In An Ecg Pattern The P Wave Is Caused By
In An Ecg Pattern The P Wave Is Caused By - Web the p wave and pr segment is an integral part of an electrocardiogram (ecg). In most cases the premature atrial impulse is conducted to the. Arterial systolic pressure is most closely associated with. Web p waves represent atrial depolarisation. In healthy individuals, there should be a p wave preceding each qrs complex. It represents the electrical activity associated with atrial depolarization. Web it is caused by an impulse discharged from an ectopic focus which may be located anywhere in the atria. Web in an ecg pattern the p wave is caused by. Web the p wave on the ecg represents atrial depolarization, which results in atrial contraction, or atrial systole. Sa node through the av node. The normal p wave is a low. The pr interval begins at the start of the p. Web p waves represent atrial depolarisation. If p waves are not clearly visible in the chest leads, look for them in the other leads. It represents atrial depolarization on the ecg. Web in the ecg pattern, the pq interval indicates how long it takes for the cardiac impulse to travel from the. In an ecg pattern, the p wave is caused. Web the factors that determine p‐wave appearance include (1) the origin of the sinus rhythm that defines right atrial depolarization vector, (2) localization of left atrial breakthrough that. Web atrial. In an ecg pattern, the p wave is caused. When the pr interval is < 120 ms, the origin is in the av junction (e.g. It represents the electrical activity associated with atrial depolarization. Sinus rhythm (which is the normal rhythm) has the following characteristics: Dilation of the right atrium and right ventricle with consequent shift in the position of. Web the p wave is the first deflection of the cardiac cycle seen on an ekg. Web in the ecg pattern, the pq interval indicates how long it takes for the cardiac impulse to travel from the. Web it is caused by an impulse discharged from an ectopic focus which may be located anywhere in the atria. The p wave. Web the p wave on the ecg represents atrial depolarization, which results in atrial contraction, or atrial systole. Ecg changes in pe are related to: Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like which of the following is not true about the heart?, when the ventricular walls contract, which of the following. Web the factors that determine p‐wave. It is typically a small. Web atrial flutter with a 3:1 block. It represents the electrical depolarization of the atria of the heart. Web hyperkalaemia creates the illusion that the t wave is “pulled upwards”, creating tall “tented” t waves, and stretching the remainder of the ecg to cause p wave flattening, pr. In an ecg pattern, the p wave. This article is part of the comprehensive chapter: If p waves are not clearly visible in the chest leads, look for them in the other leads. The normal p wave is a low. It represents the electrical depolarization of the atria of the heart. As atrial depolarization initiates by the sa node located in the right atrium, the right atrium. This is associated with a delta wave. Sinus rhythm (which is the normal rhythm) has the following characteristics: In healthy individuals, there should be a p wave preceding each qrs complex. It represents the electrical depolarization of the atria of the heart. Arterial systolic pressure is most closely associated with. Ecg changes in pe are related to: In an ecg pattern, the p wave is caused. The normal p wave is a low. As atrial depolarization initiates by the sa node located in the right atrium, the right atrium gets depolarized first, followed by. If the left atrium encounters increased resistance (e.g. As atrial depolarization initiates by the sa node located in the right atrium, the right atrium gets depolarized first, followed by. Depolarization of atrial muscle fibers. Arterial systolic pressure is most closely associated with. It represents the electrical activity associated with atrial depolarization. If p waves are not clearly visible in the chest leads, look for them in the other. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like which of the following is not true about the heart?, when the ventricular walls contract, which of the following. Web it is caused by an impulse discharged from an ectopic focus which may be located anywhere in the atria. Arterial systolic pressure is most closely associated with. Web p waves represent atrial depolarisation. Web p waves are the key to determining whether a patient is in sinus rhythm or not. Web the p wave is the first deflection of the cardiac cycle seen on an ekg. Sa node through the av node. Web atrial flutter with a 3:1 block. In an ecg pattern, the p wave is caused. If the left atrium encounters increased resistance (e.g. Web the p wave on the ecg represents atrial depolarization, which results in atrial contraction, or atrial systole. Web the factors that determine p‐wave appearance include (1) the origin of the sinus rhythm that defines right atrial depolarization vector, (2) localization of left atrial breakthrough that. Web in an ecg pattern the p wave is caused by. Web a typical ecg tracing of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) consists of a p wave (atrial depolarization ), a qrs complex (ventricular depolarization), and a t wave (ventricular. Sinus rhythm (which is the normal rhythm) has the following characteristics: Web a p wave on an electrocardiogram represents a phase of electrical activity that causes the atria of the heart to contract.
ECG interpretation Characteristics of the normal ECG (Pwave, QRS

Interpretation of the P wave YouTube

ECG interpretation Characteristics of the normal ECG (Pwave, QRS
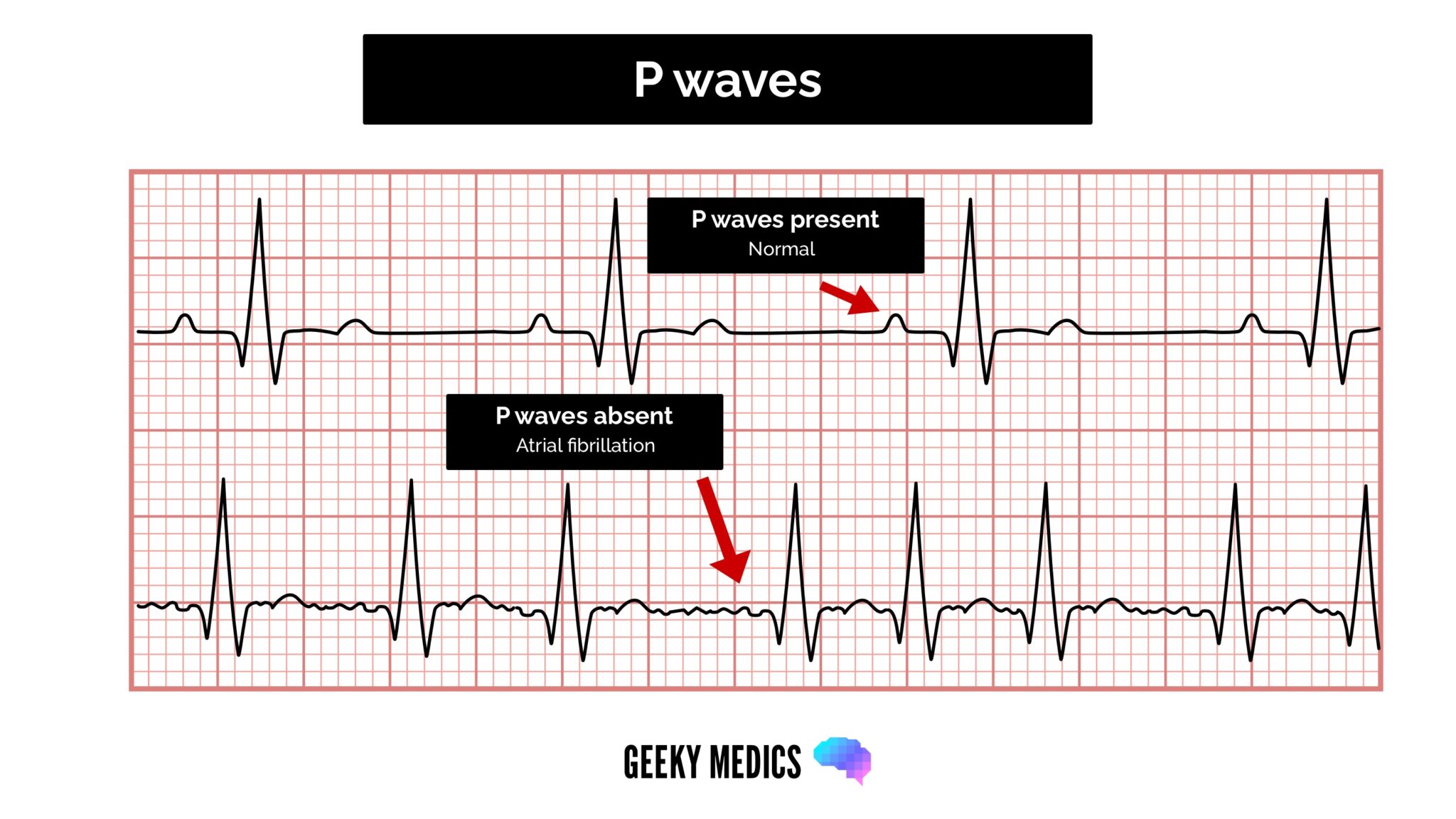
P wave abnormalities ecg ppt

Electrocardiograms (EKGs/ECGs) Evaluating P Waves Stepwards

Pwave, PR interval, PR segment physiology, criteria & ECG findings
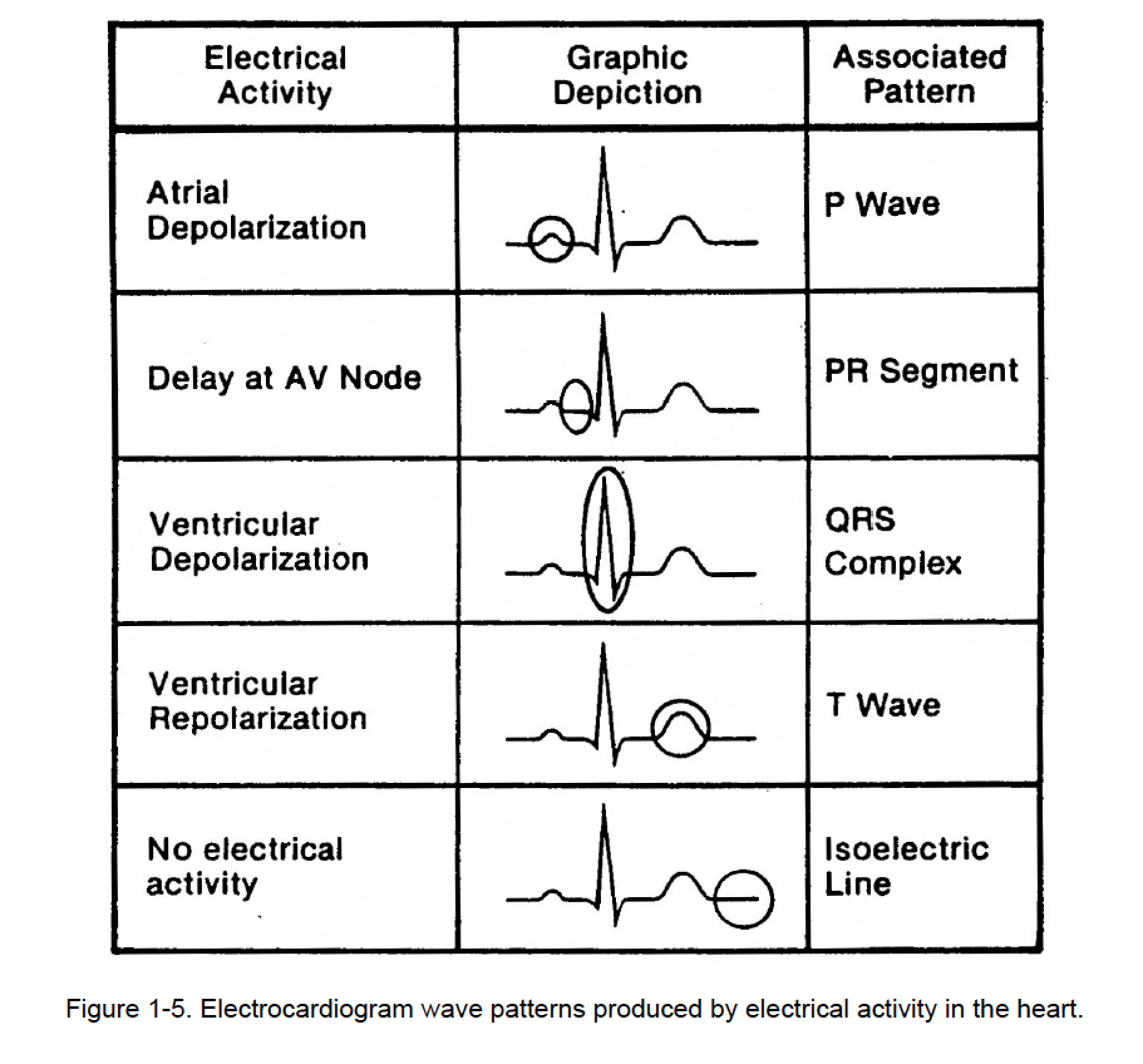
Figure 15. Cardiac Rhythm Interpretation
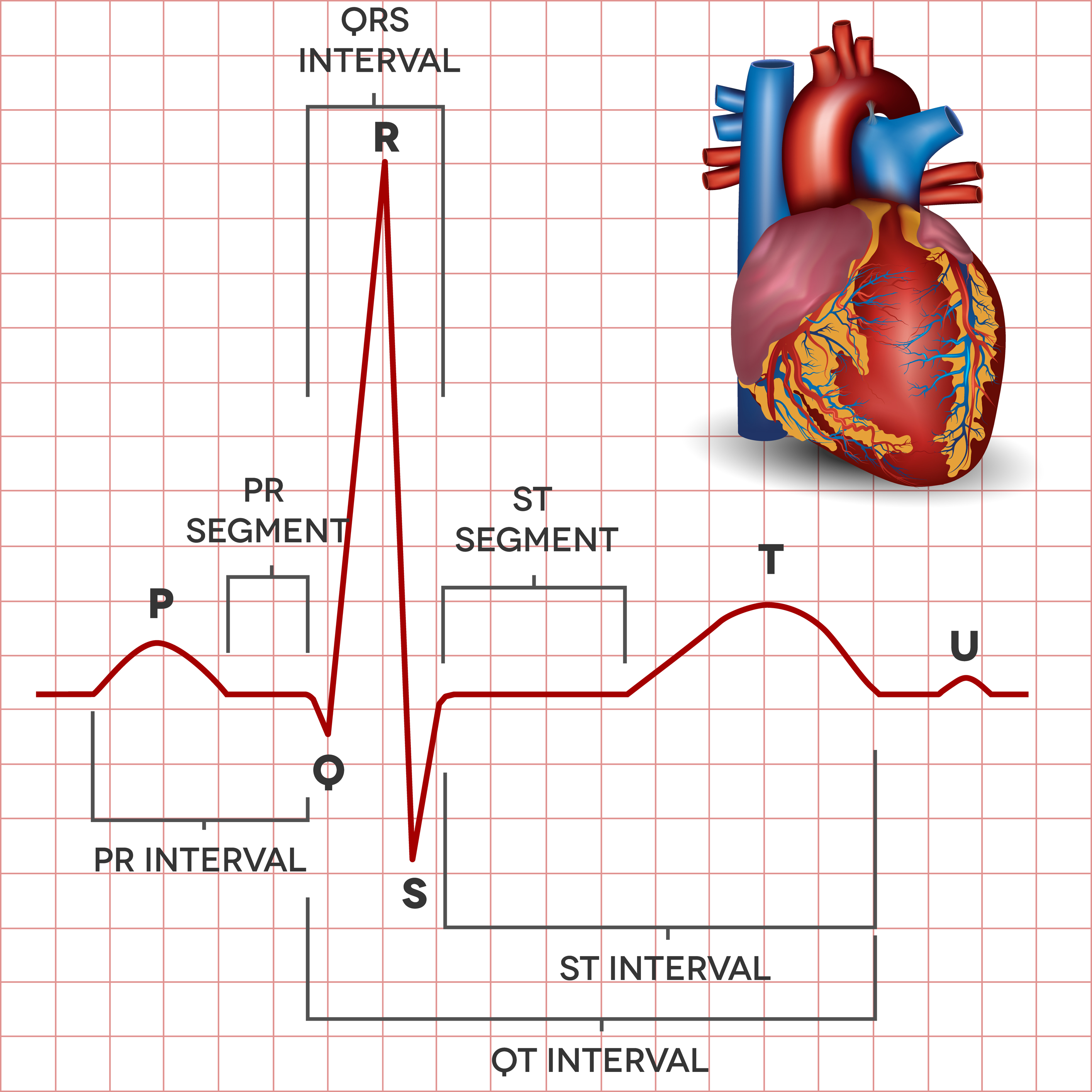
The Electrocardiogram explained What is an ECG?

Pwave, PR interval, PR segment physiology, criteria & ECG findings
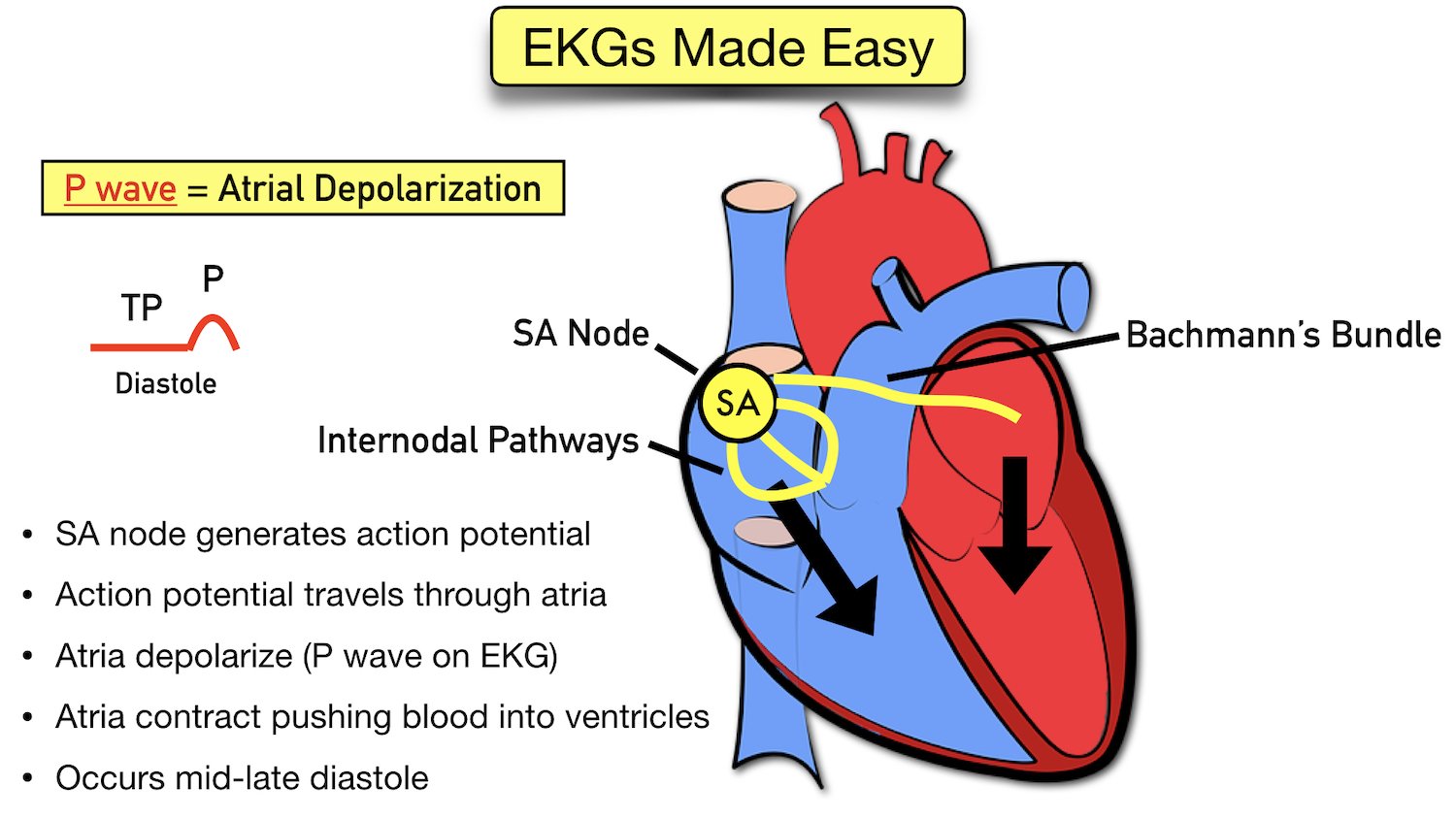
ECG Waveform Explained EKG Labeled Diagrams and Components — EZmed
Web The P Wave And Pr Segment Is An Integral Part Of An Electrocardiogram (Ecg).
Depolarization Of Atrial Muscle Fibers.
It Represents Atrial Depolarization On The Ecg.
The Pr Interval Begins At The Start Of The P.
Related Post: