Prophase Drawing
Prophase Drawing - Prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, and telophase i. In the fourth step, anaphase , the mitotic spindles pry each chromatid apart from its copy, and drag them to the opposite side of the cell. Define the quiescent g 0 phase. In this exercise, we will consider prometaphase a component of prophase. Most organisms contain many chromosomes in the nuclei of their cells (eg. In each round of division, cells go through four stages: These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Edupic graphical resource is a teacher designed free image resource for use by teachers and students. Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During this phase, the dna forms into chromosomes, which we can actually see. Prophase (sometimes divided into early prophase and prometaphase), metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Web draw an onion cell in prophase. In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Nuclear membrane breaks down, chromatin condenses, mitotic spindle forms and attaches to kinetochores. Web prophase → metaphase → anaphase → telophase. Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, and telophase i. Discuss the behavior of chromosomes during mitosis and how the cytoplasmic content divides during cytokinesis. Nuclear membrane breaks down, chromatin condenses, mitotic spindle forms and attaches to kinetochores. In this case, these cells move from g 1 of the cell cycle into a resting phase known as g 0. All images contained within are free for use by educational professionals and the students they serve without permission. Web mitosis consists of five morphologically distinct phases: Mitosis, a key part of the cell cycle, involves a series of stages. Kinetochore microtubules shorten, pulling sister chromatids to opposite poles, polar microtubules elongate, lengthening dividing cell. In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. In each round of division, cells go through four stages: Web prophase → metaphase → anaphase → telophase. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some cells do not go though mitosis. All other use is by permission only. Prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, and telophase i. Web in meiosis i, cells go through four phases: You may find that some accounts of mitosis further subdivide the process to include prometaphase between prophase and metaphase. Prophase is the first phase of mitosis. Nuclear membrane breaks down, chromatin condenses, mitotic spindle forms and attaches to kinetochores. In this phase, the chromosomes consist of two identical chromatids called sister chromatids. Web prophase is the first phase of mitosis, the process that separates the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell into two identical. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Web since cell division occurs twice during meiosis, one starting cell can produce four gametes (eggs or sperm). Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). This part of mitosis is all about preparing. Kinetochore microtubules shorten, pulling sister chromatids to opposite poles, polar microtubules. Prophase i is the first stage of meiosis i, followed by prophase ii, anaphase i, anaphase ii, metaphase i and metaphase ii. Prophase is the first phase of mitosis. Humans have 46) but the diagrams below show mitosis of an animal cell with only four chromosomes, for simplicity. Web mitosis takes place in four stages: Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Microtubules align chromosomes along metaphase plate. Web since cell division occurs twice during meiosis, one starting cell can produce four gametes (eggs or sperm). Prophase (sometimes divided into early prophase and prometaphase), metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. All other use is by permission only. Web mitosis consists of four basic phases: Prophase is the first phase of mitosis. Web prophase → metaphase → anaphase → telophase. During prophase i, chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material, creating more variation. Web in meiosis i, cells go through four phases: Web mitosis consists of four basic phases: All other use is by permission only. Prophase, in both mitosis and meiosis, is recognized by the condensing of chromosomes and separation of the centrioles in the centrosome. Define the quiescent g 0 phase. Prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, and telophase i. During prophase i, chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material, creating more variation. Discuss the behavior of chromosomes during mitosis and how the cytoplasmic content divides during cytokinesis. Mitosis, a key part of the cell cycle, involves a series of stages (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) that facilitate cell division and genetic information transmission. Web today, mitosis is understood to involve five phases, based on the physical state of the chromosomes and spindle. Web mitosis consists of four basic phases: Humans have 46) but the diagrams below show mitosis of an animal cell with only four chromosomes, for simplicity. In cytokinesis, the cytoplasm of. Web prophase → metaphase → anaphase → telophase. During interphase, the parent cell’s chromosomes are replicated, but they aren’t yet visible. You can learn more about these stages in the video on mitosis. Kinetochore microtubules shorten, pulling sister chromatids to opposite poles, polar microtubules elongate, lengthening dividing cell. These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.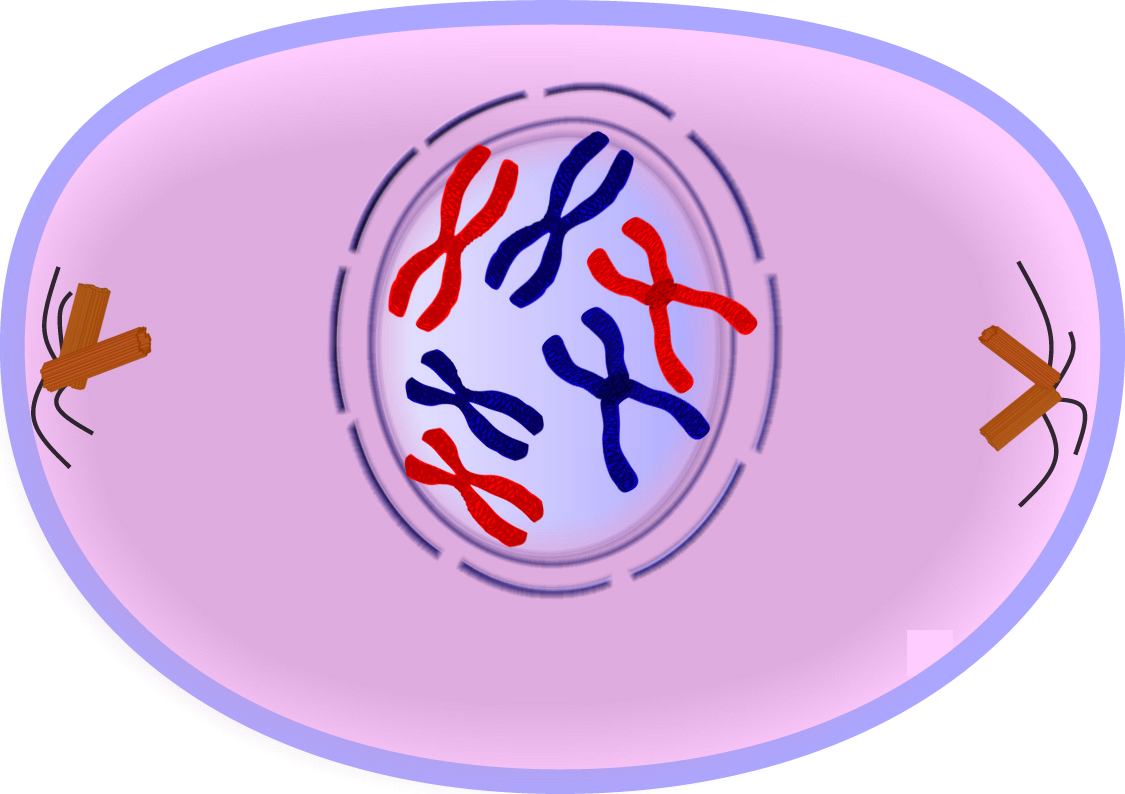
EduPic Cell Drawings
Diagram Of Prophase
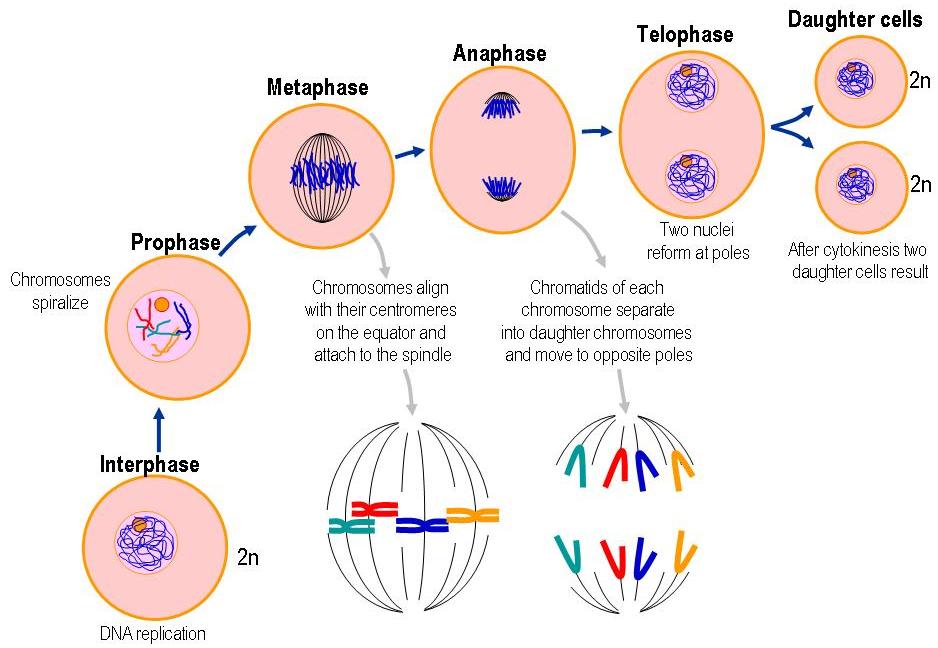
Diagram Of Prophase
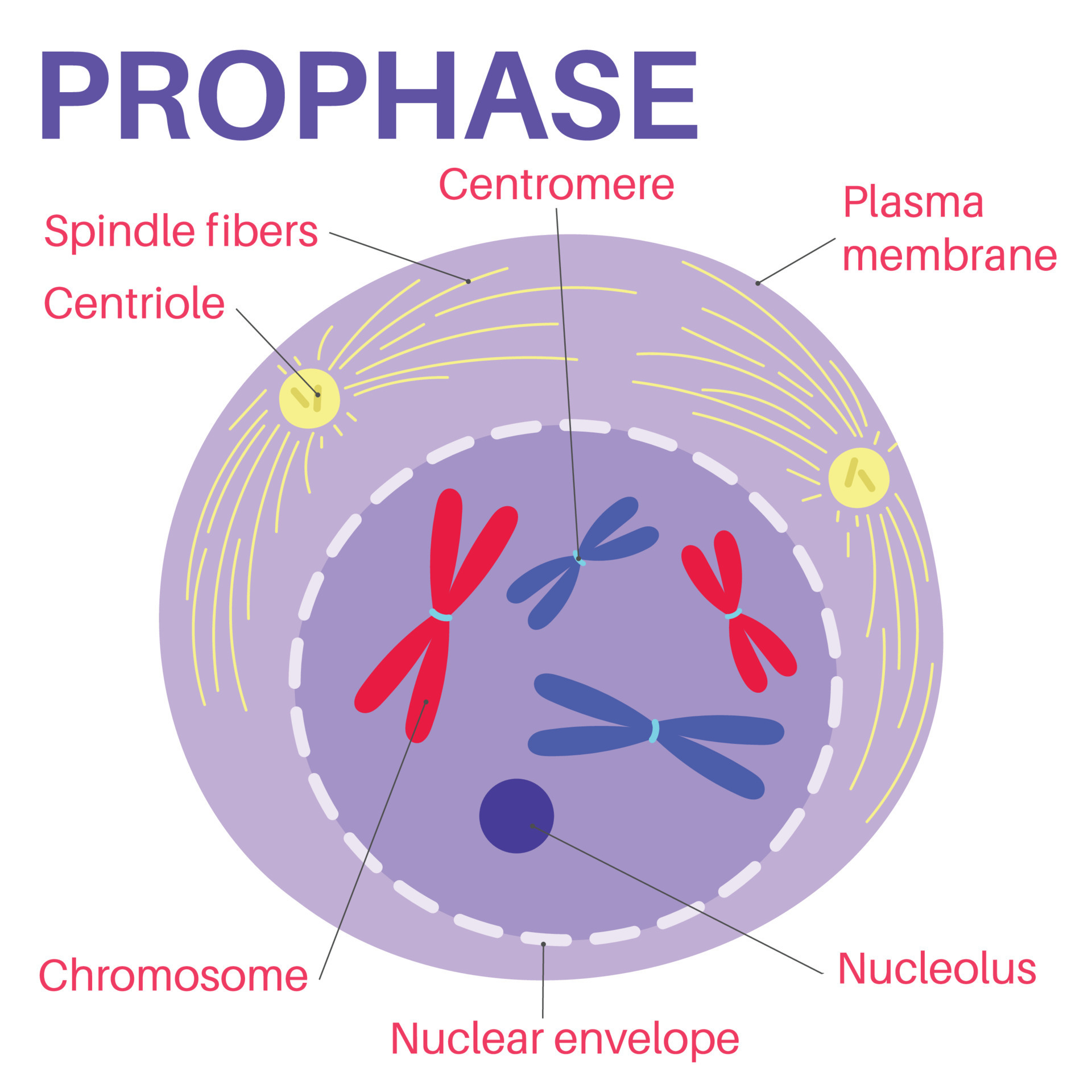
Prophase is the first stage of cell division. 14268877 Vector Art at
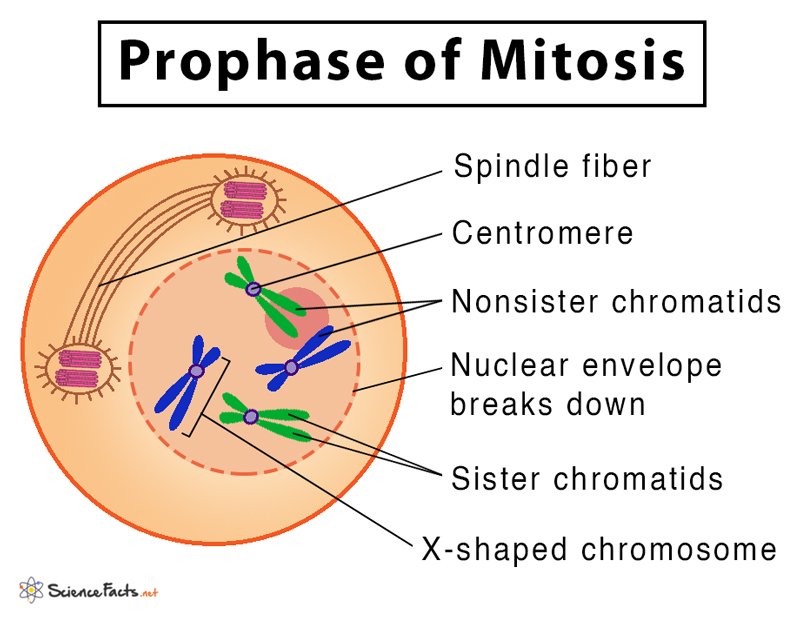
Mitosis Definition, Stages, & Purpose, with Diagram

Prophase Tutorial Sophia Learning
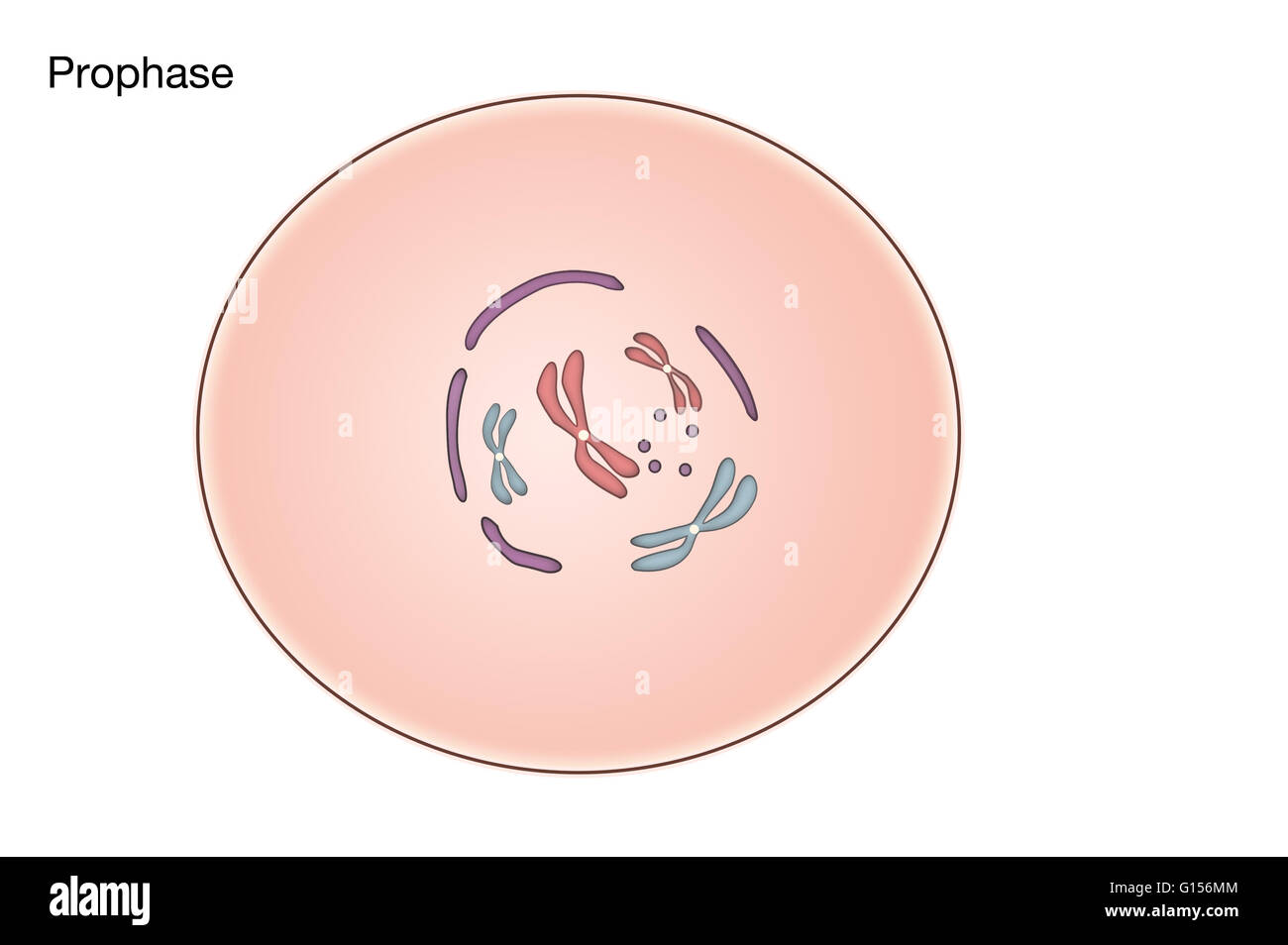
Prophase Diagrams

Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Reproduction, The Cell Cycle OpenEd CUNY

Prophase. The First Stage of Mitosis 12682013 Vector Art at Vecteezy
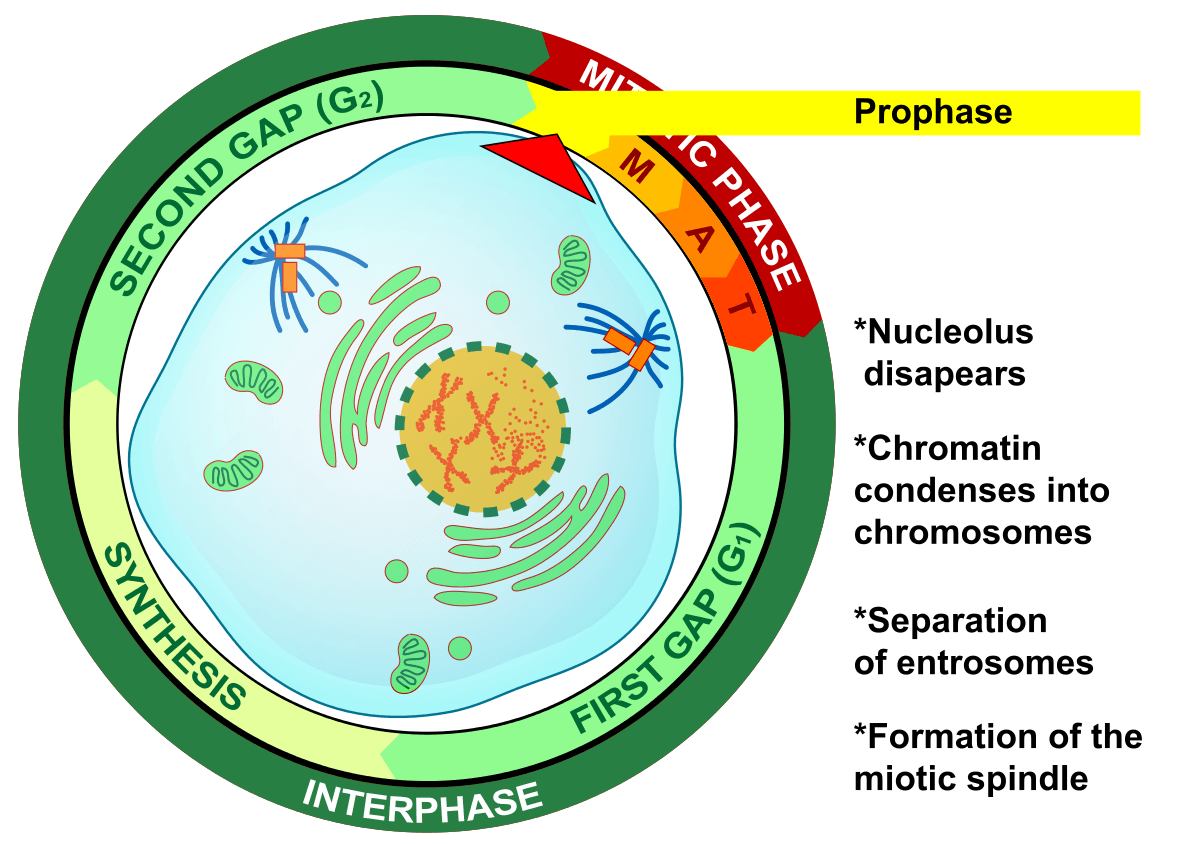
Diagram Of Prophase
In The Fourth Step, Anaphase , The Mitotic Spindles Pry Each Chromatid Apart From Its Copy, And Drag Them To The Opposite Side Of The Cell.
In This Phase, The Chromosomes Consist Of Two Identical Chromatids Called Sister Chromatids.
By The End Of This Section, You Will Be Able To:
Label The Cell Wall, Plasma Membrane, Nuclear Envelope (Or Where It Would Be), And Chromosomes.
Related Post: