Microservices Saga Pattern
Microservices Saga Pattern - For some reason the first saga s1 ends up needing to be compensated, so its compensation logic tries to withdraw the $100 originally deposited. Multiphase commits, a wider boundary context (saga patterns), and nested. A microservice publishes an event for every transaction, and the next transaction is initiated based on the event's outcome. Any data sharing between microservices must be implicit, usually by way of a messaging framework. Basically, it’s a sequence of transactions. Web therefore, this pattern helps to manage the consistency of data in the execution of distributed transactions among various microservices. Web the saga pattern is an architectural pattern for implementing a sequence of local transactions that helps maintain data consistency across different microservices. Each of these local transactions will update that service data store, and then sends a message or event to trigger the next local transaction in the saga. Web my book microservices patterns describes this pattern in a lot more detail. The saga pattern uses a sequence of local transactions (transactions within a service). This pattern ensures that the. This pattern helps manage data consistency across microservices in distributed transaction scenarios. This pattern is used to manage and maintain data consistency across multiple microservices. Web the saga design pattern is a way to manage data consistency across microservices in distributed transaction scenarios. In the saga pattern, each step. Web the following two patterns can resolve the problem: Web one of the major problems in a microservice architecture is how to handle a transaction that spans multiple services. Web what is saga pattern? A saga is a sequence of transactions that updates each service and publishes a message or event to trigger the next transaction step. Web therefore, this. A saga is a sequence of transactions that updates each service and publishes a message or event to trigger the next transaction step. The saga pattern uses a sequence of local transactions (transactions within a service). Web the saga choreography pattern helps preserve data integrity in distributed transactions that span multiple services by using event subscriptions. Web the following two. Web the saga design pattern is a way to manage data consistency across microservices in distributed transaction scenarios. A microservice purist ignores the real world issues of adopting an eventual consistency pattern. This pattern helps manage data consistency across microservices in distributed transaction scenarios. Any data sharing between microservices must be implicit, usually by way of a messaging framework. It. Each transaction is executed by a single service, and the state changes are broadcasted to other services involved in the saga. 2pc is widely used in database systems. Api gateway acts as a single entry point for clients and routes requests to appropriate microservices, often handling authentication, rate limiting, and caching. Web my book microservices patterns describes this pattern in. This pattern helps manage data consistency across microservices in distributed transaction scenarios. Web the saga pattern is as microservices architectural pattern to implement a transaction that spans multiple services. Web the following two patterns can resolve the problem: Basically, saga patterns offers to create a set of transactions that. Web the second saga s2 withdraws that $100 and closes/finalizes. Web this guide details integrating microservices for scalable, flexible software, covering design, data consistency,. The following diagram contains the rollback events in red color, which is a part of the saga workflow. Saga is an architectural pattern that provides an elegant approach to implement a transaction that spans multiple services and is asynchronous and reactive in nature. In this tutorial,. Web the saga design pattern focuses on adding data consistency and rollback capabilities to distributed microservices transactions and complex, decoupled operations. Web the saga (or saga) pattern is a microservice design pattern for managing data consistency in distributed systems. A microservice purist ignores the real world issues of adopting an eventual consistency pattern. Each smaller transaction is known as a. Each service in a saga. The saga pattern is a design pattern used to manage transactions and ensure data consistency across multiple services in a distributed system, especially in a microservices architecture. There are 2 saga pattern. Any data sharing between microservices must be implicit, usually by way of a messaging framework. The first transaction in a saga is initiated. Web my book microservices patterns describes this pattern in a lot more detail. This pattern is used to manage and maintain data consistency across multiple microservices. The following diagram contains the rollback events in red color, which is a part of the saga workflow. Basically, it’s a sequence of transactions. In this article, we’ll explore why and. It involves different actors (services) that go to act on the same entity through individual transactions aimed at updating a common data. Web the saga pattern is a failure management pattern that helps establish consistency in distributed applications, and coordinates transactions between multiple microservices to maintain data consistency. One of the problems to solve in a microservices architecture is how to handle a transaction across multiple services. Web the saga pattern is an important pattern when implementing event driven architectures. The saga pattern is the solution to implementing business transactions spanning multiple microservices. In this tutorial, we’ll explore the saga architecture pattern that lets us manage distributed transactions in a microservice architecture. Web my book microservices patterns describes this pattern in a lot more detail. Web one of the major problems in a microservice architecture is how to handle a transaction that spans multiple services. This pattern is used to manage and maintain data consistency across multiple microservices. Web the saga pattern is an architectural pattern for implementing a sequence of local transactions that helps maintain data consistency across different microservices. In a distributed transaction, multiple services can be called before a transaction is completed. This pattern ensures that the. Each of these local transactions will update that service data store, and then sends a message or event to trigger the next local transaction in the saga. Web the saga pattern is as microservices architectural pattern to implement a transaction that spans multiple services. Web the saga design pattern is provide to manage data consistency across microservices in distributed transaction cases. A saga is a sequence of transactions that updates each service and publishes a message or event to trigger the next transaction step.
Saga Pattern in Microservices Baeldung on Computer Science
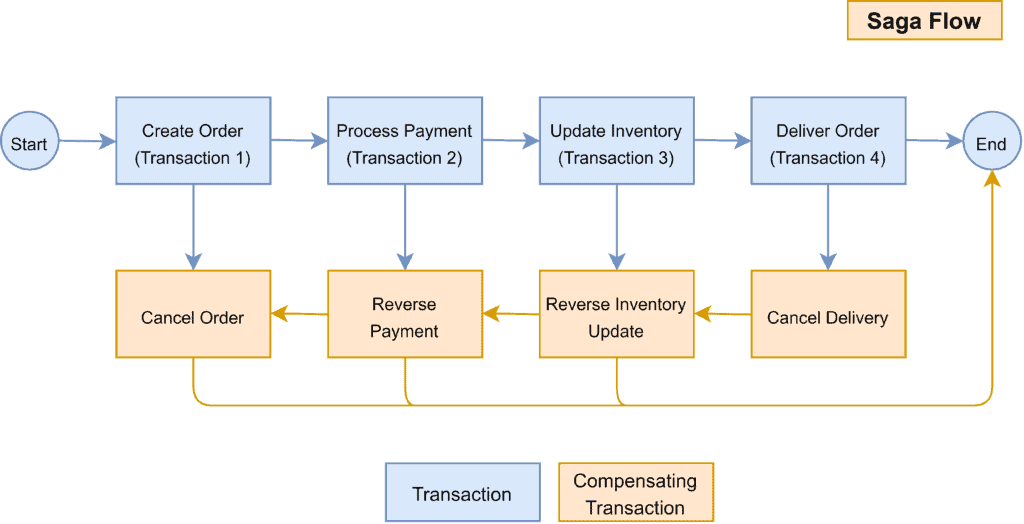
Saga Pattern in Microservices Baeldung on Computer Science
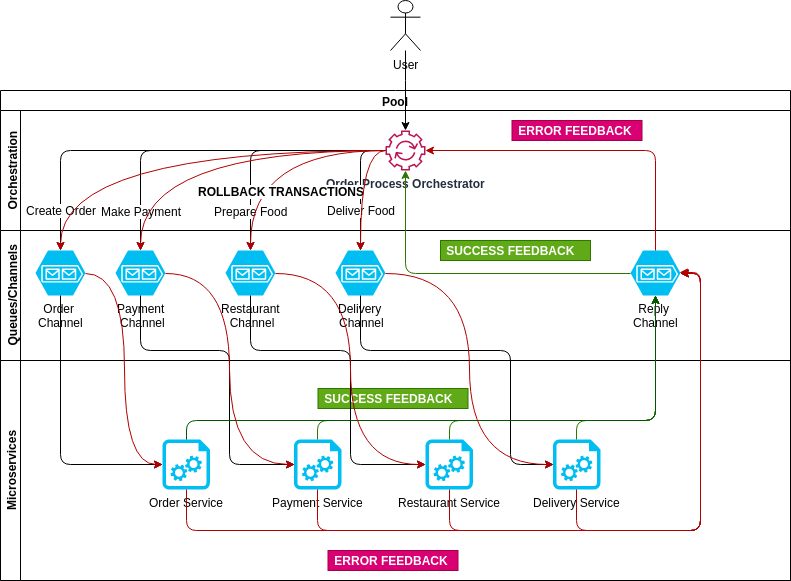
Microservices SAGA orchestration pattern Prakhar Srivastav
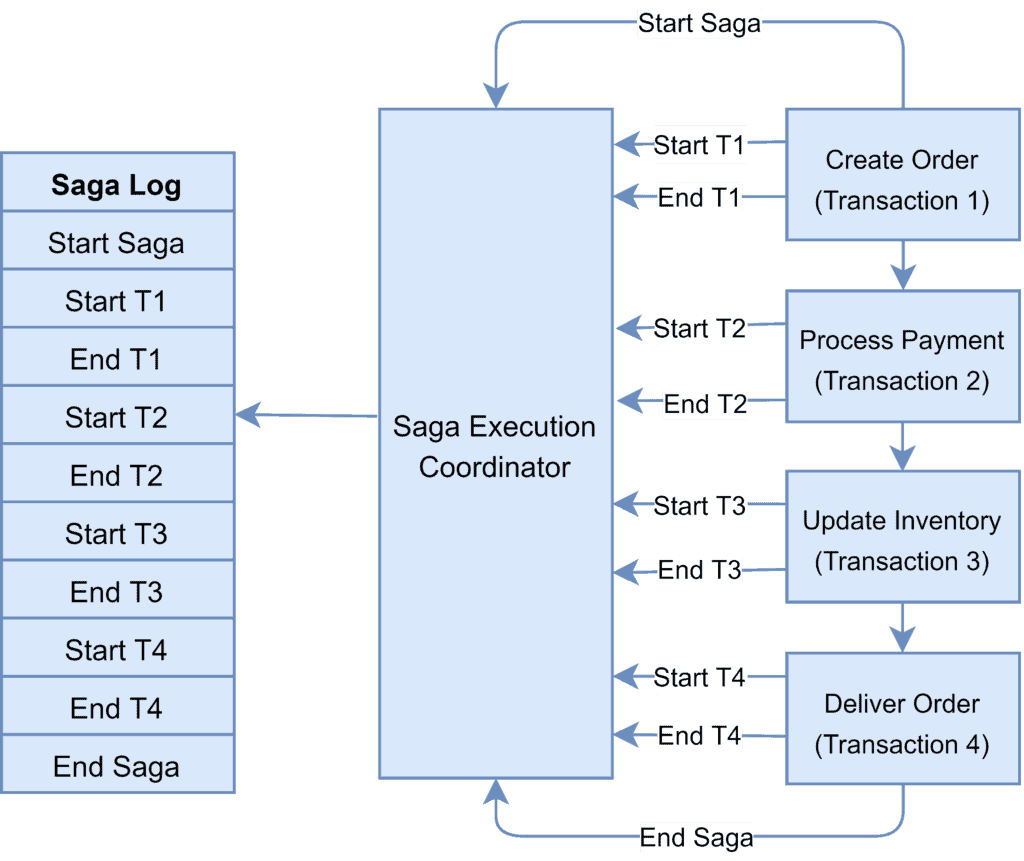
Saga Pattern in Microservices Baeldung on Computer Science
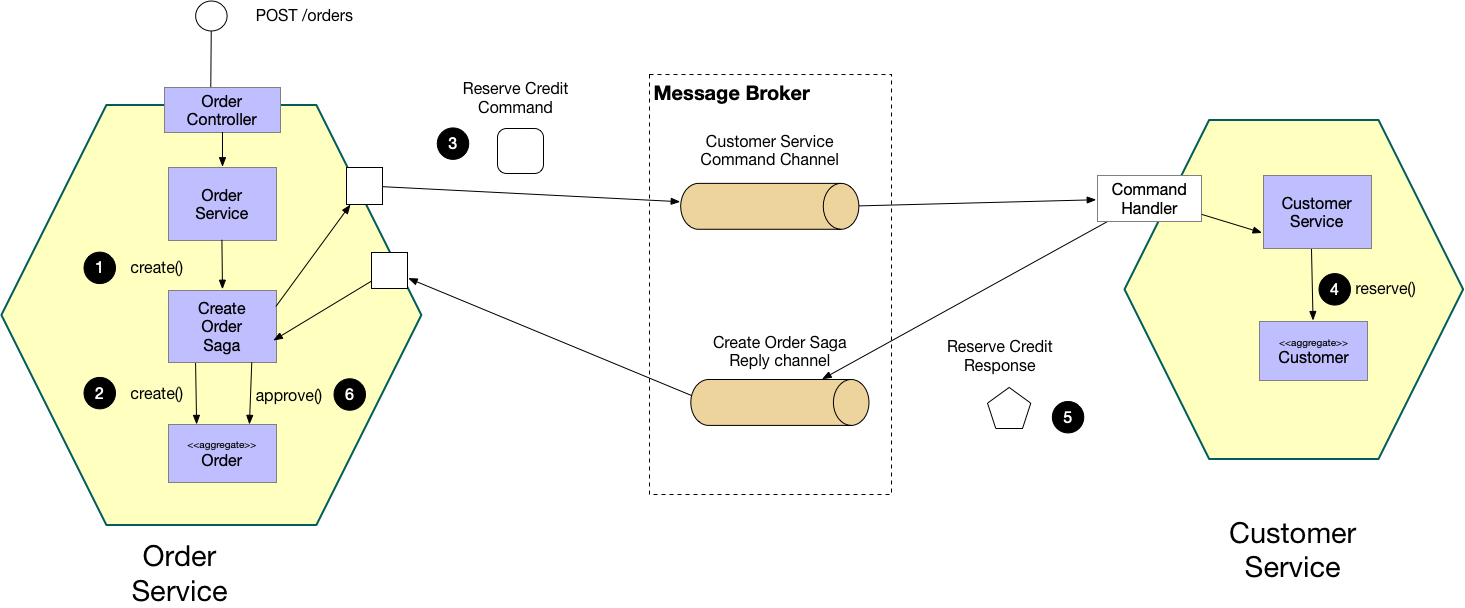
Saga Design Pattern Microservices Example Pattern Design Ideas

SAGA Design Pattern In Java Microservices with Example Java67

Saga Pattern in Microservices Baeldung on Computer Science
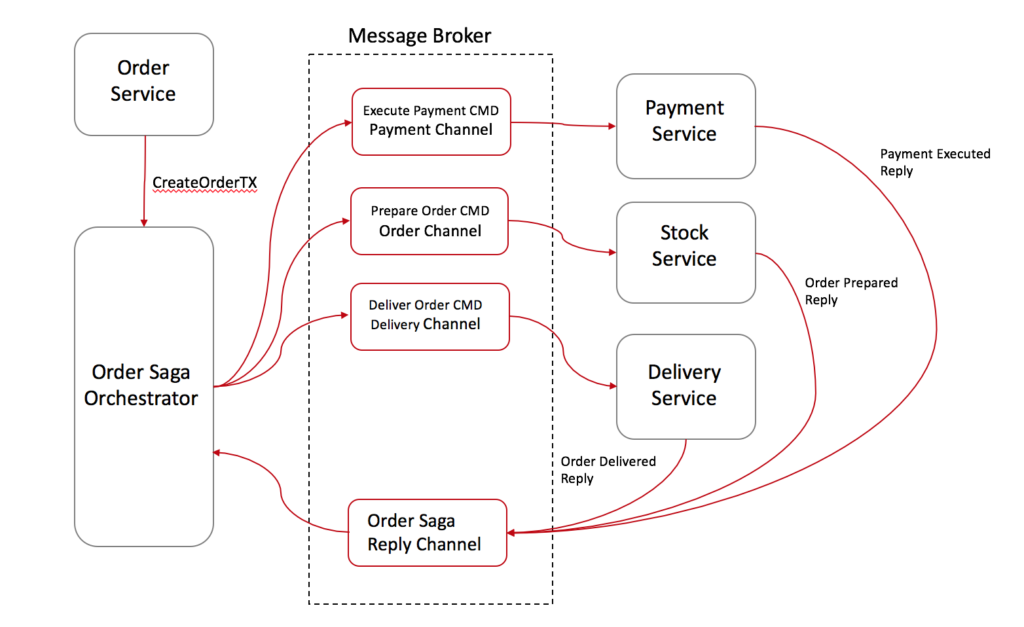
Saga Pattern How to implement business transactions using

Saga Pattern in Microservices Baeldung on Computer Science
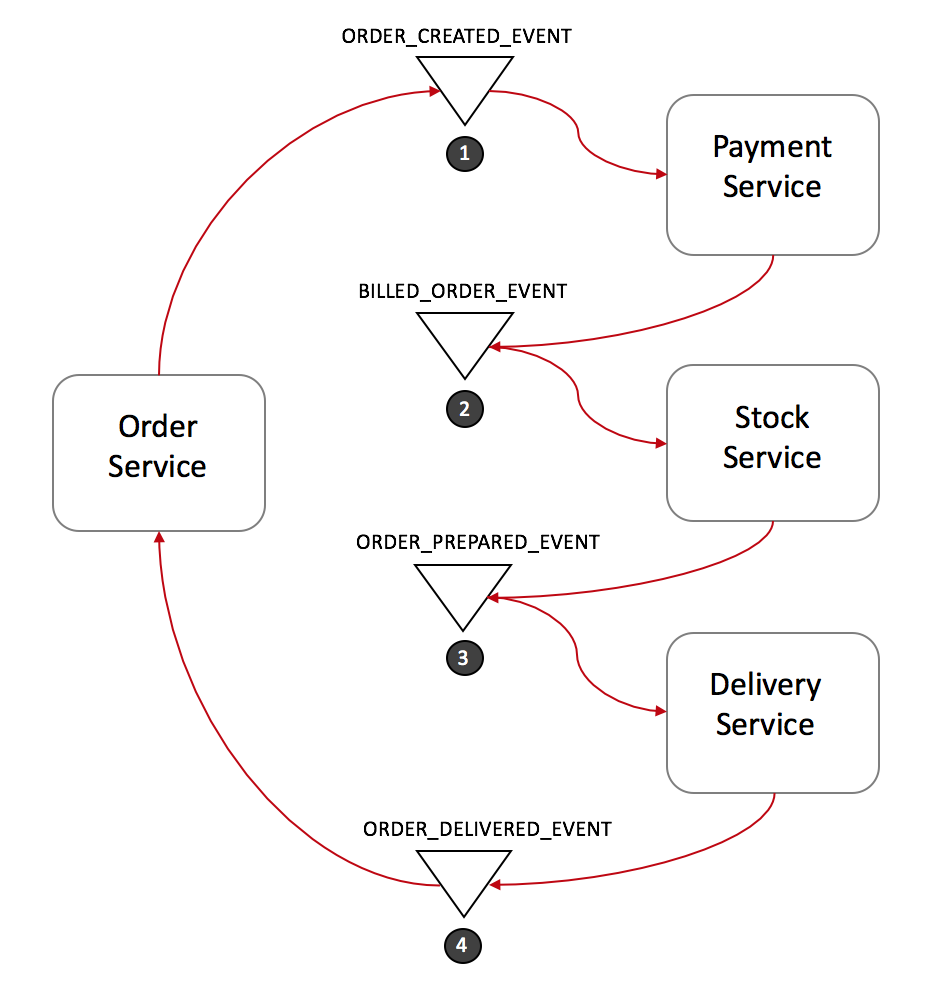
Saga Pattern Microservices Design Examples Couchbase
Web The Saga Design Pattern Is A Way To Manage Data Consistency Across Microservices In Distributed Transaction Scenarios.
Web The Saga Choreography Pattern Helps Preserve Data Integrity In Distributed Transactions That Span Multiple Services By Using Event Subscriptions.
Basically, Saga Patterns Offers To Create A Set Of Transactions That.
Each Transaction Is Executed By A Single Service, And The State Changes Are Broadcasted To Other Services Involved In The Saga.
Related Post: