Non Mendelian Patterns Of Inheritance
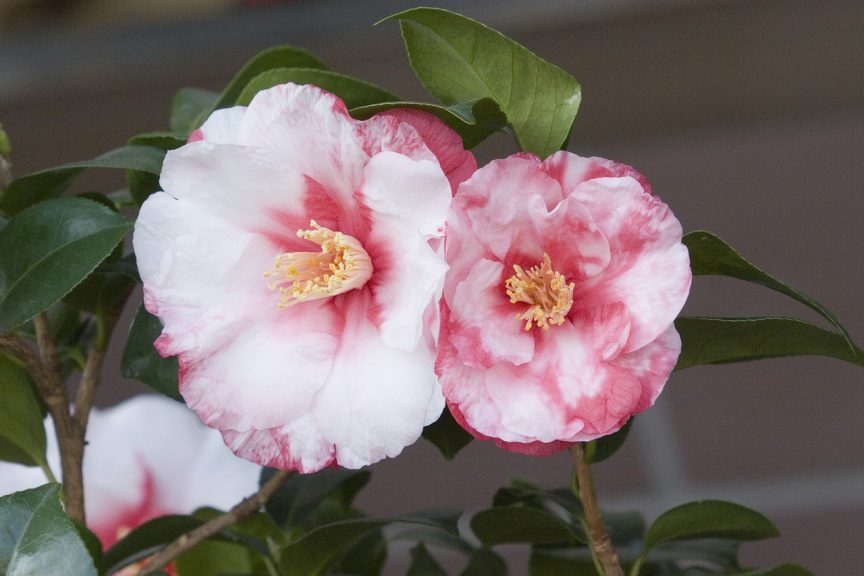
Non Mendelian Patterns Of Inheritance - Web in this tutorial, find out more about certain types of inheritance that does not follow the mendelian inheritance patterns. Examples are incomplete dominance and complete dominance. Explain how a trait with incomplete dominance will appear in a population. In mendelian inheritance, each parent contributes one of two possible alleles for a trait. In this section we’ll look at incomplete dominance and codominance, comparing them directly to complete dominance. Web the main difference between mendelian and non mendelian inheritance is that mendelian inheritance describes the determination of traits by means of dominant and recessive alleles of a particular gene whereas non mendelian inheritance describes the inheritance of traits which does not follow mendelian laws. These laws describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus. A black sheep is bred with a white sheep. Two alleles may produce an intermediate phenotype when both are present, rather than one fully determining the phenotype. It describes the inheritance of traits linked to a single gene on chromosomes. How do eyes come in so many colors? Many times inheritance is more complicated than the simple patterns observed by mendel. Web this pattern of inheritance is described as incomplete dominance, denoting the expression of two contrasting alleles such that the individual displays an intermediate phenotype. The allele for red flowers is incompletely dominant over the allele for white flowers.. They often lack uniformity in their expression in the progeny generation as they do not segregate uniformly among the progenies. These pink flowers of a heterozygote snapdragon result from incomplete dominance. Polygenic inheritance and environmental effects. Web the main difference between mendelian and non mendelian inheritance is that mendelian inheritance describes the determination of traits by means of dominant and. In these cases, molecular analysis predicts disease status relatively directly. In this section we’ll look at incomplete dominance and codominance, comparing them directly to complete dominance. Multiple allele inheritance is when a gene that is controlled by more than two alleles (e.g. Web as for incomplete dominance, we can still use mendel's rules to predict inheritance of codominant alleles. Web. Compare and contrast incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, polygenic, pleiotropy, epistasis, and epigenetics. These pink flowers of a heterozygote snapdragon result from incomplete dominance. Polygenic inheritance and environmental effects. When scientists began exploring more and more test crosses, they observed that there are several traits that do not match up with mendel’s laws. These laws describe the inheritance of traits. For example, if two people with \(l^ml^n\) genotypes had children, we would expect to see m, mn, and n blood types and \(l^ml^m\), \(l^ml^n\), and \(l^nl^n\) genotypes in their children in a \(1:2:1\) ratio (if they had. These laws describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus. Some of the variations on mendel’s rules. Web as for incomplete dominance, we can still use mendel's rules to predict inheritance of codominant alleles. Single gene disorders with mendelian inheritance patterns have contributed greatly to the identification of genes and pathways implicated in genetic disease. These laws describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus. These laws describe the inheritance of. Web the main difference between mendelian and non mendelian inheritance is that mendelian inheritance describes the determination of traits by means of dominant and recessive alleles of a particular gene whereas non mendelian inheritance describes the inheritance of traits which does not follow mendelian laws. Web codominance is a pattern of heredity in which both alleles are simultaneously expressed in. Explain how a trait with incomplete dominance will appear in a population. Explain why the human abo blood group is an example of a multiple allele trait with codominance. It describes the inheritance of traits linked to a single gene on chromosomes. In mendelian inheritance, each parent contributes one of two possible alleles for a trait. For example, if two. How do eyes come in so many colors? They often lack uniformity in their expression in the progeny generation as they do not segregate uniformly among the progenies. It describes the inheritance of traits linked to a single gene on chromosomes. Examples are incomplete dominance and complete dominance. These pink flowers of a heterozygote snapdragon result from incomplete dominance. Explain the genetic basis of human skin color. Polygenic inheritance and environmental effects. These pink flowers of a heterozygote snapdragon result from incomplete dominance. Some of the variations on mendel’s rules involve single genes. They are not specific to the dominant or recessive expression of an allele. Explain how a trait with incomplete dominance will appear in a population. Web codominance is a pattern of heredity in which both alleles are simultaneously expressed in the heterozygote (e.g. These pink flowers of a heterozygote snapdragon result from incomplete dominance. How may the human trait of adult height be. How do eyes come in so many colors? In these cases, molecular analysis predicts disease status relatively directly. Many times inheritance is more complicated than the simple patterns observed by mendel. For example, if two people with \(l^ml^n\) genotypes had children, we would expect to see m, mn, and n blood types and \(l^ml^m\), \(l^ml^n\), and \(l^nl^n\) genotypes in their children in a \(1:2:1\) ratio (if they had. It describes the inheritance of traits linked to a single gene on chromosomes. They are not specific to the dominant or recessive expression of an allele. Multiple allele inheritance is when a gene that is controlled by more than two alleles (e.g. Web the main difference between mendelian and non mendelian inheritance is that mendelian inheritance describes the determination of traits by means of dominant and recessive alleles of a particular gene whereas non mendelian inheritance describes the inheritance of traits which does not follow mendelian laws. Explain why the human abo blood group is an example of a multiple allele trait with codominance. Compare and contrast incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, polygenic, pleiotropy, epistasis, and epigenetics. Multiple allele traits are controlled by a single gene with more than two alleles. These laws describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus.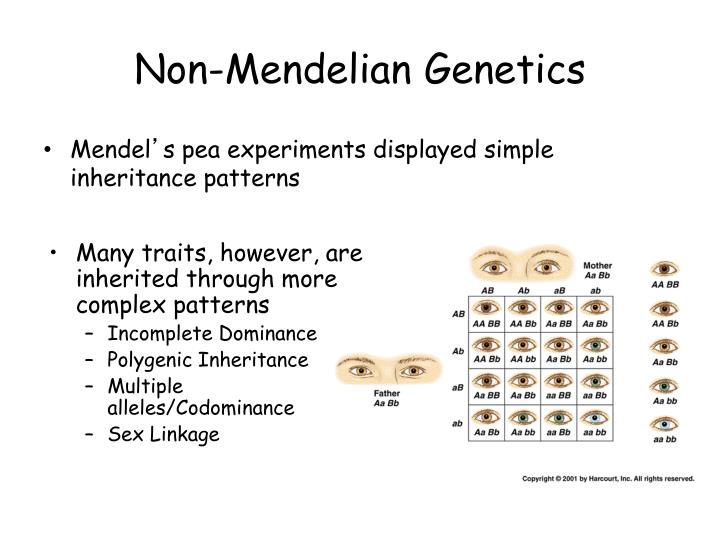
PPT Non Mendelian PowerPoint Presentation ID3719666
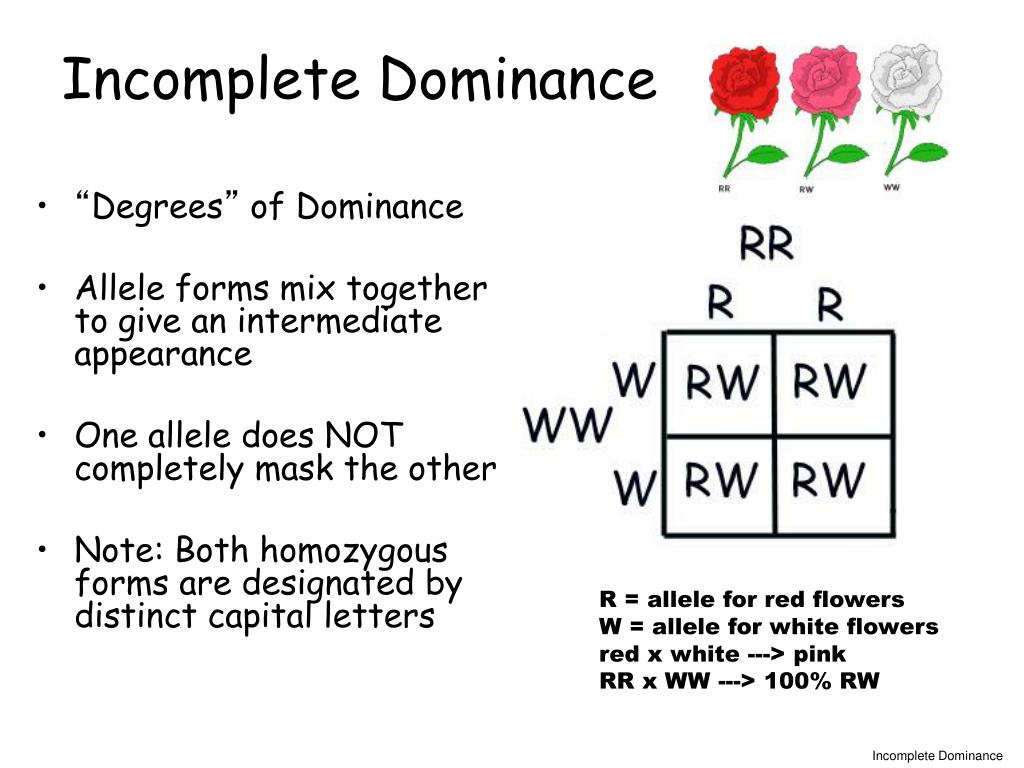
PPT Non Mendelian PowerPoint Presentation, free download
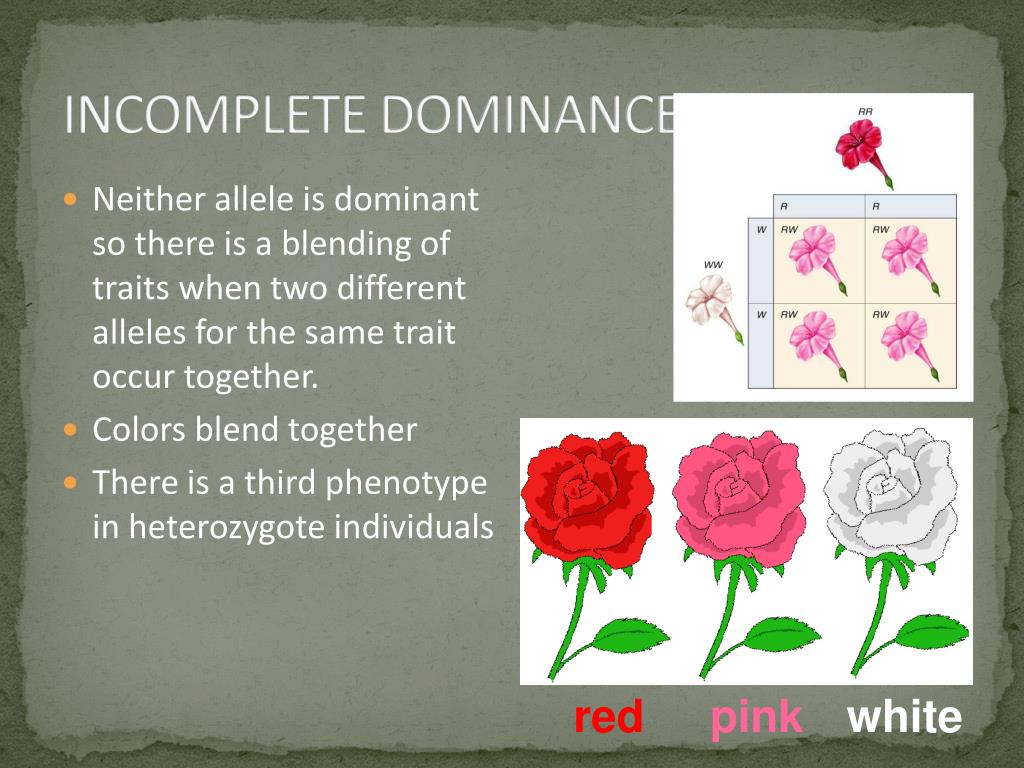
PPT Non Mendelian Inheritance Patterns PowerPoint Presentation, free

PPT NONMENDELIAN INHERITANCE PATTERNS (Modes of Inheritance) H

NonMendelian Inheritance Biology Online Tutorial
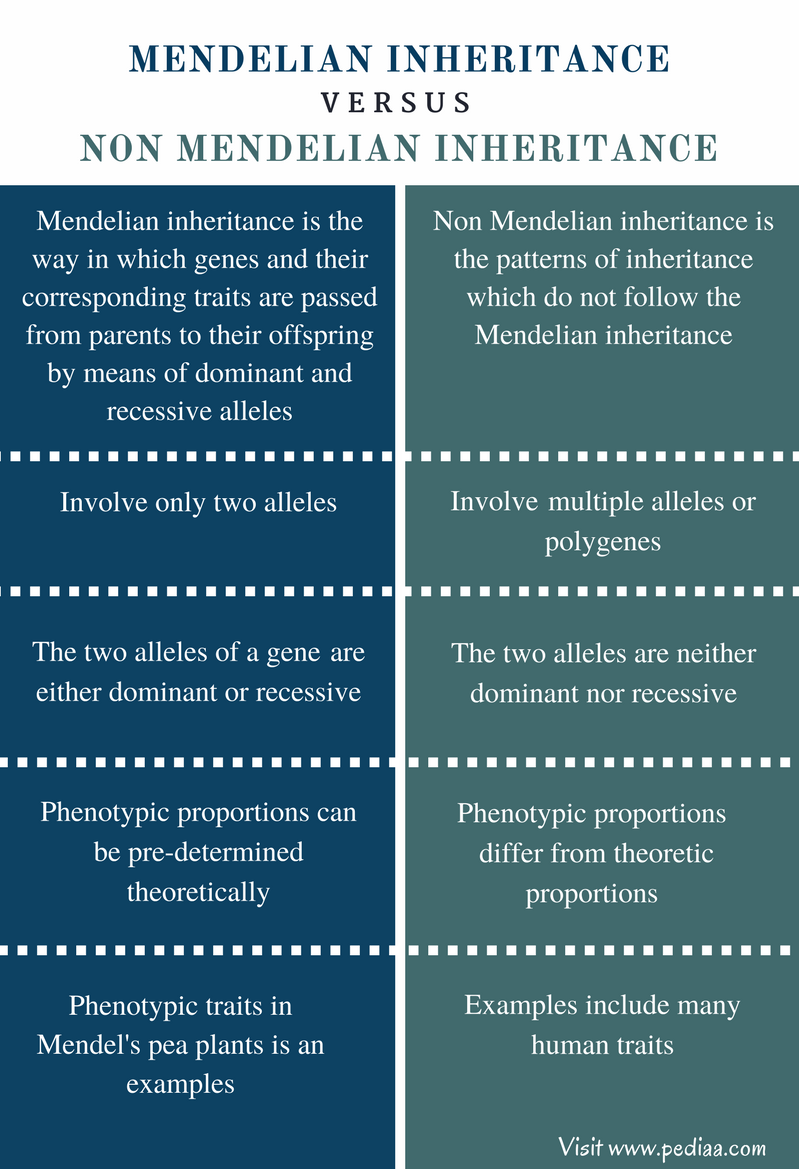
NonMendelian Inheritance Study Guide Inspirit Learning Inc

Mendelian and nonMendelian inheritance in Paramecium. (a) Mendelian
Non mendelian
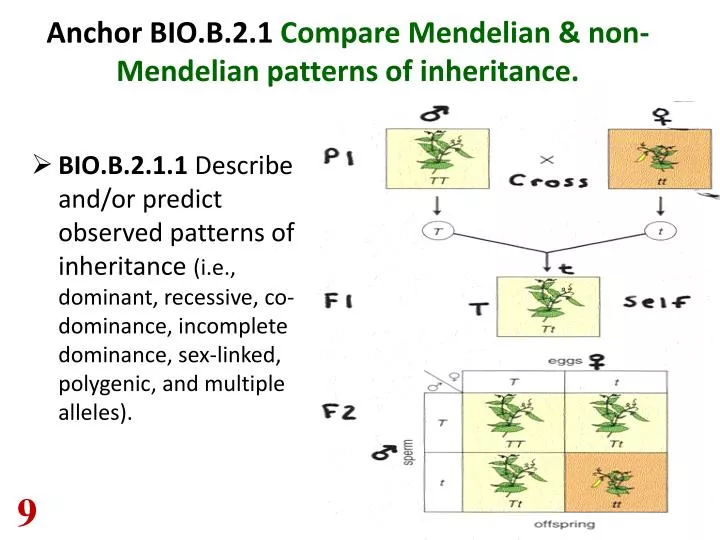
PPT Anchor BIO.B.2.1 Compare Mendelian & nonMendelian patterns of

PPT Non Mendelian Inheritance Patterns PowerPoint Presentation, free
In Mendelian Inheritance, Each Parent Contributes One Of Two Possible Alleles For A Trait.
Web In This Tutorial, Find Out More About Certain Types Of Inheritance That Does Not Follow The Mendelian Inheritance Patterns.
The Allele For Red Flowers Is Incompletely Dominant Over The Allele For White Flowers.
These Laws Describe The Inheritance Of Traits Linked To Single Genes On Chromosomes In The Nucleus.
Related Post: