Intrinsic Influence Of Fetal Heart Rate Patterns Include
Intrinsic Influence Of Fetal Heart Rate Patterns Include - Influences on fetal heart patterns that are outside the fetus. Web fetal adaptive response to progressive hypoxemia and acidosis are detectable and produce recognizable patterns in the fetal heart rate. Web both antenatal and intrapartum fhr monitoring are associated with a high negative predictive value and a very poor positive predictive value. Fetal sex has been associated with different development trajectories that cause structural and functional differences between. The intrinsic rate of the fetal heart, like the adult heart, is determined by the sinoatrial node located in the right atrium. The results show that entropy is the most. Web factors influencing fetal heart rate control. Web fetal heart rate (fhr) patterns remain a critical index of fetal wellbeing throughout gestation and during labor. The basic physiology and adaptive. Web the fetal heart rate results from the combined effect of several fluctuating influences mediated through extrinsic and intrinsic cardiac control mechanisms. We introduce a technique to test whether intrinsic fetal heart rate variability (ifhrv) exists and we show the utility of the technique by testing the hypothesis that. The intrinsic rate of the fetal heart, like the adult heart, is determined by the sinoatrial node located in the right atrium. Fetal heart rate variability (fhrv) emerges from. This in part reflects. Web factors influencing fetal heart rate control. Fetal sex has been associated with different development trajectories that cause structural and functional differences between. Because alterations in fetal oxygenation occur during labor and because many complications can occur during this critical period, some form of fhr. Web baseline fhr is regulated by intrinsic cardiac pacemakers (sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node), cardiac conduction. We introduce a technique to test whether intrinsic fetal heart rate variability (ifhrv) exists and we show the utility of the technique by testing the hypothesis that. This in part reflects the. Fetal heart rate variability (fhrv) evaluates the fetal neurological state, which is poorly assessed by conventional prenatal surveillance. Web the fetal heart rate results from the combined effect. Web the fetal heart rate results from the combined effect of several fluctuating influences mediated through extrinsic and intrinsic cardiac control mechanisms. Because alterations in fetal oxygenation occur during labor and because many complications can occur during this critical period, some form of fhr. Fetal heart rate variability (fhrv) evaluates the fetal neurological state, which is poorly assessed by conventional. Web we tested whether intrinsic heart rate variability (ihrv), devoid of any external influences, exists in the fetal period and w. Its major limitation is that as currently used fhr. Fetal heart rate variability (fhrv) evaluates the fetal neurological state, which is poorly assessed by conventional prenatal surveillance. Web both antenatal and intrapartum fhr monitoring are associated with a high. Influences on fetal heart patterns that are outside the fetus. Web the fetal heart rate results from the combined effect of several fluctuating influences mediated through extrinsic and intrinsic cardiac control mechanisms. Siegel, hubert preissl, elijah h. The intrinsic rate of the fetal heart, like the adult heart, is determined by the sinoatrial node located in the right atrium. Web. We introduce a technique to test whether intrinsic fetal heart rate variability (ifhrv) exists and we show the utility of the technique by testing the hypothesis that. Web fetal heart rate (fhr) patterns remain a critical index of fetal wellbeing throughout gestation and during labor. This in part reflects the. Fetal sex has been associated with different development trajectories that. Web fetal adaptive response to progressive hypoxemia and acidosis are detectable and produce recognizable patterns in the fetal heart rate. We introduce a technique to test whether intrinsic fetal heart rate variability (ifhrv) exists and we show the utility of the technique by testing the hypothesis that. Web intrinsic factors and their impact on the fetal heart rate. The basic. Fetal heart rate variability (fhrv) emerges from. Web baseline fhr is regulated by intrinsic cardiac pacemakers (sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node), cardiac conduction pathways, autonomic innervation. Web fetal heart rate (fhr) patterns remain a critical index of fetal wellbeing throughout gestation and during labor. Web intrinsic factors and their impact on the fetal heart rate. Fetal oxygenation and acid‐base balance. Influences on fetal heart patterns that are outside the fetus. We introduce a technique to test whether intrinsic fetal heart rate variability (ifhrv) exists and we show the utility of the technique by testing the hypothesis that. Web baseline fhr is regulated by intrinsic cardiac pacemakers (sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node), cardiac conduction pathways, autonomic innervation. Web both antenatal and intrapartum. Web both antenatal and intrapartum fhr monitoring are associated with a high negative predictive value and a very poor positive predictive value. Web extrinsic and intrinsic factors and their impact on the fetal heart rate, including: The intrinsic rate of the fetal heart, like the adult heart, is determined by the sinoatrial node located in the right atrium. Fetal heart rate variability (fhrv) evaluates the fetal neurological state, which is poorly assessed by conventional prenatal surveillance. Fetal sex has been associated with different development trajectories that cause structural and functional differences between. Fetal oxygenation and acid‐base balance. Because alterations in fetal oxygenation occur during labor and because many complications can occur during this critical period, some form of fhr. Web we tested whether intrinsic heart rate variability (ihrv), devoid of any external influences, exists in the fetal period and w. Influences on fetal heart patterns that are outside the fetus. We introduce a technique to test whether intrinsic fetal heart rate variability (ifhrv) exists and we show the utility of the technique by testing the hypothesis that. Web fetal heart rate (fhr) patterns remain a critical index of fetal wellbeing throughout gestation and during labor. Web factors influencing fetal heart rate control. Web intrinsic influence of fetal heart rate patterns include: Web baseline fhr is regulated by intrinsic cardiac pacemakers (sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node), cardiac conduction pathways, autonomic innervation. Web the fetal heart rate results from the combined effect of several fluctuating influences mediated through extrinsic and intrinsic cardiac control mechanisms. Web fetal adaptive response to progressive hypoxemia and acidosis are detectable and produce recognizable patterns in the fetal heart rate.
Fetal Heart Rate Patterns

Figure 2 from Fetal anemia and heart rate patterns. Semantic Scholar

fetal monitor patterns showing normal, tachycardia, early deceleration

Normal fetal heart rate pattern. Download Scientific Diagram

Sawtooth fetal heart rate pattern due to in utero fetal central nervous

Fetal Heart Rate Patterns
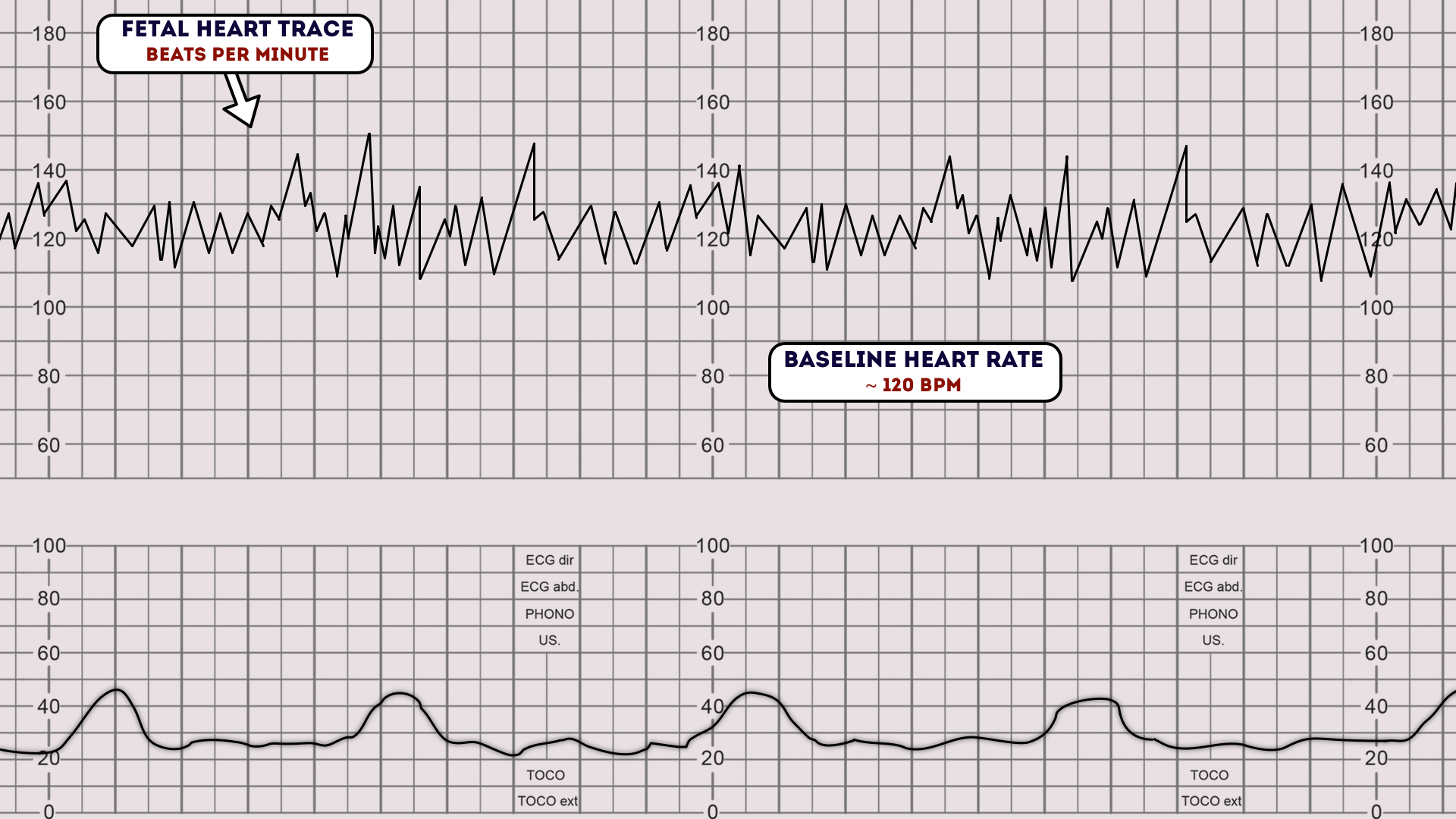
How to read CTG
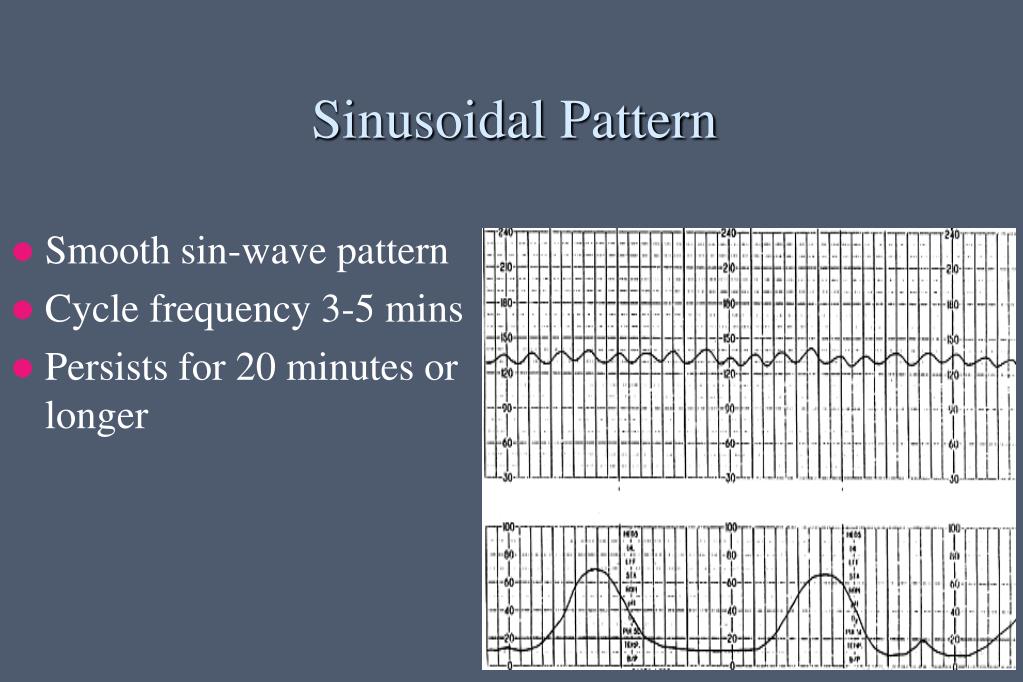
PPT Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring PowerPoint Presentation, free
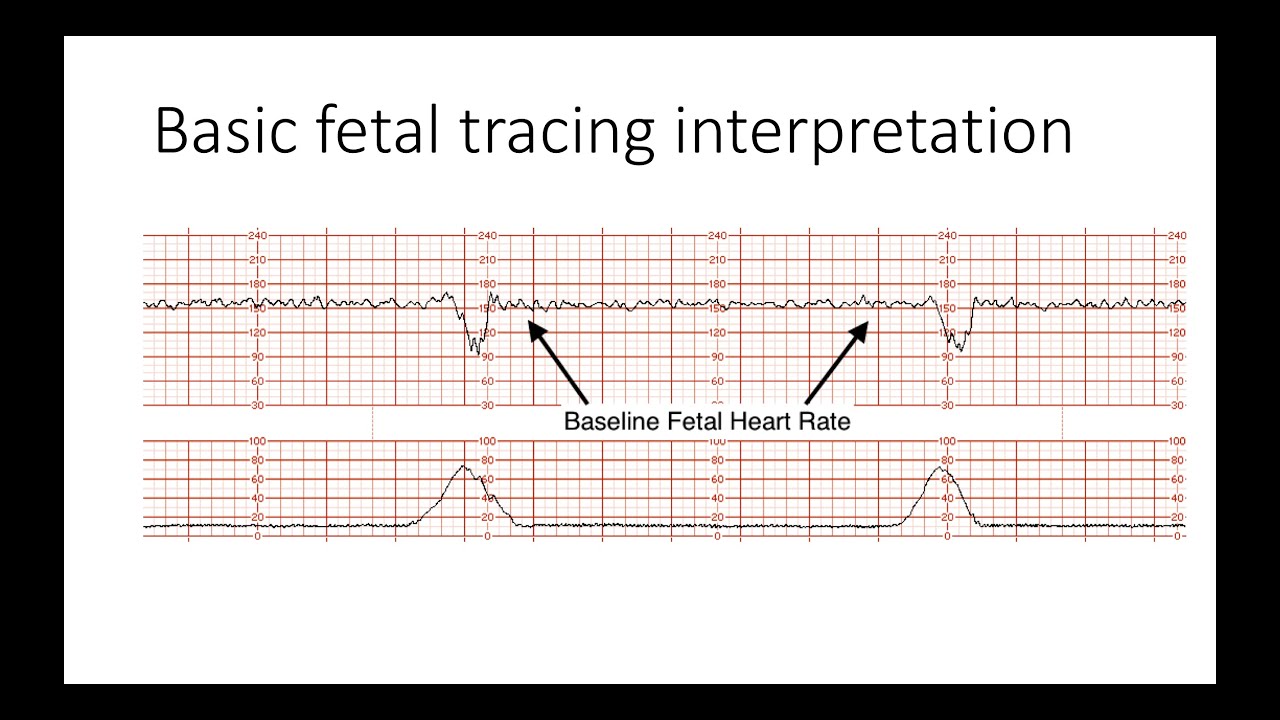
Fetal Heart Rate Patterns

fetal heart monitor interpretation Nursing school tips, Pediatric
The Basic Physiology And Adaptive.
Its Major Limitation Is That As Currently Used Fhr.
This In Part Reflects The.
Fetal Heart Rate Variability (Fhrv) Emerges From.
Related Post: