Radial Nerve Referral Pattern
Radial Nerve Referral Pattern - Web the radial nerve is a major peripheral nerve of the upper limb. Refer to orthotic services for a splint. Web we identified the branching points of the radial nerve after determining which muscle it innervated. Depending on the severity and the cause. Review the presentation of a patient with radial nerve entrapment. Clarifying the literature and understanding variations and their clinical implications. This nerve has both motor and sensory functions. Web radial nerve pathologies include compressive syndromes, entrapment neuropathy, focal intrinsic lesions and peripheral nerve sheath tumours. Cervical radiculopathy is a disease process marked by nerve compression from herniated disk material or arthritic bone spurs. The radial nerve exhibits significant variability in the posterior forearm. The function of your radial nerve is to supply movement (motor) and sensory information between your brain and parts of your arm, wrist and hand. Outline the management options available for radial nerve injury. The radial nerve runs down the arm and to the fingertips. Web what causes radial nerve palsy? A healthcare practitioner may order a diagnostic test to. Web radial nerve pathologies include compressive syndromes, entrapment neuropathy, focal intrinsic lesions and peripheral nerve sheath tumours. The motor branch of your radial nerve stimulates the: However, there is enough consistency to identify an archetypal pattern and order of innervation. Describe interprofessional team strategies for improving care and outcomes in patients with radial nerve entrapment. Radial nerve palsy may occur. A person may experience pain in the chest and torso when the nerve compression or irritation occurs in the mid back region. Web the radial nerve is the biggest branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus and one of its five terminal branches. Review the symptoms after 6 weeks, and refer for neurological assessment if there is no. Web table of contents. However, there is enough consistency to identify an archetypal pattern and order of innervation. The nerve travels down the upper arm, at times very close to the humerus (upper arm bone). The motor branches stimulate the posterior arm muscles, posterior forearm muscles, and extrinsic wrist and hand extensors. The radial nerve has a long and tortuous. The radial nerve exhibits significant variability in the posterior forearm. Radial nerve palsy may occur as a result of upper arm fractures or direct pressure on the arm over a sustained period of time. Review the symptoms after 6 weeks, and refer for neurological assessment if there is no evidence of improvement. Web what causes radial nerve palsy? However, there. A person may experience pain in the chest and torso when the nerve compression or irritation occurs in the mid back region. In the axilla, it lies behind the axillary and upper brachial arteries and passes anterior to the tendons of teres minor, latissimus dorsi and subscapularis. Clarifying the literature and understanding variations and their clinical implications. What is the. The radial nerve is the largest terminal branch of the brachial plexus. Web the radial nerve is one of the terminal branches of the posterior cord. Web radial nerve pathologies include compressive syndromes, entrapment neuropathy, focal intrinsic lesions and peripheral nerve sheath tumours. Review the presentation of a patient with radial nerve entrapment. Radicular pain is also referring to pain. A healthcare practitioner may order a diagnostic test to determine the extent of nerve involvement. A person may experience pain in the chest and torso when the nerve compression or irritation occurs in the mid back region. Radial nerve palsy may occur as a result of upper arm fractures or direct pressure on the arm over a sustained period of. Radicular pain is also referring to pain that is felt at a location that is away from the initial point of injury, but in this case it is a nerve root that is irritated and the pain is felt along the course of that nerve in the body. This nerve has both motor and sensory functions. Review the symptoms after. Web when the nerve reaches your elbow, it passes through the radial tunnel, which is a collection of muscles. Outline the management options available for radial nerve injury. This impingement typically produces neck and radiating arm pain. Web what causes radial nerve palsy? However, there is enough consistency to identify an archetypal pattern and order of innervation. This creates unwanted pressure on your radial nerve, often causing nagging pain. The nerve travels down the upper arm, at times very close to the humerus (upper arm bone). The function of your radial nerve is to supply movement (motor) and sensory information between your brain and parts of your arm, wrist and hand. Thoracic radiculopathy is an uncommon condition that may be misdiagnosed as shingles, heart, abdominal, or gallbladder complications. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin. Describe interprofessional team strategies for improving care and outcomes in patients with radial nerve entrapment. Web notably, the radial nerve often innervated brachialis (60%), and its superficial branch often innervated extensor carpi radialis brevis (25.7%). This impingement typically produces neck and radiating arm pain or numbness, sensory deficits, or motor dysfunction in the neck and upper extremities. [1] We shall also consider the clinical consequences of damage to the nerve. Identify the etiology of radial nerve injury. In the axilla, it lies behind the axillary and upper brachial arteries and passes anterior to the tendons of teres minor, latissimus dorsi and subscapularis. Web table of contents. Refer to orthotic services for a splint. The radial nerve is the largest terminal branch of the brachial plexus. The radial nerve exhibits significant variability in the posterior forearm. Web referral pattern for the suboccipital muscles leading to cervicogenic headaches.
Radial nerve anatomy, radial nerve palsy and radial nerve injury

C5 C6 Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Stretches & Exercises
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/radial-nerve-injury-2488802-FINAL-fd11d7465f8f465db5848ea726e89b65.png)
Radial Nerve Anatomy, Function, and Treatment
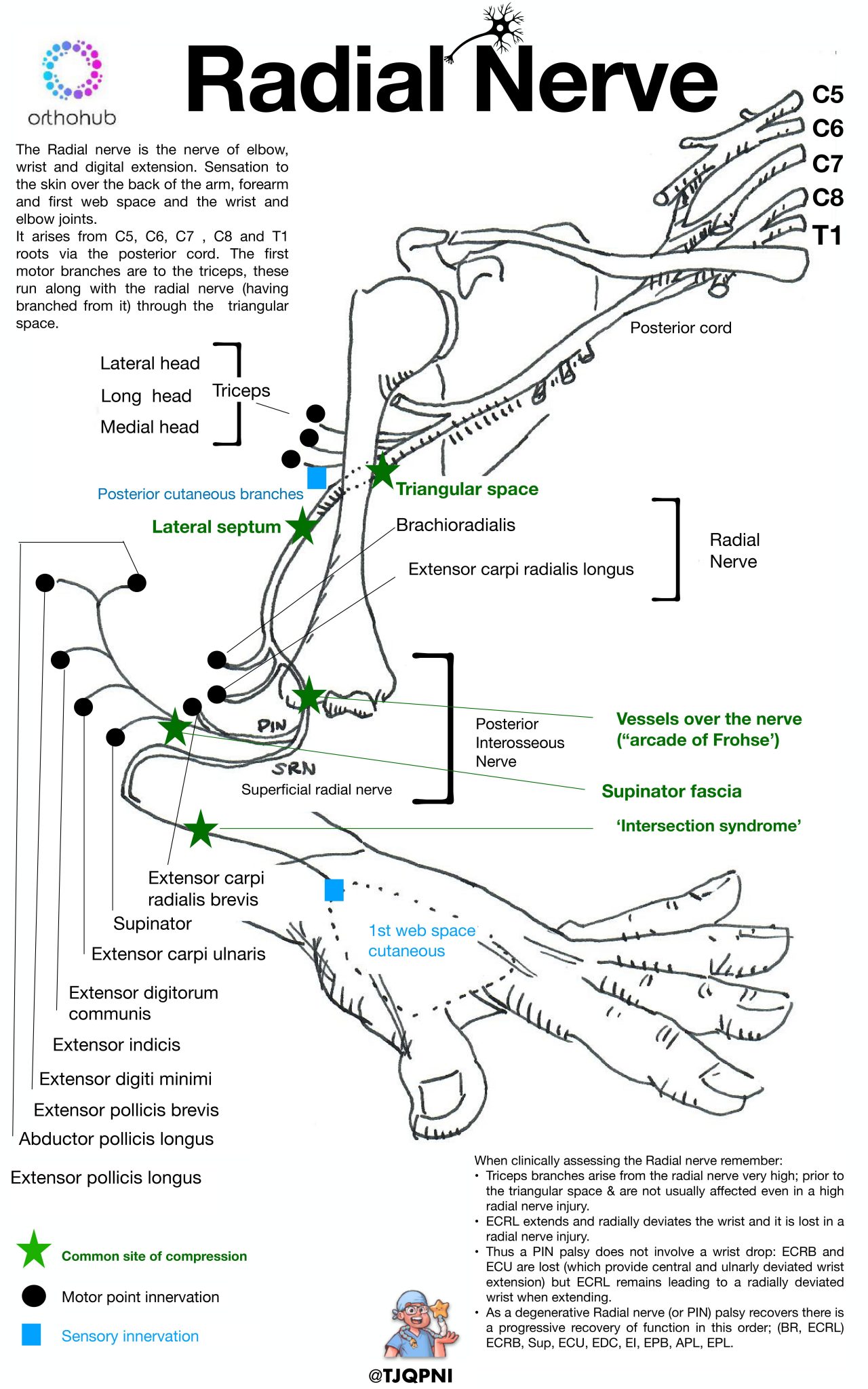
How to examine the radial nerve with Tom Quick Orthohub
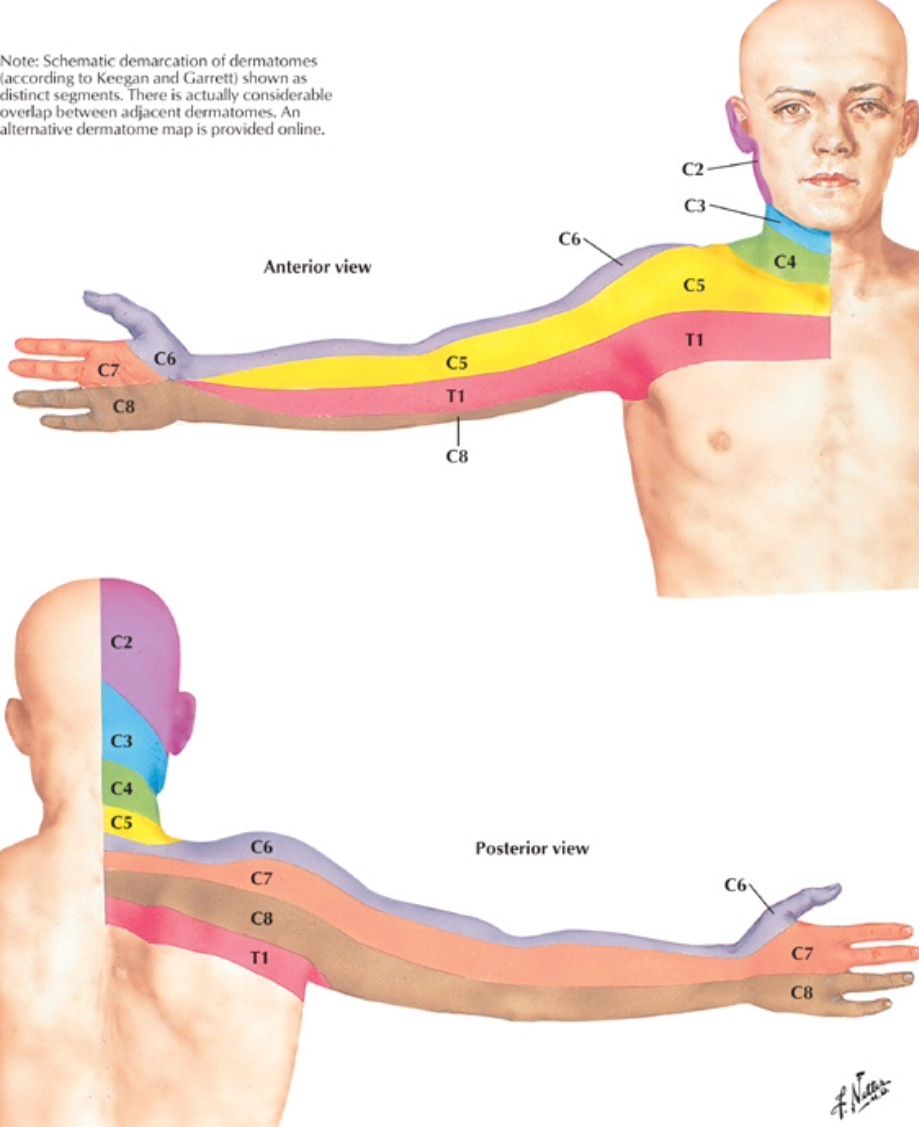
Cervical Radiculopathy Spine Orthobullets
.jpg)
Radiopaedia Drawing Radial nerve at shoulder English labels

Nerve compression causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment
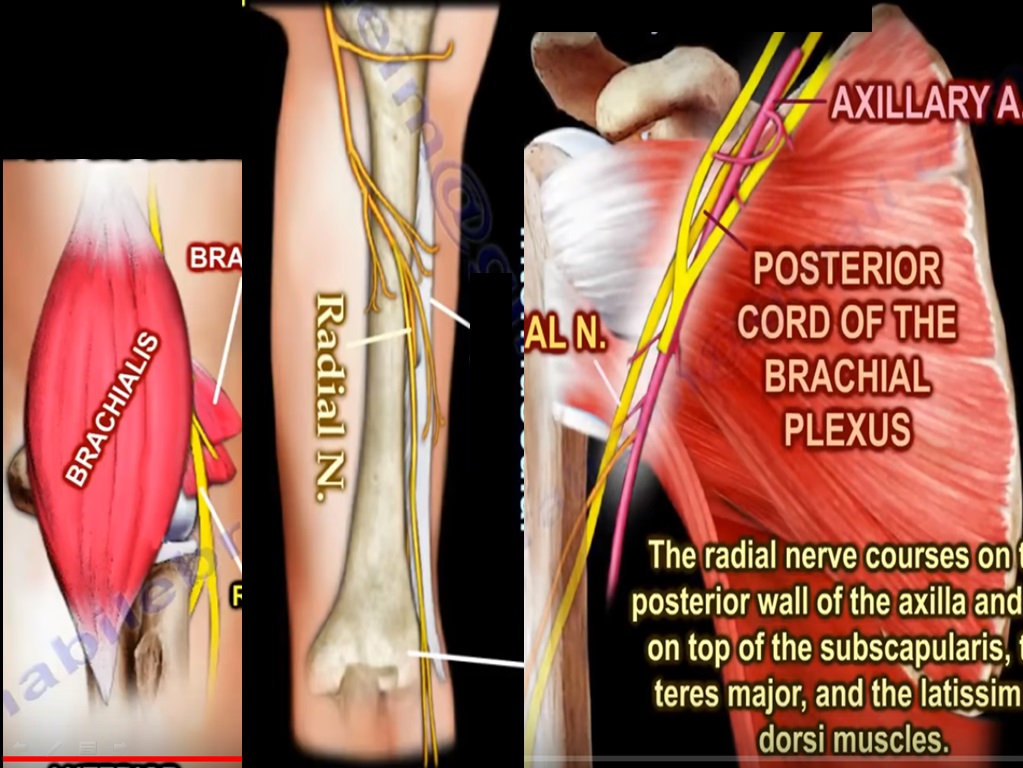
Anatomy of the Radial Nerve —

Radial Nerve and its Clonical Correlation made Simple Radial nerve

Radial nerve anatomy, radial nerve palsy and radial nerve injury
Identify The Etiology Of Radial Nerve Entrapment.
Web The Radial Nerve Is One Of The Terminal Branches Of The Posterior Cord.
Web The Radial Nerve Is A Major Peripheral Nerve Of The Upper Limb.
Review The Symptoms After 6 Weeks, And Refer For Neurological Assessment If There Is No Evidence Of Improvement.
Related Post: