Isolated Obstructive Pattern On Spirometry
Isolated Obstructive Pattern On Spirometry - Testing is needed to con rm. Persistent or irreversible airflow obstruction is defined as obstruction that does not disappear or completely resolve after inhaled bronchodilator use. Web respiratory infections are common causes of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive lung disease (aecopd). The first step is determining the validity of the test. Due to asthma or copd. Apply an organized approach to interpreting pulmonary function tests. Web pattern recognition is key.a low fev1/fvc ratio (the forced expiratory volume in 1 second divided by the forced vital capacity) indicates an obstructive pattern, whereas a normal value indicates either a restrictive or a normal pattern. Understand the physiology of the core pulmonary function tests: The fvc may be normal in milder disease but will be. Web in adults, an isolated low fev 1 pattern (an fev 1 below the lower limit of normal with a preserved fvc and fev 1 /fvc) has been associated with the risk of developing airway obstruction. We explored whether the pathogens causing aecopd and clinical features changed from. Examples of obstructed and restricted ow loops. Ow limitation is observed during spirometry. Obstructive defects should be assessed for reversibility, as indicated by an. Web based on whether trajectories of the fev1/fvc ratio and fvc were low (ie, low from childhood or adulthood) or normal, four patterns of. Web respiratory infections are common causes of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive lung disease (aecopd). We explored whether the pathogens causing aecopd and clinical features changed from. If the observed fev 1 /fvc ratio is down 10 or more from the predicted, obstruction is present. The first step is determining the validity of the test. Typical spirometry findings in obstructive. The fvc and fev 1are reduced proportionately • obstructive patterns appear when the airways are obstructed e.g. The prevalence of the four lifetime spirometry patterns was as follows: Web the fev1/fvc ratio and fvc are used together to identify obstructive defects and restrictive or mixed patterns. Our objective was to examine the prevalence, stability, and clinical significance of an isolated. We explored whether the pathogens causing aecopd and clinical features changed from. Web therefore, the diagnosis of copd necessarily requires findings of persistent airway obstruction on spirometry. Obstructive spirometry pattern is usually, but not always, accompanied by fev 1 <lln. Due to asthma or copd. Typical spirometry findings in obstructive lung disease include: Spirometry may also be used periodically to monitor your lung condition and check whether a treatment for a chronic lung condition is helping you breathe better. Web a restrictive pattern is indicated by an fvc below the fifth percentile based on nhanes iii data in adults, or less than 80% in patients five to 18 years of age. Web fev. Web a restrictive pattern is indicated by an fvc below the fifth percentile based on nhanes iii data in adults, or less than 80% in patients five to 18 years of age. Understand the physiology of the core pulmonary function tests: Web pattern recognition is key.a low fev1/fvc ratio (the forced expiratory volume in 1 second divided by the forced. • restrictive patterns appear in conditions where the lung volume is reduced e.g. Web spirometry is a diagnostic test of several common respiratory disperses such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd). Next, the determination of an obstructive or restrictive ventilatory. Examples of obstructed and restricted ow loops. Persistent or irreversible airflow obstruction is defined as obstruction that does. Apply an organized approach to interpreting pulmonary function tests. Web spirometry is used to diagnose asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) and other conditions that affect breathing. Web based on whether trajectories of the fev 1 /fvc ratio and fvc were low (ie, low from childhood or adulthood) or normal, four patterns of lifetime spirometry obstruction or restriction were identified. Web therefore, the diagnosis of copd necessarily requires findings of persistent airway obstruction on spirometry. 3 asthma is diagnosed based on characteristic symptoms including wheezing, dyspnea, and cough and presence of variable airway obstruction, while copd is characterized by definitely irreversible and progressive airway. An obstructive pattern is characterized by fev 1 /fvc < lln. Fev1/vc < lln (ats) or. Web spirometry is used to diagnose asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) and other conditions that affect breathing. In other words, without airflow obstruction, most of the fvc should be exhaled in the first second of forced exhalation. An obstructive pattern is characterized by fev 1 /fvc < lln. Due to asthma or copd. Our objective was to examine the. Typical spirometry findings in obstructive lung disease include: Persistent or irreversible airflow obstruction is defined as obstruction that does not disappear or completely resolve after inhaled bronchodilator use. Obstructive spirometry pattern is usually, but not always, accompanied by fev 1 <lln. Web therefore, the diagnosis of copd necessarily requires findings of persistent airway obstruction on spirometry. Testing is needed to con rm. And neither low fev 1 /fvc ratio nor low fvc, labelled as reference, 60·2%. Web a restrictive pattern is indicated by an fvc below the fifth percentile based on nhanes iii data in adults, or less than 80% in patients five to 18 years of age. Spirometry with low fvc (< 80%) can only suggest restriction. In other words, without airflow obstruction, most of the fvc should be exhaled in the first second of forced exhalation. Either forced (fvc) or slow (svc) vital capacity can be used to determine fev1/vc ratio obstruction present. Web a simplified and stepwise method is key to interpreting spirometry. The fvc may be normal in milder disease but will be. Ow limitation is observed during spirometry. The prevalence of the four lifetime spirometry patterns was as follows: It is also instrumental in monitoring the progression of various respiratory disorders. Spirometry may also be used periodically to monitor your lung condition and check whether a treatment for a chronic lung condition is helping you breathe better.
Spirometry Obstructive Pattern
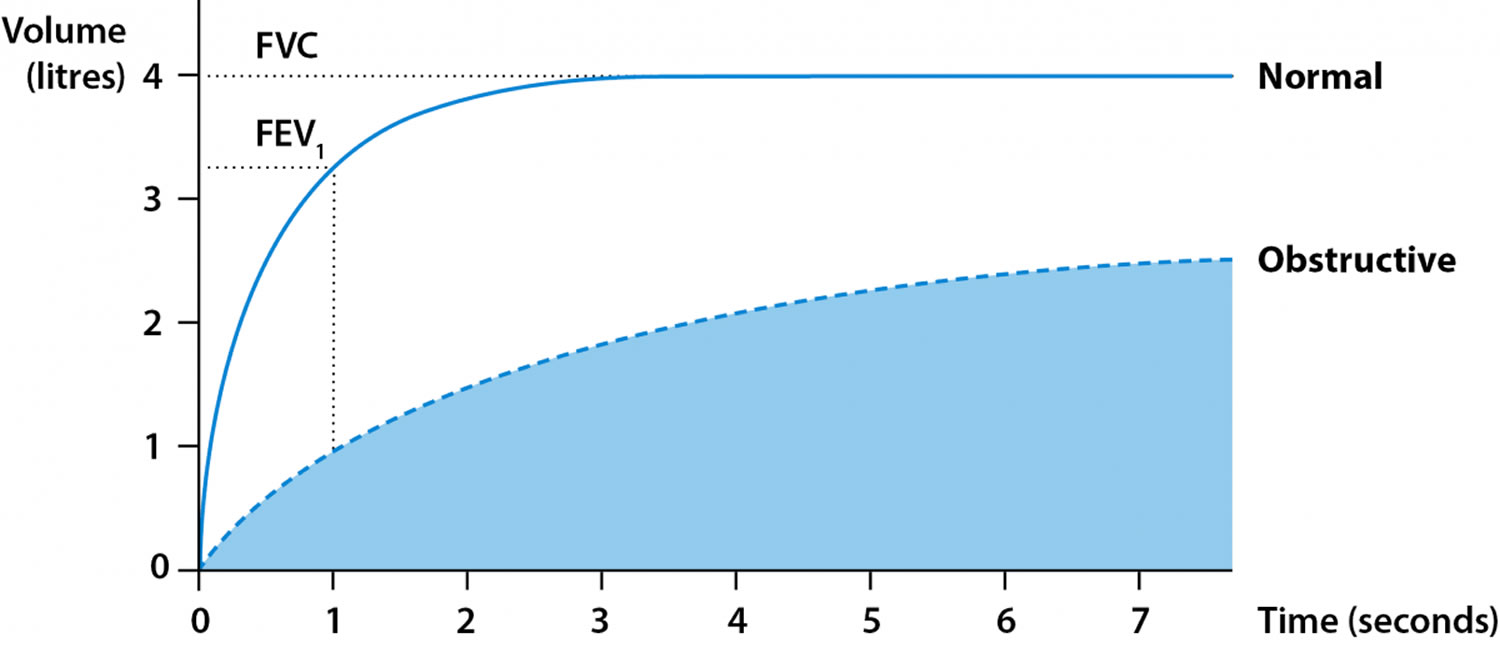
Spirometry test, spirometry results & spirometry interpretation

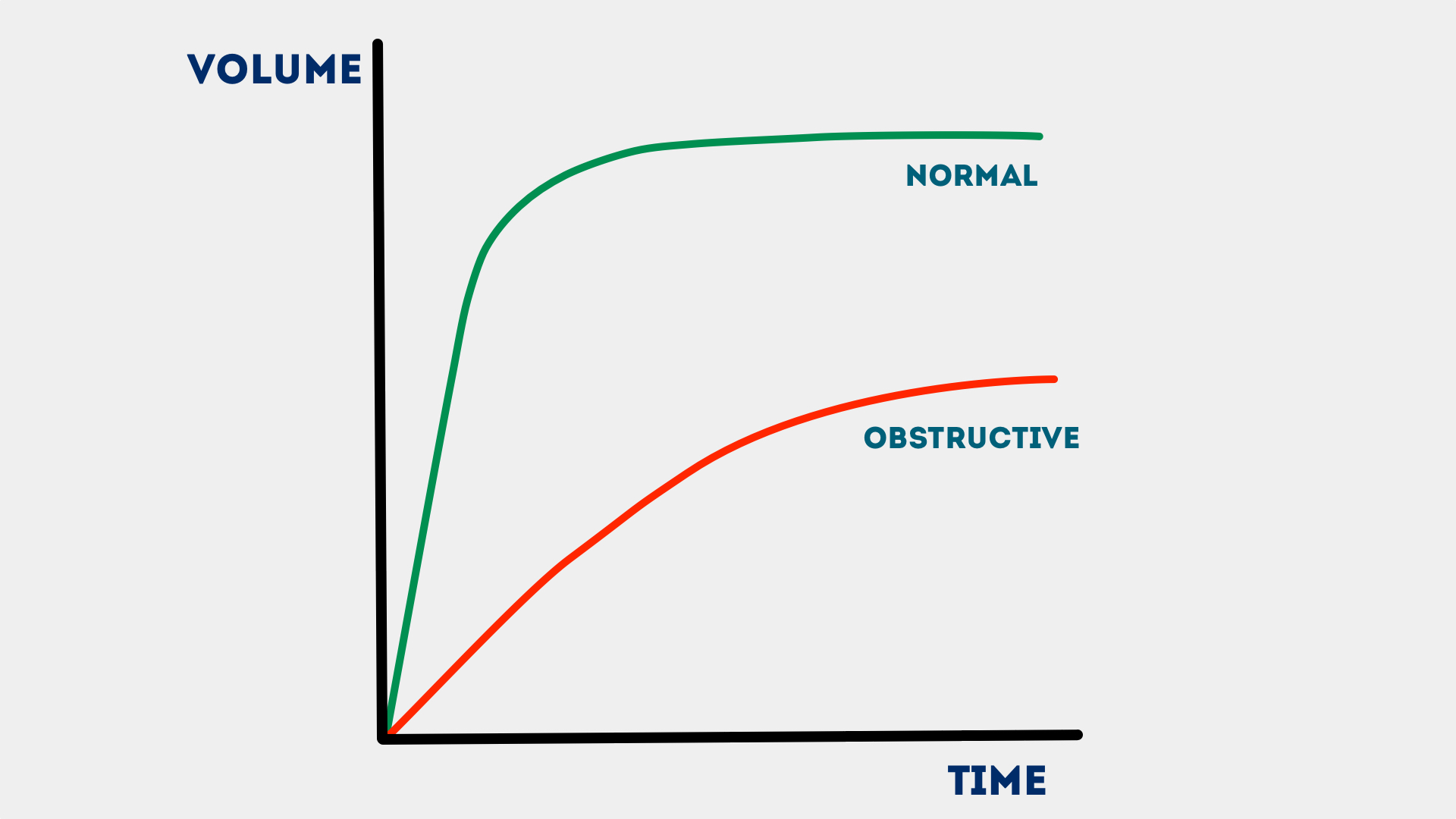
Obstructive Vs Restrictive Lung Disease Spirometry
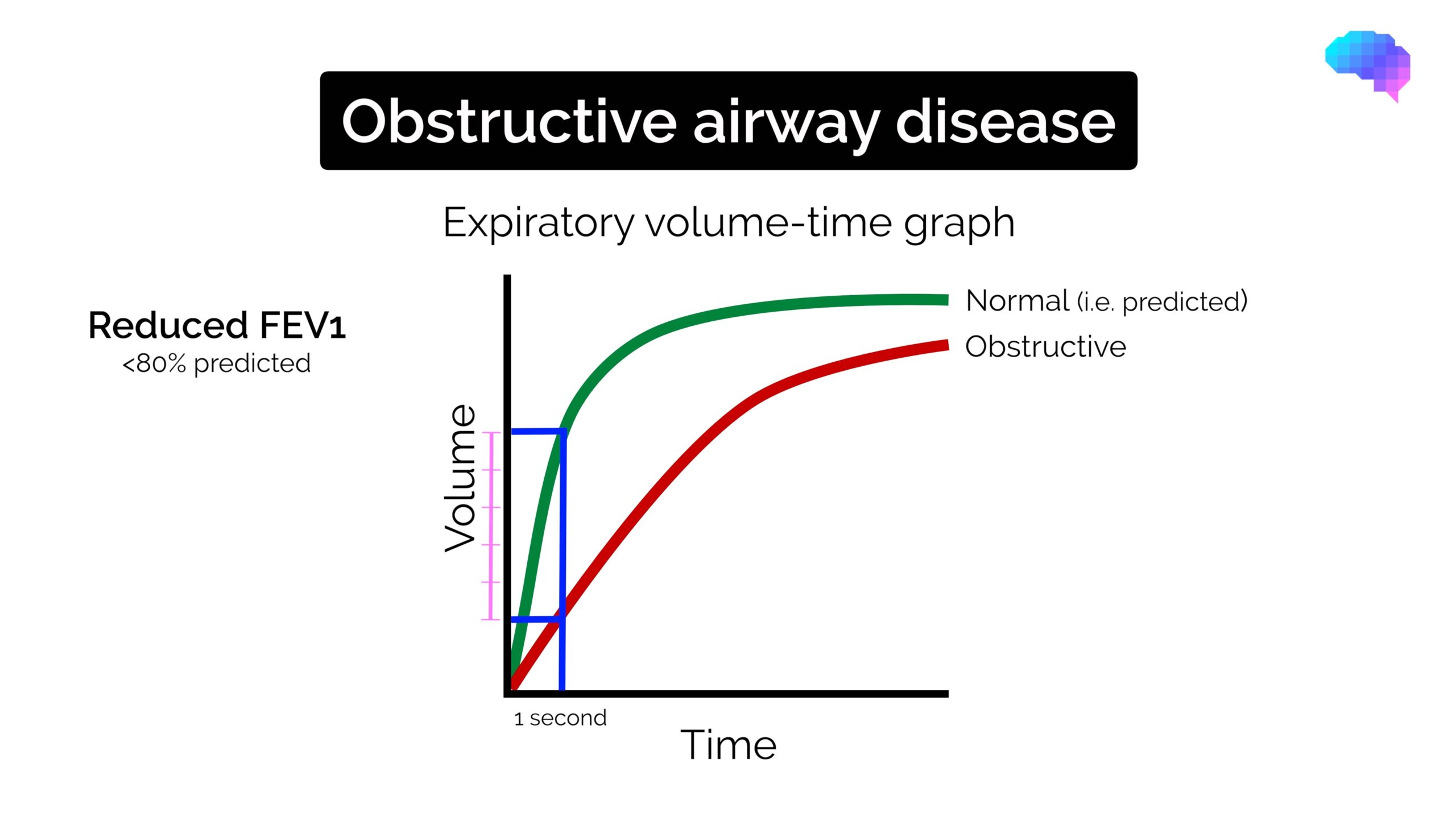
Spirometry Interpretation Obstructive vs Restrictive Geeky Medics
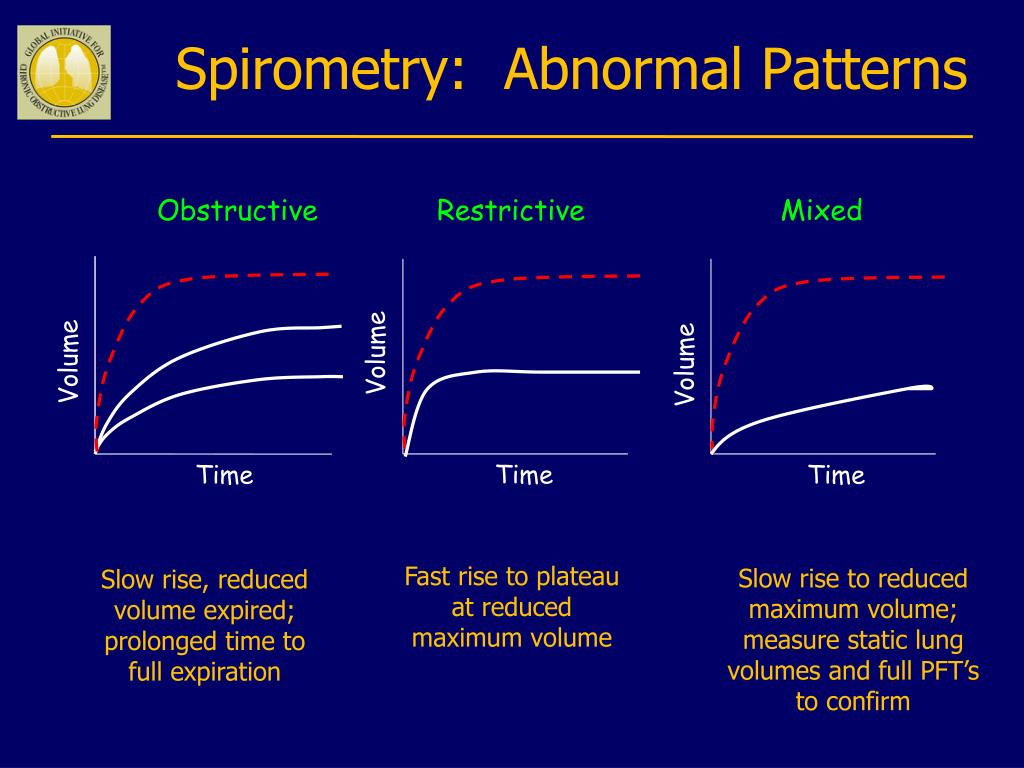
PPT Spirometry in Primary Care PowerPoint Presentation, free download

Pulmonary Function Tests for the Radiologist RadioGraphics
Spirometry Interpretation Obstructive vs Restrictive Geeky Medics

Spirometry test, spirometry results & spirometry interpretation

Pulmonary Function Testing Flow Volume Loop Patterns GrepMed
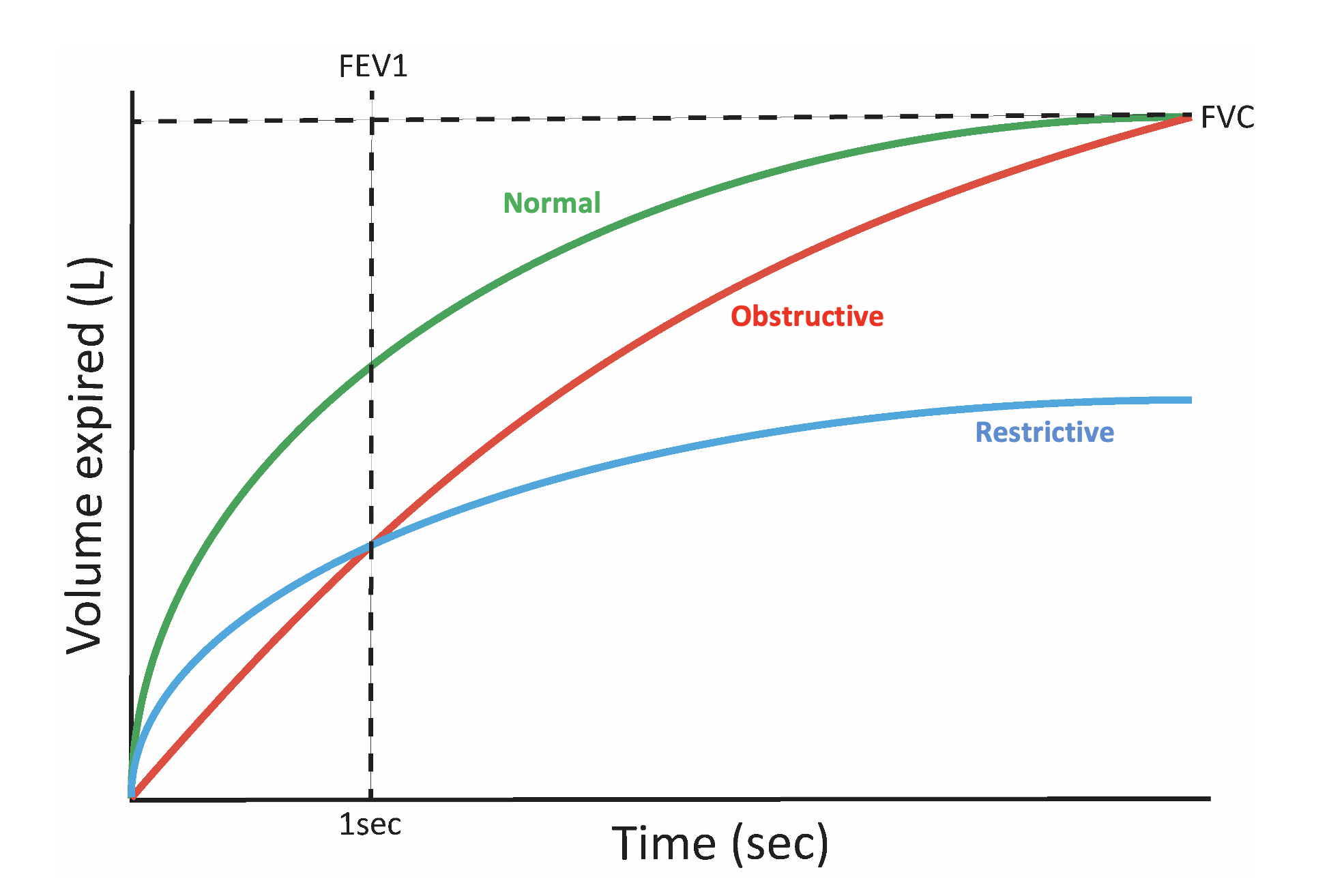
Spirometry OSCEstop OSCE Learning
Web In Adults, An Isolated Low Fev 1 Pattern (An Fev 1 Below The Lower Limit Of Normal With A Preserved Fvc And Fev 1 /Fvc) Has Been Associated With The Risk Of Developing Airway Obstruction.
Obstructive Defects Should Be Assessed For Reversibility, As Indicated By An.
Apply An Organized Approach To Interpreting Pulmonary Function Tests.
Understand The Physiology Of The Core Pulmonary Function Tests:
Related Post: