Nucleic Acid Drawing Easy
Nucleic Acid Drawing Easy - The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Describe the structure of nucleic acids and define the two types of nucleic acids. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that carry the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms and viruses. Interactive drawing and exploration of nucleic acid structures. Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. Explain rna's structure and roles. By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: In this section, we will examine the structures of dna and rna, and how these structures are related to the functions these molecules perform. Web a web app for drawing and exploring nucleic acid structures. Get editable icons and illustrations of nucleic acids. Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. Web nucleic acid, naturally occurring chemical compound that is capable of being broken down to yield phosphoric acid, sugars,. By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: By the end of this section, you will be able to: They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Peptides differ from proteins by amount of amino acid residues the molecule contains. A web app for drawing. Explain the structure and roles of rna. As a library, nlm provides access to scientific literature. Create professional science figures in minutes with biorender scientific illustration software. Web these chains contain two or more amino acids (forming amino acid polymers) that are coupled by a peptide bond. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. The repeating, or monomer, units that are linked together to form nucleic acids are. Web the nucleic acids, dna and rna, may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Explain the structure and roles of rna. The four interfaces cover. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Nucleic acids research 51 (w1) doi: Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. Web the image below shows structural drawings of the four dna and the four rna. As a library, nlm provides access to scientific literature. Get editable icons and illustrations of nucleic acids. Describe the basic structure of nucleic acids. However, manually drawing structures is laborious and infeasible for structures thousands of nucleotides long. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. A web app for drawing and exploring nucleic acid structures. The bond is a special linkage between the nitrogen atom of one amino acid and the carboxyl carbon atom of another. Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. Explain the structure and roles of rna. However, manually drawing structures is laborious and infeasible for structures. Web a web app for drawing and exploring nucleic acid structures. The repeating, or monomer, units that are linked together to form nucleic acids are. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. By the end of this section, you will be able to: However, manually drawing structures is laborious and. The bond is a special linkage between the nitrogen atom of one amino acid and the carboxyl carbon atom of another. However, manually drawing structures is laborious and infeasible for structures thousands of nucleotides long. Nucleic acids research 51 (w1) doi: Describe the basic structure of nucleic acids. The repeating, or monomer, units that are linked together to form nucleic. Describe the basic structure of nucleic acids. To identify the different molecules that combine to form nucleotides. Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. Two dna strands link together in an antiparallel direction and are twisted to form a double helix. Nucleic acids research 51. Explain the structure and role of dna. Email contact@rnacanvas.app or visit the github page. Interactive drawing and exploration of nucleic acid structures. Web rnacanvas offers extensive options to customize drawings of nucleic acid secondary structures and tertiary interactions based on graphical user interaction, with drawings edited using ‘tools’ and forms. Web moof's medical biochemistry video course: Describe the structure of nucleic acids and define the two types of nucleic acids. To identify the different molecules that combine to form nucleotides. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. Peptides differ from proteins by amount of amino acid residues the molecule contains. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that carry the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms and viruses. Create professional science figures in minutes with biorender scientific illustration software. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. The four interfaces cover virtually all conceivable use cases. Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna).
19.2 Nucleic Acid Structure The Basics of General, Organic, and

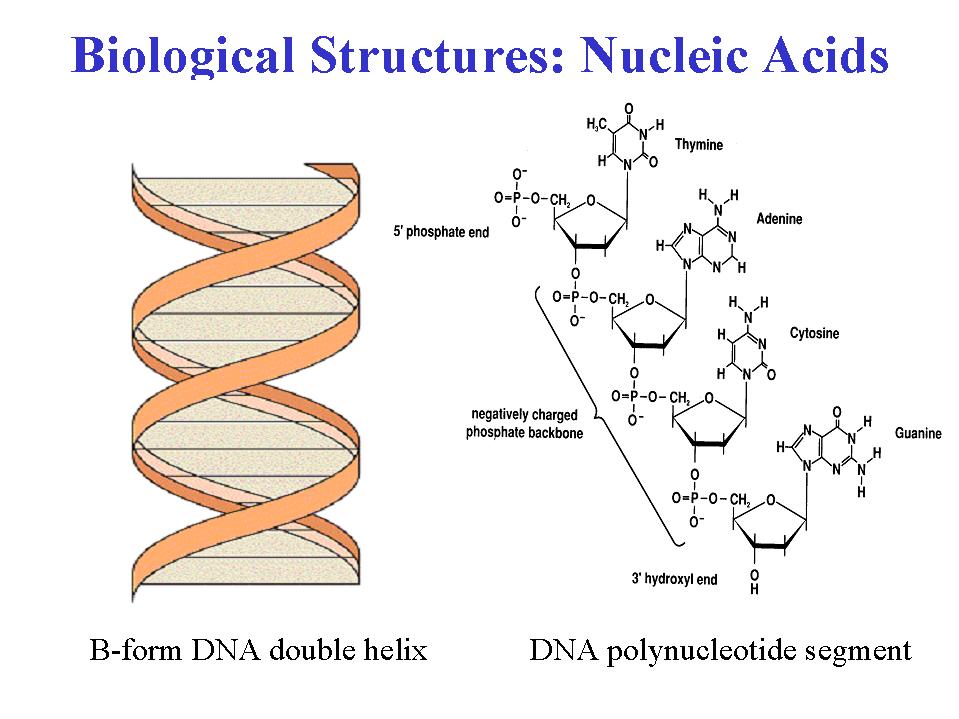
Nucleic Acids RNA and DNA Structure Biochemistry YouTube
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotide_base-5b6335bdc9e77c002570743e.jpg)
Draw And Label The Three Parts Of A Nucleotide Pensandpieces
Nucleic Acids Jack's AP Biology Journal

Cell Biology Glossary Nucleic Acids Sugars & Bases Draw It to Know It

Nucleic acid definition, nucleic acid structure, function & types
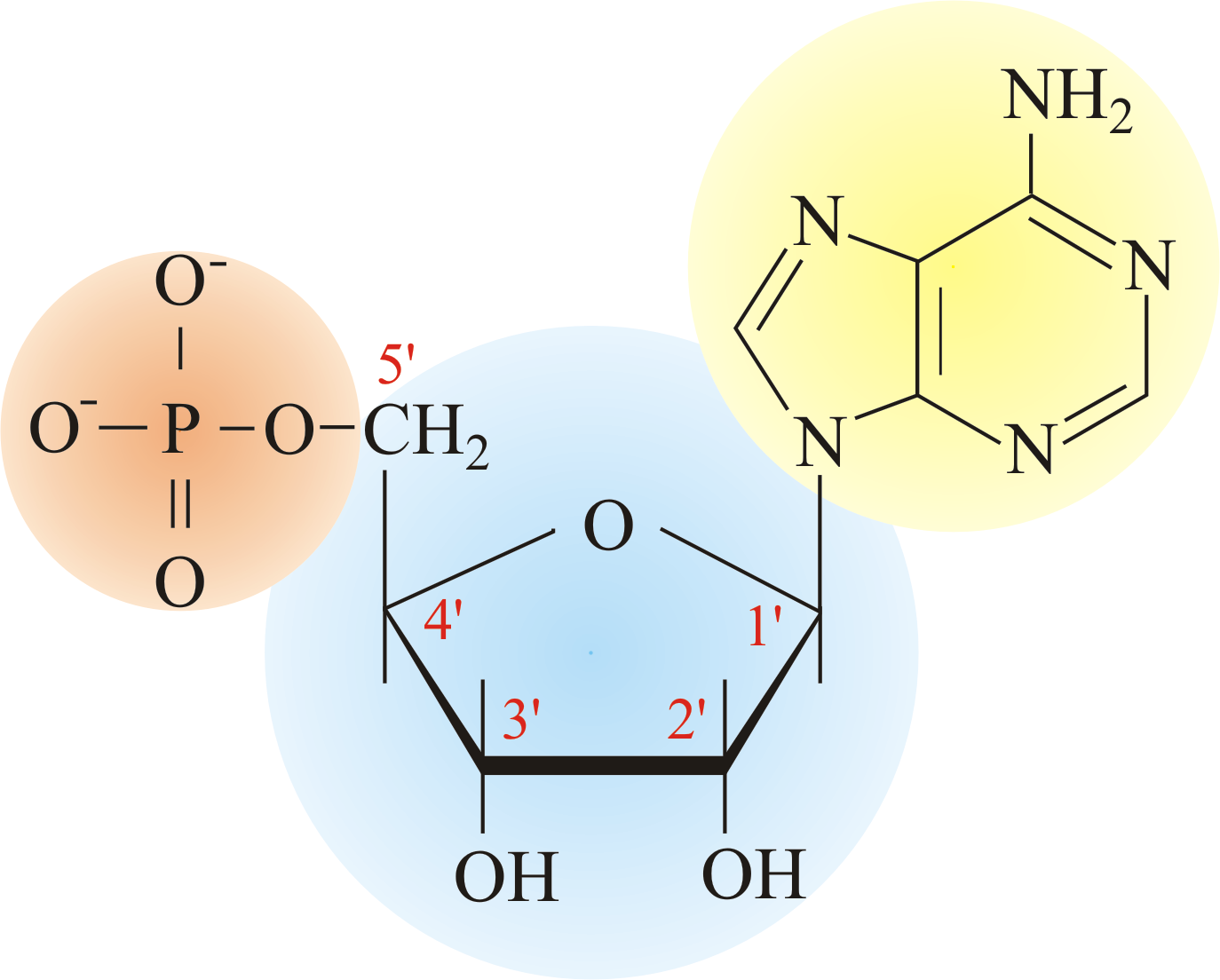
Molecular structure of nucleic acids Science online
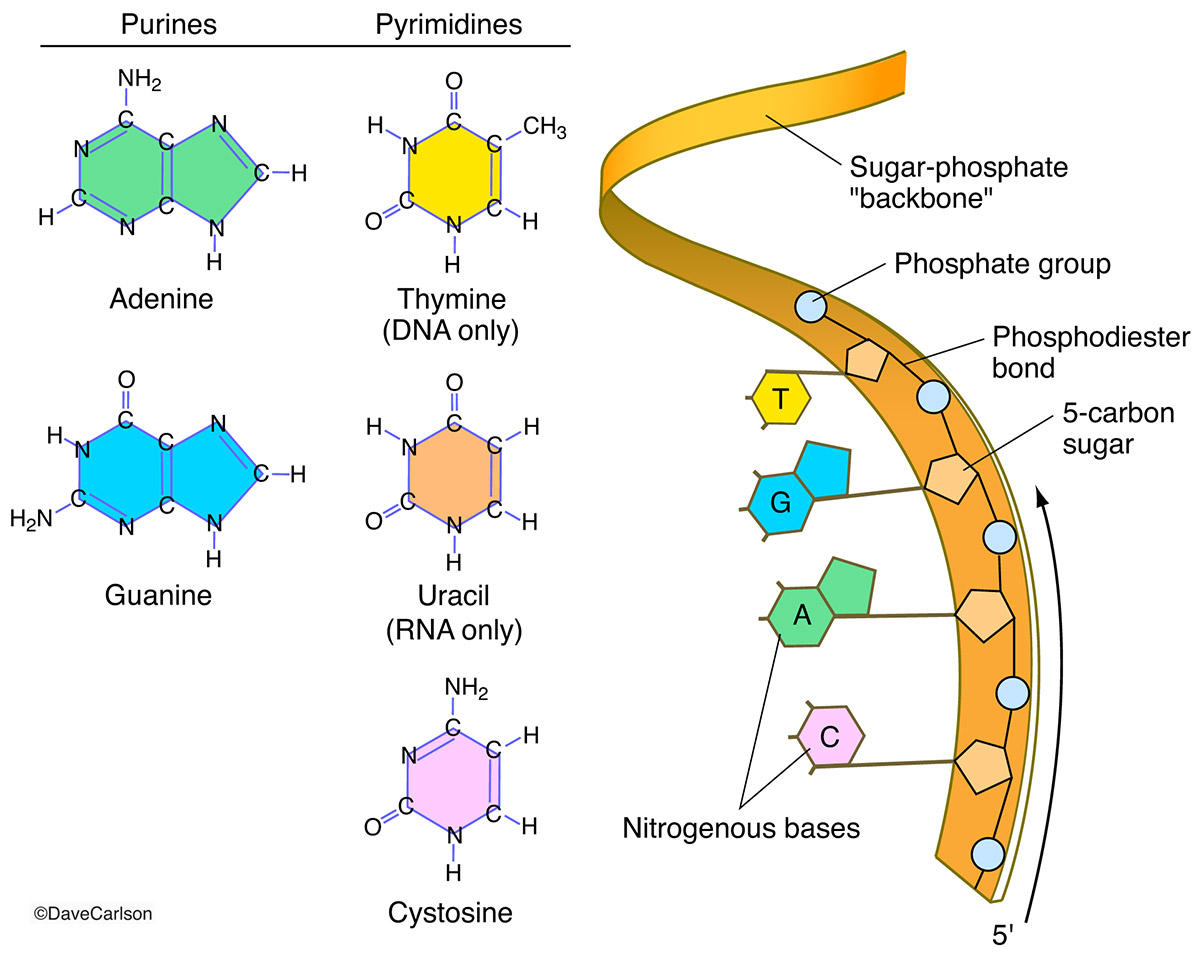
Nucleic Acid Structure Carlson Stock Art

Basic Structure of Nucleic Acids YouTube

How To Draw A Dna Strand Easy Dna Synthesis Wikipedia Anthony Gibby
The Repeating, Or Monomer, Units That Are Linked Together To Form Nucleic Acids Are.
Web A Web App For Drawing And Exploring Nucleic Acid Structures.
The Bond Is A Special Linkage Between The Nitrogen Atom Of One Amino Acid And The Carboxyl Carbon Atom Of Another.
As A Library, Nlm Provides Access To Scientific Literature.
Related Post: