How Do You Draw Orbital Diagrams
How Do You Draw Orbital Diagrams - Web every subshell has a # of orbits s/p/d/f that can each hold 2 electrons each (one has the opposite spin of the other). This is known as the aufbau principal. Web we build electron configurations by filling the lowest energy orbitals first then filling progressively higher energy orbitals. Web however, recall that the more electronegative atom will be lower on the diagram. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here. Carbon (atomic number 6) has six electrons. Web an electron configuration diagram is a model that depicts the position of electrons as they orbit the nucleus of an atom. A p orbital along the y axis is labeled p y and one along the z axis is a p z orbital. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major. Each box represents one orbital, and each arrow indicates one. This is known as the aufbau principal. Each box represents one orbital, and each arrow indicates one. Orbitals are generally drawn as three. Web drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here. Typically, they only show the outermost electrons. Electrons are represented by dots or crosses and are positioned in energy levels, or ‘shells’, around the central nucleus. Web when drawing orbital diagrams, we include empty boxes to depict any empty orbitals in the same subshell that we are filling. Web the electrons in an atom are arranged in shells that surround. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major. Electrons in successive atoms on the. Web we build electron configurations by filling the lowest energy orbitals first then filling progressively higher energy orbitals. Web © 2024 google llc. Each box represents one orbital, and each arrow indicates one. Electrons in successive atoms on the. A p orbital along the y axis is labeled p y and one along the z axis is a p z orbital. Web © 2024 google llc. Web however, recall that the more electronegative atom will be lower on the diagram. Each box represents one orbital, and each arrow indicates one. Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. This is known as the aufbau principal. Electrons are represented by dots or crosses and are positioned in energy levels, or ‘shells’, around the central nucleus. Orbitals are generally drawn as three. Web a p orbital which extends along the. Web we build electron configurations by filling the lowest energy orbitals first then filling progressively higher energy orbitals. Web every subshell has a # of orbits s/p/d/f that can each hold 2 electrons each (one has the opposite spin of the other). Web when drawing orbital diagrams, we include empty boxes to depict any empty orbitals in the same subshell. Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here. Orbitals are generally drawn as three. Web © 2024 google llc. Web when drawing orbital diagrams, we include empty. Web the electrons in an atom are arranged in shells that surround the nucleus, with each successive shell being farther from the nucleus. Web start typing, then use the up and down arrows to select an option from the list.? Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom.. Electrons in successive atoms on the. Web for a given atom, the s orbitals also become higher in energy as n increases because of their increased distance from the nucleus. Web when drawing orbital diagrams, we include empty boxes to depict any empty orbitals in the same subshell that we are filling. Web a p orbital which extends along the. Each box represents one orbital, and each arrow indicates one. Web © 2024 google llc. Electrons are represented by dots or crosses and are positioned in energy levels, or ‘shells’, around the central nucleus. Web every subshell has a # of orbits s/p/d/f that can each hold 2 electrons each (one has the opposite spin of the other). Web the. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major. Web drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here. Web when drawing orbital diagrams, we include empty boxes to depict any empty orbitals in the same subshell that we are filling. This is known as the aufbau principal. This article will explore the. Each box represents one orbital, and each arrow indicates one. Typically, they only show the outermost electrons. Web however, recall that the more electronegative atom will be lower on the diagram. Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. Electrons in successive atoms on the. Web by lee johnson. The best way to learn how to draw mo diagrams is to work on practice problems. Web we build electron configurations by filling the lowest energy orbitals first then filling progressively higher energy orbitals. Web start typing, then use the up and down arrows to select an option from the list.? Orbitals are generally drawn as three.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams For Polyatomic Molecules
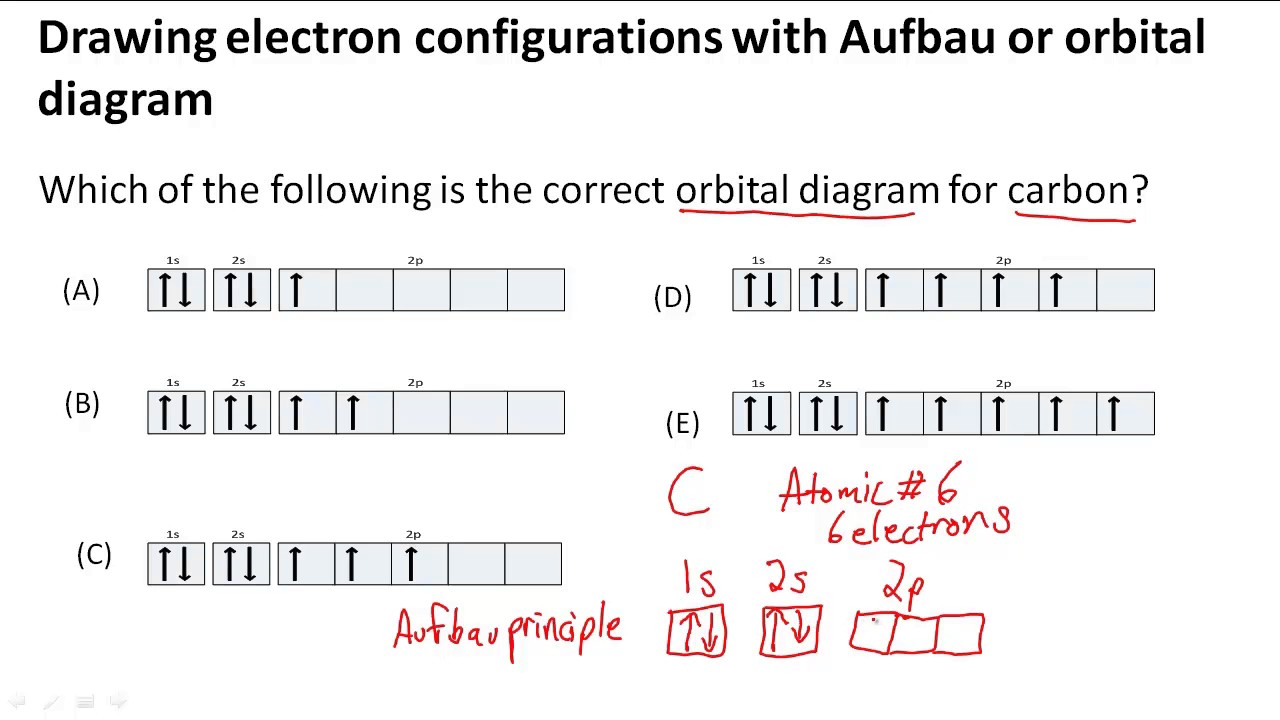
Drawing electron configurations with Aufbau/orbital diagram YouTube

How To Do Orbital Diagrams exatin.info

Atomic orbitals explained polizhuge

Draw The Orbital Diagram alternator
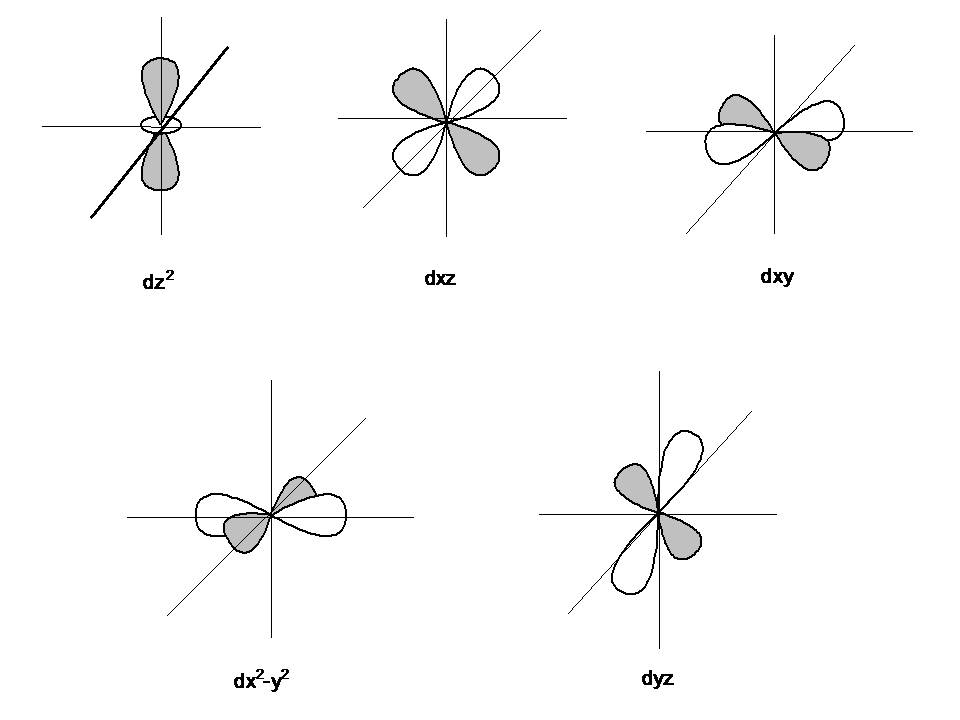
How To Draw Orbitals Deepcontrol3

How to Draw Shapes of Orbitals

How To Draw Orbitals Deepcontrol3
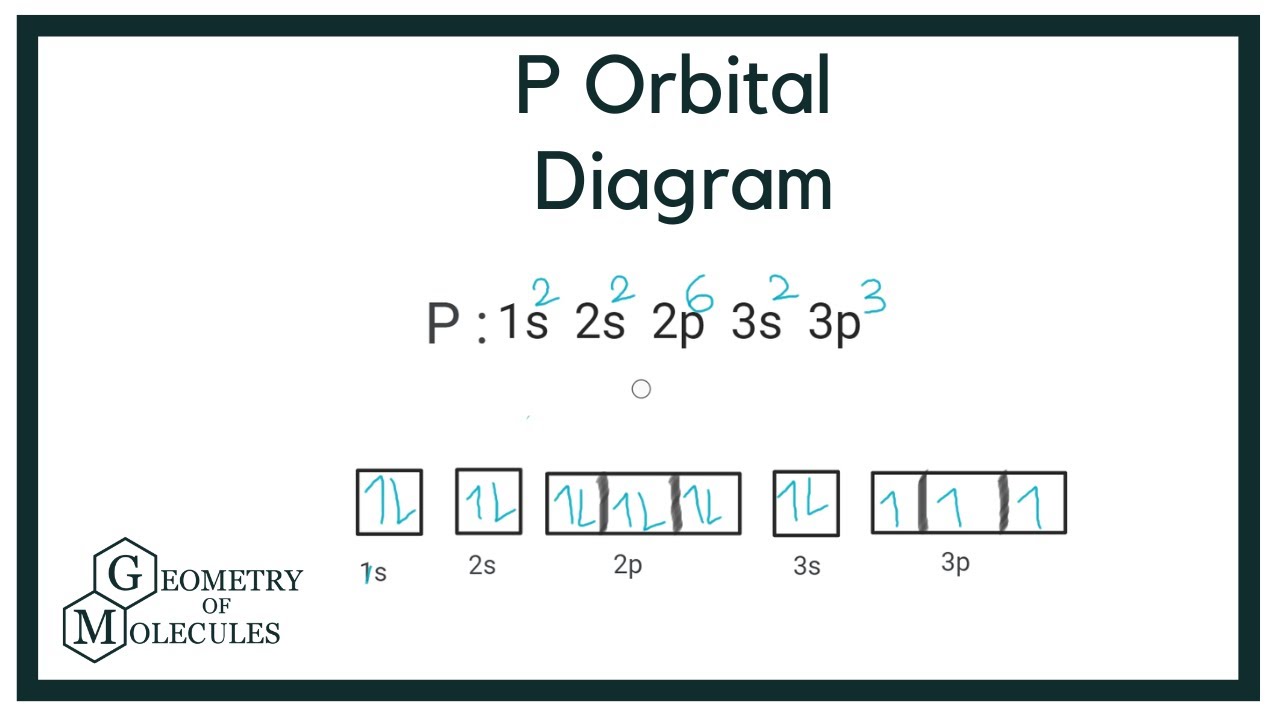
P Orbital diagram How to draw orbital diagram of Phosphorus YouTube

how to draw shapes of d orbitals elliottlyde
This Is Sometimes Called The Bohr, Or The ‘Solar System’, Model.
Carbon (Atomic Number 6) Has Six Electrons.
Web Molecular Orbital Diagrams.
Web For A Given Atom, The S Orbitals Also Become Higher In Energy As N Increases Because Of Their Increased Distance From The Nucleus.
Related Post: