How To Draw Dipole Dipole Interactions
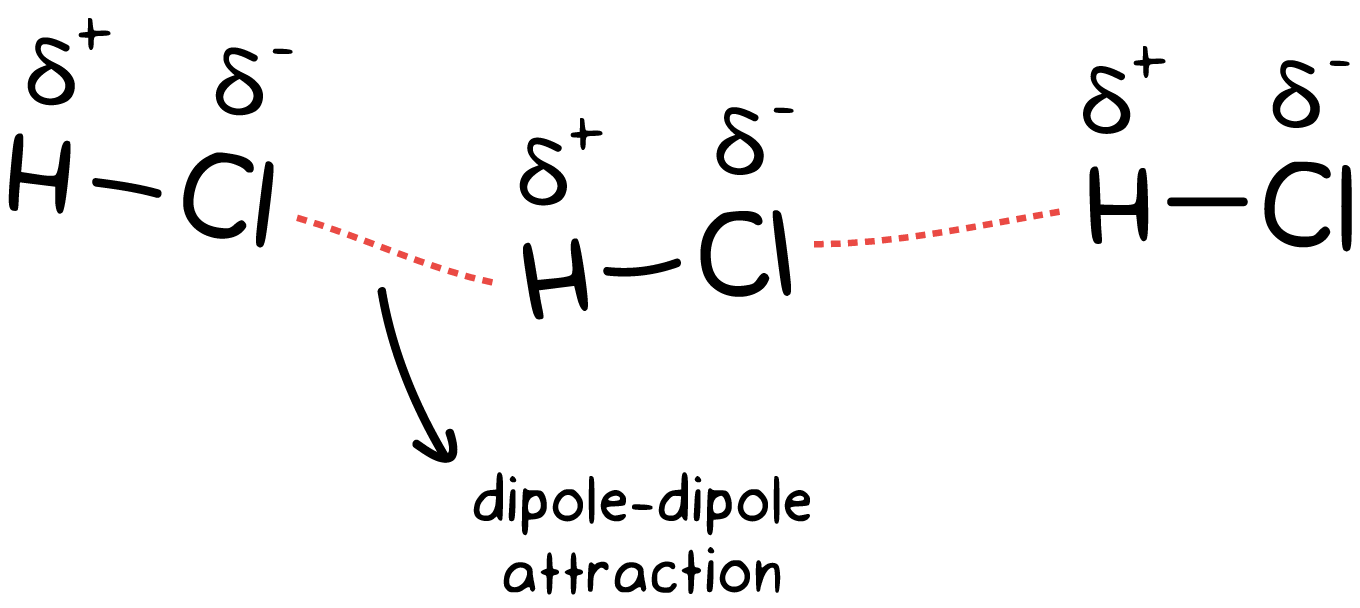
How To Draw Dipole Dipole Interactions - The prerequisite for this type of attraction to exist is partially charged ions—for example, the case of polar covalent bonds such as hydrogen chloride, hcl . Their strength is proportional to the magnitude of the dipole moment and to 1/r 6, where r is the distance between dipoles. Web the dipole moment of a molecule can be calculated by equation 1: For molecules of similar size and mass, the strength of these forces increases with increasing polarity. The dipole moment acts in the direction of the vector quantity. An example of a polar molecule i s h 2o. Is the dipole moment vector. Draw a box around the hydrogen bond donor and a circle around the hydrogen bond acceptor. 138k views 6 years ago new ap & general chemistry video playlist. Web electric and magnetic dipole moments are two fundamental electromagnetic excitations that have been extensively studied. An electric monopole is a single charge, while a dipole is two opposite charges closely spaced to. The dipoles can be side by side but pointing in opposite directions, or they can be end to end. Is the vector representing the position of ith. The positive region of one molecule is attracted to the negative region of another and repulsed. Web for an heme to form properly, multiple steps must occur, all of which involve dipole interactions. They are much weaker than ionic or covalent bonds and have a significant effect only when the molecules. These forces occur when the partially positively charged part of a molecule interacts with the partially negatively charged part of the neighboring molecule. As a. These forces occur when the partially positively charged part of a molecule interacts with the partially negatively charged part of the neighboring molecule. Draw a box around the hydrogen bond donor and a circle around the hydrogen bond acceptor. Web when a positive and negative dipole approach each other, it creates an attractive intermolecular interaction whereas two positive dipoles or. Generally, the positive end of one molecule is attracted to the negative end of another molecule. Web how do you determine what forces act when you have big and diverse molecule like an anhydride, e.g. The dipole moment acts in the direction of the vector quantity. Web the organic chemistry tutor. Web when a positive and negative dipole approach each. Schematic illustration of the 3dom microscopy. →μ = ∑ i qi→ri. An electric monopole is a single charge, while a dipole is two opposite charges closely spaced to. They are much weaker than ionic or covalent bonds and have a significant effect only when the molecules. Web when a positive and negative dipole approach each other, it creates an attractive. Two such arrangements are possible: 138k views 6 years ago new ap & general chemistry video playlist. Web when a positive and negative dipole approach each other, it creates an attractive intermolecular interaction whereas two positive dipoles or two negative dipoles will create a repulsive intermolecular interaction. Their strength is proportional to the magnitude of the dipole moment and to. Web research presents 2d dipole orientation method for mapping cells. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into ion dipole forces and ion induced dipole interactions. Schematic illustration of the 3dom microscopy. Generally, the positive end of one molecule is attracted to the negative end of another molecule. 138k views 6 years ago new ap & general chemistry video. Web electric and magnetic dipole moments are two fundamental electromagnetic excitations that have been extensively studied. Web the dipole moment of a molecule can be calculated by equation 1: Their strength is proportional to the magnitude of the dipole moment and to 1/r 3, where r is the distance between dipoles. 460k views 6 years ago new ap & general. Web research presents 2d dipole orientation method for mapping cells. Generally, the positive end of one molecule is attracted to the negative end of another molecule. Web when a positive and negative dipole approach each other, it creates an attractive intermolecular interaction whereas two positive dipoles or two negative dipoles will create a repulsive intermolecular interaction. Is the vector representing. An electric monopole is a single charge, while a dipole is two opposite charges closely spaced to. The relative strength of these forces can be understood in terms of coulomb's law, which tells us that the electrostatic attraction between ion and dipole is directly related to the magnitudes of the ion charge and the dipole and inversely related to the. 1 start by drawing the structures of the molecules. The relative strength of these forces can be understood in terms of coulomb's law, which tells us that the electrostatic attraction between ion and dipole is directly related to the magnitudes of the ion charge and the dipole and inversely related to the distance between them. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into. An electric monopole is a single charge, while a dipole is two opposite charges closely spaced to. For molecules of similar size and mass, the strength of these forces increases with increasing polarity. The prerequisite for this type of attraction to exist is partially charged ions—for example, the case of polar covalent bonds such as hydrogen chloride, hcl . In section 8.8 we learned that polar covalent bonds occur between atoms of different electronegativity ( section 8.7 ), where the more electronegative atom attracts the electrons more than the electropositive atom, and based on the geometry, this may. Two such arrangements are possible: An example of a polar molecule i s h 2o. Is the dipole moment vector. Schematic illustration of the 3dom microscopy. However, as a third independent family of electromagnetic multipole theory, the toroidal dipole moment was first introduced by zel'dovich in 1958 as an explanation for the parity violation of the weak interaction in. The positive region of one molecule is attracted to the negative region of another and repulsed by the positive region of another molecule. Their strength is proportional to the magnitude of the dipole moment and to 1/r 3, where r is the distance between dipoles. Web the organic chemistry tutor. Web when a positive and negative dipole approach each other, it creates an attractive intermolecular interaction whereas two positive dipoles or two negative dipoles will create a repulsive intermolecular interaction.
Iondipole Forces (Interaction) Definition and Examples
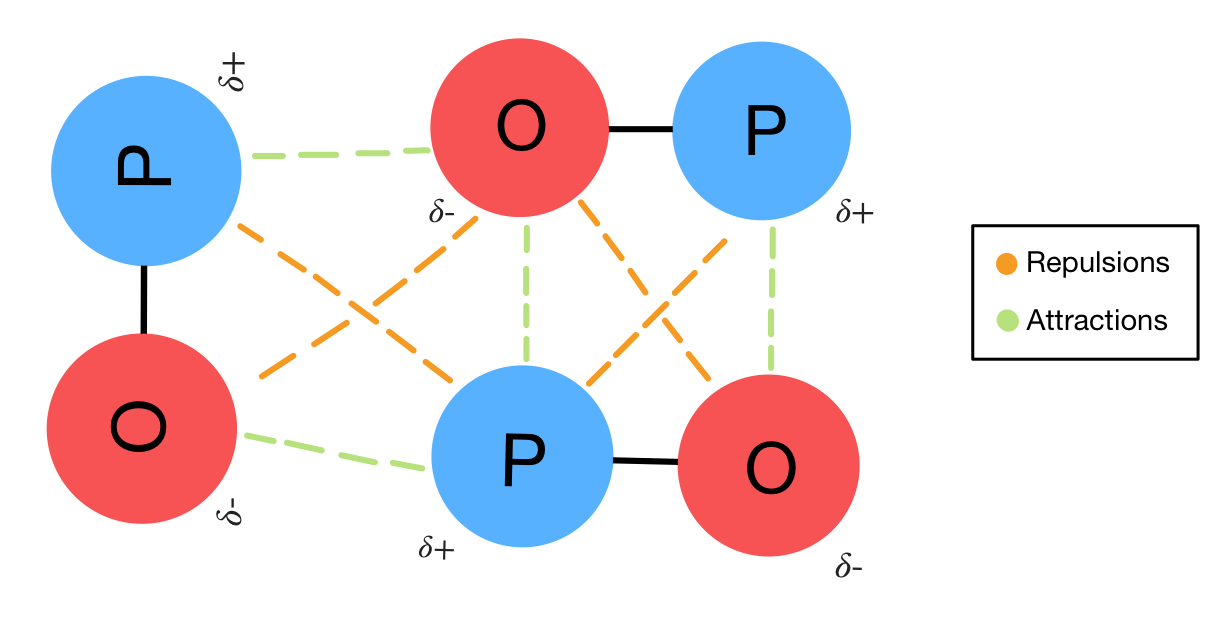
DipoleDipole Interactions — Definition & Overview Expii
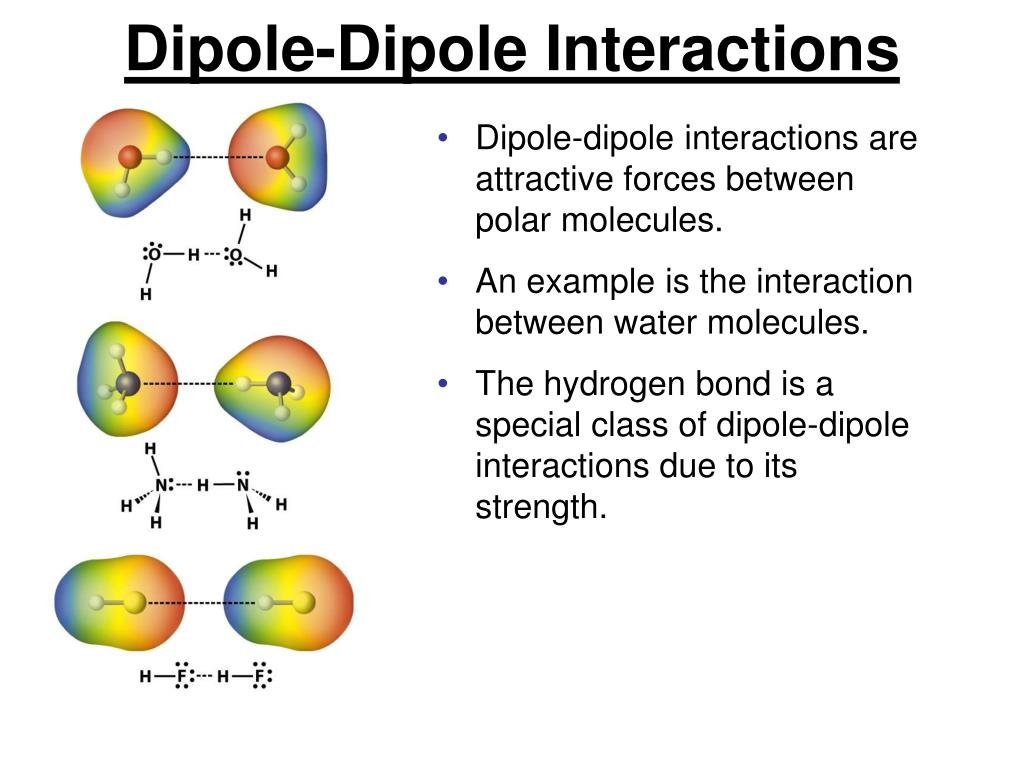
PPT Chapter 11 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5852920

DipoleDipole Interactions — Definition & Overview Expii

Dipole Dipole Forces of Attraction Intermolecular Forces YouTube
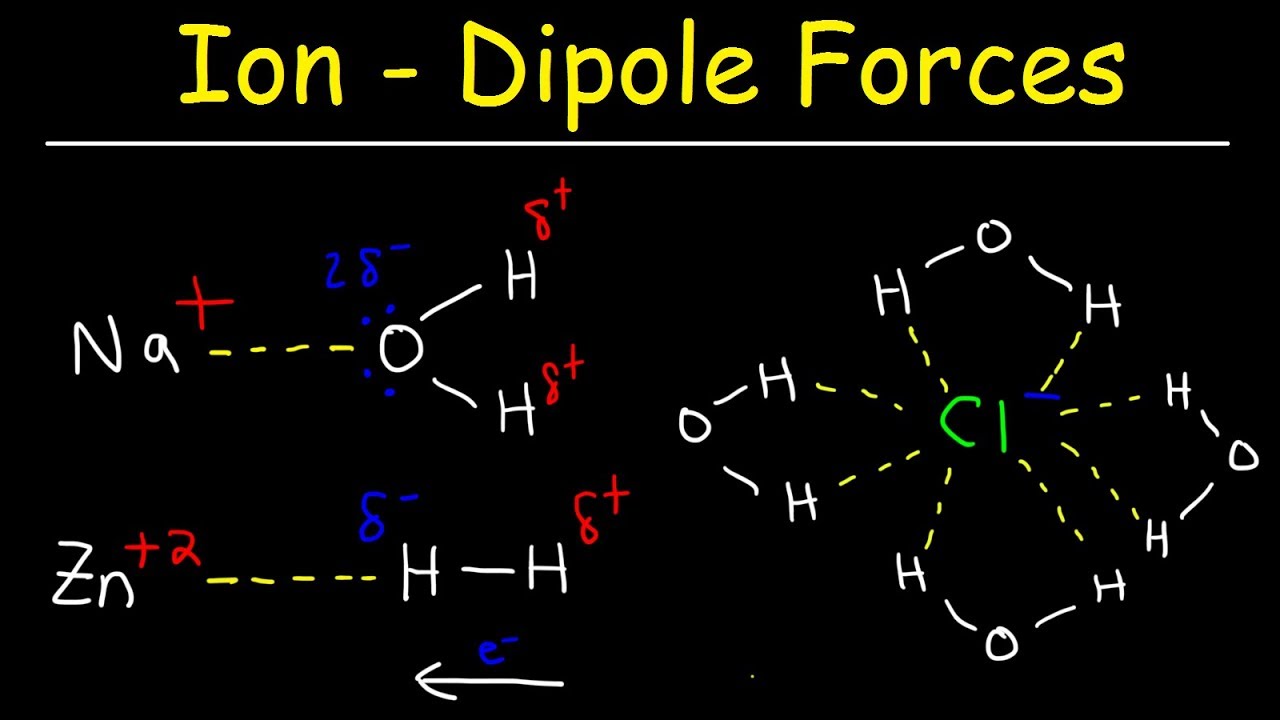
Ion Dipole Forces & Ion Induced Dipole Interactions Chemistry YouTube
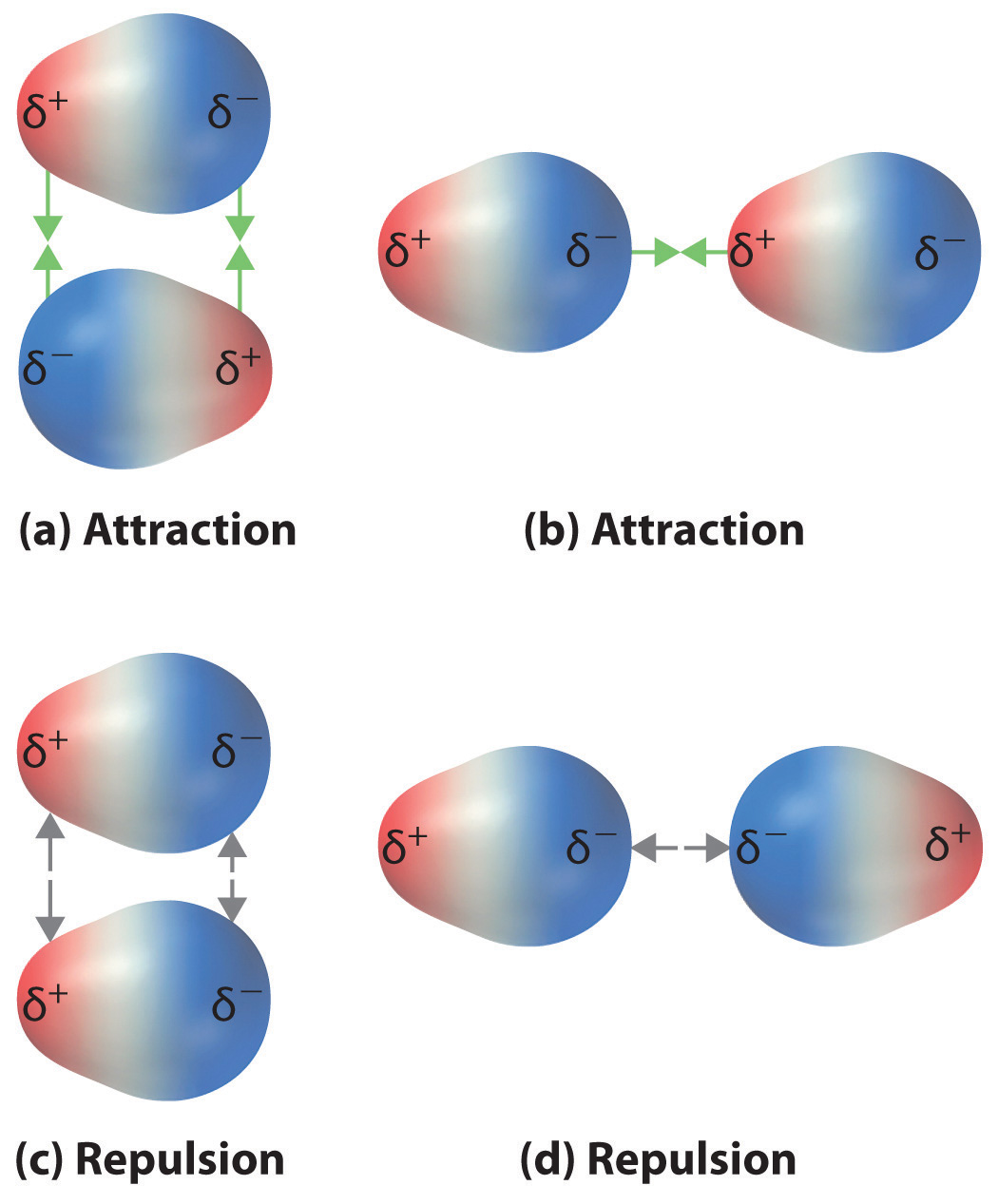
CH103 Chapter 5 Covalent Bonds and Introduction to Organic Molecules

Iondipole Forces (Interaction) Definition and Examples

Dipoledipole, London Dispersion and Hydrogen Bonding Interactions
Intermolecular Force Types and Examples StudiousGuy
Web If Two Ethyl Ether Molecules Are Brought Together, The Opposite Partial Charges Will Be Attracted To One Another.
Web How Temporary Dipoles Give Rise To Intermolecular Attractions.
These Interactions Align The Molecules To Increase The Attraction.
Web For An Heme To Form Properly, Multiple Steps Must Occur, All Of Which Involve Dipole Interactions.
Related Post: