Huntingtons Disease Pattern Of Inheritance
Huntingtons Disease Pattern Of Inheritance - The earliest symptoms are often subtle problems with mood or mental/psychiatric abilities. Predictive genetic test a genetic test can be given if you have a family history of the disease but don't have symptoms. Web among genetic disorders, the huntington’s disease inheritance pattern is not typical, but more about this shortly. Web who is at risk. It produces a protein called huntingtin. Genetics and pathology of huntington's disease. Inheritance is independent of gender. Having a working familiarity with the basic genetics of hd is key to understanding the inheritance and expression of the disease. This chapter addresses two aspects of huntington’s disease (hd). Web huntington described the autosomal dominant inheritance pattern of this condition, which is accompanied by a loss of motor control leading to jerky movements, altered personality and. Web single gene disorders, like huntington’s disease and cystic fibrosis, actually follow mendelian inheritance patterns. Common symptoms include uncontrollable movements and changes to your thinking, behavior. If one parent carries the abnormal gene, each of their biological children has a 50 percent chance of huntington's disease inheritance. Web patterns of inheritance of the symptoms of huntington's disease suggestive of an. Web huntington disease is a progressive brain disorder that causes uncontrolled movements, emotional problems, and loss of thinking ability (cognition). The probability of each offspring inheriting an affected gene is 50%. This means that a person needs only one copy of the nontypical gene to develop the disorder. Web huntington's disease follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. If one parent. Web the genetic counselor also can answer questions about the inheritance patterns of huntington's disease. Explore symptoms, inheritance, genetics of this condition. Web patterns of inheritance of the symptoms of huntington's disease suggestive of an effect of genomic imprinting. Genetics and pathology of huntington's disease. What is the inheritance pattern for the huntington’s disease allele? Web huntington described the autosomal dominant inheritance pattern of this condition, which is accompanied by a loss of motor control leading to jerky movements, altered personality and. If both parents have the faulty gene the child has a 75 % chance of inheriting it. A person who inherits the hd gene, and survives long enough, will sooner or later develop. Inheritance is independent of gender. Huntington’s disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. The gene responsible for huntington’s disease (hd) is called htt. Web huntington described the autosomal dominant inheritance pattern of this condition, which is accompanied by a loss of motor control leading to jerky movements, altered personality and. Web huntington's disease is autosomal dominant, meaning inheritance of. What is the inheritance pattern for the huntington’s disease allele? The gene responsible for huntington’s disease (hd) is called htt. The probability of each offspring inheriting an affected gene is 50%. Huntington’s disease is an inherited condition that causes brain cells to slowly lose function and die. With the exception of genes on the sex chromosomes, a person inherits two. Web who is at risk. It is caused by changes in the htt gene and is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Hd is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Heredity is the only known cause of huntington’s disease. Common symptoms include uncontrollable movements and changes to your thinking, behavior. Huntington's disease is a condition that stops parts of the brain working properly over time. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. This means that a person needs only one copy of the nontypical gene to develop the disorder. A person who inherits the hd gene, and survives long enough, will sooner or later develop the disease. The probability. Web the genetic counselor also can answer questions about the inheritance patterns of huntington's disease. Predictive genetic test a genetic test can be given if you have a family history of the disease but don't have symptoms. Huntington’s disease is an inherited condition that causes brain cells to slowly lose function and die. Having a working familiarity with the basic. Every child conceived naturally to a parent who has the faulty gene has a 50 % chance of inheriting it and the disease. The earliest symptoms are often subtle problems with mood or mental/psychiatric abilities. Web who is at risk. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Having a working familiarity with the basic genetics of hd is key. It is caused by changes in the htt gene and is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. If one parent carries the abnormal gene, each of their biological children has a 50 percent chance of huntington's disease inheritance. It affects individuals from childhood to old age and. Web huntington disease is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by the elongation of cag repeats on the short arm of chromosome 4p16.3 in the htt gene. The probability of each offspring inheriting an affected gene is 50%. Web huntington's disease is autosomal dominant, meaning inheritance of just a single copy of an abnormal chromosome from a biological parent is enough to cause it. Web patterns of inheritance of the symptoms of huntington's disease suggestive of an effect of genomic imprinting. Web huntington disease is a progressive brain disorder that causes uncontrolled movements, emotional problems, and loss of thinking ability (cognition). The child needs only one copy of the gene from either parent to develop the disease. Huntington’s disease is an inherited condition that causes brain cells to slowly lose function and die. Predictive genetic test a genetic test can be given if you have a family history of the disease but don't have symptoms. This means that a person needs only one copy of the nontypical gene to develop the disorder. The interaction of symptomatology (rigidity/chorea) in huntington's disease (hd) with age of onset (ao) was examined using data from the research roster for huntington's disease patients and families. Huntington's disease ( hd ), also known as huntington's chorea, is an incurable neurodegenerative disease [7] that is mostly inherited. Web with so many recent breakthroughs in human genome research, we now know quite a bit about the genetic basis of huntington’s disease. Web the genetic counselor also can answer questions about the inheritance patterns of huntington's disease.
Patterns of Inheritance · Anatomy and Physiology

Huntington's disease (HD) Part 2; Inheritance Pattern YouTube

How is Huntington's Disease Inherited?
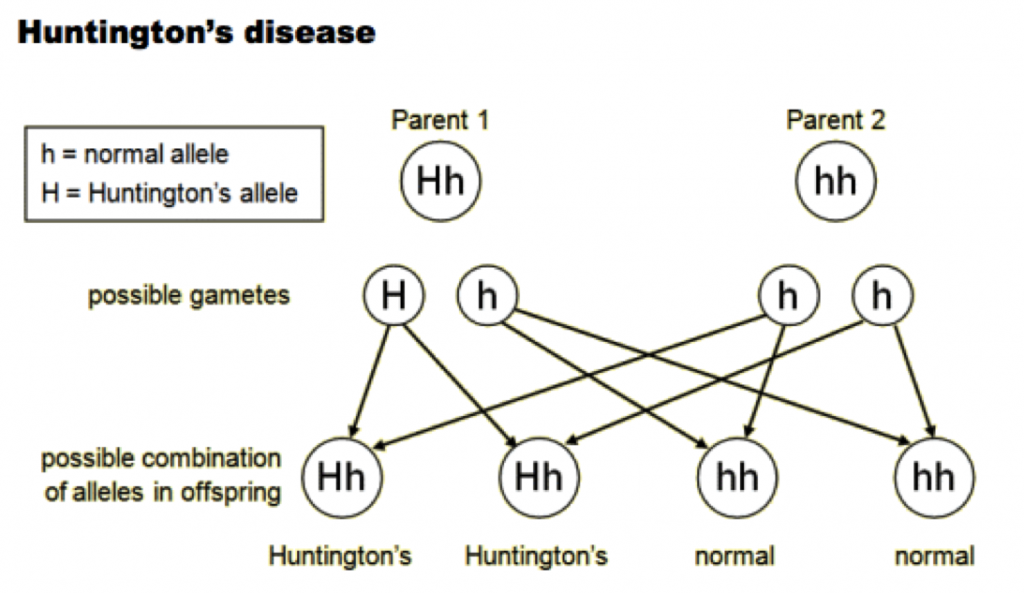
3.4 Inheritance The Biology Classroom
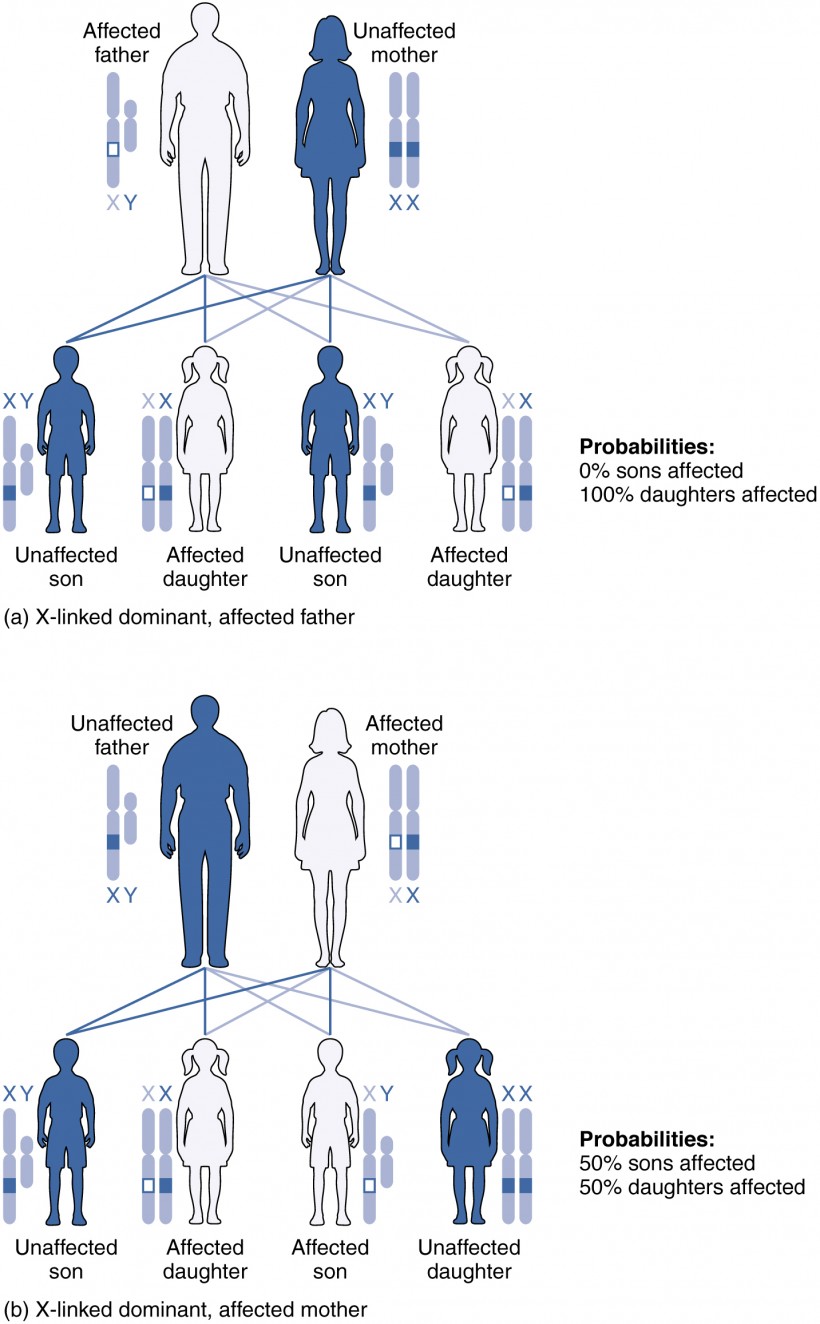
Patterns of Inheritance Anatomy and Physiology II
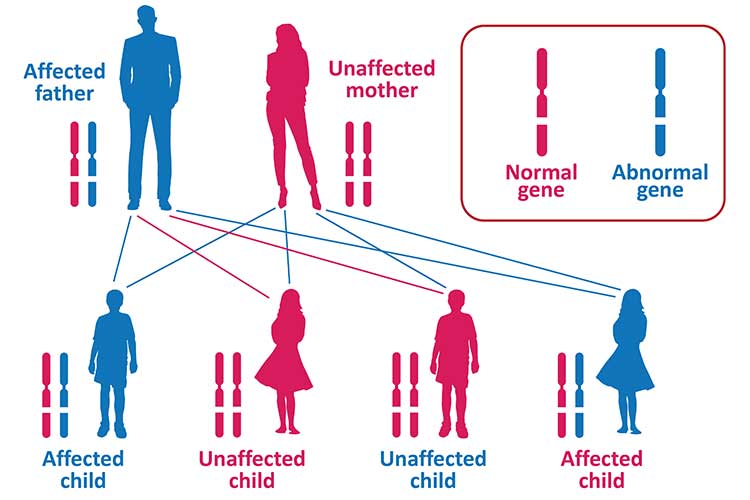
Degenerative Diseases Huntington’s Ausmed

Huntington's Disease Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
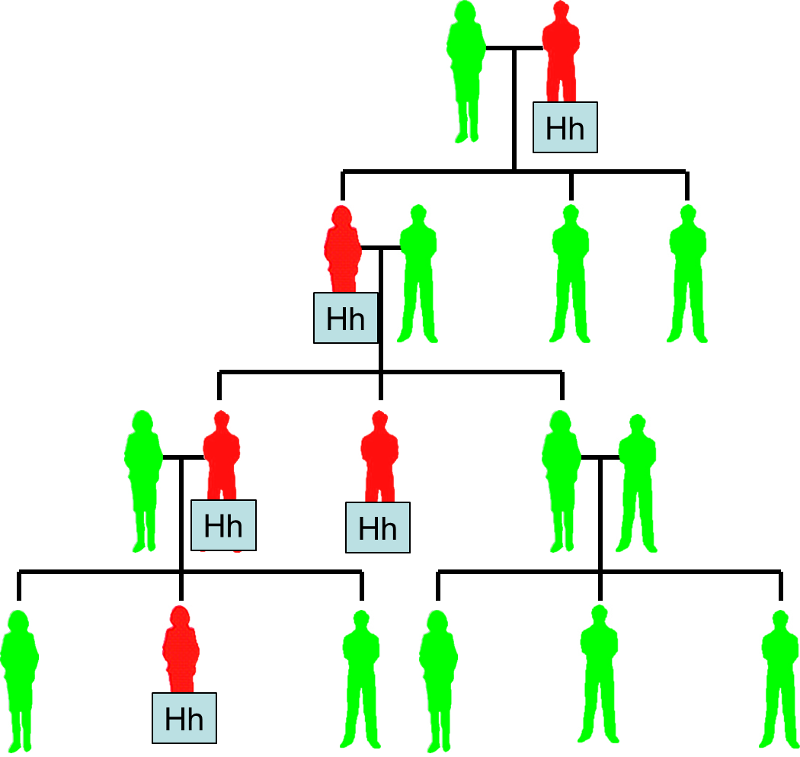
Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance
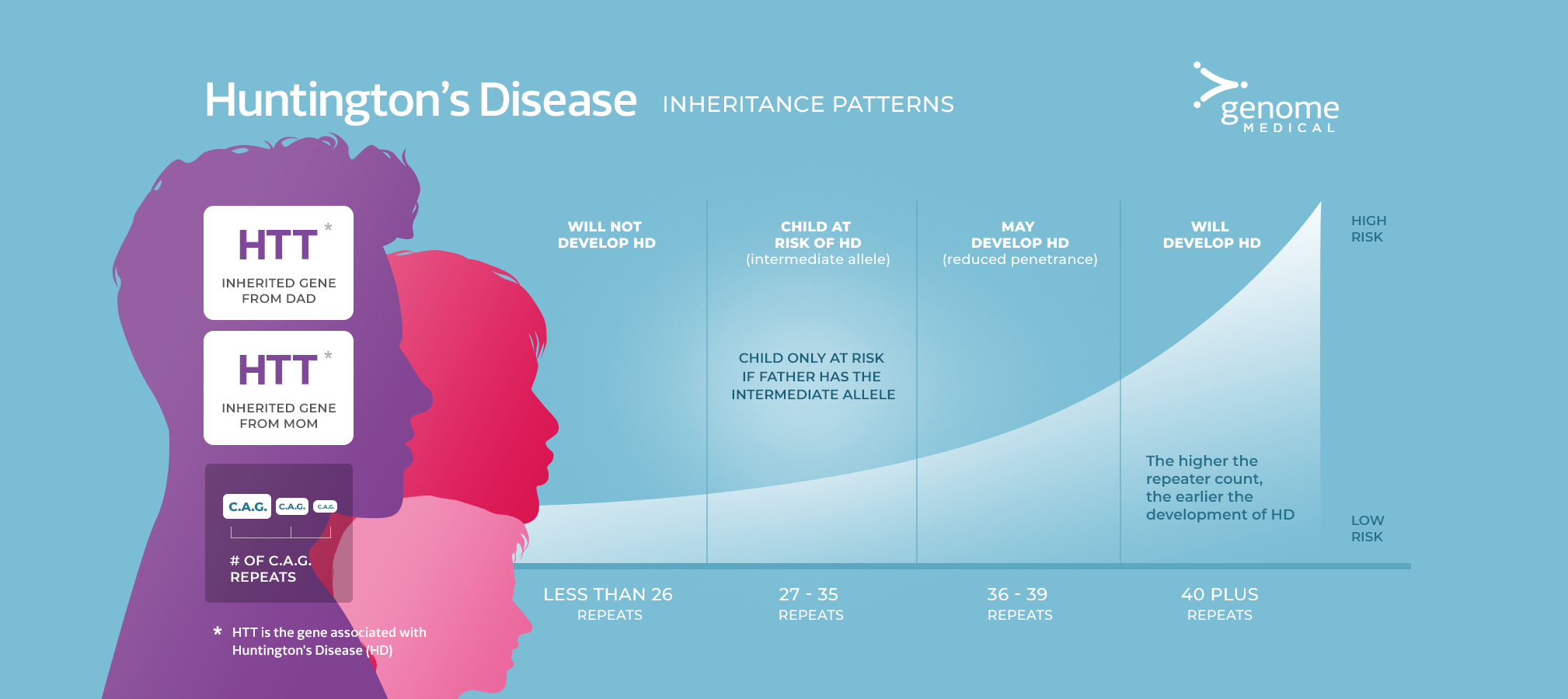
What is the Huntington’s Disease Inheritance Pattern?

Huntington's Disease Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Ultimate Guide
Genetics And Pathology Of Huntington's Disease.
Huntington Disease (Hd) Is An Inherited Condition That Causes Progressive Degeneration Of Neurons In The Brain.
It Affects The Cells In Parts Of Your Brain That Regulate Voluntary Movement And Memory.
Web Who Is At Risk.
Related Post: