Is The Template Strand The Coding Strand
Is The Template Strand The Coding Strand - Web the template strand comprises nucleotide sequences which are complementary to these present in each the transcribed mrna and the coding strand. Web in gene expression, the coding strand serves as a template for the synthesis of messenger rna (mrna), which carries the genetic information to the ribosomes for. It runs in the 3′ to 5′ direction, which is opposite to the direction of the coding strand and the mrna. It is complementary to the. Most codons specify an amino acid. Web it is also called (+) strand, or nontemplate strand. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Major types of cellular rna. Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a template). Identify the key steps of transcription, the function of. Web in gene expression, the coding strand serves as a template for the synthesis of messenger rna (mrna), which carries the genetic information to the ribosomes for. So that means that the. Its counterpart, the antisense strand, guides the creation of a complementary rna strand during transcription. Here are some features of codons: Web the dna strand known as the. Here are some features of codons: One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Template strand or “ antisense. The term coding strand is not appropriate because the. Cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. Template strand or “ antisense. Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a template). Web the strand of dna from which mrna is formed after transcription is known as the template strand or the antisense strand. The template strand is usually directed 3’ to. As. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand ) is the dna strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the rna transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). It runs in the 3′ to 5′ direction, which is opposite to the direction of. Template strand or “ antisense. Web the coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Most codons specify an amino acid. Web on the other hand, the template strand, also known as the antisense strand, serves as a template for rna synthesis during transcription. As the rna polymerase moves along the template strand in 3′→ 5′ direction, the rna. Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a template). Identify the key steps of transcription, the function of. Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to produce rna. Web either dna strand can be a template. It is. Web the template strand, a fundamental component of dna, is pivotal in the intricate process of mrna synthesis, facilitated by the principle of complementary base. Cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. It is complementary to the. Web the strand of dna from which mrna is formed after transcription is known as the template. Template strand or “ antisense. Web the template strand is one of the dna strands whose base sequence helps in building mrna through complementary base sequencing. Major types of cellular rna. Web the dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint for the production of rna, whereas the coding strand is the other strand. As the rna. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. It runs in the 3′ to 5′ direction, which is opposite to the direction of the coding strand and the mrna. Template strand or “ antisense. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Web the template strand, a fundamental component of. Identify the key steps of transcription, the function of. The term coding strand is not appropriate because the. As the rna polymerase moves along the template strand in 3′→ 5′ direction, the rna chain grows in 5′→ 3′ direction. Here are some features of codons: Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an. It is also known as sense strand (plus. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand ) is the dna strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the rna transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a template). Web the template strand, a fundamental component of dna, is pivotal in the intricate process of mrna synthesis, facilitated by the principle of complementary base. Major types of cellular rna. Its counterpart, the antisense strand, guides the creation of a complementary rna strand during transcription. Most codons specify an amino acid. Web the term template strand is still appropriate because one of the dna strands is used as a template to make the rna. Cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. The template strand is usually directed 3’ to. The template strand of dna plays a crucial role in the synthesis of mrna through complementary base pairing. It is complementary to the. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Web the coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Web in gene expression, the coding strand serves as a template for the synthesis of messenger rna (mrna), which carries the genetic information to the ribosomes for. Identify the key steps of transcription, the function of.
IMP Coding (Sense) vs Template (AntiSense) Strands Biology activity

Template Strand Vs Coding Strand Understanding The Difference GRAPHICOLD

Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Differences
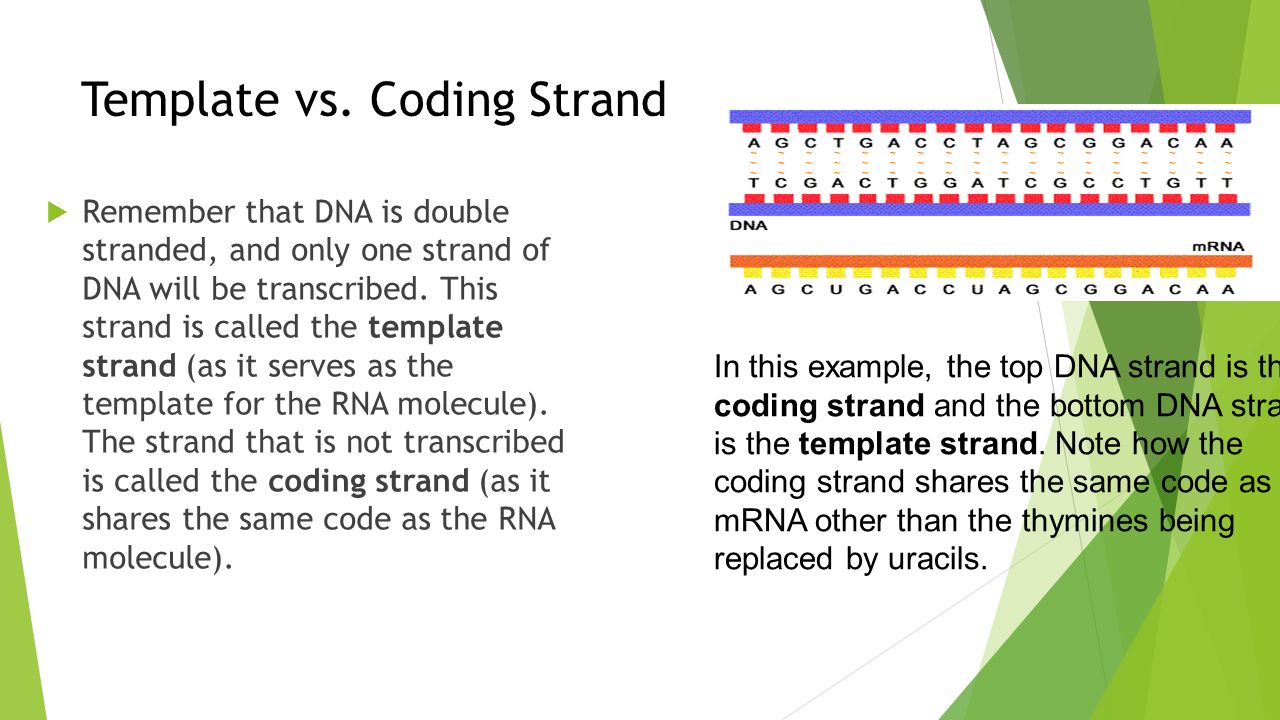
Difference Between Template And Coding Strand

Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Compare the Difference

Template and coding strand targeting of spacers. A Schematic

Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Definition

Template and coding strands of DNA YouTube
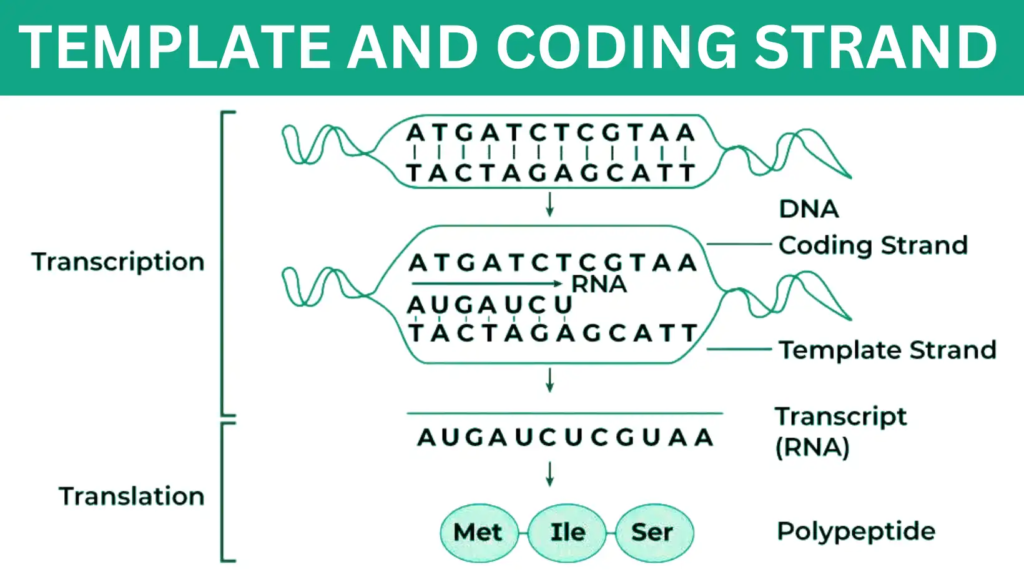
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand
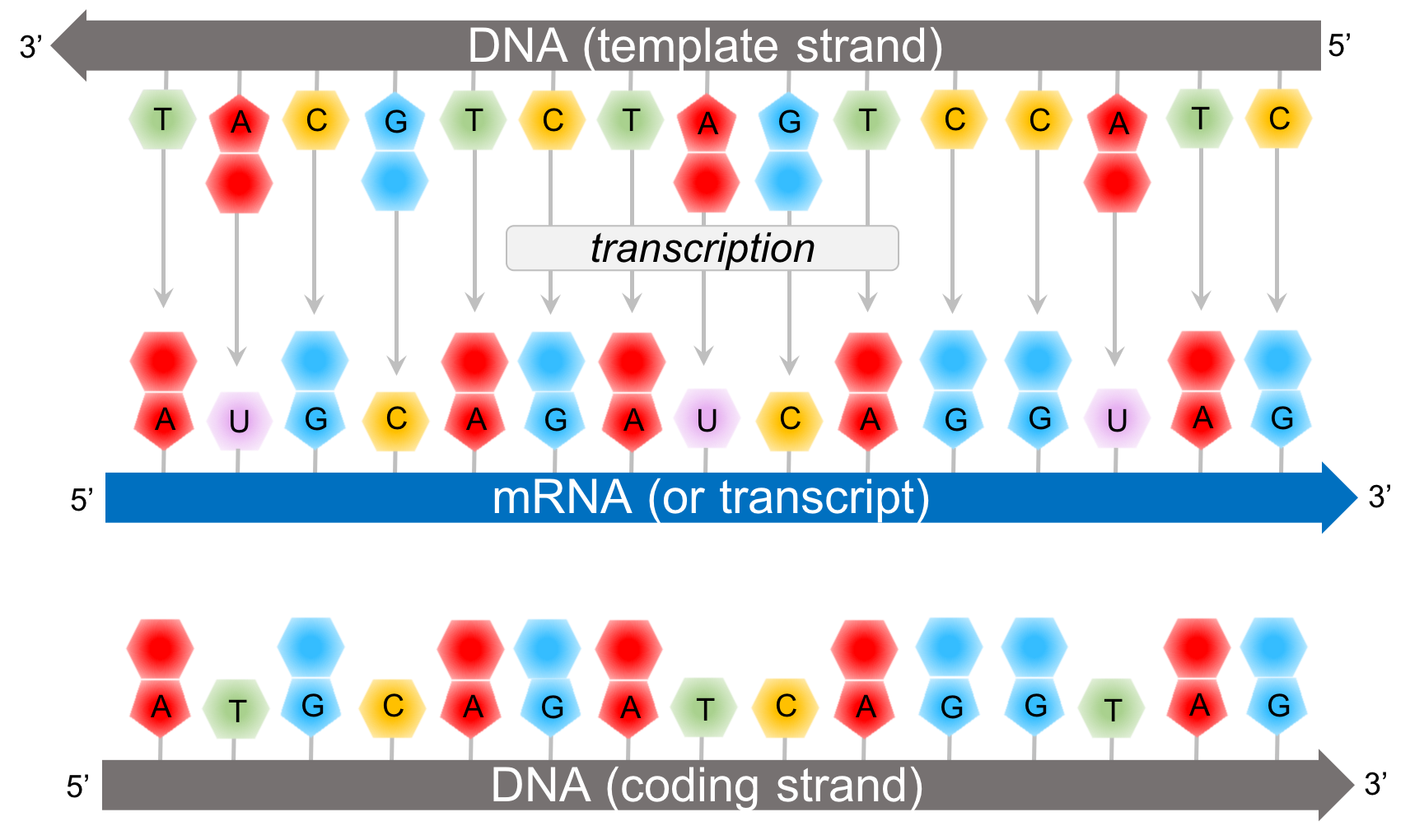
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
Web Either Dna Strand Can Be A Template.
The Coding Strand = Sense Strand, Both Of Which Are The Same As The Resulting Mrna (With Thymine Replacing Uracil).
As The Rna Polymerase Moves Along The Template Strand In 3′→ 5′ Direction, The Rna Chain Grows In 5′→ 3′ Direction.
Here Are Some Features Of Codons:
Related Post: