Lung Patterns Dogs
Lung Patterns Dogs - Emphasis will be placed on the diagnostic evaluation, paying special attention to interpretation of imaging findings and discrimination of these. The lung appears diffusely more opaque or hazy. An alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Web there are 4 pulmonary patterns described. Web common lung patterns include: Web all four lung patterns were represented with the same frequency (four hundred rois). Radiographic abnormalities may help identify or suggest a primary cause of pulmonary hypertension; Web most common in chronic lung diseases but also in neoplasia, toxic inhalation. The contrast between the lung and vessels is diminished, and the vascular markings are poorly marginated. A bronchial pattern is diffuse thickening of the airway walls giving the appearance of thick lines and rings throughout the lungs. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema is a common cause of respiratory distress in small breed dogs with chronic valvular disease (eg, mitral endocardiosis), such as cavalier king charles spaniels. Characteristic findings include an increased opacity in the lungs that partially obscures blood vessel margins, which may be due to the presence of edema, pus, blood or other material in the lungs. Web. Web the pattern approach to interpreting lung lesions simplifies your life. Web there are 4 pulmonary patterns described. A total collapse of the alveoli (atelectasis) leads to a. Web these characteristic opacity changes are called lung patterns. A bronchial pattern is diffuse thickening of the airway walls giving the appearance of thick lines and rings throughout the lungs. A bronchial pattern is important to recognize, because, while it may be a normal variant in an aged. •application of lung patterns to common clinical. Identification of the lung pattern is helpful, as a list of differential diagnoses can be determined for that particular lung pattern. Anthony fischetti, dvm, ms, dacvr, reviews the radiographic principles of lung patterns in dogs. Web see table 1 for differential diagnosis for common lung patterns in dogs and cats. Characteristic findings include an increased opacity in the lungs that partially obscures blood vessel margins, which may be due to the presence of edema, pus, blood or other material in the lungs. In cats, single circumscribed mass lesions are less common, whereas a diffuse lung. Web •review of lung patterns. An alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Web all four lung patterns were represented with the same frequency (four hundred rois). For reasons of simplicity we will not discuss mixed patterns. Web primary lung tumors in dogs may occur as single or multiple. Emphasis will be placed on the diagnostic evaluation, paying special attention to interpretation of imaging findings and discrimination of these. Web the pattern approach to interpreting lung lesions simplifies your life. Web most common in chronic lung diseases but also in neoplasia, toxic inhalation. The left cranial lobe is characterized by two distinct segments, the cranial and caudal segments (. A bronchial pattern is diffuse thickening of the airway walls giving the appearance of thick lines and rings throughout the lungs. Web the pattern approach to interpreting lung lesions simplifies your life. A bronchial pattern is important to recognize, because, while it may be a normal variant in an aged. Web there are 4 pulmonary patterns described. Web upper airway. In cats, single circumscribed mass lesions are less common, whereas a diffuse lung pattern or. Characteristic findings include an increased opacity in the lungs that partially obscures blood vessel margins, which may be due to the presence of edema, pus, blood or other material in the lungs. A bronchial pattern is diffuse thickening of the airway walls giving the appearance. Radiographic abnormalities may help identify or suggest a primary cause of pulmonary hypertension; Web the pattern approach to interpreting lung lesions simplifies your life. Web all four lung patterns were represented with the same frequency (four hundred rois). Viral, bacterial or fungal) atelectasis (detected by the mediastinal shift when the alveoli are empty) bronchial. Web see table 1 for differential. Web these characteristic opacity changes are called lung patterns. Web canine and feline lungs have identical lobation with four lobes of the right lung (the cranial, middle, caudal, and accessory lobes) and two lobes of the left lung (the cranial and caudal lobes). Examples of interstitial, alveolar, bronchial, and vascular lung patterns will be illustrated. An alveolar pattern is the. Web these characteristic opacity changes are called lung patterns. A bronchial pattern is diffuse thickening of the airway walls giving the appearance of thick lines and rings throughout the lungs. However, advanced imaging or additional diagnostic testing is necessary to confirm a diagnosis. Web see table 1 for differential diagnosis for common lung patterns in dogs and cats. The lung appears diffusely more opaque or hazy. Radiographic abnormalities may help identify or suggest a primary cause of pulmonary hypertension; Lymphoma in dogs, primary pulmonary neoplasia in cats) pus (pneumonia; A total collapse of the alveoli (atelectasis) leads to a. Web upper airway obstruction due to brachycephalic airway disease is a common cause of respiratory distress in brachycephalic dogs, such as english bulldogs. Web canine and feline lungs have identical lobation with four lobes of the right lung (the cranial, middle, caudal, and accessory lobes) and two lobes of the left lung (the cranial and caudal lobes). Web all four lung patterns were represented with the same frequency (four hundred rois). Web radiographic features of pulmonary hypertension in dogs and cats. Web common lung patterns include: Cardiogenic pulmonary edema is a common cause of respiratory distress in small breed dogs with chronic valvular disease (eg, mitral endocardiosis), such as cavalier king charles spaniels. Interstitial patterns indicate disease or disruption of the interstitium. A bronchial pattern is important to recognize, because, while it may be a normal variant in an aged.
Radiographic Approach to the Coughing Pet MSPCAAngell

Thoracic radiography of a dog with pneumonic plague (case 2). Left

Common Pulmonary Diseases in Dogs Clinician's Brief

Dog lung lobes (from Dogs Monthly) Lung anatomy, Lunges, Dog anatomy
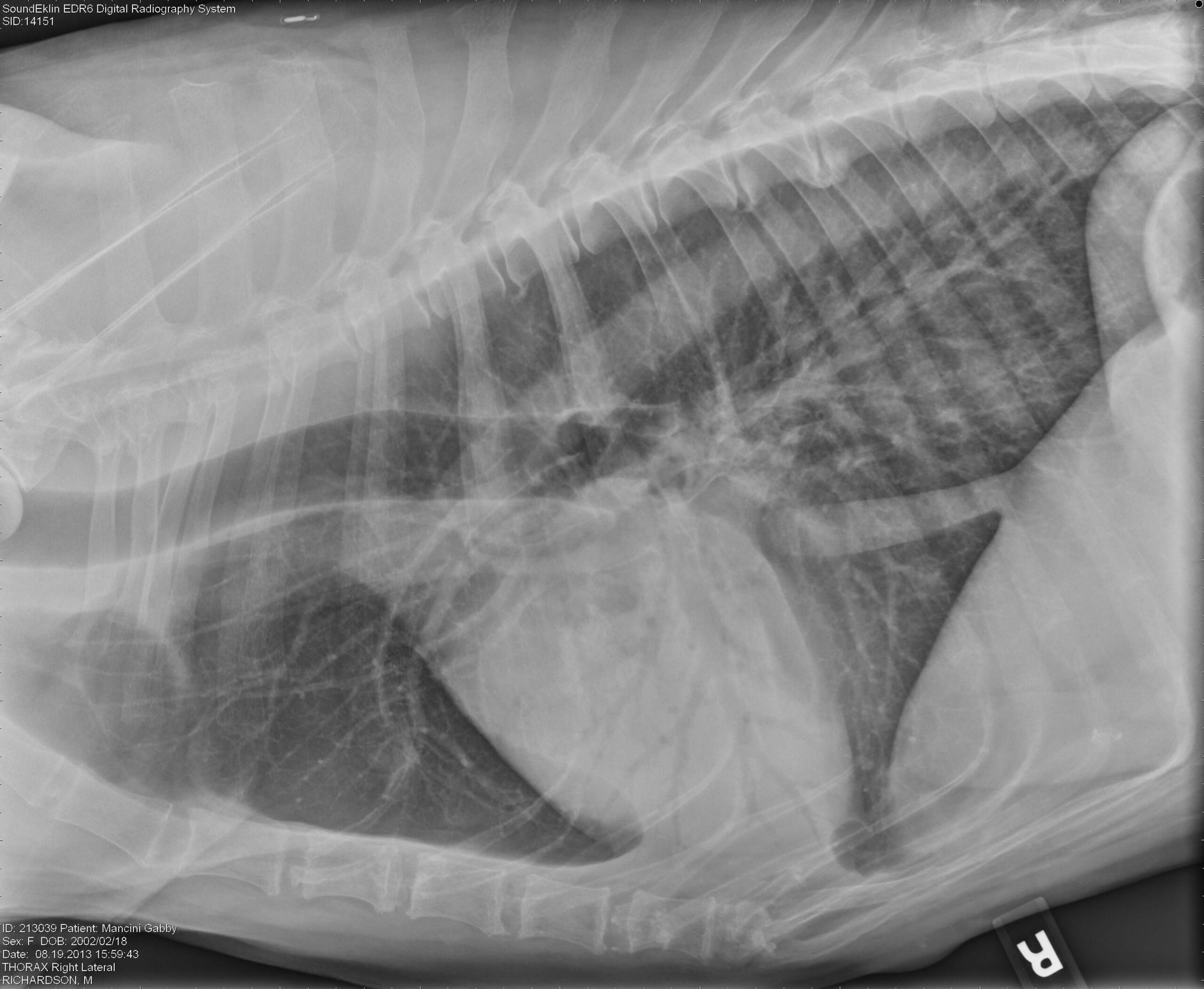
Interpreting thoracic radiograph lung patterns VETgirl Veterinary

Topographical distribution and radiographic pattern of lung lesions in

Thoracic radiographs of the canine patient. An interstitial pattern was

Photomicrographs of sections of the lung from the dog in Figure 1. AAn

Chronic & Persistent Coughing in a Dog Clinician's Brief

Topographical distribution and radiographic pattern of lung lesions in
In Cats, Single Circumscribed Mass Lesions Are Less Common, Whereas A Diffuse Lung Pattern Or.
Viral, Bacterial Or Fungal) Atelectasis (Detected By The Mediastinal Shift When The Alveoli Are Empty) Bronchial.
Structured And Unstructured Increased Opacities.
Web Dogs And Cats With Respiratory Tract Disorders Can Present To Veterinarians For A Variety Of Clinical Signs Including Nasal Discharge, Sneeze, Reverse Sneeze, Noisy Breathing (Snoring/Stertor, Stridor, Wheeze), Cough, Alterations In Respiratory Rate Or Effort, And Respiratory Distress.
Related Post: