Myotonic Dystrophy Inheritance Pattern
Myotonic Dystrophy Inheritance Pattern - In genetics, inheritance doesn’t refer to property or financial assets. Web inheritance both types of myotonic dystrophy are inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. Myotonic dystrophy is rare, autosomal dominant muscle disorder. As myotonic dystrophy is passed from one generation to the next, the disorder generally It is a subtype of myotonic dystrophy type 1. Web myotonic dystrophy is caused by a specific genetic change (mutation) within the dmpk gene on chromosome 19. Web myotonic dystrophy is a genetic condition that causes progressive muscle weakness and wasting. In most cases, an affected person has one parent with the condition. Web both dm1 and dm2 are inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning it takes only one flawed allele, one copy carrying the abnormal expansion, to cause symptoms of the disease. When a trait is autosomal dominant, only one parent needs to have an altered gene to pass it on. Half of the children of a biological parent with an autosomal trait will get that trait. They result in multisystem disorders characterized by skeletal muscle weakness and myotonia (difficulty relaxing muscles after use), cardiac abnormalities, cataracts, and other abnormalities. Both types of myotonic dystrophy are inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. How does repeat length relate to the severity of. Autosomal refers to the type of chromosome that carries the dm mutation—autosomes versus sex chromosomes. The two forms of the disease are genetically distinct. How genetic neuromuscular disease is passed from one generation to another. Both affect voluntary muscles and one also affects involuntary muscles. Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (dm1) and myotonic dystrophy type 2 (dm2), both dominantly inherited with. The clinical findings, which span a continuum from mild to severe, have been categorized into three somewhat overlapping phenotypes: If one parent has the disorder, every child of that person has a 50% chance of inheriting the gene flaw that causes it. Facebook twitter linkedin email printfriendly share. It is a subtype of myotonic dystrophy type 1. The normal number. In most cases, an affected person has one parent with the condition. How genetic neuromuscular disease is passed from one generation to another. Over time, a person may lose their strength and have issues. The wide variability in the scope and severity of dm1 symptoms, even within the same family. In autosomal dominant inheritance, having one copy of the altered. When a trait is autosomal dominant, only one parent needs to have an altered gene to pass it on. Web myotonic dystrophy (dm) is a type of muscular dystrophy, a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle loss and weakness. While dm2 is caused by the expansion of a cctg tetramer in cnbp on chromosome 3. How genetic neuromuscular. The condition follows a ‘dominant’ inheritance pattern, which means. The dmpk gene contains lots of cs,ts and gs repeated over and over like this:. Web myotonic dystrophy (dm) includes two major types — dm1 and dm2 — both caused by genetic defects. Facebook twitter linkedin email printfriendly share. Myotonia is classically absent in infancy. Our dna is made up of lots of individual building blocks represented by the letters a,c,t and g. The condition follows a ‘dominant’ inheritance pattern, which means. Myotonia is classically absent in infancy. When a trait is autosomal dominant, only one parent needs to have an altered gene to pass it on. The normal number of ctg repeats in this. While dm2 is caused by the expansion of a cctg tetramer in cnbp on chromosome 3. How genetic neuromuscular disease is passed from one generation to another. In autosomal dominant inheritance, having one copy of the altered (mutated) gene in each cell will cause the disorder. Disease mechanism | myotonic dystrophy foundation. Web myotonia is characterized by impaired relaxation of. It is the process by which genetic information is. When a trait is autosomal dominant, only one parent needs to have an altered gene to pass it on. Web the inheritance pattern of disease (autosomal dominant inheritance). The normal number of ctg repeats in this region is 5 to 37. Half of the children of a biological parent with an. They result in multisystem disorders characterized by skeletal muscle weakness and myotonia (difficulty relaxing muscles after use), cardiac abnormalities, cataracts, and other abnormalities. When a trait is autosomal dominant, only one parent needs to have an altered gene to pass it on. Both types of myotonic dystrophy are inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Web both type 1 and type. The clinical findings, which span a continuum from mild to severe, have been categorized into three somewhat overlapping phenotypes: In dm, muscles are often unable to relax after contraction. The possibility of changes in symptom scope and severity over time. Disease mechanism | myotonic dystrophy foundation. How genetic neuromuscular disease is passed from one generation to another. Web myotonic dystrophy (dm) is a type of muscular dystrophy, a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle loss and weakness. Both affect voluntary muscles and one also affects involuntary muscles. How does repeat length relate to the severity of myotonic dystrophy? Web myotonic dystrophy (dm) includes two major types — dm1 and dm2 — both caused by genetic defects. Let’s break that language down. The condition is clinically and genetically heterogeneous, typically affecting the skeletal muscle with characteristic paradoxical weakness, wasting, and myotonia [ 1 ]. It typically affects muscles of movement and commonly the electrical conduction system of the heart, breathing muscles, swallowing muscles, bowels, lens of the eye and brain. Web congenital myotonic dystrophy (cmd) is an autosomal dominant neuromuscular disorder with multisystem involvement. Web myotonic dystrophy is a genetic condition that causes progressive muscle weakness and wasting. Features include severe hypotonia and generalized muscle weakness; Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (dm1) and myotonic dystrophy type 2 (dm2), both dominantly inherited with significant overlap in clinical manifestations.
Figure 1 from Myotonic Dystrophy Type 2 An Update on Clinical Aspects
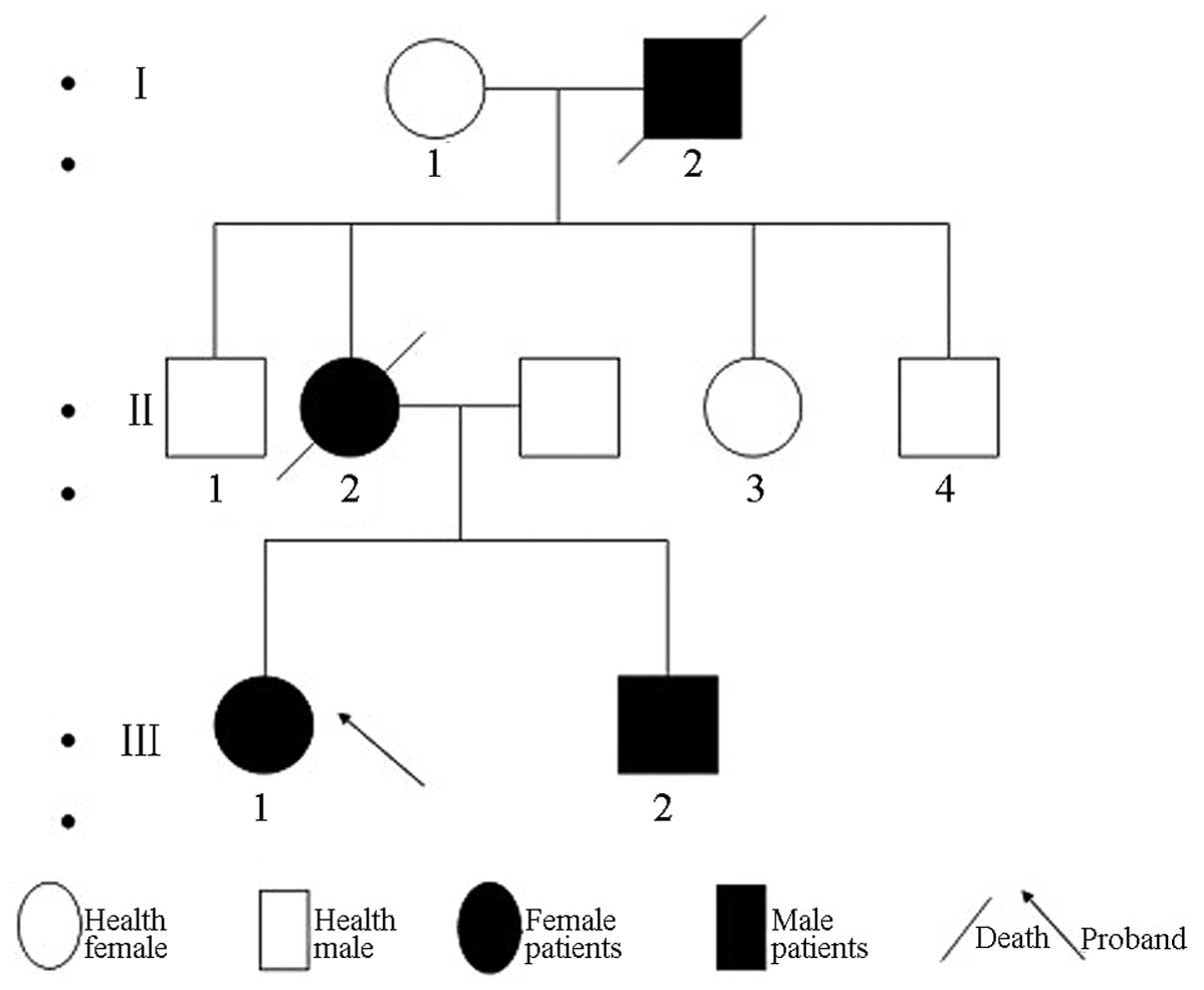
Clinical, pathological and characteristics of a pedigree with

Muscular Dystrophy Inheritance Pattern
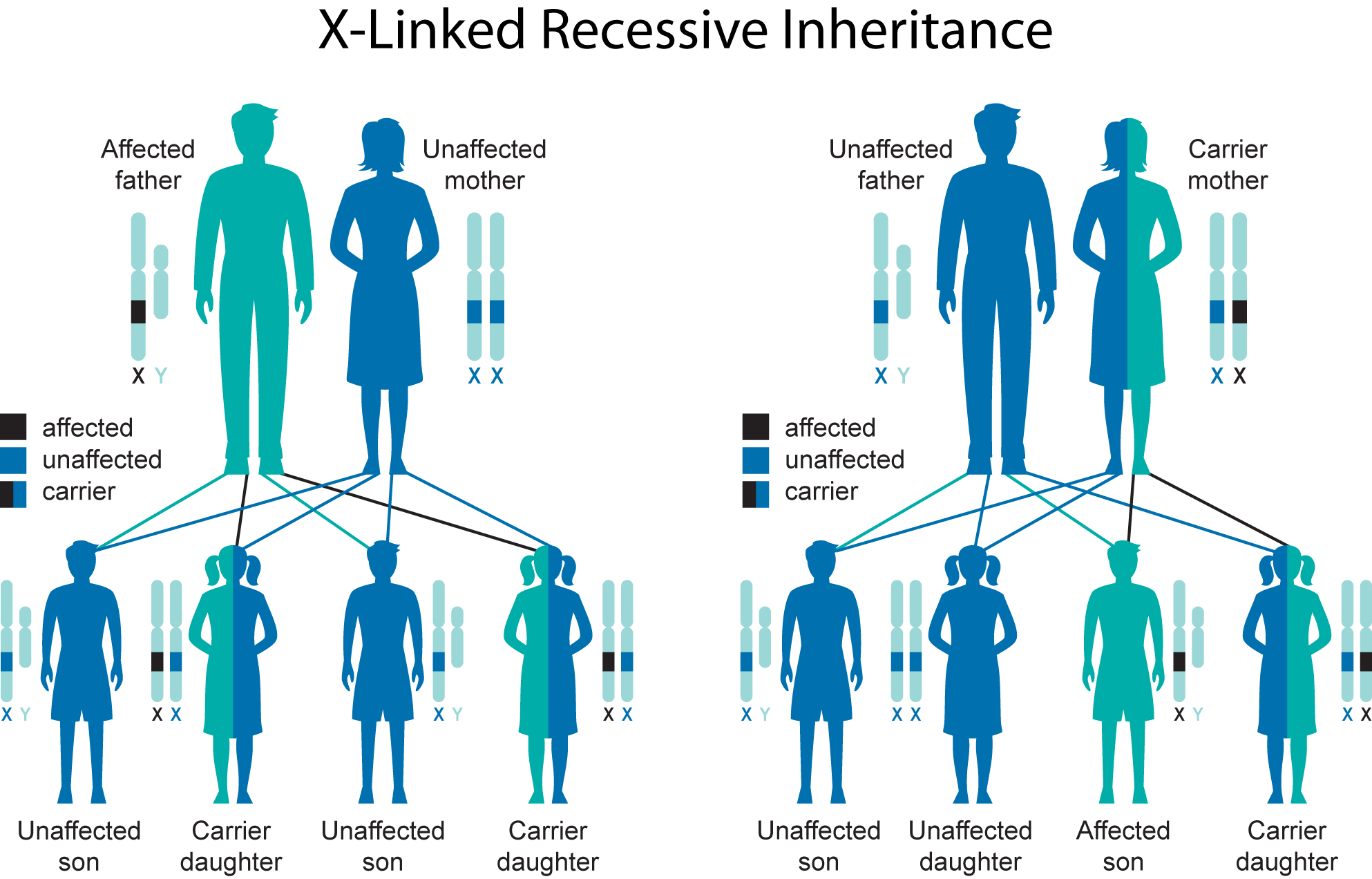
and Inheritance NFED
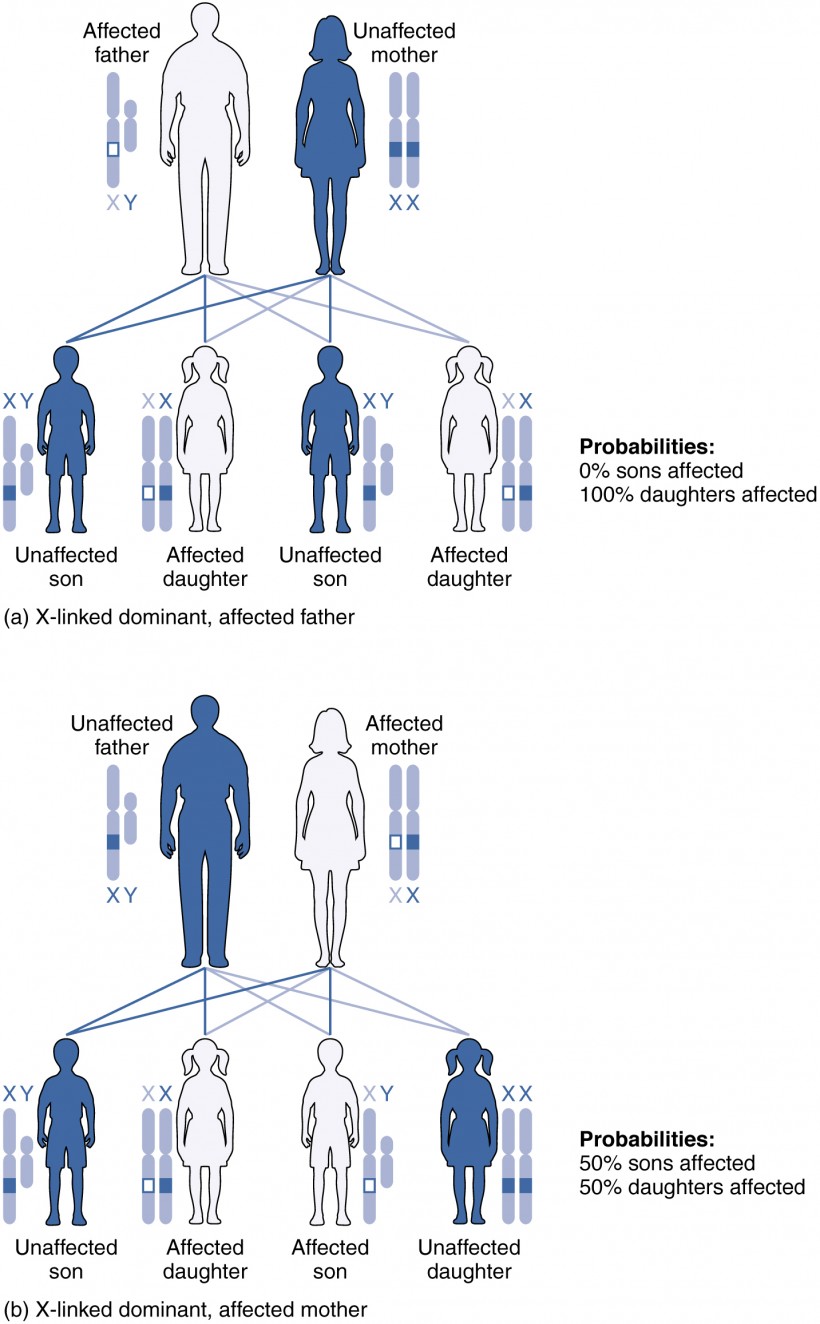
Patterns of Inheritance Anatomy and Physiology II

Muscular Dystrophy Causes, Types, Symptoms, Prognosis, Treatment

Shank sign in myotonic dystrophy type1 (DM1) Journal of Clinical

Steinert's myotonic dystrophy Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment

The given pedigree shows inheritance of1) Myotonic dystrophy2

Myotonic dystrophy gradually worsening muscle loss and weakness
Web By Amy Bernstein | Wednesday, February 16, 2022.
Symptoms Begin At Adolescence Or Early Adulthood And Include Myotonia, Weakness, And Wasting Of Distal Limb Muscles And Facial Muscles.
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance, Having One Copy Of The Altered (Mutated) Gene In Each Cell Will Cause The Disorder.
Web Both Dm1 And Dm2 Are Inherited In An Autosomal Dominant Pattern, Meaning It Takes Only One Flawed Allele, One Copy Carrying The Abnormal Expansion, To Cause Symptoms Of The Disease.
Related Post: