Pattern Of Electronegativity
Pattern Of Electronegativity - Different elements have different electronegativities based on a number of factors such as size and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology,. Web electronegativity is the measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards it in a covalent bond. Atoms with high electronegativity have a stronger. Use the periodic trend for electronegativity (en) to complete the table. Web electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons. Web electronegativity is the measure of an element’s ability to attract a bonding pair of electrons towards itself. Electronegativity increases moving left to right across a period, from the alkali metals to the halogens. Electronegativity difference values greater 2.0 indicate an ionic bond. Web electronegativity is defined as an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards it in a chemical bond. Web electronegativity, symbolized as χ, is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. Web electronegativity follows a trend (periodicity) on the periodic table. Web electronegativity is defined as an atom's tendency to attract electrons shared in a bond, or strip another atom of its outermost. How do you calculate electronegativity difference? The pauling scale is the most commonly used. Web electronegativity is defined as an atom's tendency to attract electrons shared in a bond, or strip another atom of its outermost electrons. The higher the electronegativity, the greater an atom’s propensity to attract electrons. Web electronegativity is the measure of an atom’s ability to attract. 1 3 11 19 37 55 87 118 atomic number 0 1 2 3 4 electronegativity (pauling scale) tabular electronegativity (pauling scale) data. Values for electronegativity run from 0 to 4. Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the. It can also be used to predict if the resulting molecule will be polar or nonpolar. Use the periodic trend for electronegativity (en) to complete the table. Values for electronegativity run from 0 to 4. Web the electronegativity (χ) of an element is the relative ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a chemical compound and increases. Across a period from left to right the electronegativity of atoms increases. Web electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons. Web electronegativity is the measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards it in a covalent bond. The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons. Why does electronegativity fall as you go down a group? The pauling scale is the most commonly used. Fluorine (the most electronegative element) is assigned a value of 4.0, and values range down to cesium and francium which are the least electronegative at 0.7. Different elements have different electronegativities based on a number of factors such as size and number. Web the electronegativity (χ) of an element is the relative ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a chemical compound and increases diagonally from the lower left of the periodic table to the upper right. Thus, in general, electronegativity is big in the upper right of the periodic table and decreases down and to the left. The. Electronegativity is defined as the ability of an atom in a particular molecule to attract electrons to itself. Web electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract a pair of electrons in a chemical bond. Why does electronegativity fall as you go down a group? Electronegativity is important because it makes bonding between atoms possible. It's good to know. Different elements have different electronegativities based on a number of factors such as size and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Web electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract shared electrons to itself. If two bonded atoms have the same electronegativity values as each other, they share electrons equally in a covalent bond. An atom's electronegativity is. Web patterns of electronegativity in the periodic table. Web the chart shows the patterns of electronegativity in groups 1 and 7. There are several different ways of measuring it, the most common being the pauling scale. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology,. It was first described by linus pauling. Web electronegativity is a chemical property that measures how likely an atom is to attract a shared pair of electrons towards itself in a covalent bond. Web determine if a molecule is polar or nonpolar. Web it pretty much follows the same pattern you would expect based on ionization energy and electron affinity. Web electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract shared electrons to itself. It is caused by the attractive electrostatic force between the positively charged nucleus and the negatively charged electrons. Electronegativity is used to predict whether a bond between atoms will be ionic or covalent. Different elements have different electronegativities based on a number of factors such as size and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. As you go down a group, electronegativity decreases because the bonding pair of electrons is increasingly distant from the attraction of the nucleus. Plot of electronegativity (pauling scale) vs atomic number. Fluorine (the most electronegative element) is assigned a value of 4.0, and values range down to caesium and francium which are the least electronegative at 0.7. Web electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons. Given a pair of compounds, predict which would have a higher melting or boiling point. Web electronegativity is defined as an atom's tendency to attract electrons shared in a bond, or strip another atom of its outermost electrons. On the periodic table, electronegativity generally increases as you move from left to right across a period and decreases as you move down a group. Electronegativity increases moving left to right across a period, from the alkali metals to the halogens. It's good to know that h's electronegativity is between b and c.Here is another video that describes ionization energy trends in the
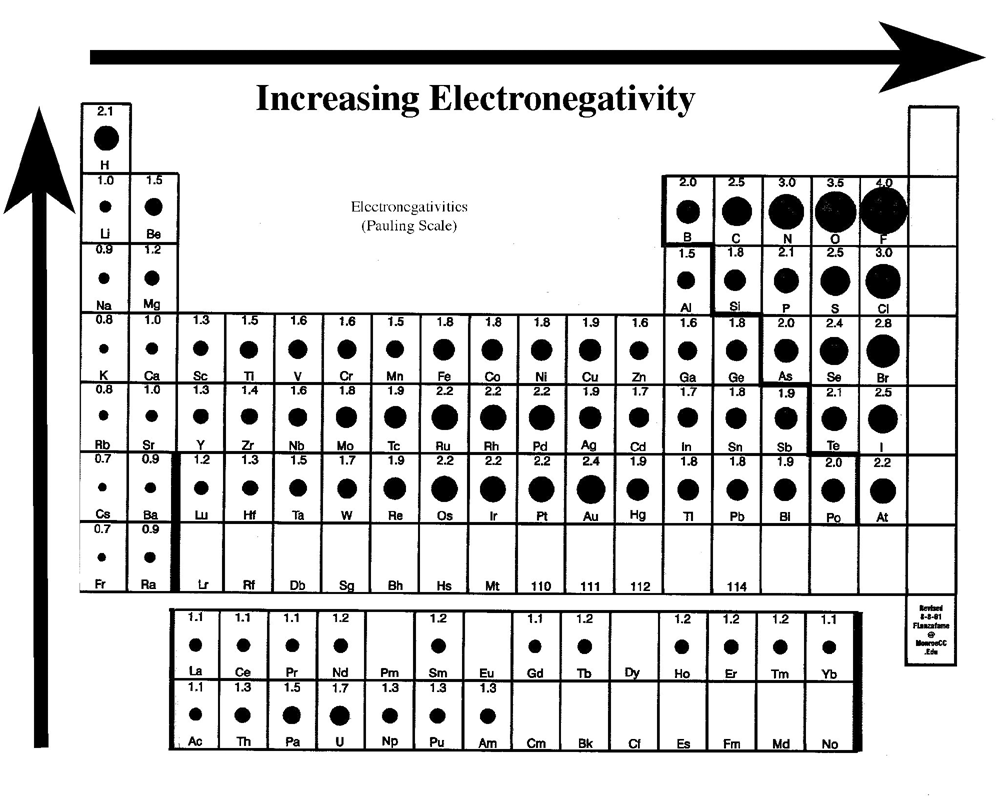
Periodic Trends copy Screen 4 on FlowVella Presentation Software
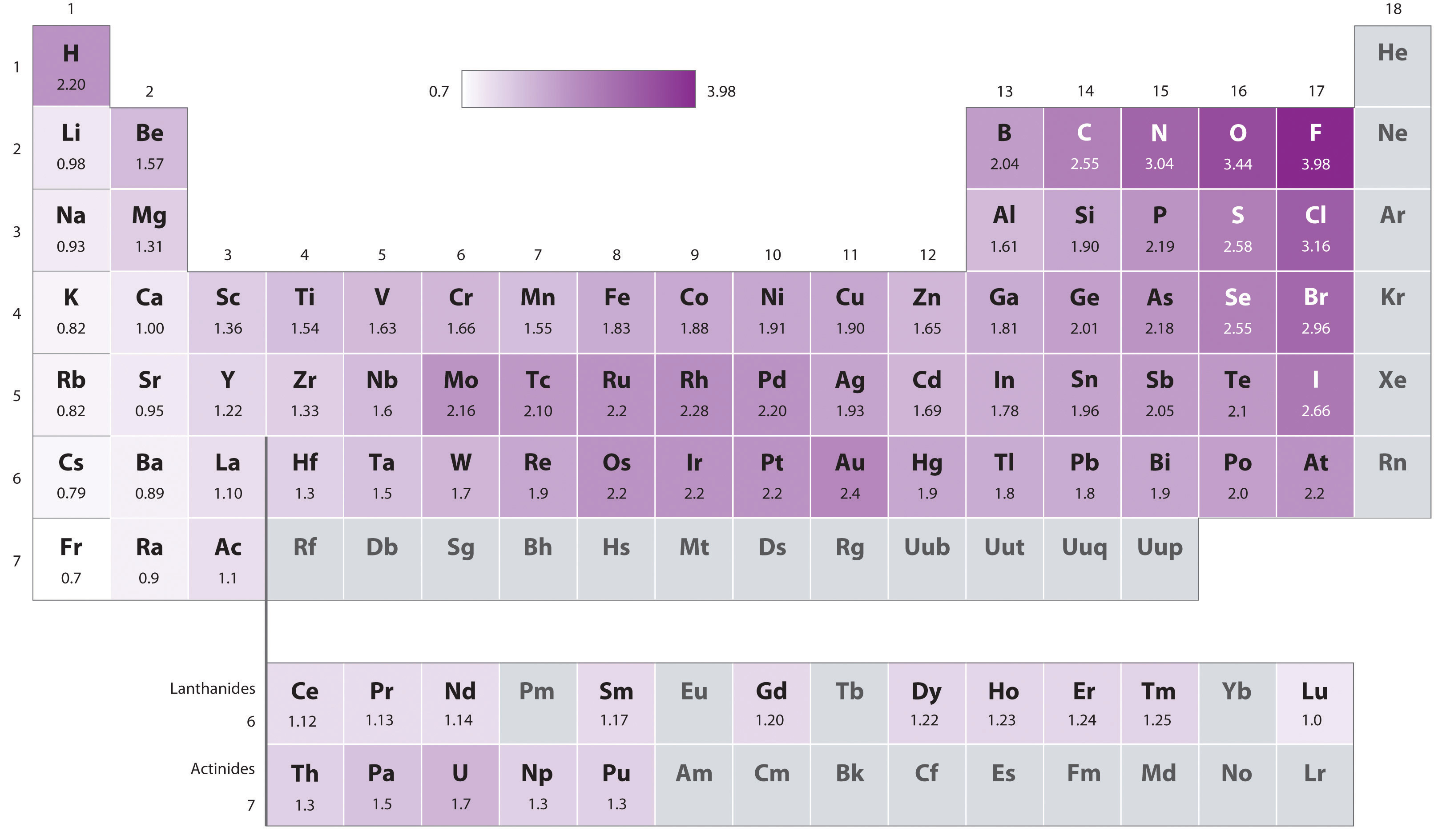
8.4 Bond Polarity and Electronegativity Chemistry LibreTexts

List of Electronegativity Values of the Elements
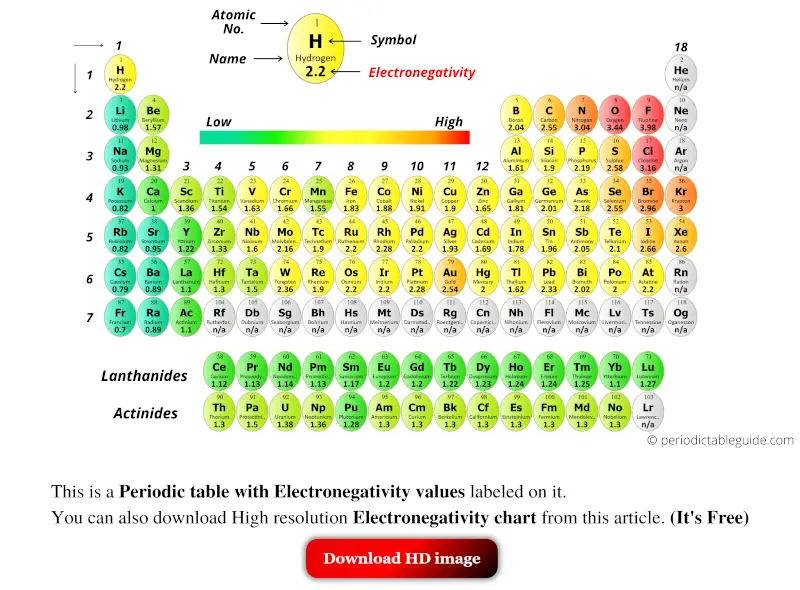
Periodic table with Electronegativity Values (Labeled Image)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/PeriodicTableEnegativity-56a12c955f9b58b7d0bcc69d.png)
Printable Periodic Table of the Elements Electronegativity
Periodic Table of Electronegativities

Electronegativity Definition and Trend

Electronegativity Table Easy Hard Science

Electronegativity Definition, Value Chart, and Trend in Periodic Table
Web The Chart Shows The Patterns Of Electronegativity In Groups 1 And 7.
As A Result, The Most Electronegative Elements Are Found On The Top Right Of The Periodic Table, While The.
Atoms With High Electronegativity Have A Stronger.
As You Move From Left To Right.
Related Post:

.PNG)