Reactivity Pattern Periodic Table
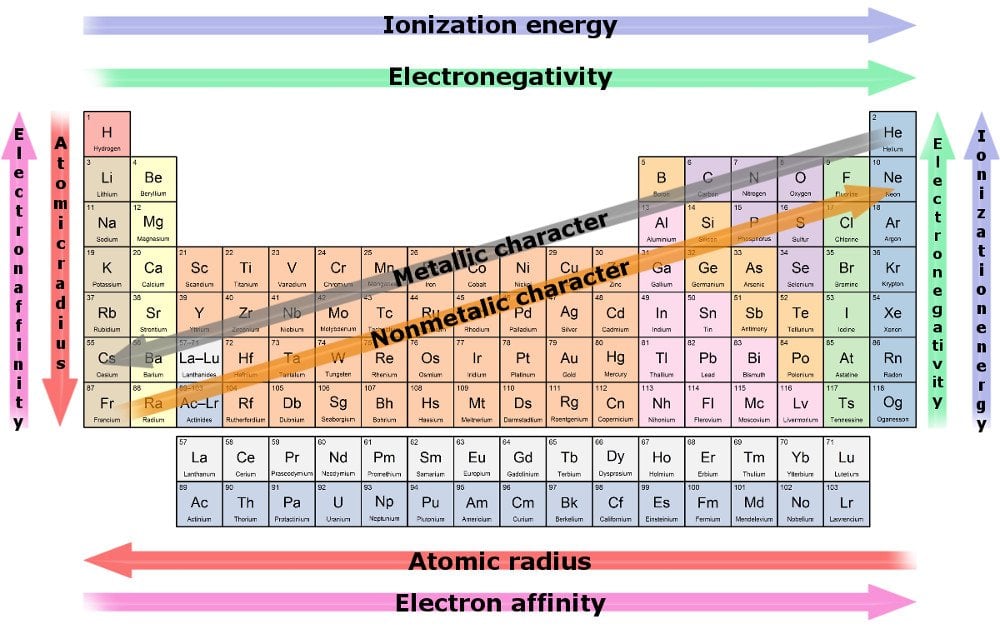
Reactivity Pattern Periodic Table - Web electron affinity is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral atom in the gaseous state, which can reveal a lot about an element's reactivity. Non metals prefer to attract electrons and metals prefer to lose electrons in general. Periodic table and atomic structure. 150k views 3 years ago chemistry. Electron shells and the bohr model. Knowing the atomic structure, periodic trends, and patterns within the periodic table can help explain and predict the. Part of chemistry periodic table. Web the reactivity series of metals, also known as the activity series, refers to the arrangement of metals in the descending order of their reactivities. 1.4 electronic structure of atoms. Four major factors affect reactivity of metals: Electronegativity is closely connected to the basic idea of chemical reactions: Web electron affinity is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral atom in the gaseous state, which can reveal a lot about an element's reactivity. Electron shells and the bohr model. How likely it is to form bonds, and with which other elements.. These are factors that affect the interactions of electrons that chemical reactions undergo. The periodic table as a list of elements arranged so as to demonstrate trends in their physical and chemical properties. Web for higher chemistry, learn how the arrangement of elements in the periodic table reflects patterns in bonding and reactivity. Electron shells and the bohr model. Click. The periodic table is a list of the elements organized in a way that elements which react similarly appear in groups or families. Structure & reactivity in organic, biological and inorganic chemistry (schaller) structure & reactivity in organic, biological and inorganic chemistry iii: Use small pieces of metal. Use tweezers when lifting alkali metals. Web four major factors affect reactivity. Periodic table and atomic structure. 4.9 (25 reviews) get a hint. Atomic radii (covalent radii only). Electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius, melting point, and metallic character. Web trends in the periodic table — reactivity! Web we will see how the numbers of electrons in energy levels and sublevels are the most important factor in determining patterns of chemical reactivity of the elements. Reactivity in organic, biological and inorganic chemistry 1. The data provided by the reactivity series can be used to predict whether a metal can. Structure & reactivity in organic, biological and inorganic. Click the card to flip 👆. Nuclear charge, atomic radius, shielding effect and sublevel arrangement (of electrons). These are factors that affect the interactions of electrons that chemical reactions undergo. Non metals prefer to attract electrons and metals prefer to lose electrons in general. Reactivity describes the ability of a molecule or atom to undergo a chemical reaction, followed by. Use tweezers when lifting alkali metals. Periodic trends, arising from the arrangement of the periodic table, provide chemists with an invaluable tool to quickly predict an element's properties. The periodic table as a list of elements arranged so as to demonstrate trends in their physical and chemical properties. Why does reactivity of metals increase from right to left on the. The periodic table is a list of the elements organized in a way that elements which react similarly appear in groups or families. They are presented a second compound with the same general formula but containing an unknown element x. Web interactive periodic table showing names, electrons, and oxidation states. Web periodic trends refer to the way in which physical. Nuclear charge, atomic radius, shielding effect and sublevel arrangement (of electrons). Nuclear charge, atomic radius, shielding effect and sublevel arrangement (of electrons). Why does reactivity of metals increase from right to left on the periodic table. 150k views 3 years ago chemistry. Click the card to flip 👆. Structure & reactivity in organic, biological and inorganic chemistry (schaller) structure & reactivity in organic, biological and inorganic chemistry iii: Use small pieces of metal. Use tweezers when lifting alkali metals. In this short series, we look at what makes certain elements. Students a formula for a binary ionic compound. Click the card to flip 👆. Web four major factors affect reactivity of metals: Use tweezers when lifting alkali metals. Web the reactivity series of metals, also known as the activity series, refers to the arrangement of metals in the descending order of their reactivities. Use small pieces of metal. Structure & reactivity in organic, biological and inorganic chemistry (schaller) structure & reactivity in organic, biological and inorganic chemistry iii: Visualize trends, 3d orbitals, isotopes, and mix compounds. Web patterns of reactivity vary depending on the size of the nucleus, the number of electrons and the number of shells. Web as we will see below, the periodic table organizes elements in a way that reflects their number and pattern of electrons, which makes it useful for predicting the reactivity of an element: These are factors that affect the interactions of electrons that chemical reactions undergo. Why does reactivity of metals increase from right to left on the periodic table. Knowing the atomic structure, periodic trends, and patterns within the periodic table can help explain and predict the. This property is dependent on characteristics such as electronegativity and ionization energy. Atomic radii (covalent radii only). Web periodic trends refer to the way in which physical properties of atoms change across the periodic table. Periodic table and atomic structure.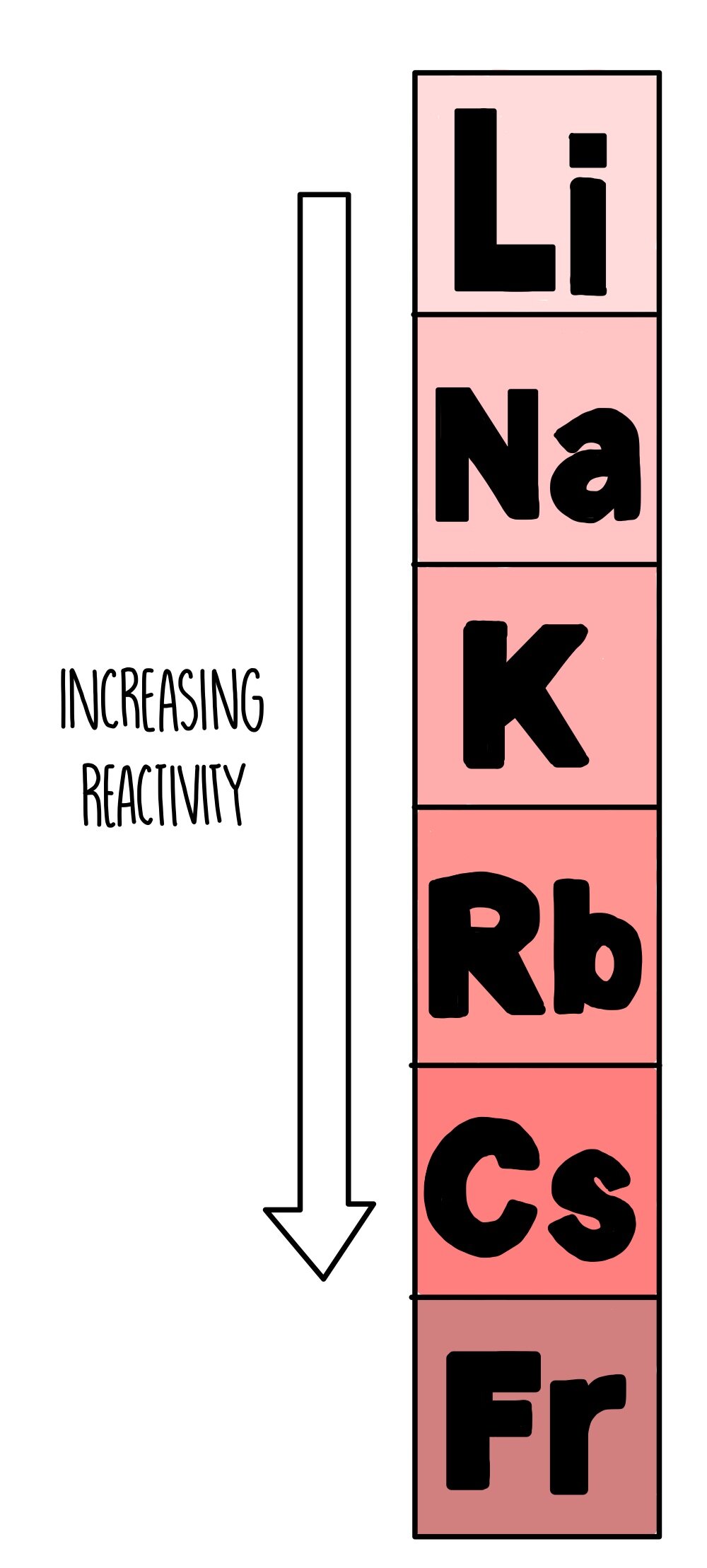
The Periodic Table (AQA) — the science hive
Periodic Table Reactivity Chart

Reactivity shown in the periodic table. Download Scientific Diagram

Reactivity periodic table tewstee
Periodic Table Reactivity Periodic Table Timeline
Reactivity Chart Periodic Table
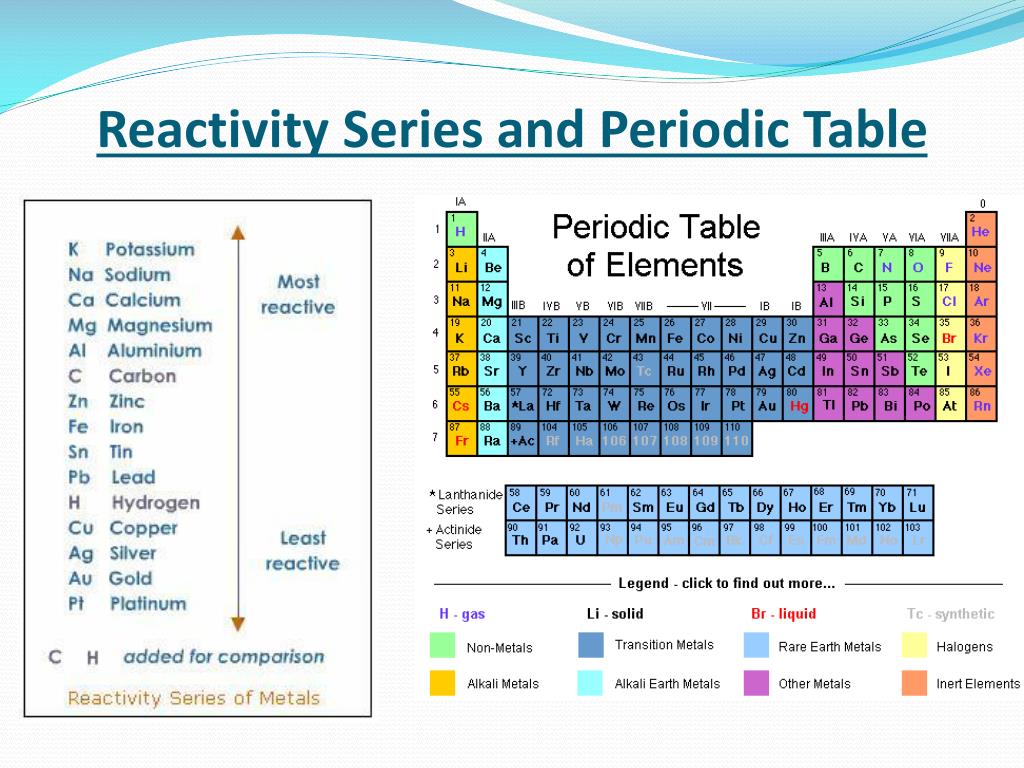
Periodic Table Reactivity Series Periodic Table Timeline
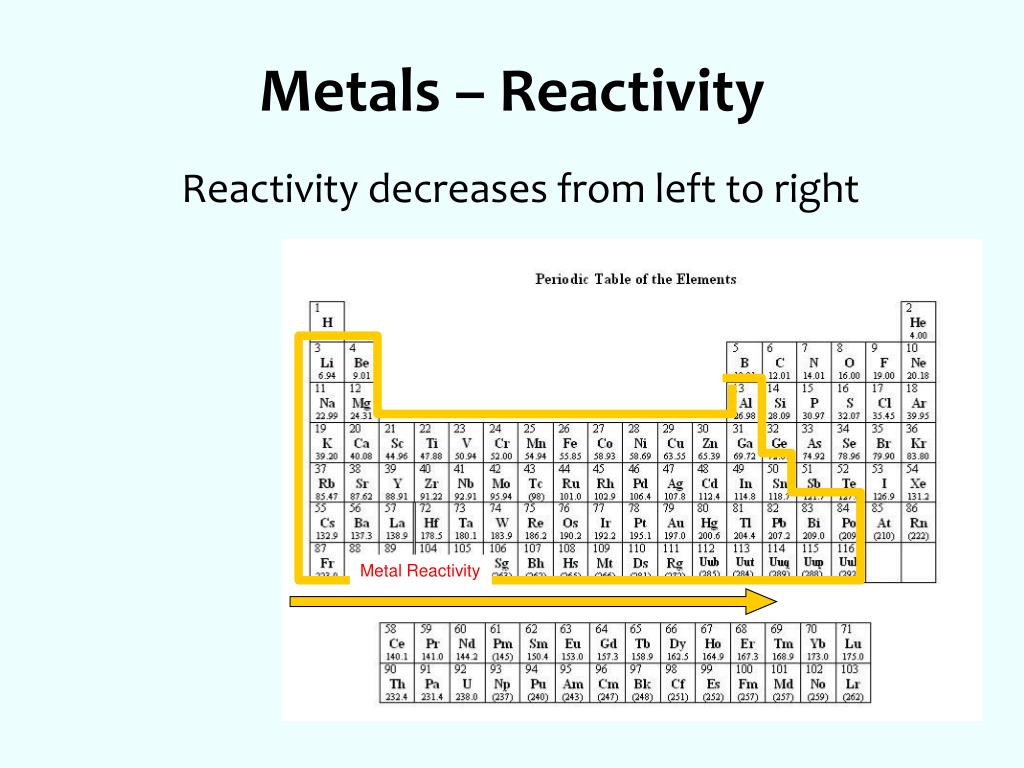
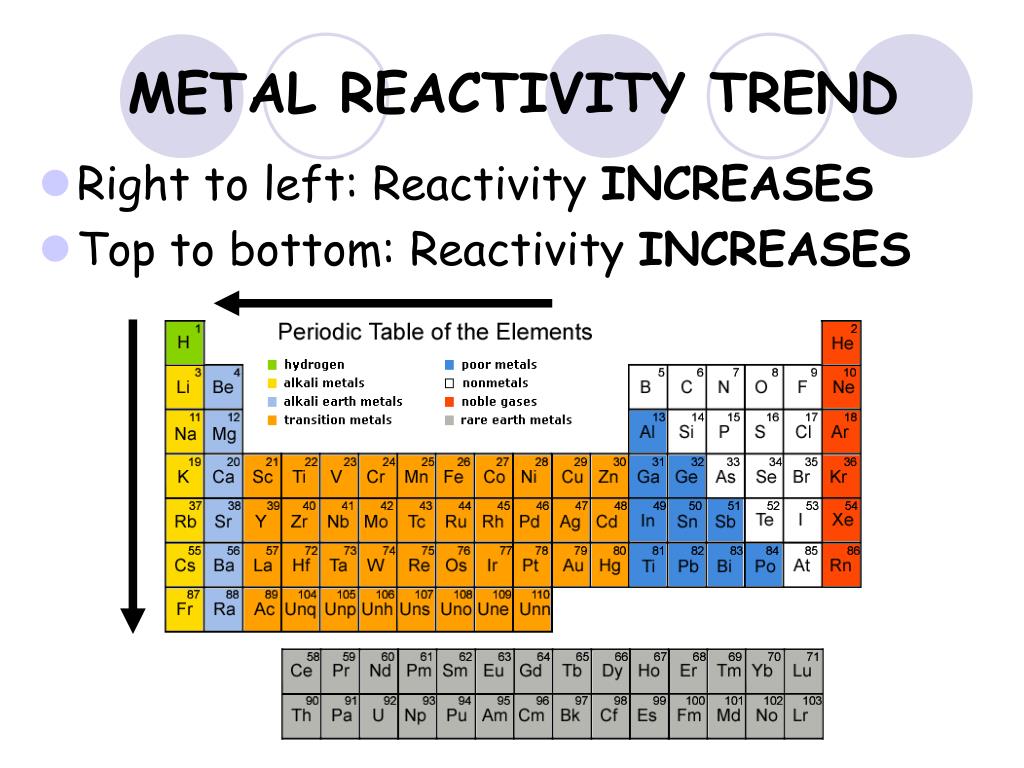
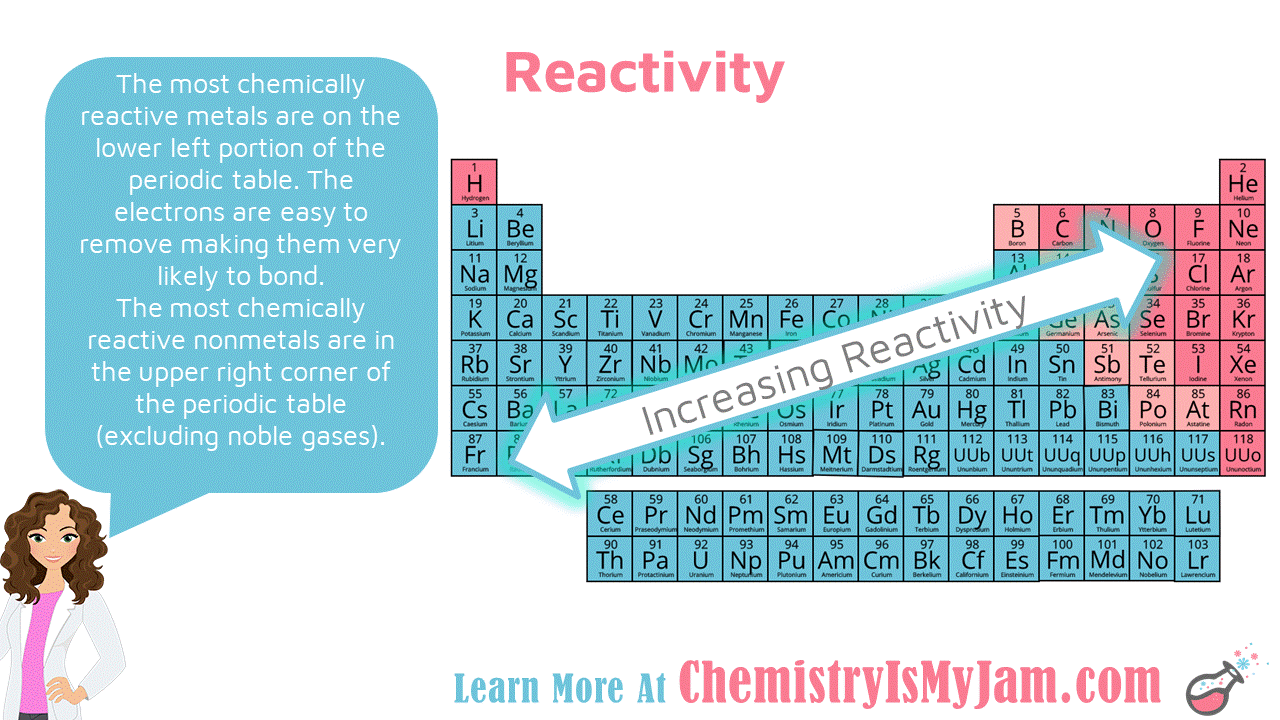
Reactivity trend across periodic table maGinX

chemistryp2t7 / The Periodic Table of Elements
Periodic Table Reactivity Arrows Periodic Table Timeline
Non Metals Prefer To Attract Electrons And Metals Prefer To Lose Electrons In General.
Web Major Periodic Trends Include:
Group 1 Metals Are Very Reactive.
They Are Presented A Second Compound With The Same General Formula But Containing An Unknown Element X.
Related Post: