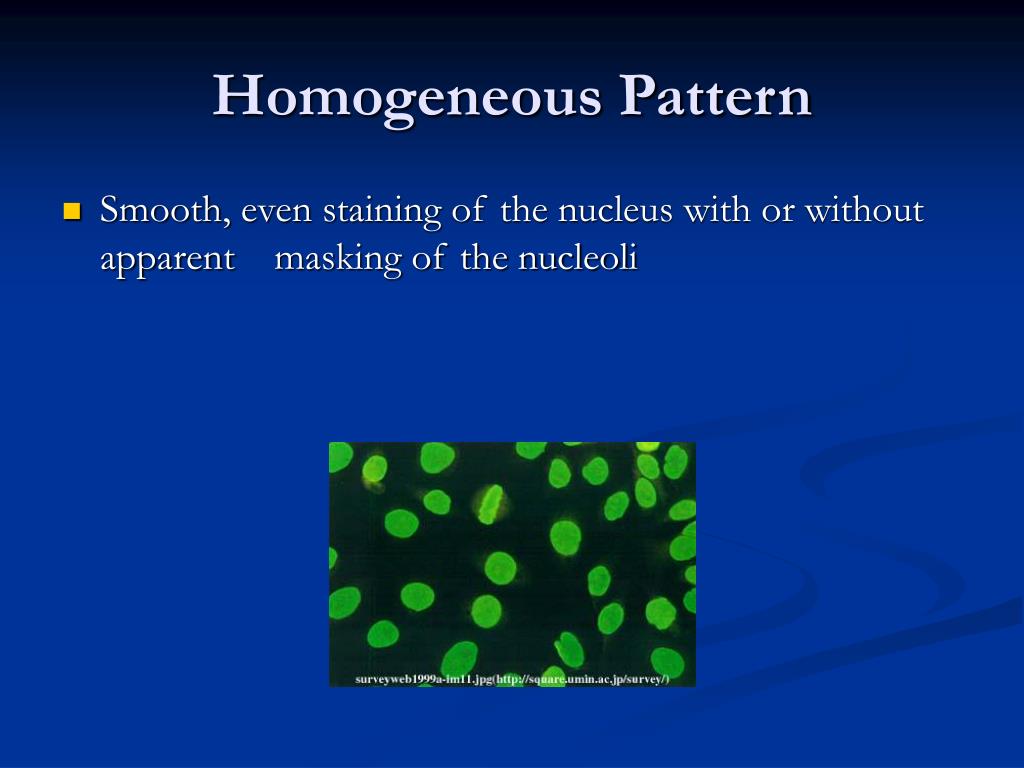
Nuclear Homogeneous Pattern
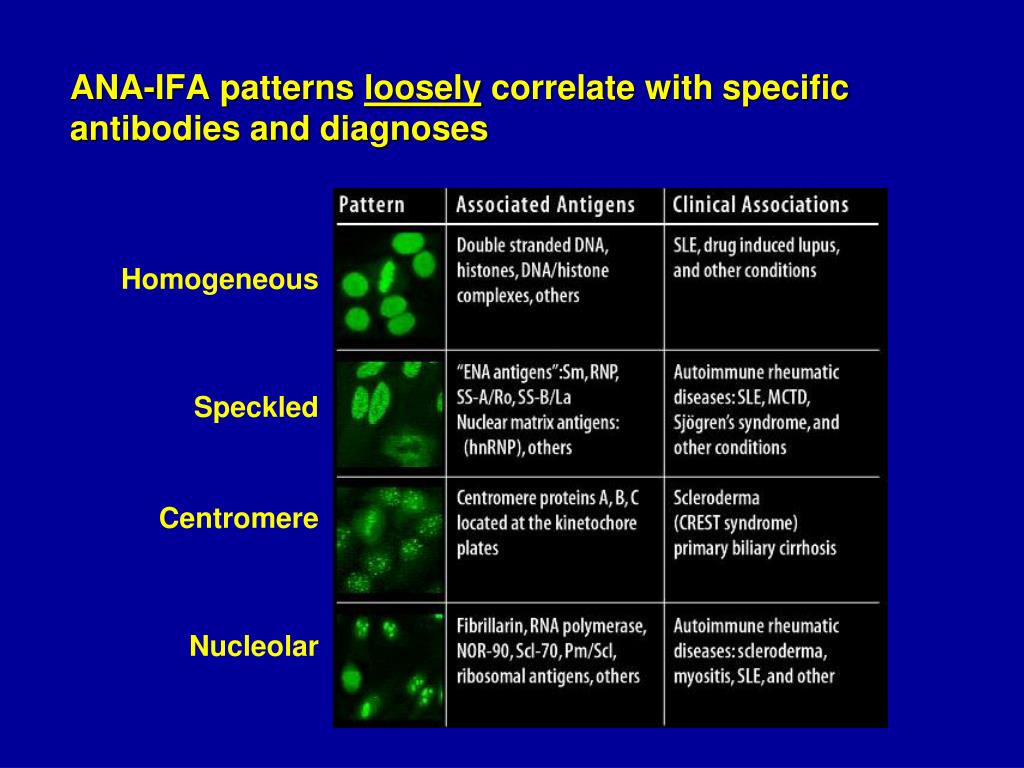
Nuclear Homogeneous Pattern - It’s the most common type of staining pattern. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less than. Diagram shows what pathologists see under the microscope in. Interphase cells show homogeneous nuclear staining while mitotic. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. Doctors may order an ana test if you have signs or. Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. The nucleus of a cell contains genetic. Web ana pattern refers to the distribution of staining produced by autoantibodies reacting with antigens in these cells. The nucleoli maybe stained or not. The nucleoli maybe stained or not stained depending on cell substrate. Antibodies that attack healthy proteins within the cell nucleus are called antinuclear antibodies (anas). Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. This part of the ana test gives an estimate of how many anti. Web each pattern is assigned an alphanumeric ac code (anticell). The nucleus of a cell contains genetic. Web a homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus. Web a positive nuclear staining result will usually come back with a more detailed staining pattern, such as speckled (fig. A peripheral pattern indicates that fluorescence occurs at the. A homogenous staining pattern means the. Web antinuclear antibodies are a unique group of autoantibodies that have the ability to attack structures in the nucleus of cells. A homogenous pattern can mean any autoimmune disease but more specifically, lupus or sjögren’s syndrome. It’s the most common type of staining pattern. 1) the titre, and 2) the pattern. Web homogeneous and regular fluorescence across all nucleoplasm. Web a homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus. When active, usually a homogenous pattern on ana or less commonly speckled, rim, or nucleolar. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. A peripheral pattern indicates that fluorescence occurs. The ana test gives two types of results: Homogeneous and regular fluorescence across all nucleoplasm. It’s the most common type of staining pattern. Web a positive nuclear staining result will usually come back with a more detailed staining pattern, such as speckled (fig. These patterns were recently defined by the international consensus on ana. Web ana pattern refers to the distribution of staining produced by autoantibodies reacting with antigens in these cells. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles. Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. It’s the most common type of staining pattern. Web in iif, ana can display different nuclear patterns depending on the targeted antigen. Web how the ana test works. Web homogeneous and regular fluorescence across all nucleoplasm. This part of the ana test gives an estimate of how many anti. 1) the titre, and 2) the pattern. There are a few types of patterns reported :. A homogenous pattern can mean any autoimmune disease but more specifically, lupus or sjögren’s syndrome. Web a positive nuclear staining result will usually come back with a more detailed staining pattern, such as speckled (fig. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. Interphase cells show homogeneous nuclear staining while mitotic. Antibodies that attack healthy proteins. Diagram shows what pathologists see under the microscope in. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. This part of the ana test gives an estimate of how many anti. Web how the ana test works. Web a homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus. Web a positive nuclear staining result will usually come back with a more detailed staining pattern, such as speckled (fig. The nucleoli maybe stained or not. A titer (a measure of how much ana. Diagram shows what pathologists see under the microscope in. There are a few types of patterns reported :. Diagram shows what pathologists see under the microscope in. A homogenous pattern can mean any autoimmune disease but more specifically, lupus or sjögren’s syndrome. The nucleus of a cell contains genetic. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. These patterns were recently defined by the international consensus on ana. A peripheral pattern indicates that fluorescence occurs at the. Web ana pattern refers to the distribution of staining produced by autoantibodies reacting with antigens in these cells. An ana test detects antinuclear antibodies (ana) in your blood. Web in iif, ana can display different nuclear patterns depending on the targeted antigen. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles. It’s the most common type of staining pattern. Their presence in serum may indicate an. Web patterns that are reported include, homogeneous, speckled, centromere, and others. The nucleoli maybe stained or not. Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. Web how the ana test works.
Representative images of selected major HEp2 cell patterns. (A

37+ Ana Pattern Nuclear Dense Fine Speckled FayneHjalte
Homogeneous Ana Pattern Pagswa
PPT Topic 3 Autoimmunity PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID

ANA Patterns
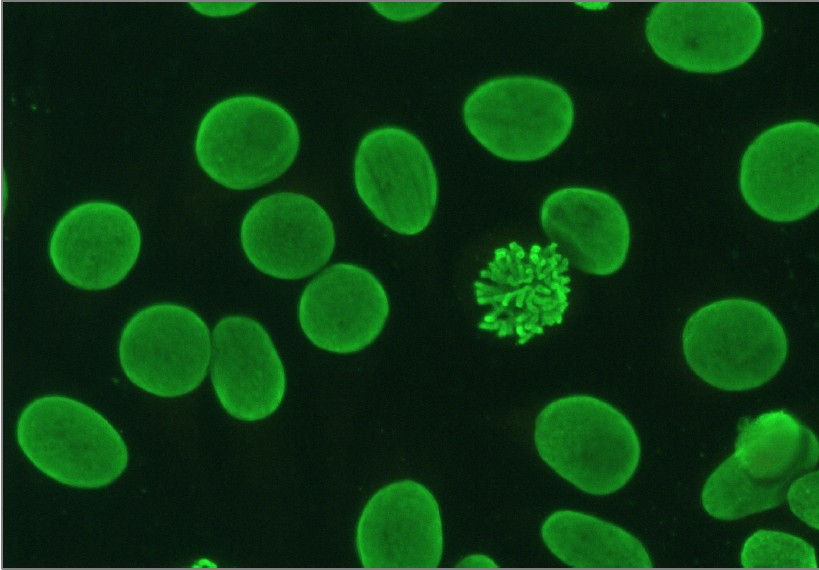
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) homogeneous pattern positive control

ANA Patterns

Indirect immunofluorescence with typical nuclear patterns of MSA and

ANA Patterns

(A) Nuclear fine speckled tending to be homogeneous. Cells present
Doctors May Order An Ana Test If You Have Signs Or.
Interphase Cells Show Homogeneous Nuclear Staining While Mitotic.
Homogeneous And Regular Fluorescence Across All Nucleoplasm.
Normal Value Ranges May Vary Slightly Among Different Laboratories.
Related Post: