How To Draw Acceleration Vs Time Graph
How To Draw Acceleration Vs Time Graph - Acceleration is slope of velocity vs time. This tutorial breaks down how to easily and effectively interpret an acceleration vs time graph to figure out how the velocity is being. Displacement = velocity × time. Web the graph below shows a constant acceleration of 4 m/s 2 for a time of 9 s. Web since δ v δ t is the definition of acceleration, the slope of a velocity graph must equal the acceleration of the object. When the motion equations cannot be used. Web adjust the initial position and the shape of the velocity vs. Time graph to find the change in momentum and solves an example problem to find the final velocity of a spaceship. If the slope is negative and not changing, the velocity is a negative constant. It helps us calculate the other kinematic quantities even when no other option is available, i.e. Time graph that is a straight line? If that slope is not changing, the velocity is constant. S = v × t Web how to sketch acceleration time graph from velocity time graph. Web how would you use a position vs. Web it was learned earlier in lesson 4 that the slope of the line on a velocity versus time graph is equal to the acceleration of the object. Web these are acceleration vs time graphs. Web finally, the acceleration vs time graph (on the right) shows how quickly something is speeding up or slowing down, relative to an observer. In. The acceleration vs time graph. If that slope is not changing, the velocity is constant. Watch how the graphs of position vs. Acceleration is defined as, \ (\begin {array} {l}\delta a=\frac {\delta v} {\delta t}\end {array} \) by multiplying both sides of the equation by the change in time δt, we get. Web how to read a position vs. This physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into motion graphs such as position time graphs, velocity time graphs, and acceleration time. Web finally, the acceleration vs time graph (on the right) shows how quickly something is speeding up or slowing down, relative to an observer. Drawing line graphs can help you understand motion. Web since δ v δ t. In this tutorial we cover the third type of motion graph: Time curve, and the slope of a velocity vs. Recall that linear equations have the general form. Web how would you use a position vs. The slope of a position vs. Web how to sketch acceleration time graph from velocity time graph. The acceleration vs time graph. Acceleration is slope of velocity vs time. This means that when the slope is steep, the object will be changing velocity rapidly. Motion graphs, also known as kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram the motion of objects in physics. 186k views 8 years ago kinematics physics calculus ibsl math motion graph displacement. Time curve is used to construct a velocity vs. When the motion equations cannot be used. Web the graph is linear (that is, a straight line). Recall that linear equations have the general form. Web how to sketch acceleration time graph from velocity time graph. Using the graph to determine displacement, distance, average velocity, average speed, instantaneous velocity, and instantaneous speed. If that slope is not changing, the velocity is constant. 1.7k views 3 years ago kinematic graphs. Time curve, and the slope of a velocity vs. It helps us calculate the other kinematic quantities even when no other option is available, i.e. Web the graph below shows a constant acceleration of 4 m/s 2 for a time of 9 s. Web adjust the initial position and the shape of the velocity vs. Use increments of 0.5 s in your graphs. Displacement = velocity × time. Web how would you use a position vs. Time change as they adjust to match the motion shown on the velocity vs. Web the graph below shows a constant acceleration of 4 m/s 2 for a time of 9 s. It helps us calculate the other kinematic quantities even when no other option is available, i.e. If the slope is. S = v × t Acceleration is slope of velocity vs time. Any line above the time axis (a=0) indicates positive acceleration. Web how to read a position vs. Want to join the conversation? If that slope is not changing, the velocity is constant. Time graph by sliding the points up or down. It helps us calculate the other kinematic quantities even when no other option is available, i.e. The number m is called the slope of the line (the vertical rise over the horizontal run). Velocity is the slope of position vs. Motion graphs, also known as kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram the motion of objects in physics. Displacement = velocity × time. If the object is moving with an acceleration of +4 m/s/s (i.e., changing its velocity by 4 m/s per second), then the slope of. Watch how the graphs of position vs. Time graph to construct a velocity vs. Web these are acceleration vs time graphs.
Velocity Time Graph Meaning of Shapes Teachoo Concepts
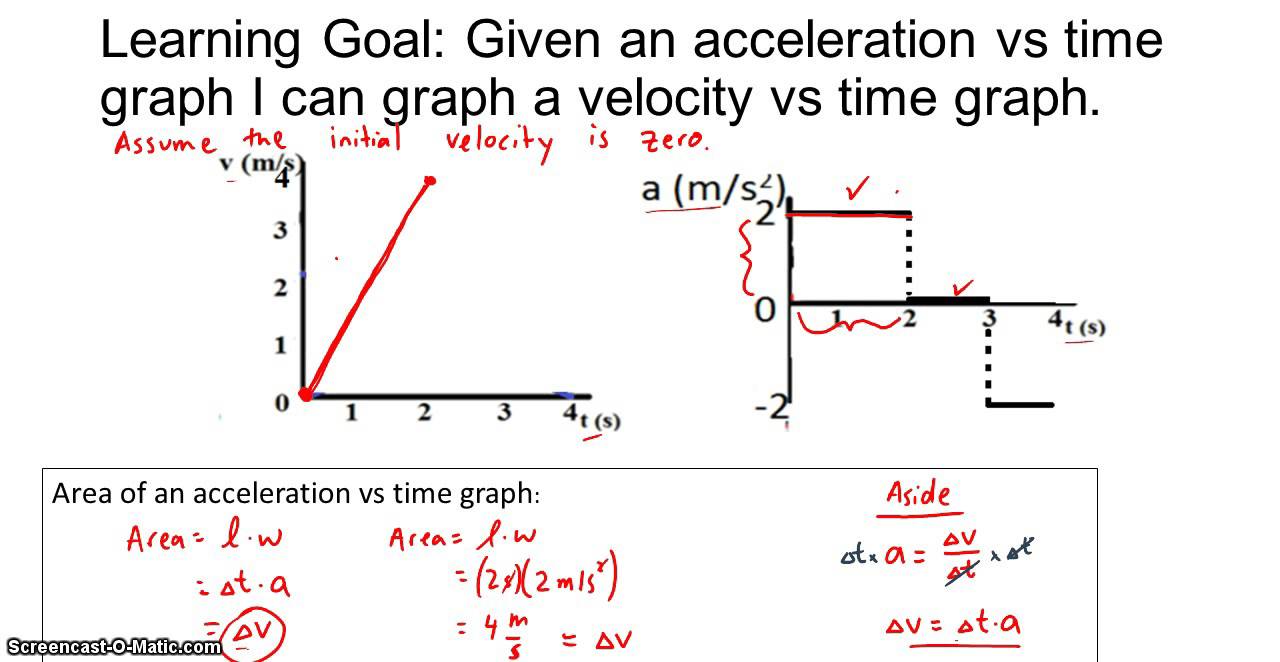
Drawing Velocity Graphs Given Acceleration Graphs YouTube
Acceleration Physics

Drawing Acceleration vs Time Graphs YouTube
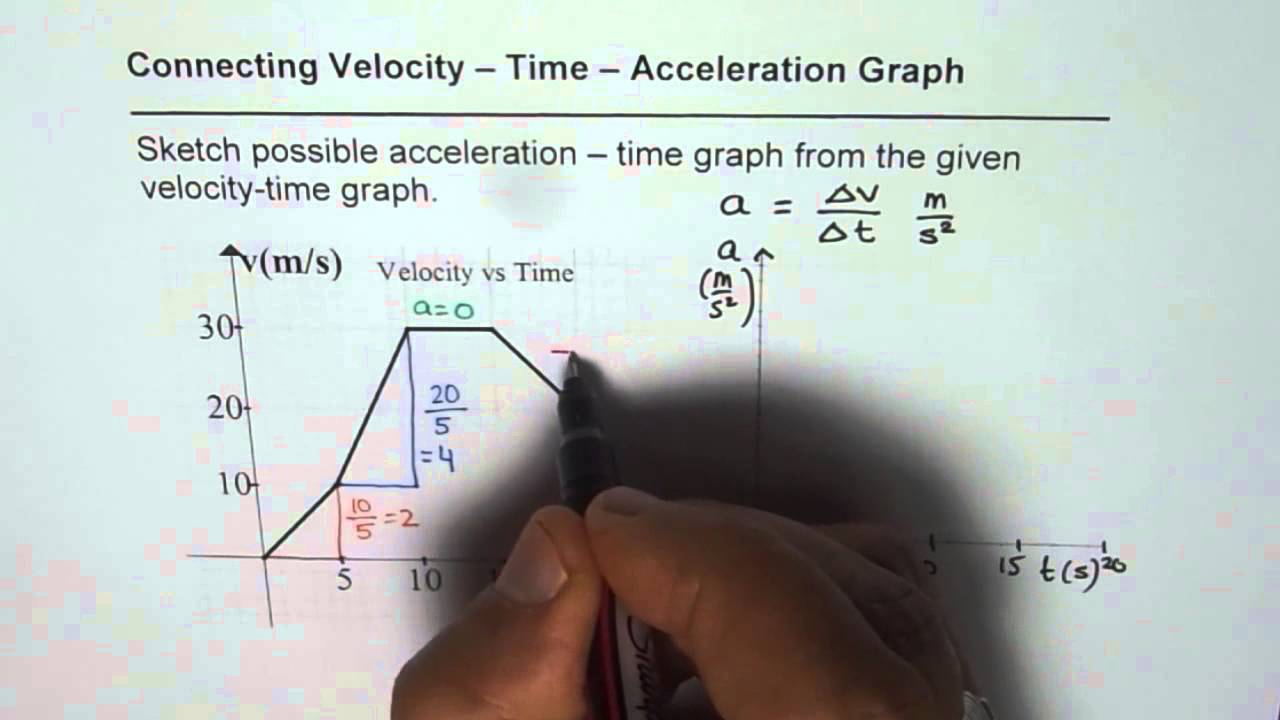
How to Sketch Acceleration Time Graph From Velocity Time Graph YouTube

Constant Acceleration Graph Velocity Vs Time Detailed Insights

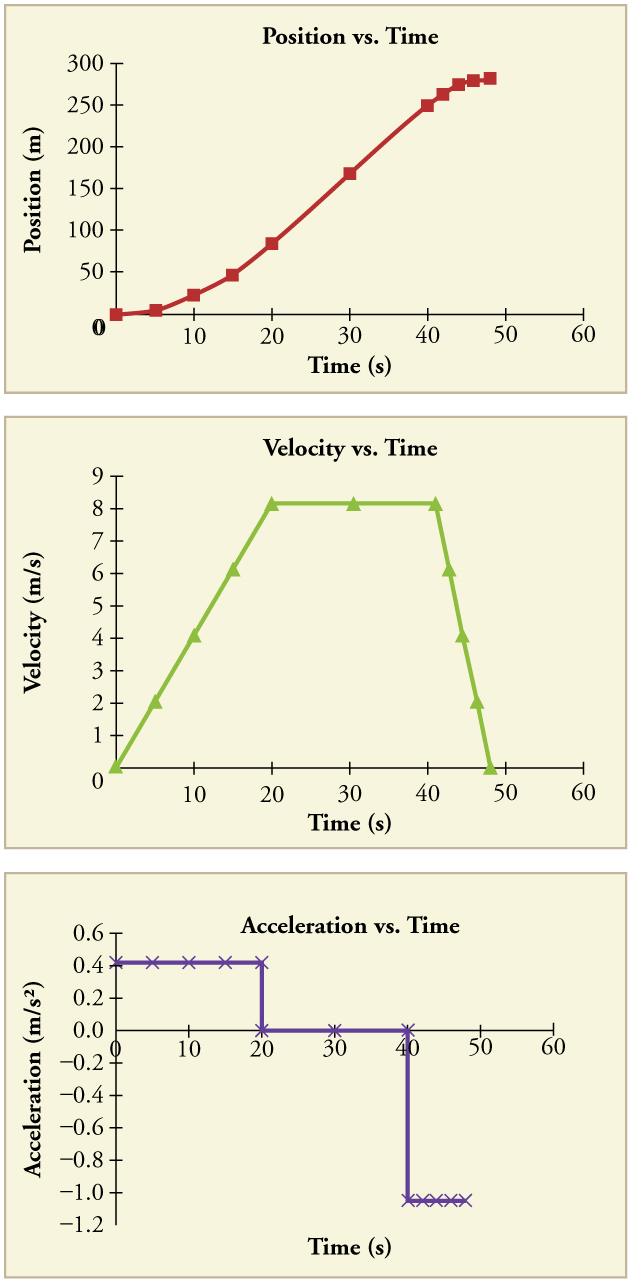
Position, Velocity, and Acceleration vs. Time Graphs GeoGebra

Draw the position time graph for stationary body +ve velocity ve

How to Calculate Acceleration From a Velocity Time Graph Tutorial YouTube
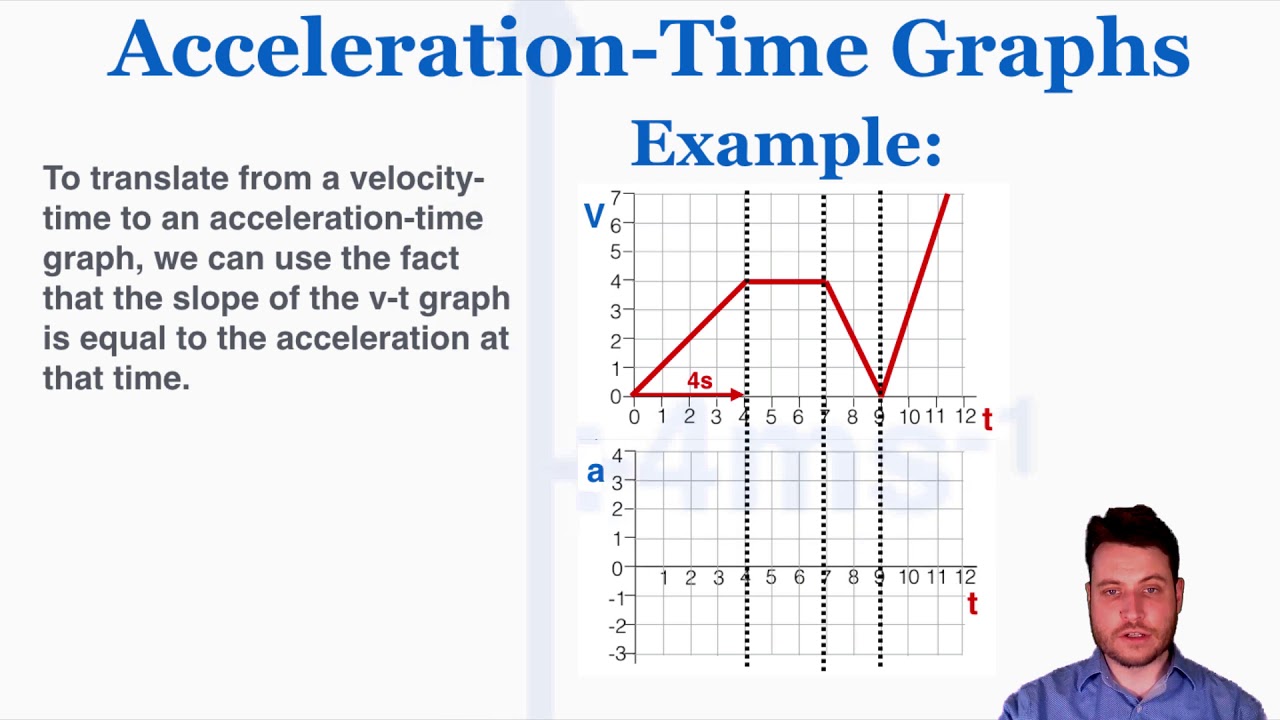
AccelerationTime Graphs IB Physics YouTube
Because All Of These Are Visual Representations Of A Movement, It Is Important To Know Your Frame Of Reference.
The Slope Of A Position Vs.
Using The Graph To Determine Displacement, Distance, Average Velocity, Average Speed, Instantaneous Velocity, And Instantaneous Speed.
If The Acceleration Is Zero, Then The Slope Is Zero (I.e., A Horizontal Line).
Related Post: