Positive Posterior Drawer Test
Positive Posterior Drawer Test - What is the anterior drawer test? Assessing for the presence of the posterior sag sign enhances the tests diagnostic accuracy. Then the examiner attempts to translate the lower leg posteriorly. The test is considered positive if there is a lack of end feel or excessive posterior translation. Excessive displacement of the tibia anteriorly suggests that the anterior cruciate ligament is injured, whereas excessive posterior displacement of the tibia may indicate injury of the posterior cruciate ligament. The anterior drawer test is a physical examination doctors use to test the stability of the knee’s anterior cruciate ligament (acl). Any thorough exam should compare the contralateral, uninjured leg. Web the mri posterior drawer test to assess posterior cruciate ligament functionality and knee joint laxity | scientific reports. Web the anterior drawer test pulls the tibia forward to evaluate the acl, while the posterior drawer test pushes the tibia backward to assess the pcl. A positive result in either test indicates ligament laxity or injury, with the degree of movement and lack of end, feel in the tibia determining the severity of the injury. The posterior drawer test evaluates the integrity of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl) in the knee. Quadriceps active test / active drawer test. .1 (the accuracy of the clinical examination in the setting of posterior cruciate ligament injuries). A positive result in either test indicates ligament laxity or injury, with the degree of movement and lack of end, feel in. Excessive posterior translation of the talus. .1 (the accuracy of the clinical examination in the setting of posterior cruciate ligament injuries). Web the anterior drawer test pulls the tibia forward to evaluate the acl, while the posterior drawer test pushes the tibia backward to assess the pcl. Enroll in our online course:. Other tests to assess the posterior cruciate ligament. 21 of the most useful orthopaedic tests in clinical practice. The lachman test is done to check for. Web what is the lachman test and what is it used for? Web the test is considered positive if there is a lack of end feel or excessive anterior translation relative to the contralateral side. The patient, whose body mass index (bmi). Web several clinical tests have been shown to effectively assess pcl laxity, with the posterior drawer test possessing the highest sensitivity and specificity. Web after a positive anterior drawer test. 21 of the most useful orthopaedic tests in clinical practice. A pcl tear typically occurs as a result of a fall directly on a flexed knee. Excessive displacement of the. A positive result in either test indicates ligament laxity or injury, with the degree of movement and lack of end, feel in the tibia determining the severity of the injury. 497k views 8 years ago knee assessment. Web the posterior drawer test is part of a normal knee exam. Web may 9, 2024. Don't be confused by the resting position. Assessing for the presence of the posterior sag sign enhances the tests diagnostic accuracy. The lachman test is done to check for. Other ebm consult related content. The patient, whose body mass index (bmi) was 22.5, did not have any chronic diseases, such as hypertension or coronary heart disease, nor did he have any endocrine or metabolic. .1 (the accuracy. Additionally, the pcl plays a vital role in stabilizing the knee. Quadriceps active test / active drawer test. Enroll in our online course:. Web the posterior drawer test and the lachman test were positive, while the front drawer test was negative, and no laxity of the collateral ligament was found. Web special test:posterior drawer test (ankle): Web the posterior drawer test and the lachman test were positive, while the front drawer test was negative, and no laxity of the collateral ligament was found. Web this video demonstrates the posterior sag sign and posterior drawer test in a patient with a pcl tear. Web the examiner grasps the proximal lower leg, approximately at the tibial plateau or. Excessive posterior translation of the talus. When your healthcare provider examines the knee, they inspect the joint, test ligaments and mobility, determine if there is swelling, and perform specific manipulations to detect abnormalities. The anterior drawer test is a physical examination doctors use to test the stability of the knee’s anterior cruciate ligament (acl). Web this review analyses the most. Web the anterior drawer test pulls the tibia forward to evaluate the acl, while the posterior drawer test pushes the tibia backward to assess the pcl. Web after a positive anterior drawer test. You’ll lie on your back and your provider will move your lower leg to check how far your knee moves. When your healthcare provider examines the knee,. The patient, whose body mass index (bmi) was 22.5, did not have any chronic diseases, such as hypertension or coronary heart disease, nor did he have any endocrine or metabolic. Any thorough exam should compare the contralateral, uninjured leg. Positive posterior drawer test of the knee. Web what is the lachman test and what is it used for? 21 of the most useful orthopaedic tests in clinical practice. A positive result in either test indicates ligament laxity or injury, with the degree of movement and lack of end, feel in the tibia determining the severity of the injury. A positive test occurs when the tibia excessively translates posteriorly beyond the resting position or if the movement lacks a solid end feel. Additionally, the pcl plays a vital role in stabilizing the knee. Excessive posterior translation of the talus. The lachman test is done to check for. Enroll in our online course:. Isolated pcl tears are less common and usually result from a direct blow to the proximal tibia. Web several clinical tests have been shown to effectively assess pcl laxity, with the posterior drawer test possessing the highest sensitivity and specificity. Web the posterior drawer test and the lachman test were positive, while the front drawer test was negative, and no laxity of the collateral ligament was found. Assessing for the presence of the posterior sag sign enhances the tests diagnostic accuracy. Then the examiner attempts to translate the lower leg posteriorly.
Posterior Drawer Test Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Injury Knee
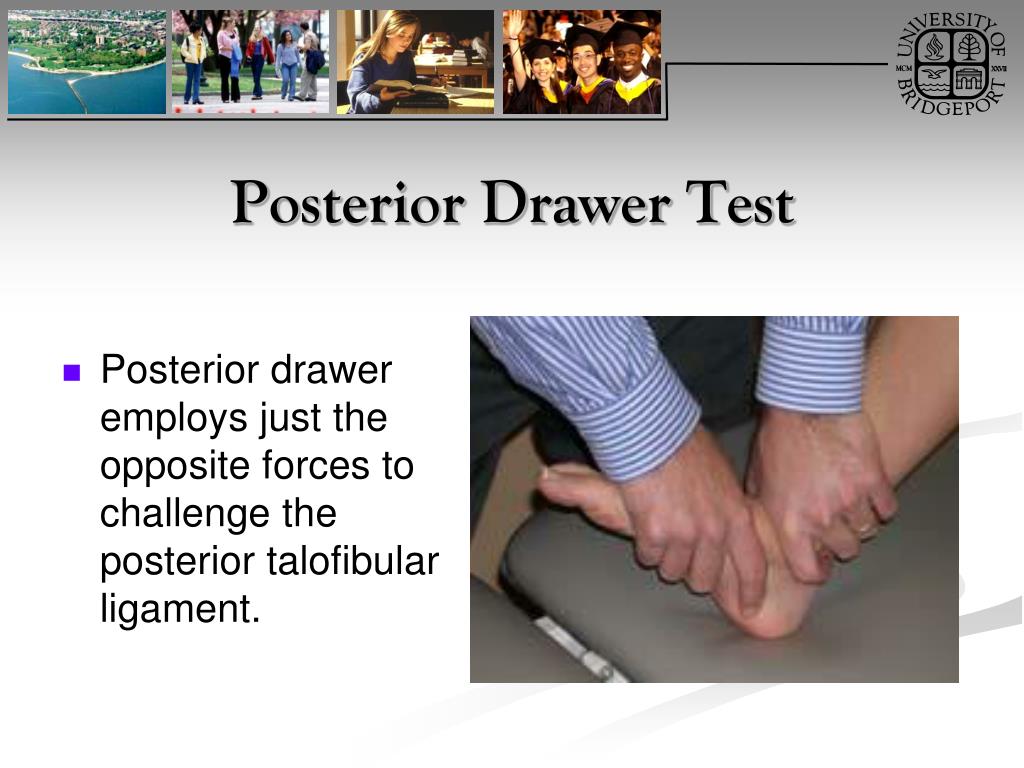
PPT Ankle and Foot Orthopaedic Tests Orthopedics and Neurology DX 612
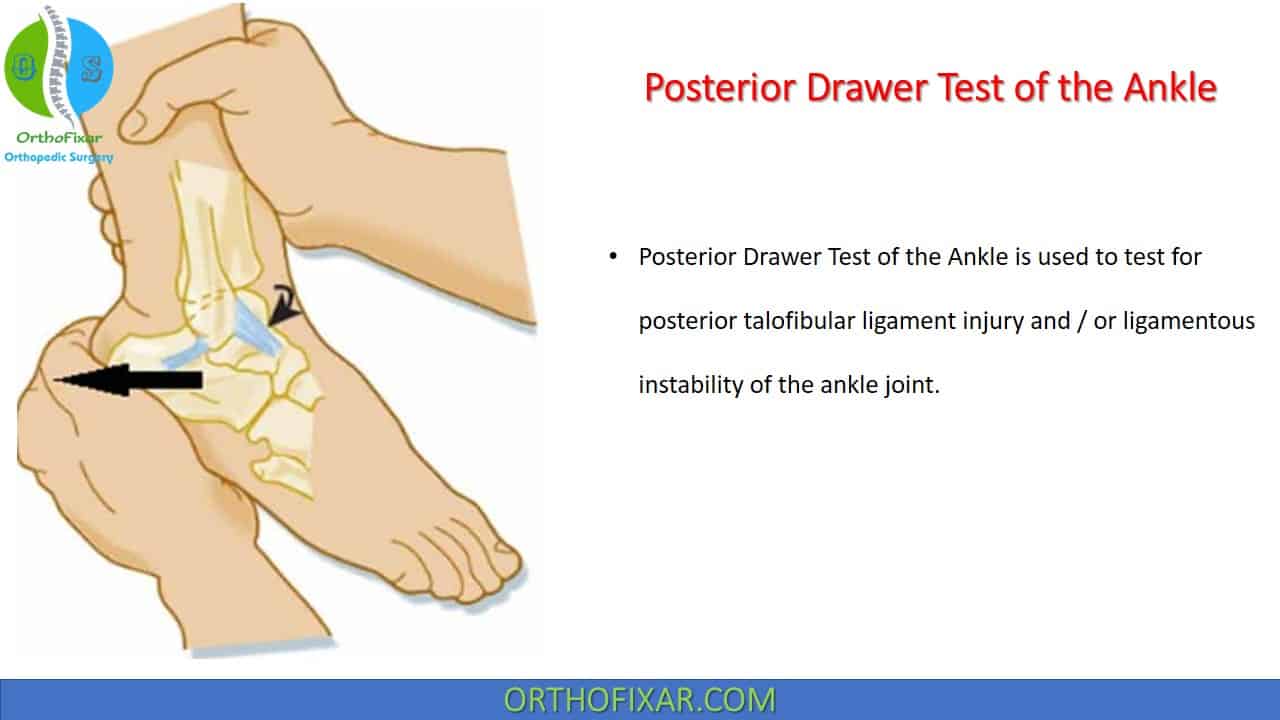
Posterior Drawer Test Of The Ankle 2024

Posterior Drawer Test Of The Knee • Easy Explained OrthoFixar 2022 in

PPT Femur Patellar surface femur Lateral condyle & epicondyle Head

Medicine Notes, Emergency Medicine, Physical Therapy Education, Nurse
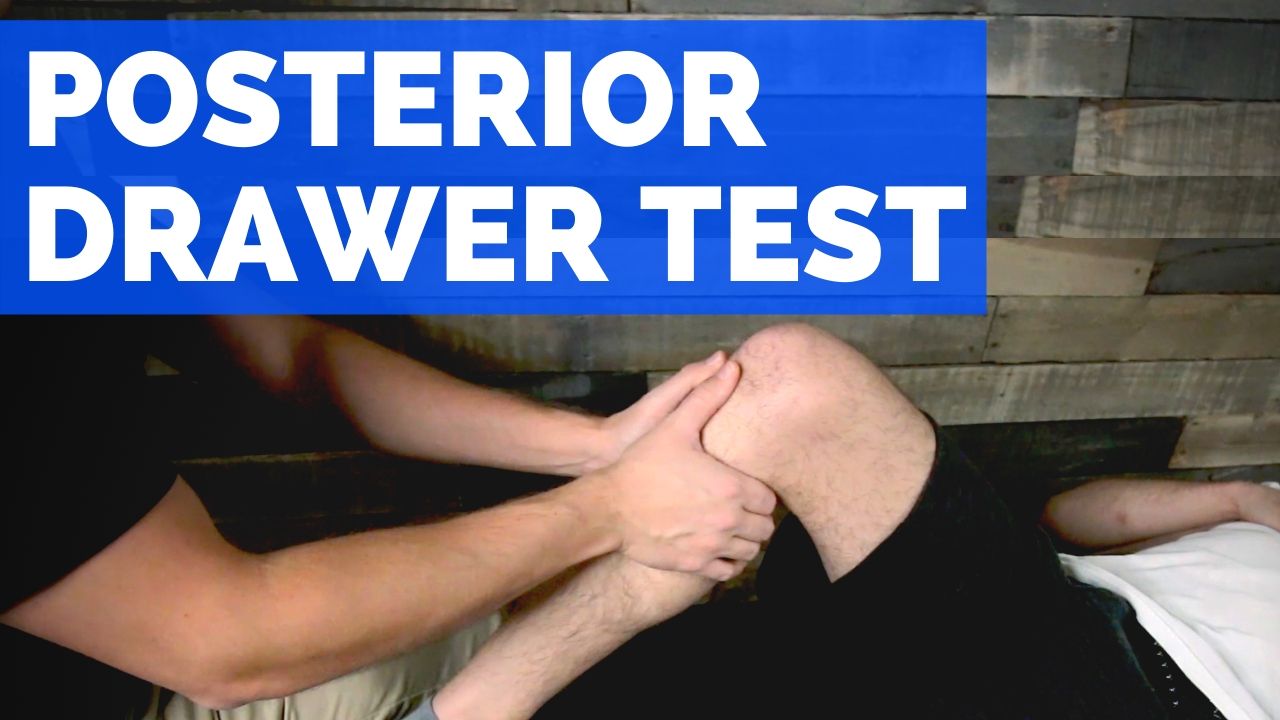
Posterior Drawer Test • PTProgress
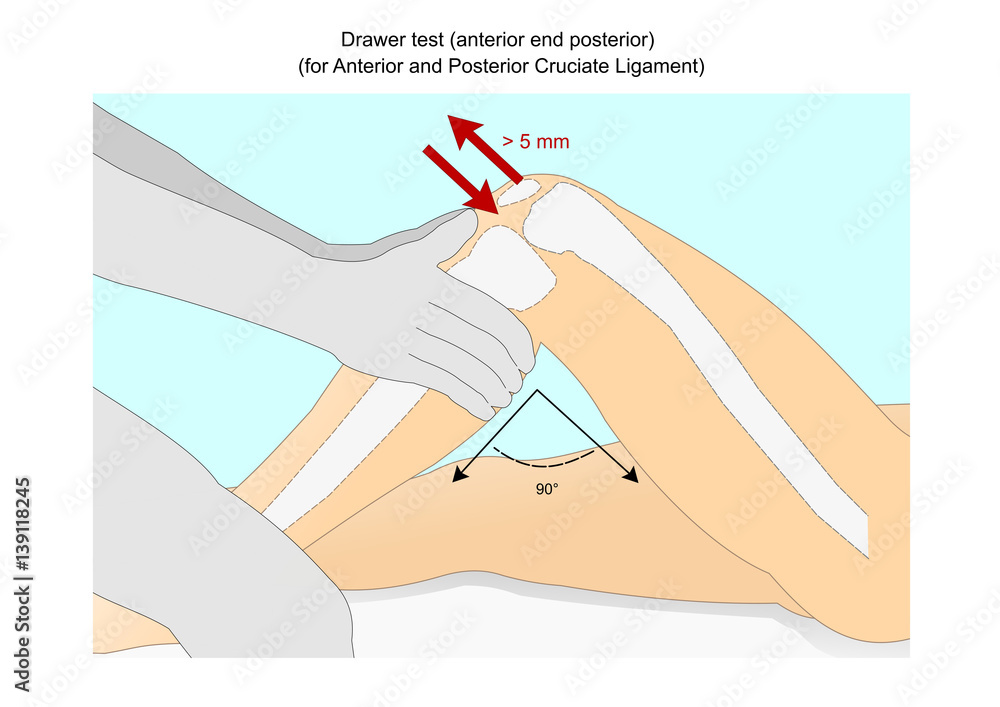
Drawer test to check the integrity of the anterior and posterior

Posterior Drawer Test

Knee Tests The Knee Resource
Sudden Hyperflexion Or Extension Injury.
Increased Posterior Displacement Of The Proximal Tibia, As Compared To The Uninvolved Side, Is Indicative Of A Partial Or Complete Tear Of The Pcl.
This Is One Of The.
Web If The Tibia Pulls Forward Or Backward More Than Normal, The Test Is Considered Positive.
Related Post: