Nucleolar Speckled Ana Pattern
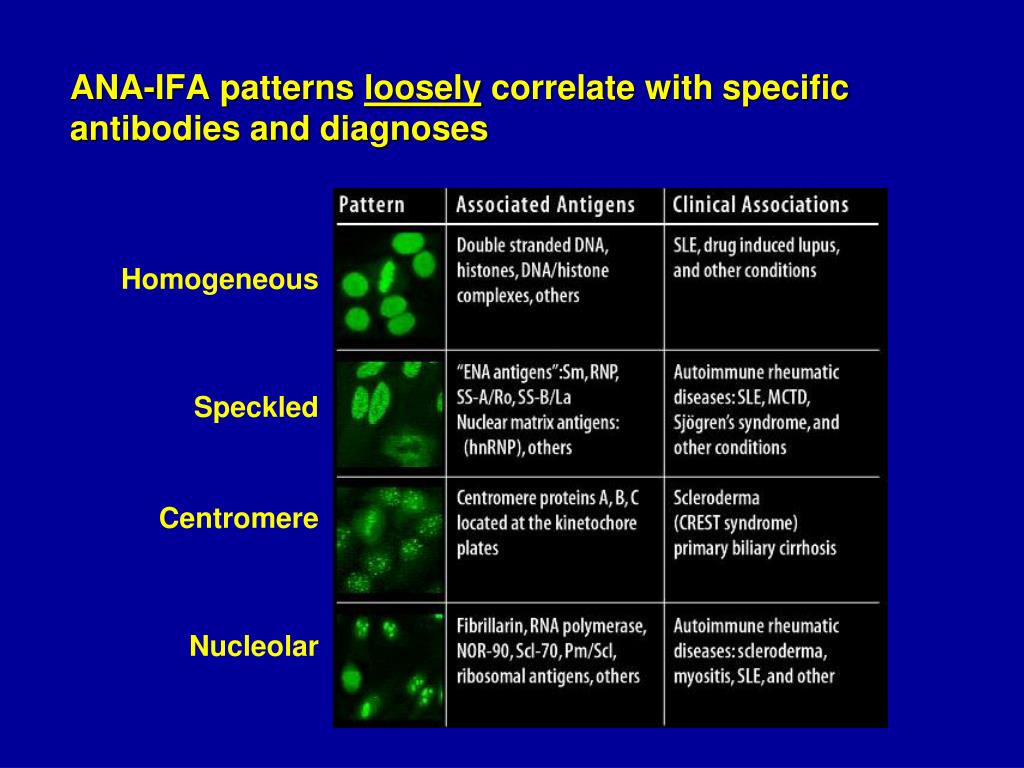
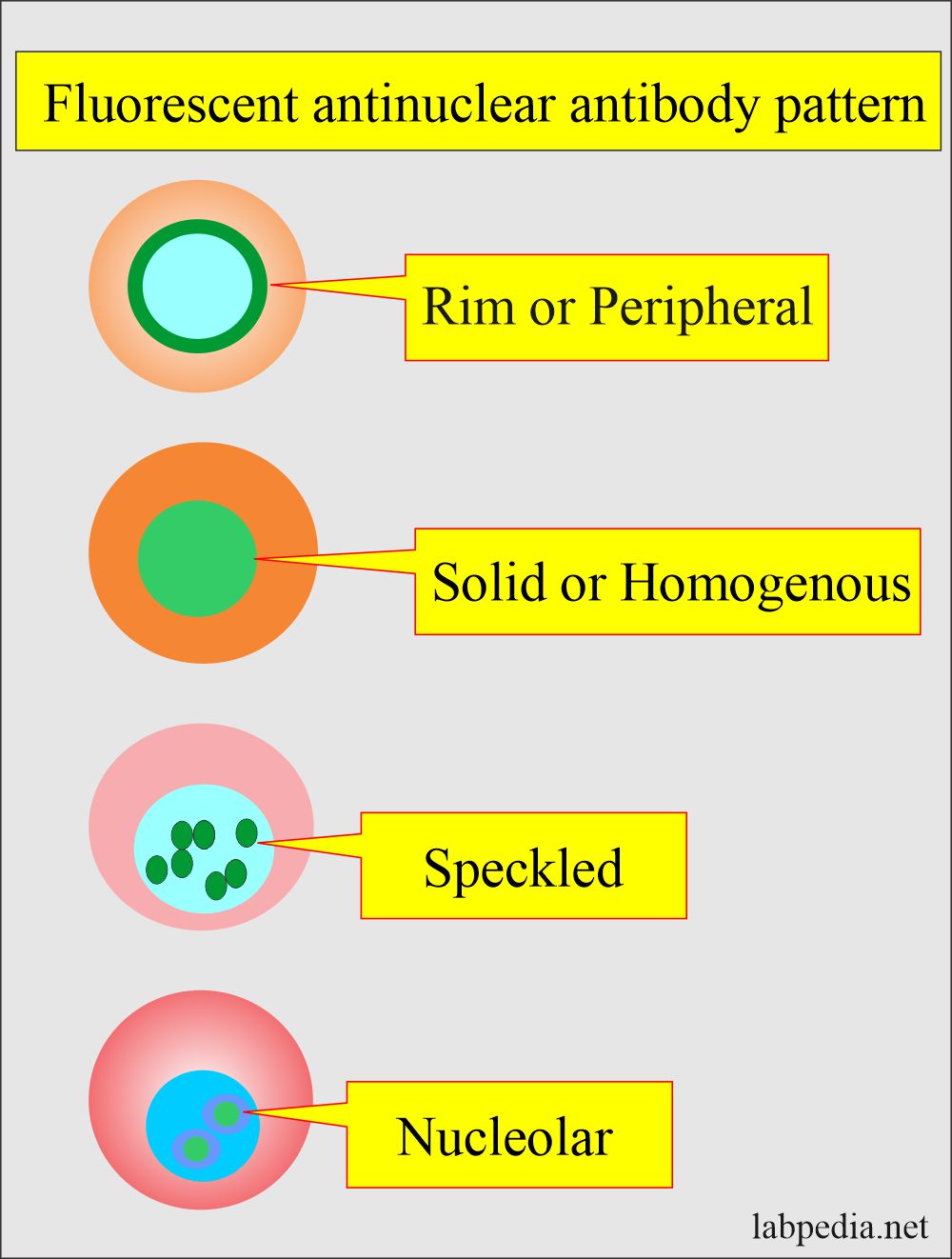
Nucleolar Speckled Ana Pattern - Identification of a certain pattern can lead to diagnosis of a certain autoimmune disease. How the test is performed. The level or titer and the pattern. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens. Updated on october 14, 2022. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less than 7% of the patients each. This pattern can be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis. The nucleoli may be stained or not stained. Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. Web depending on the subtype of ana present in the serum and the targeted antigen, several staining patterns are reported, namely, nuclear patterns, nucleolar patterns, cell cycle patterns, or cytoplasmatic patterns. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens. Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus. The quantity of ana in the serum (intensity) and, when the ana is positive, the pattern of antibody binding to the nucleus (staining. Web a homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled patterns of various sizes and densities (fine speckled, large speckled, etc.). The nucleoli may be stained or not stained. An ana test detects antinuclear antibodies (ana) in your blood. A titer (a measure of how much ana is in the blood). Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin mass not stained. Web antibodies that attack healthy proteins within the cell nucleus are called antinuclear antibodies (anas). Web the results of ana testing are reported in two components: Ana test results are most often reported in 2. Web depending on the subtype of ana present in the serum and the targeted antigen, several staining patterns are reported, namely, nuclear patterns, nucleolar patterns, cell cycle patterns, or cytoplasmatic patterns. The nucleoli may be stained or not stained. Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. It is found in many disease states, including sle and. When antibodies to dna and deoxyribonucleoprotein are present (rim and homogenous pattern), there may be interference with the detection of speckled pattern. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens. Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns,. Fine tiny speckles across all nucleoplasm. This pattern can be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis. It is found in many disease states, including sle and scleroderma. A nucleolar staining pattern means ana staining is present around the. How the test is performed. The significance of ana pattern. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. Web depending on the subtype of ana present in the serum and the targeted antigen, several staining patterns are reported, namely, nuclear patterns, nucleolar patterns, cell cycle patterns, or cytoplasmatic patterns. Understanding the ana blood test (antinuclear antibody test) by carol eustice.. How the test is performed. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less than 7% of the patients each. A centromere staining pattern means the ana staining is present along the chromosomes. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens. The nucleoli. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin mass not stained. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin mass not stained. The significance of ana pattern. Doctors may order an ana test if you have signs or symptoms of an autoimmune disorder. It is found in many disease states, including sle and scleroderma. Identification of a certain pattern can lead to diagnosis of a certain autoimmune disease. When antibodies to dna and deoxyribonucleoprotein are present (rim and homogenous pattern), there may be interference with the detection of speckled pattern. Web antibodies that attack healthy proteins within the cell nucleus are called antinuclear antibodies (anas). A centromere staining pattern means the ana staining is. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. Identification of a certain pattern can lead to diagnosis of a certain autoimmune disease. When antibodies to dna and deoxyribonucleoprotein are present (rim and homogenous pattern), there may be interference with the detection of speckled pattern. Web the most frequent ana patterns were coarse speckled pattern (154 patients, 31.2%), nucleolar pattern (89 patients, 18.0%), fine speckled pattern (57 patients, 11.5%), and speckled pattern (48 patients, 9.7%). Ana pattern is almost always. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less than 7% of the patients each. While these patterns are not specific to any one illness, certain illnesses can more frequently be associated with one pattern or another. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. Web speckled pattern correlates with antibody to nuclear antigens extractable by saline; A centromere pattern may indicate scleroderma. Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus. Web depending on the subtype of ana present in the serum and the targeted antigen, several staining patterns are reported, namely, nuclear patterns, nucleolar patterns, cell cycle patterns, or cytoplasmatic patterns. Web a homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled patterns of various sizes and densities (fine speckled, large speckled, etc.). Updated on october 14, 2022. A titer (a measure of how much ana is in the blood) and a pattern (where the ana was detected in the cells). Medically reviewed by scott zashin, md.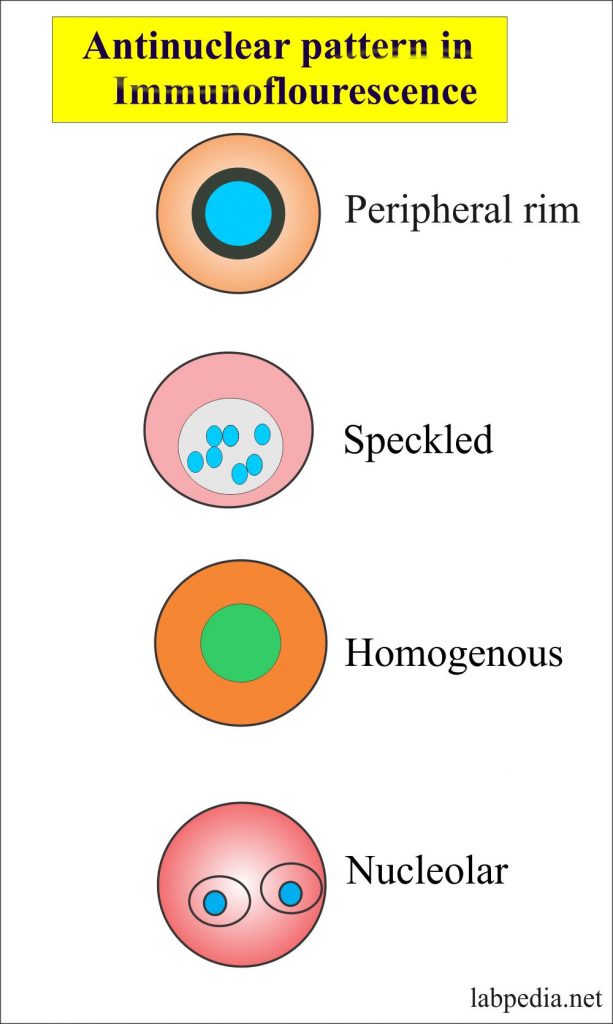
Ana Nucleolar Pattern Chumado

Ana Test Patterns

Common ANA patterns by IIF a, negative sample; b, homogeneous; c

ANA Patterns

Ana With Speckled Pattern Chumado
Ana Titer 1 160 Speckled Pattern Chumado

Example of nucleolar pattern of ANA detected by indirect... Download
ANA Nucleolar University of Birmingham
Antinuclear Factor (ANF), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) and Its
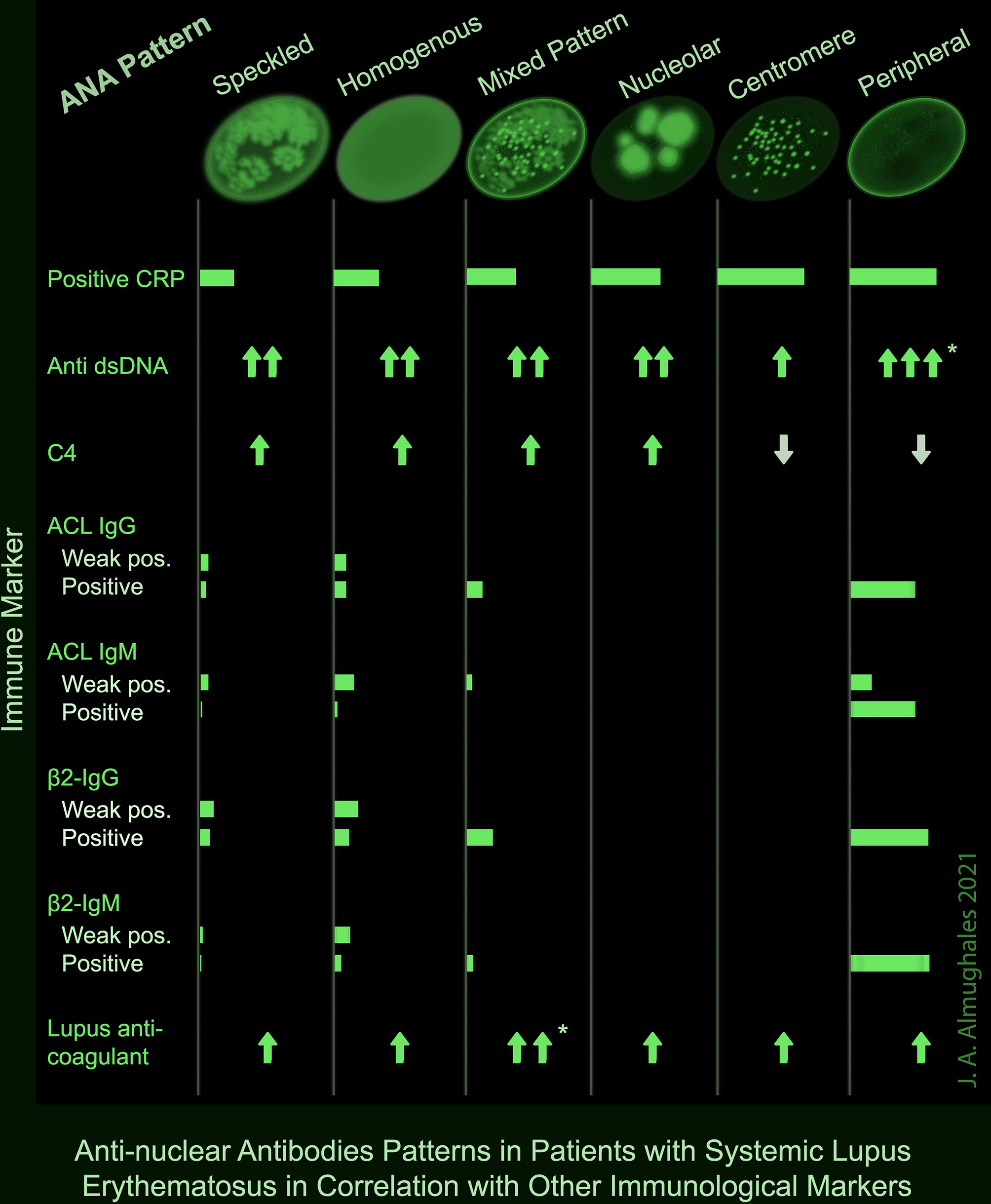
Frontiers AntiNuclear Antibodies Patterns in Patients With Systemic
A Centromere Staining Pattern Means The Ana Staining Is Present Along The Chromosomes.
This Pattern Can Be Associated With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Sjögren’s Syndrome, Systemic Sclerosis, Polymyositis, And Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Web Scleroderma Or Systemic Sclerosis:
The Quantity Of Ana In The Serum (Intensity) And, When The Ana Is Positive, The Pattern Of Antibody Binding To The Nucleus (Staining Pattern).
Related Post: