Reticulonodular Pattern On Cxr
Reticulonodular Pattern On Cxr - Diseases with a predominantly reticular pattern can be subdivided by the acuteness of their presentation. Reticular—fine or coarse linear shadows; Associated with signs of volume loss; Web detecting diffuse lung infiltrates on chest radiography is a common clinical problem. Plain chest radiography remains the first diagnostic approach to diffuse infiltrative lung disease but has limited diagnostic sensitivity and specificity. Web pattern recognition should be combined with knowledge of clinical factors in order to generate a limited and meaningful differential diagnosis [table 2]. Web reticulation can be subdivided by the size of the intervening pulmonary lucency into fine, medium and coarse. These are interlobular septal thickening, honeycombing, and irregular reticulation. Three principal patterns of reticulation may be seen. Imaging findings include a bronchopneumonia pattern with centrilobular nodules, bronchial wall thickening, ggo, and patchy consolidation, which later leads to lobar distribution. Diseases with a predominantly reticular pattern can be subdivided by the acuteness of their presentation. For example, kaposi sarcoma (ks). When infiltrates are present, the particular pattern is of limited value for differentiating among cardiogenic pulmonary edema, noncardiogenic, pulmonary edema, hemorrhage, atelectasis, and pneumonia. The scarring associated with interstitial lung disease eventually affects your ability to breathe and get enough. Many people diagnosed with interstitial lung diseases are initially treated with a corticosteroid (prednisone), sometimes in combination with other drugs that suppress the immune system. The scarring associated with interstitial lung disease eventually affects your ability to breathe and get enough oxygen into your bloodstream. Unless clarified, the term is an unhelpful addition to radiology reports. Reticular opacities seen on. Web an interstitial lung pattern is a regular descriptive term used when reporting a plain chest radiograph. Web detecting diffuse lung infiltrates on chest radiography is a common clinical problem. Imaging findings include a bronchopneumonia pattern with centrilobular nodules, bronchial wall thickening, ggo, and patchy consolidation, which later leads to lobar distribution. Web the chest radiograph revealed a diffuse, coarse. The most commonly reported interstitial abnormalities are reticular and reticulonodular patterns and the most commonly reported alveolar findings are hazy pulmonary opacities. Reticular—fine or coarse linear shadows; Linear, reticular, reticulonodular, and nodular. Three principal patterns of reticulation may be seen. Web cxr (pa and lateral) shows bilateral and extensive reticular nodular changes slightly more prominent in the upper lung zones. Three principal patterns of reticulation may be seen. Many diverse pathological processes can cause diffuse lung disease. A practical approach is to divide these into four patterns: Web pattern recognition should be combined with knowledge of clinical factors in order to generate a limited and meaningful differential diagnosis [table 2]. These are interlobular septal thickening, honeycombing, and irregular reticulation. Unless clarified, the term is an unhelpful addition to radiology reports. When infiltrates are present, the particular pattern is of limited value for differentiating among cardiogenic pulmonary edema, noncardiogenic, pulmonary edema, hemorrhage, atelectasis, and pneumonia. The most commonly reported interstitial abnormalities are reticular and reticulonodular patterns and the most commonly reported alveolar findings are hazy pulmonary opacities. Associated with signs. Web based on currently available, scientific evidence, however, your doctor may recommend: Diseases with a predominantly reticular pattern can be subdivided by the acuteness of their presentation. Web the chest radiograph revealed a diffuse, coarse reticulonodular pattern with no zonal predominance and short kerley b lines at the periphery of the mid and lower zones of the left lung. Make. Web an interstitial lung pattern is a regular descriptive term used when reporting a plain chest radiograph. Web detecting diffuse lung infiltrates on chest radiography is a common clinical problem. Reticular opacities seen on hrct in patients with diffuse lung disease can indicate lung infiltration with interstitial thickening or fibrosis. Can sometimes give a fine reticulonodular pattern 3. Linear, reticular,. Linear, reticular, reticulonodular, and nodular. Web atypical pneumonia is a term used inconsistently through time and in different parts of the world. Make a specific diagnosis of ild when supportive findings are present in the history or on radiologic imaging (e.g., dilated esophagus and ild in scleroderma. Web the chest radiograph revealed a diffuse, coarse reticulonodular pattern with no zonal. Diseases with a predominantly reticular pattern can be subdivided by the acuteness of their presentation. A reticulonodular pattern is often difficult to distinguish from a purely reticular or nodular pattern, and in such a case a differential diagnosis should. Many people diagnosed with interstitial lung diseases are initially treated with a corticosteroid (prednisone), sometimes in combination with other drugs that. A reticulonodular interstitial pattern is produced by either overlap of reticular shadows or by the presence of reticular shadowing and pulmonary nodules.while this is a relatively common appearance on a chest radiograph, very few diseases are confirmed to show this pattern pathologically.examples include: The most commonly reported interstitial abnormalities are reticular and reticulonodular patterns and the most commonly reported alveolar findings are hazy pulmonary opacities. Web pattern recognition should be combined with knowledge of clinical factors in order to generate a limited and meaningful differential diagnosis [table 2]. Interlobular septal thickening is an. Reticular—fine or coarse linear shadows; Acute, not a common pattern. Web the chest radiograph may show reticulonodular opacities or patchy areas of consolidations. Many diverse pathological processes can cause diffuse lung disease. Web list and identify on a chest radiograph and computed tomographic (ct) scan the four patterns of interstitial lung disease (ild): Web an explanation of alveolar vs. Web reticulation can be subdivided by the size of the intervening pulmonary lucency into fine, medium and coarse. Linear, reticular, reticulonodular, and nodular. Can sometimes give a fine reticulonodular pattern 3. Plain chest radiography remains the first diagnostic approach to diffuse infiltrative lung disease but has limited diagnostic sensitivity and specificity. Web cxr (pa and lateral) shows bilateral and extensive reticular nodular changes slightly more prominent in the upper lung zones. A reticulonodular pattern results from a combination of reticular and nodular opacities.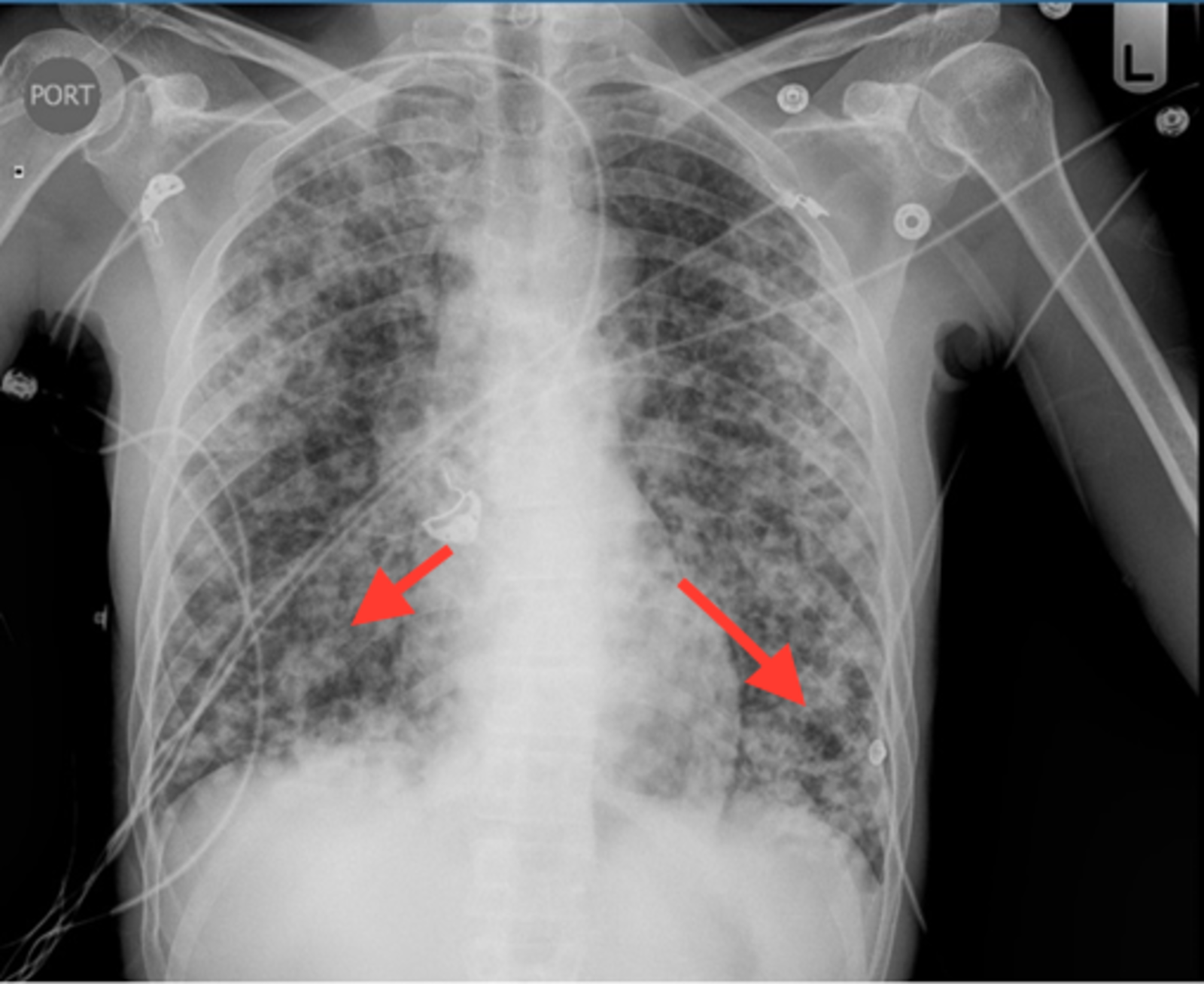
Cureus Recurrent Pneumocystis Pneumonia with Radiographic

Chest X‑ray PA view showing reticulonodular markings in bilateral lung

Interstitial Changes Chest X Ray Medschool vrogue.co

Chest Xray AP view showing reticulonodular infiltrates and
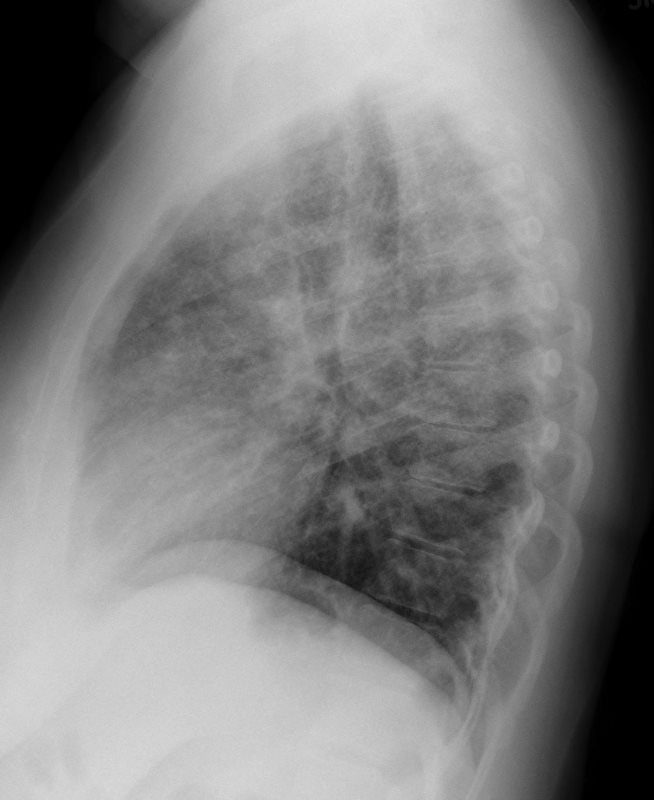
CXR Reticulonodular Pattern Lungs
The Radiology Assistant Chest XRay Lung disease
Figure1.Chest radiograph showing areas of reticulonodular and ground

Chest Xrays reticulonodular pattern with perihilar distribution
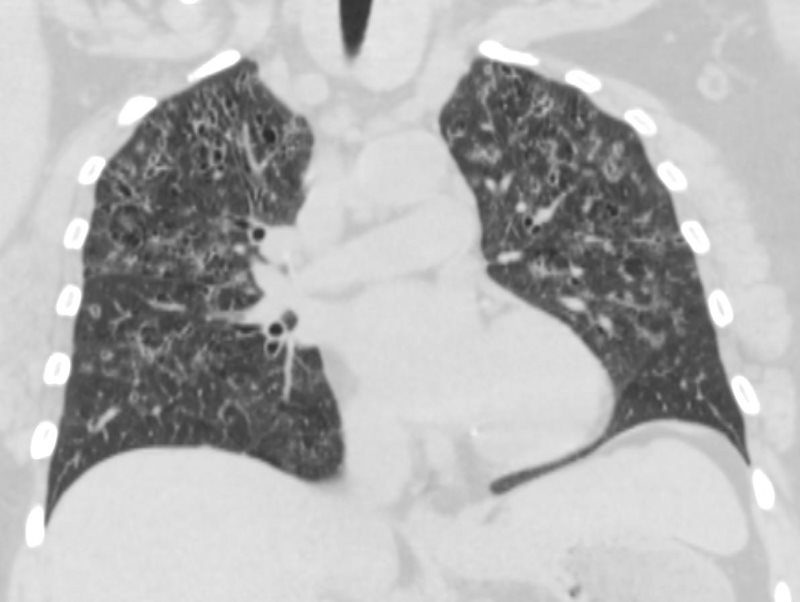
CXR Reticulonodular Pattern Lungs
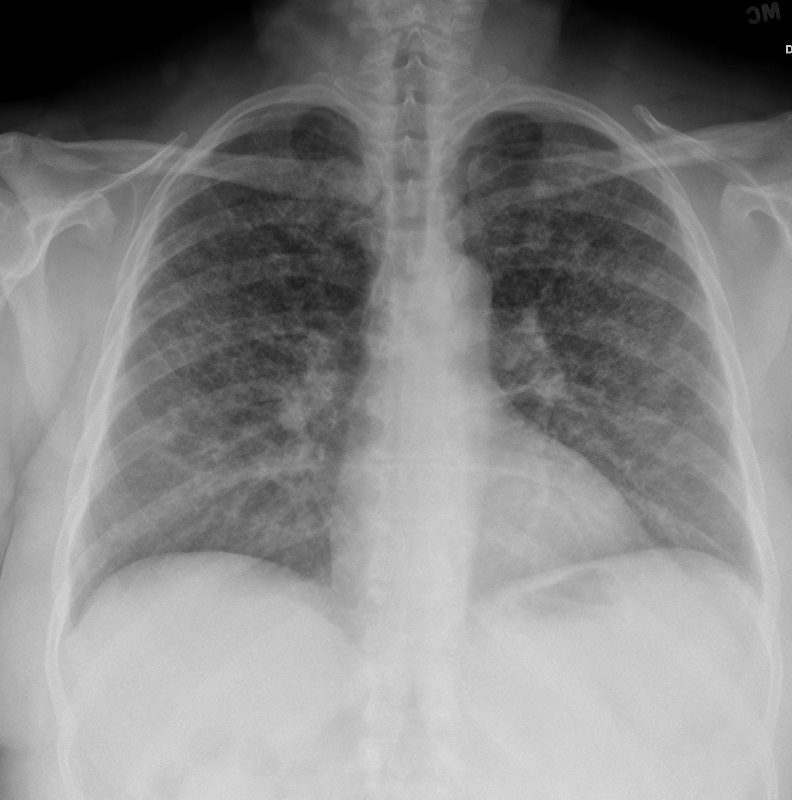
CXR Reticulonodular Pattern Lungs
Web Atypical Pneumonia Is A Term Used Inconsistently Through Time And In Different Parts Of The World.
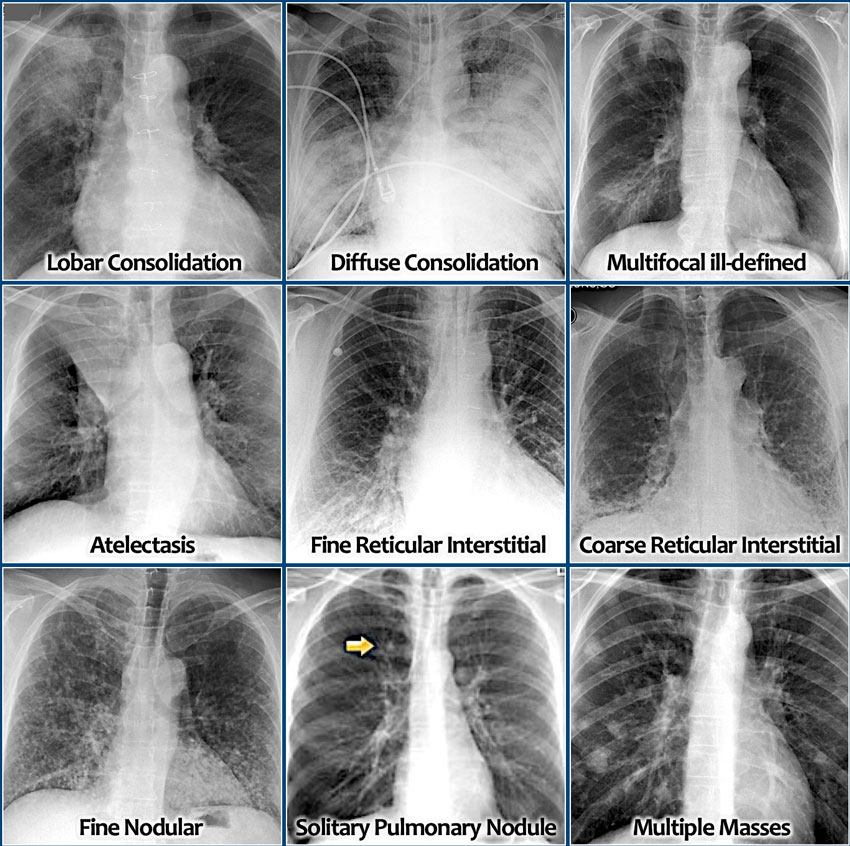
Three Principal Patterns Of Reticulation May Be Seen.
When Infiltrates Are Present, The Particular Pattern Is Of Limited Value For Differentiating Among Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema, Noncardiogenic, Pulmonary Edema, Hemorrhage, Atelectasis, And Pneumonia.
Diagnosis Was Confirmed By A Transbronchial Biopsy.
Related Post: