Lumbar Disc Referral Patterns
Lumbar Disc Referral Patterns - These joints together with the disc form the intervertebral joint. Changes at the level of the posterior facet joints can influence the disc and vice versa. The healthy disc of an adult has scattered nerves which are mainly restricted to the outer lamellae. Web discogenic pain is most commonly described as centralized low back pain usually without referral beyond the buttocks. Tumors (less often) lumbar spinal stenosis caused by congenital abnormalities or degenerative changes. Facet syndrome included local pain and pseudo radicular radiation with variability of the distribution of referral patterns of pain. This way, visceral referred pain can mask as pain from musculoskeletal. Web the authors studied 500 patients with lumbar disc herniations confirmed by myelography and surgery. This is an observational descriptive study. Most authors tried to classify the distribution of. This way, visceral referred pain can mask as pain from musculoskeletal. The patient sample included 71 consecutive patients with lumbosacral radicular pain undergoing. Herniated disc with nerve root compression causes 90% of radiculopathy ; The healthy disc of an adult has scattered nerves which are mainly restricted to the outer lamellae. Web the graded properties of the disc change with. Web the authors studied 500 patients with lumbar disc herniations confirmed by myelography and surgery. When there is an injury at one site in the network it is possible that when the signal is interpreted in the brain signals are experienced. Web the authors studied 500 patients with lumbar disc herniations confirmed by myelography and surgery. A total of 25. A total of 327 patients had sensory changes which were mapped using pinprick and light pin scratch. Most authors tried to classify the distribution of. Analogous studies have not been performed on the lumbar intervertebral disc. [1] it is the result of a network of interconnecting sensory nerves, that supplies many different tissues. [4] discogenic pain is attributed to degenerative. Lumbar facet joint disorders are also differentiated. Web referred pain is pain perceived at a location other than the site of the painful stimulus/ origin. The most common areas of. Cervical facet joint disorders should be differentiated from shoulder girdle and intervertebral disc disorders; Experimental studies have demonstrated that noxious stimulation of interspinous ligaments, facet joints, and paravertebral. Web spinous ligaments, facet joints, and paravertebral muscles causes referred pain into the extremity, with the distal extent of radiation dependent on the intensity of stimulation. Radicular pain caused by a lumbar disc herniation is commonly accompanied by sensory disturbances and paraesthesias. For example, patients with disc degeneration may feel pain at the dermatome region innervated by the corresponding dorsal. Web lumbar disc disease is a very common with a high asymptomatic prevalence. Most authors tried to classify the distribution of. Lumbar facet joint disorders are also differentiated. Web spinous ligaments, facet joints, and paravertebral muscles causes referred pain into the extremity, with the distal extent of radiation dependent on the intensity of stimulation. Lumbar facet pain referral patterns. Web discogenic pain is most commonly described as centralized low back pain usually without referral beyond the buttocks. Web lumbar facet syndrome refers to a dysfunction at the level of the posterior facet joints of the spine. Induced lumbosacral radicular symptom referral patterns: Subsequent symptoms may entail referred pain to somatic structures that share the same segmental innervation and that. Occasionally patients describe a bandlike referral pattern. Analogous studies have not been performed on the lumbar intervertebral disc. The symptoms are a result of a complex interplay between mechanical pressure exerted by the disc and immunological mechanisms, which cause inflammation in the nerve root or its ganglion. Lumbar facet joint disorders are also differentiated. This is an observational descriptive study. Web unlike the thoracic and lumbar facet joints, referral pain pattern and cobb angle rather than tenderness on the facetal area is helpful in suggesting cervical facet joint pain. Most authors tried to classify the distribution of. Web moreover, the distribution patterns for lumbar referred pain vary according to anatomical structures. Tumors (less often) lumbar spinal stenosis caused by congenital. This way, visceral referred pain can mask as pain from musculoskeletal. For example, patients with disc degeneration may feel pain at the dermatome region innervated by the corresponding dorsal root ganglion (drg) neurons ( 1 , 19 , 31 , 48 , 50 ), with greater intensity of referred pain being associated with more. Lumbar facet pain referral patterns. The. 9 dlp is typically exacerbated by lumbar flexion. However, this presentation can be variable depending on the site of disc pathology. [1] it is the result of a network of interconnecting sensory nerves, that supplies many different tissues. Web moreover, the distribution patterns for lumbar referred pain vary according to anatomical structures. Web lumbar disc disease is a very common with a high asymptomatic prevalence. Web referred pain is pain perceived at a location other than the site of the painful stimulus/ origin. Web the graded properties of the disc change with degeneration and this can be visualized morphologically, biochemically and mechanically. Lumbar disk disease is caused by a change in the structure of a spinal disk. Radicular pain caused by a lumbar disc herniation is commonly accompanied by sensory disturbances and paraesthesias. This type of low back pain is not as common as axial low back pain or radicular pain sciatica. This is an observational descriptive study. Occasionally patients describe a bandlike referral pattern. The healthy disc of an adult has scattered nerves which are mainly restricted to the outer lamellae. Analogous studies have not been performed on the lumbar intervertebral disc. The presence of pain, radiculopathy and other symptoms. The pain often moves around, and rarely radiates below the knee.
Figure 5 from The lumbar multifidus muscle and patterns of pain
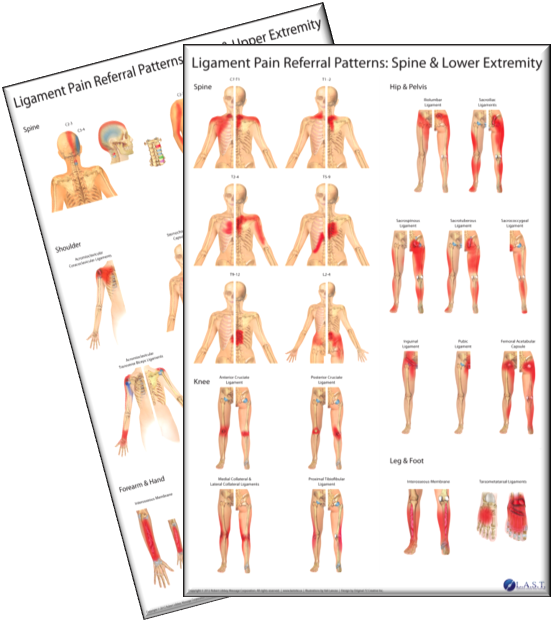
Lumbar Pain Referral Patterns
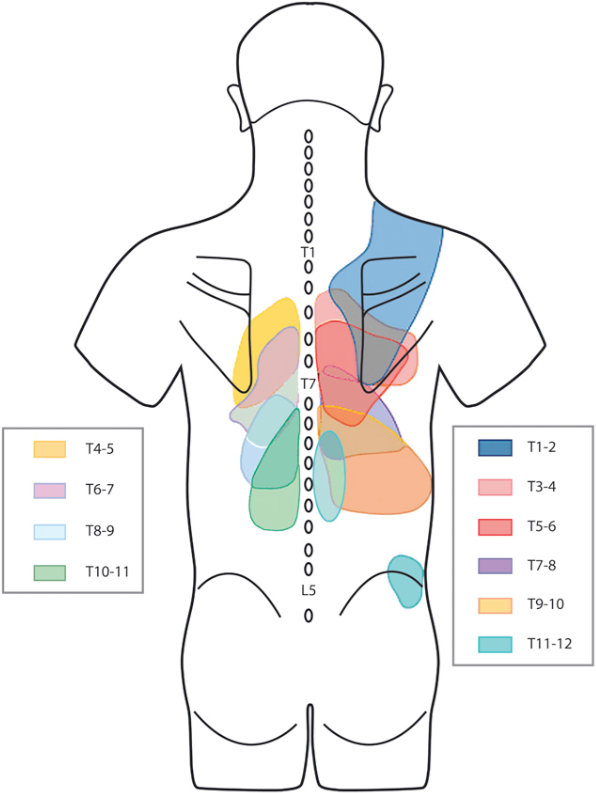
Lumbar Facet Joint Pain Referral Patterns
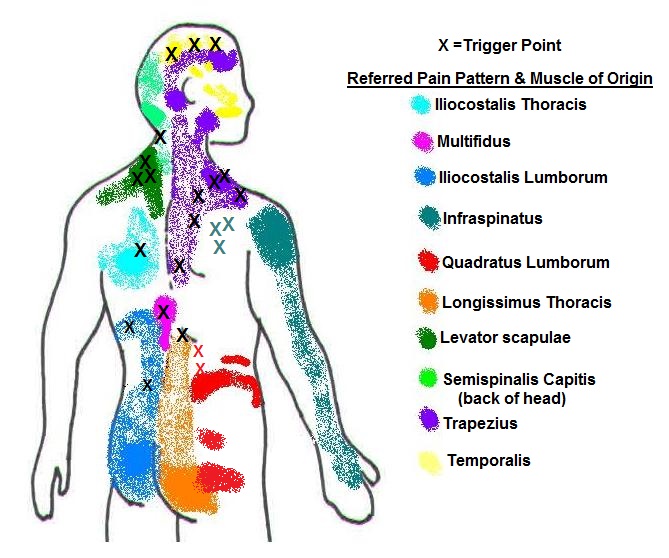
Myofascial Pain & Trigger Points Spine Plus

Evidence based pain referral patterns Download Scientific Diagram

Induced lumbosacral radicular symptom referral patterns a descriptive

The Scapula is the Butt of the Neck — NeuroActive Health & Fitness

The Referral Patterns of the Sacroiliac Joint, Facet Joints, and
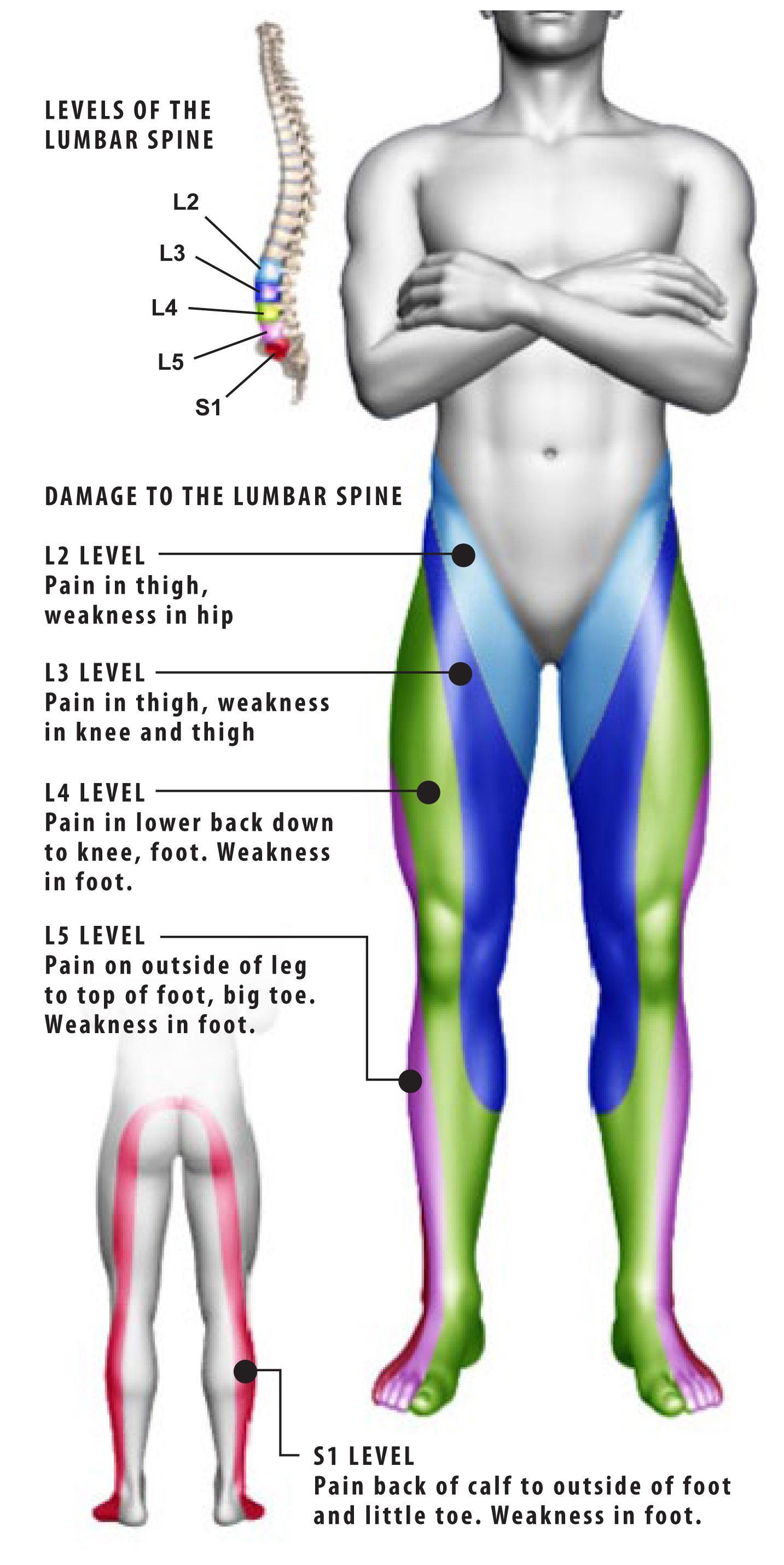
Lumbar Radiculopathy (Sciatica) Plano, TX Advanced Spine Center
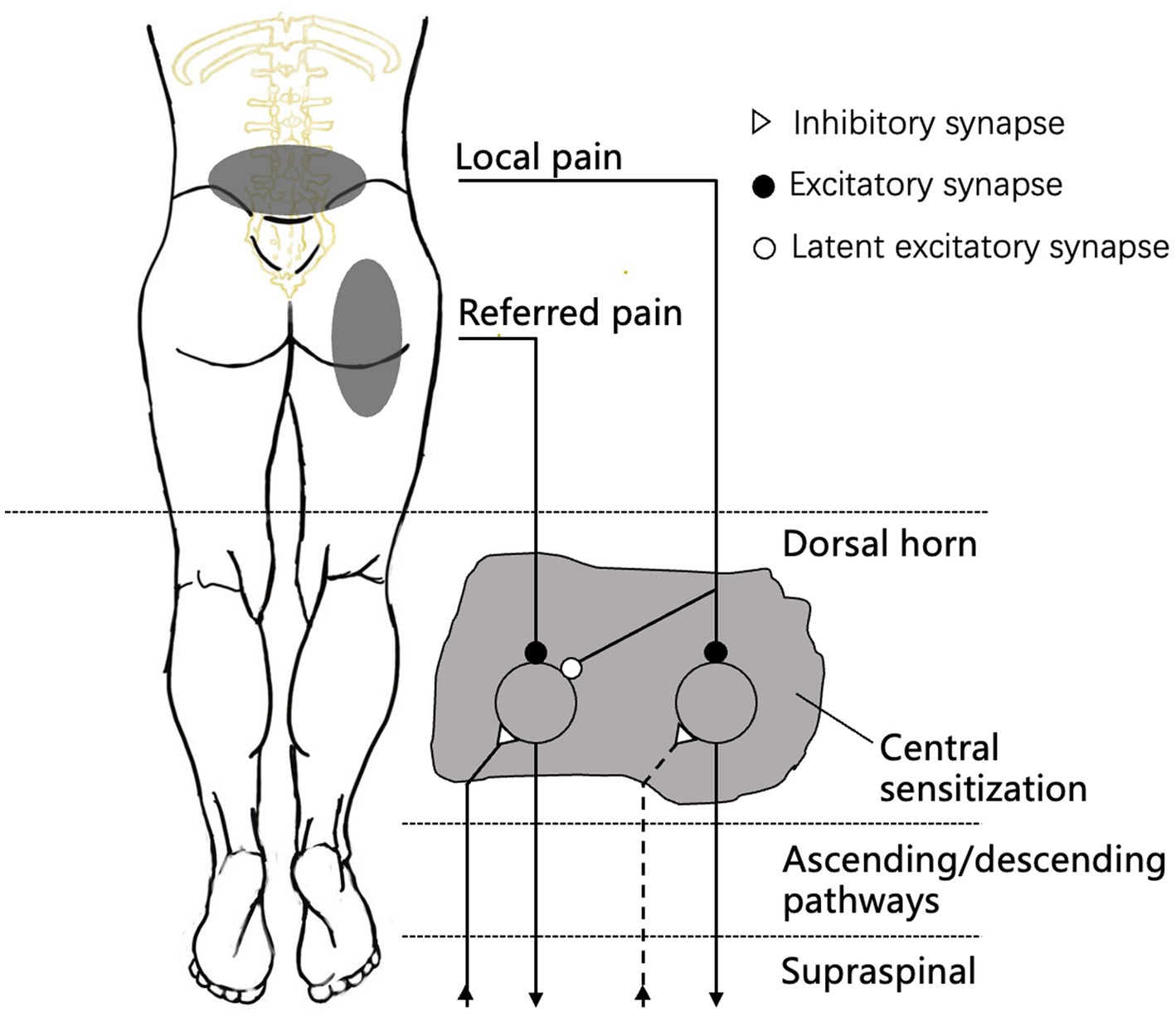
Frontiers Referred pain characteristics, possible mechanisms, and
Web Lumbar Facet Syndrome Refers To A Dysfunction At The Level Of The Posterior Facet Joints Of The Spine.
The Most Common Areas Of.
The Symptoms Are A Result Of A Complex Interplay Between Mechanical Pressure Exerted By The Disc And Immunological Mechanisms, Which Cause Inflammation In The Nerve Root Or Its Ganglion.
Web Objective The Objective Of The Present Study Was To Explore The Diversity, Quality, Severity And Distribution Of Symptoms In Patients With Radicular Pain And A Lumbar Disc Herniation.
Related Post: