Pattern Visual Evoked Potential
Pattern Visual Evoked Potential - The visual evoked potential (vep) is a means of extracting from the spontaneous electrical activity in the brain, electrical changes that are directly related. This test measures the electrical signals your visual cortex (a region of your brain) generates in response to visual. Web visually evoked potentials elicited by flash stimuli can be recorded from many scalp locations in humans. Web the retinal (white noise electroretinogram, wnerg) and cortical responses (visual evoked potential, wnvep) were simultaneously recorded with the. The visual cortex is primarily activated. Web evoked by patterned stimuli are “pattern” veps or pveps. Web visual evoked potentials (veps; Web evoked potentials, whether auditory, visual, or somatosensory, are extracted from the eeg by a simple program. Web visual evoked potential (vep): Web this review covers a brief history of visual evoked potentials, the most commonly used stimuli to initiate visual evoked potentials, the methods of recording,. Web this review covers a brief history of visual evoked potentials, the most commonly used stimuli to initiate visual evoked potentials, the methods of recording,. Responses evoked by unpatterned stimuli are “flash” veps or fveps. Web visual evoked potential (vep): The visual cortex is primarily activated. Visual stimuli stimulate both primary visual cortices. Responses evoked by unpatterned stimuli are “flash” veps or fveps. This technique of extracting a relevant signal from random noise is. Web visual evoked potential (vep): Web a visual evoked potential is an evoked potential caused by a visual stimulus, such as an alternating checkerboard pattern on a computer screen. The visual cortex is primarily activated. Responses evoked by unpatterned stimuli are “flash” veps or fveps. Choice of stimulus patterned visual. The visual evoked potential (vep) is a means of extracting from the spontaneous electrical activity in the brain, electrical changes that are directly related. Web evoked potentials, whether auditory, visual, or somatosensory, are extracted from the eeg by a simple program. Web visual evoked potential/response. Web evoked potentials, whether auditory, visual, or somatosensory, are extracted from the eeg by a simple program. Web visual evoked potential (vep): Web evoked by patterned stimuli are “pattern” veps or pveps. Web this review covers a brief history of visual evoked potentials, the most commonly used stimuli to initiate visual evoked potentials, the methods of recording,. This technique of. Web evoked potentials, whether auditory, visual, or somatosensory, are extracted from the eeg by a simple program. Web evoked by patterned stimuli are “pattern” veps or pveps. Web visual evoked potential (vep): Choice of stimulus patterned visual. Web the retinal (white noise electroretinogram, wnerg) and cortical responses (visual evoked potential, wnvep) were simultaneously recorded with the. The visual cortex is primarily activated. Web visual evoked potential/response (vep/ver) measures the electrical signal generated at the visual cortex in response to visual stimulation. Web visual evoked potential (vep): This test measures the electrical signals your visual cortex (a region of your brain) generates in response to visual. Web the retinal (white noise electroretinogram, wnerg) and cortical responses (visual. Web pattern onset/offset visual evoked potentials (onset/offset veps) the pattern reversal stimulus is the preferred stimulus choice for most clinical situations. This test measures the electrical signals your visual cortex (a region of your brain) generates in response to visual. Web visual evoked potentials (veps) have a role in evaluating patients with neurologic disease affecting the optic pathway. The visual. Web evoked potentials, whether auditory, visual, or somatosensory, are extracted from the eeg by a simple program. The visual evoked potential (vep) is a means of extracting from the spontaneous electrical activity in the brain, electrical changes that are directly related. This technique of extracting a relevant signal from random noise is. Web pattern onset/offset visual evoked potentials (onset/offset veps). Web this review covers a brief history of visual evoked potentials, the most commonly used stimuli to initiate visual evoked potentials, the methods of recording,. Web pattern onset/offset visual evoked potentials (onset/offset veps) the pattern reversal stimulus is the preferred stimulus choice for most clinical situations. Web evoked potentials, whether auditory, visual, or somatosensory, are extracted from the eeg by. Web visual evoked potential (vep) is an electrical wave, triggered by a visual stimulus, produced by electrical activity in the visual cortex, and recorded by the electrodes on the. Web the retinal (white noise electroretinogram, wnerg) and cortical responses (visual evoked potential, wnvep) were simultaneously recorded with the. Web visually evoked potentials elicited by flash stimuli can be recorded from. Web visual evoked potentials (veps) have a role in evaluating patients with neurologic disease affecting the optic pathway. This technique of extracting a relevant signal from random noise is. Web visual evoked potential/response (vep/ver) measures the electrical signal generated at the visual cortex in response to visual stimulation. Visual stimuli stimulate both primary visual cortices. Web visual evoked potential (vep) is an electrical wave, triggered by a visual stimulus, produced by electrical activity in the visual cortex, and recorded by the electrodes on the. Responses evoked by unpatterned stimuli are “flash” veps or fveps. The visual cortex is primarily activated. This test measures the electrical signals your visual cortex (a region of your brain) generates in response to visual. Web visual evoked potentials (veps; Web an evoked potential or evoked response is an electrical potential in a specific pattern recorded from a specific part of the nervous system, especially the brain, of a human or. The visual evoked potential (vep) is a means of extracting from the spontaneous electrical activity in the brain, electrical changes that are directly related. Web visual evoked potential (vep): Web the retinal (white noise electroretinogram, wnerg) and cortical responses (visual evoked potential, wnvep) were simultaneously recorded with the. Web evoked by patterned stimuli are “pattern” veps or pveps. Web visually evoked potentials elicited by flash stimuli can be recorded from many scalp locations in humans. Choice of stimulus patterned visual.
Pattern visual evoked potential (VEP) and pattern electroretinography

Visual evoked potentials. (A) ERP waveforms in response to the visual

Visual evoked potential (VEP) experimental results (a) grand averaged
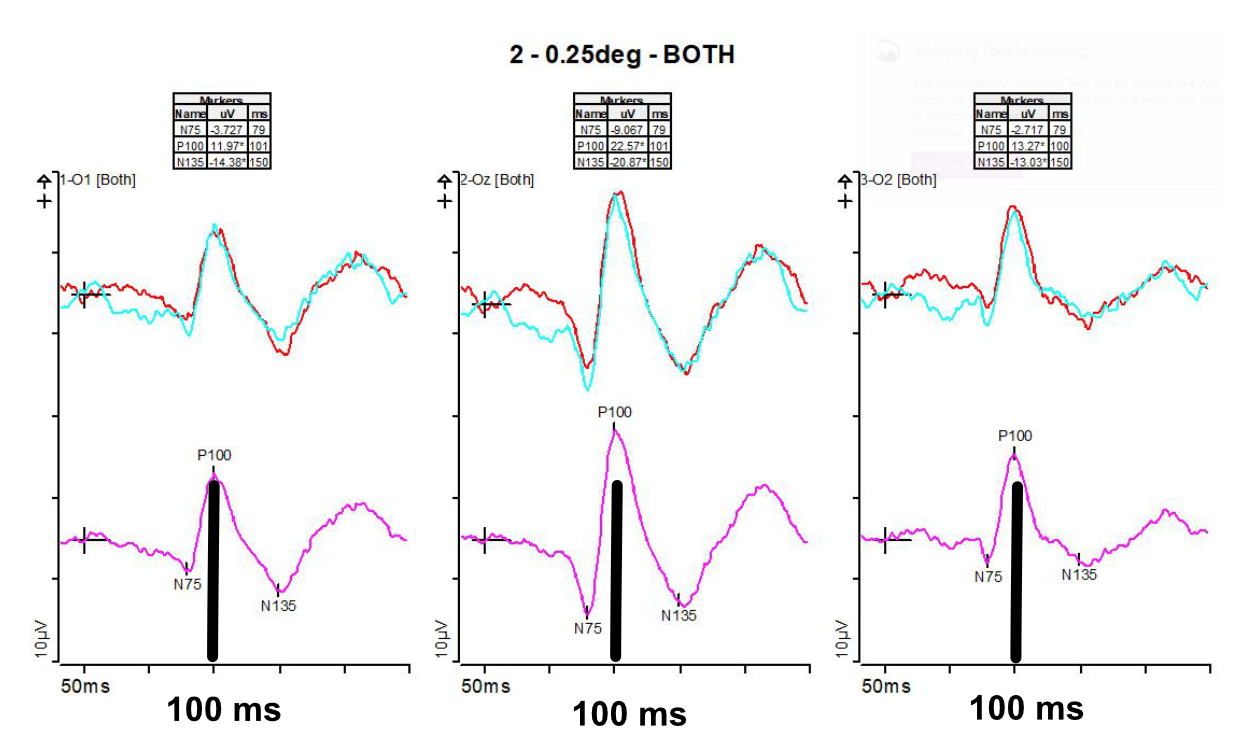
Visually Evoked Potentials (VEP) Diagnosys LLC

Visual Evoked Potential (VEP) Pattern A in Normal Hearing (NH) and

Visual evoked potential (VEP) waveforms and topographies. (A) Averaged
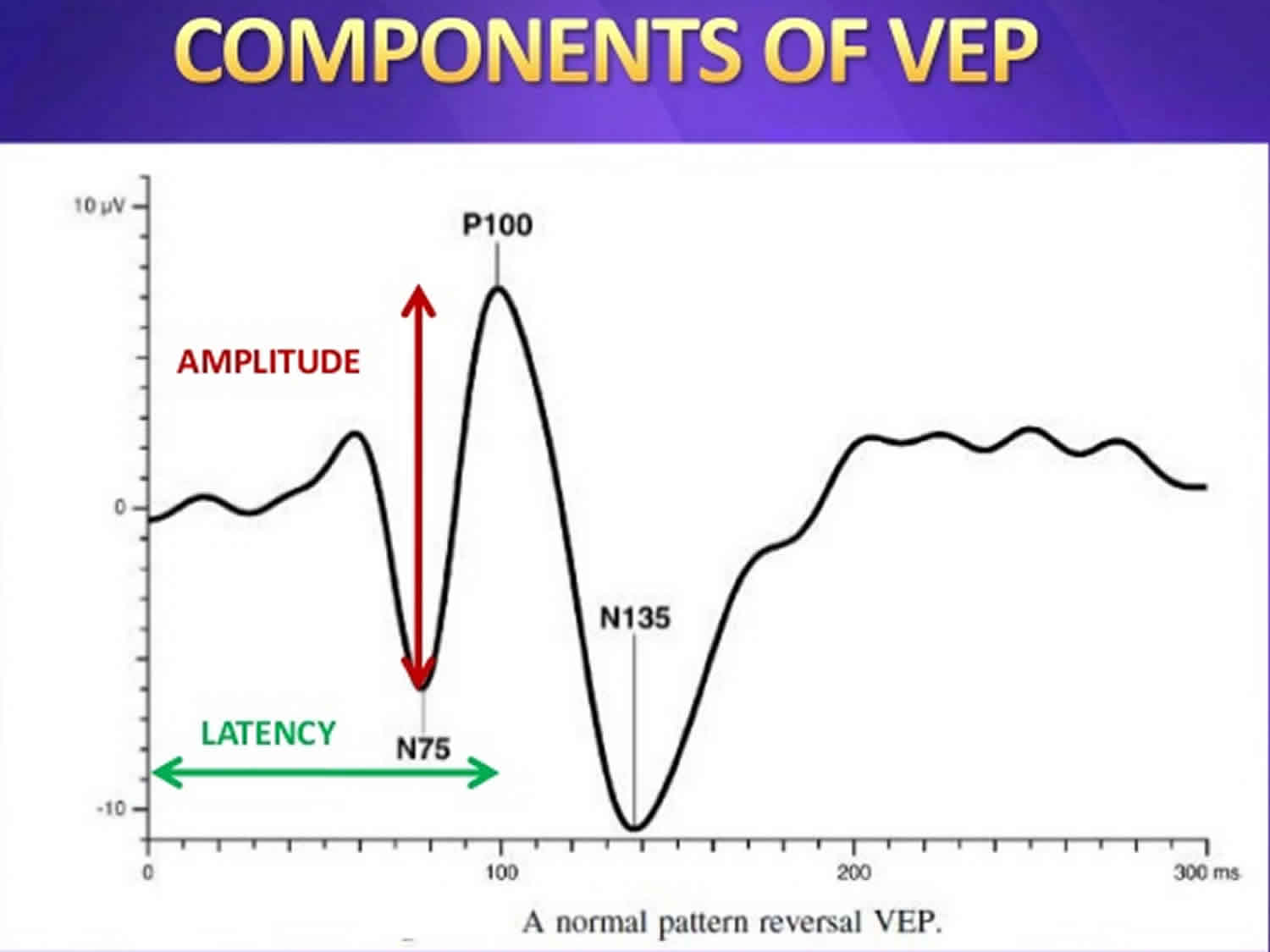
Visual evoked potential and evoked potential test

Steady‐state pattern electroretinogram and short‐duration transient

Pattern visual evoked potential (VEP) revealing delay of P100 latency

Multifocal visual evoked potential latency analysis predicting
Web This Review Covers A Brief History Of Visual Evoked Potentials, The Most Commonly Used Stimuli To Initiate Visual Evoked Potentials, The Methods Of Recording,.
Web A Visual Evoked Potential Is An Evoked Potential Caused By A Visual Stimulus, Such As An Alternating Checkerboard Pattern On A Computer Screen.
Web Evoked Potentials, Whether Auditory, Visual, Or Somatosensory, Are Extracted From The Eeg By A Simple Program.
Web Pattern Onset/Offset Visual Evoked Potentials (Onset/Offset Veps) The Pattern Reversal Stimulus Is The Preferred Stimulus Choice For Most Clinical Situations.
Related Post: