Nuclear Ab Pattern Speckled
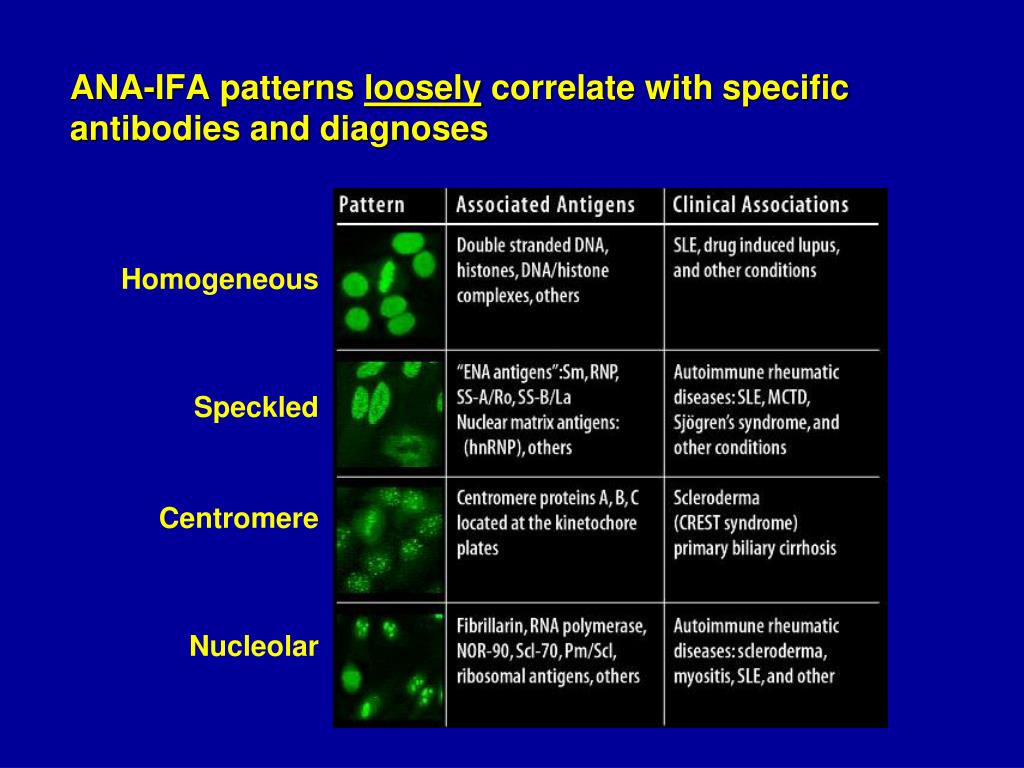
Nuclear Ab Pattern Speckled - Web an ana test looks for antinuclear antibodies in your blood. An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your own cells, tissues, and/or organs by mistake. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. When antibodies to dna and deoxyribonucleoprotein are present (rim and homogenous pattern), there may be interference with the detection of speckled pattern. Regardless of reproductive condition and cell type, all cells analyzed in this study presented a positive antibody labeling in the nucleoplasm, which was. A homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled patterns of. Web a positive nuclear staining result will usually come back with a more detailed staining pattern, such as speckled (fig. Web anas present different patterns depending on the staining of the cell nucleus in the laboratory: Web a positive ana test is usually reported as both a ratio (called a titer) and a pattern, such as smooth or speckled. Web patterns that are reported include, homogeneous, speckled, centromere, and others. Web the most frequent ana patterns were coarse speckled pattern (154 patients, 31.2%), nucleolar pattern (89 patients, 18.0%), fine speckled pattern (57 patients, 11.5%), and speckled pattern (48 patients, 9.7%). Web an ana test looks for antinuclear antibodies in your blood. Many different types of proteins are found in the nucleus that perform many different functions. Certain diseases are more. Many different types of proteins are found in the nucleus that perform many different functions. Speckled fluorescence due to an antibody directed against different nuclear antigens. A speckled pattern is also found in lupus. The ana test identifies autoantibodies that target substances contained inside cells. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric. Web while an ana test can't confirm a specific diagnosis, it can rule out some diseases. Web positive results are reported as 1) the immunofluorescence pattern (eg homogenous, speckled etc) and 2) the titre to indicate if this is a high positive or low positive ana result. Common ana pattern is speckled; If the test finds antinuclear antibodies in your. Web the most frequent ana patterns were coarse speckled pattern (154 patients, 31.2%), nucleolar pattern (89 patients, 18.0%), fine speckled pattern (57 patients, 11.5%), and speckled pattern (48 patients, 9.7%). Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana are present throughout the nucleus. Web “antinuclear antibodies” are a specific. Samples are initially diluted to a 1 in 80 dilution (titre 1:80). Web a positive nuclear staining result will usually come back with a more detailed staining pattern, such as speckled (fig. Web a homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus. This pattern is almost exclusive to systemic lupus. Rong wang,. Positive results are further diluted to a titre of 1:160, 1:320 and a final titre of 1:640. Web anas present different patterns depending on the staining of the cell nucleus in the laboratory: When antibodies to dna and deoxyribonucleoprotein are present (rim and homogenous pattern), there may be interference with the detection of speckled pattern. It’s also called an ana. The ana test identifies autoantibodies that target substances contained inside cells. A homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled patterns of. Certain diseases are more likely to have certain patterns. While these patterns are not specific to any one illness, certain illnesses can more frequently be associated with one pattern. Web the most frequent ana patterns were coarse speckled pattern (154 patients, 31.2%), nucleolar pattern (89 patients, 18.0%), fine speckled pattern (57 patients, 11.5%), and speckled pattern (48 patients, 9.7%). Web “antinuclear antibodies” are a specific type of antibody directed against the nucleus of a cell. Certain diseases are more likely to have certain patterns. A speckled pattern is also. Web the most frequent ana patterns were coarse speckled pattern (154 patients, 31.2%), nucleolar pattern (89 patients, 18.0%), fine speckled pattern (57 patients, 11.5%), and speckled pattern (48 patients, 9.7%). A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana are present throughout the nucleus. Web a positive nuclear staining result will usually come back with a more detailed staining. Web the most frequent ana patterns were coarse speckled pattern (154 patients, 31.2%), nucleolar pattern (89 patients, 18.0%), fine speckled pattern (57 patients, 11.5%), and speckled pattern (48 patients, 9.7%). The nucleus is essentially the “command centre” or “brain” of any cell in the body. A speckled pattern is also found in lupus. Although the name implies that the test. When antibodies to dna and deoxyribonucleoprotein are present (rim and homogenous pattern), there may be interference with the detection of speckled pattern. Web positive results are reported as 1) the immunofluorescence pattern (eg homogenous, speckled etc) and 2) the titre to indicate if this is a high positive or low positive ana result. This pattern is common in lupus and other connective tissue diseases, such as sjogren's syndrome. Although the name implies that the test detects only autoantibodies directed against components of. Regardless of reproductive condition and cell type, all cells analyzed in this study presented a positive antibody labeling in the nucleoplasm, which was. Web the most frequent ana patterns were coarse speckled pattern (154 patients, 31.2%), nucleolar pattern (89 patients, 18.0%), fine speckled pattern (57 patients, 11.5%), and speckled pattern (48 patients, 9.7%). A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases, including lupus and sjögren’s syndrome. Web while an ana test can't confirm a specific diagnosis, it can rule out some diseases. Web an antinuclear antibody test is a blood test that looks for certain kinds of antibodies in your body. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Many different types of proteins are found in the nucleus that perform many different functions. Web a positive nuclear staining result will usually come back with a more detailed staining pattern, such as speckled (fig. Web speckled pattern correlates with antibody to nuclear antigens extractable by saline; It’s also called an ana or fana (fluorescent antinuclear antibody) test. Web a homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus. An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your own cells, tissues, and/or organs by mistake.
Ana With Speckled Pattern Chumado

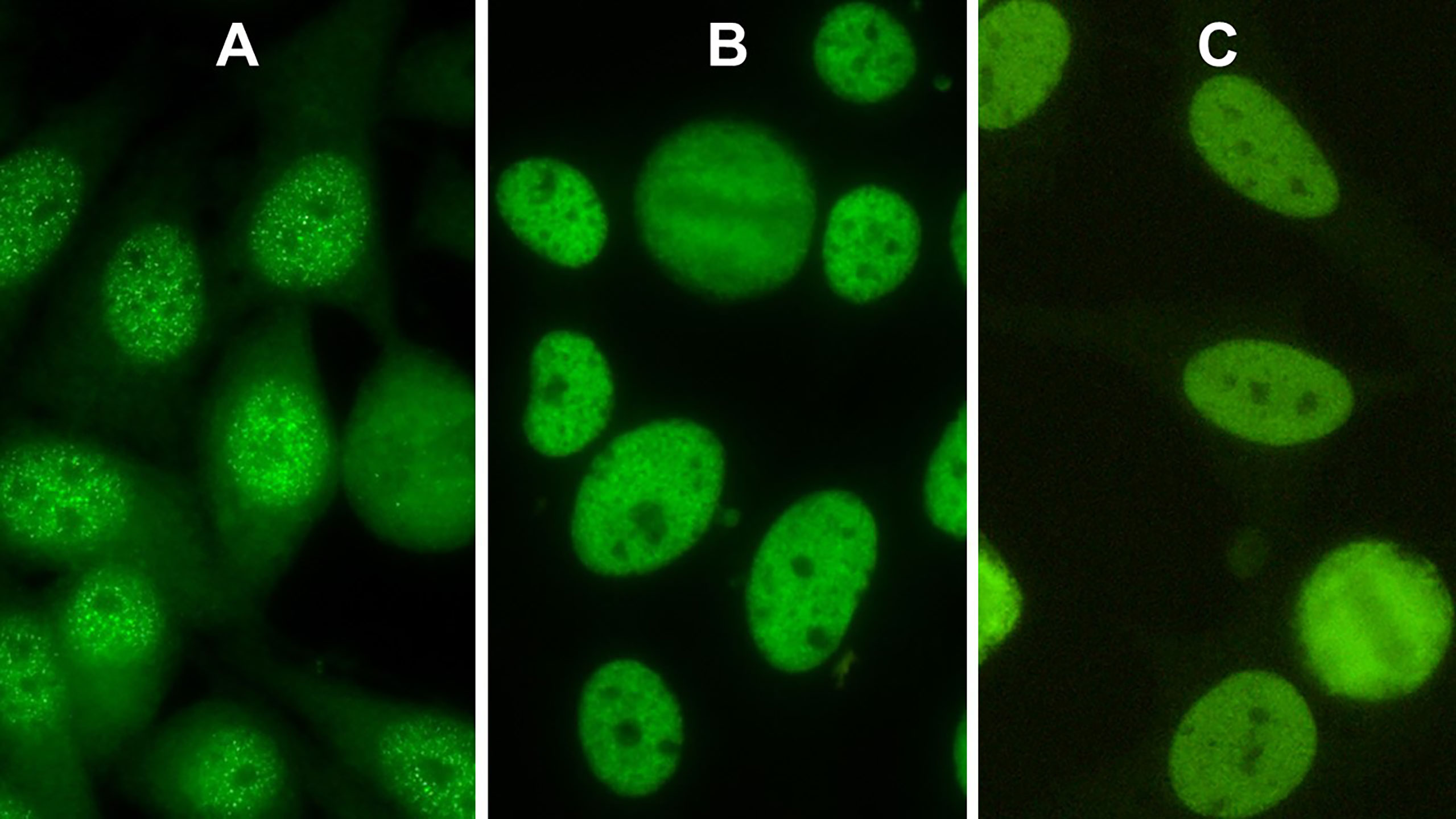
Nuclear speckled antinuclear antibody staining pattern profile. (A
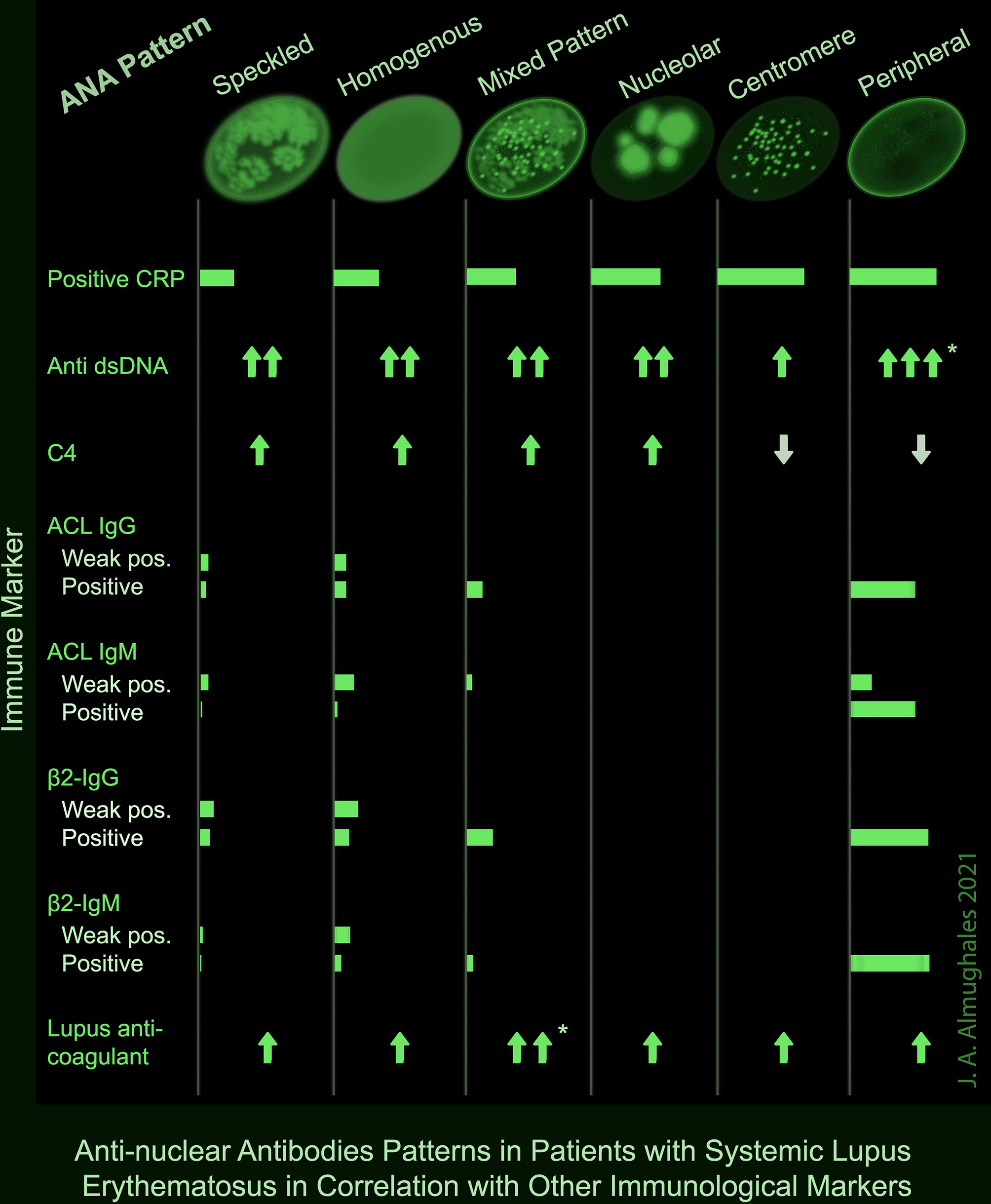
Frontiers AntiNuclear Antibodies Patterns in Patients With Systemic

Nuclear speckled antinuclear antibody staining pattern profile. (A
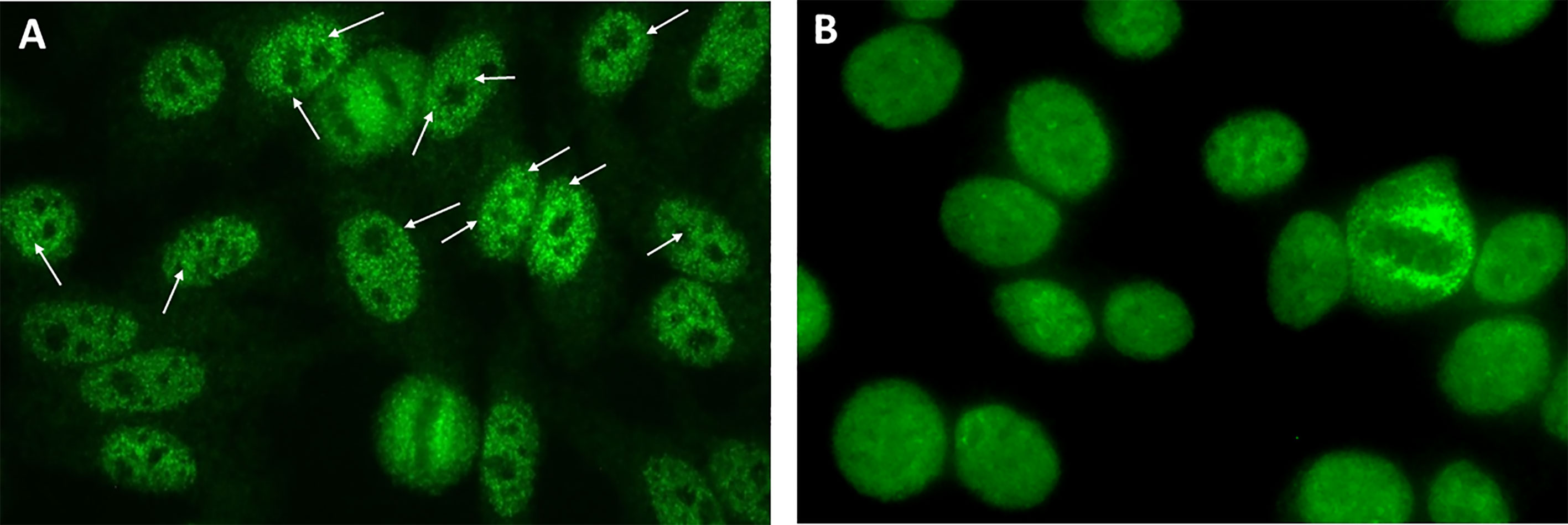
Frontiers Strong Association of the Myriad Discrete Speckled Nuclear
AntiDNA, (antidoublestranded DNA antibodies, AntidsDNA Ab) and

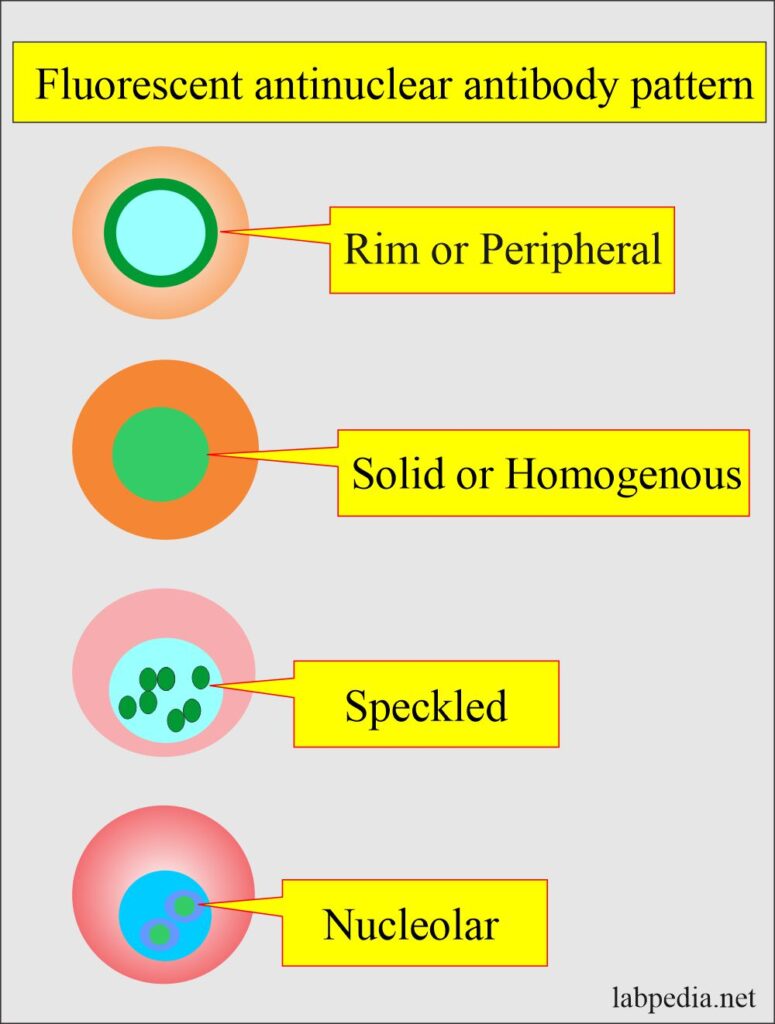
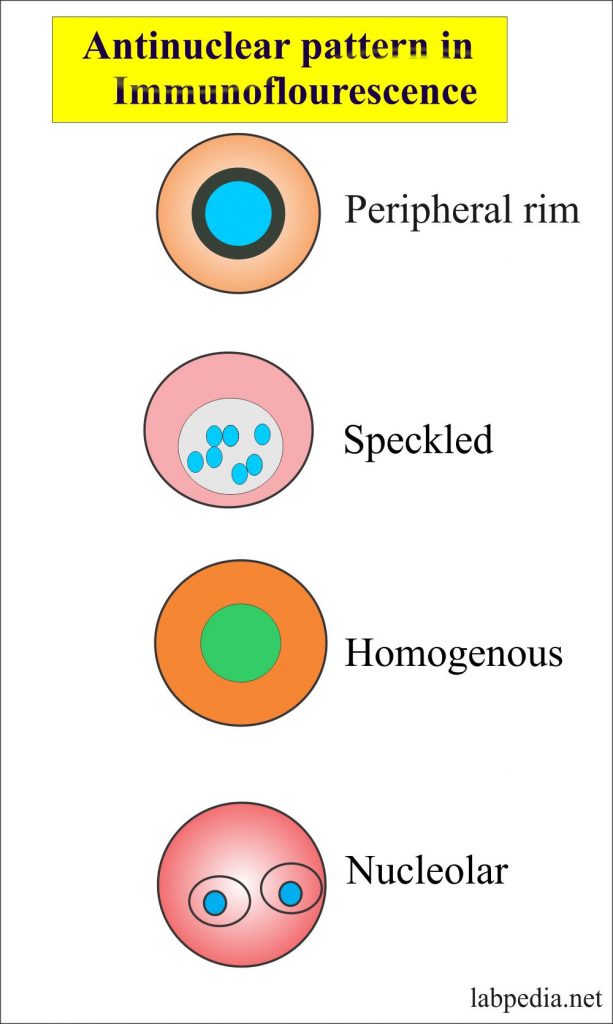
International consensus on antinuclear antibody patterns definition of
Positive Ana Speckled Pattern Chumado
Ana Titer 1 160 Speckled Pattern Chumado
Frontiers Commentary Strong Association of the Myriad Discrete
The Ana Test Identifies Autoantibodies That Target Substances Contained Inside Cells.
Samples Are Initially Diluted To A 1 In 80 Dilution (Titre 1:80).
Web A Positive Ana Test Is Usually Reported As Both A Ratio (Called A Titer) And A Pattern, Such As Smooth Or Speckled.
While These Patterns Are Not Specific To Any One Illness, Certain Illnesses Can More Frequently Be Associated With One Pattern Or Another.
Related Post: