With Right Bundle Branch Block.) Carotid Sinus Massage Can Increase Av Block And Better Expose The Typical Flutter Waves.
Atrial Flutter Is The Only Diagnosis Causing This Baseline Appearance, Which Is Why It.
1 The Ecg In Type I (Typical) Afl Is Characterized By An Inverted Sawtooth Flutter (F) Wave Pattern In.
After Questioning Him, It Was Clear That He Had Been Having Palpitations And Near Dizzy Spells On And Off For A Couple Of Weeks.
Related Post: