Hep2 Cell Patterns
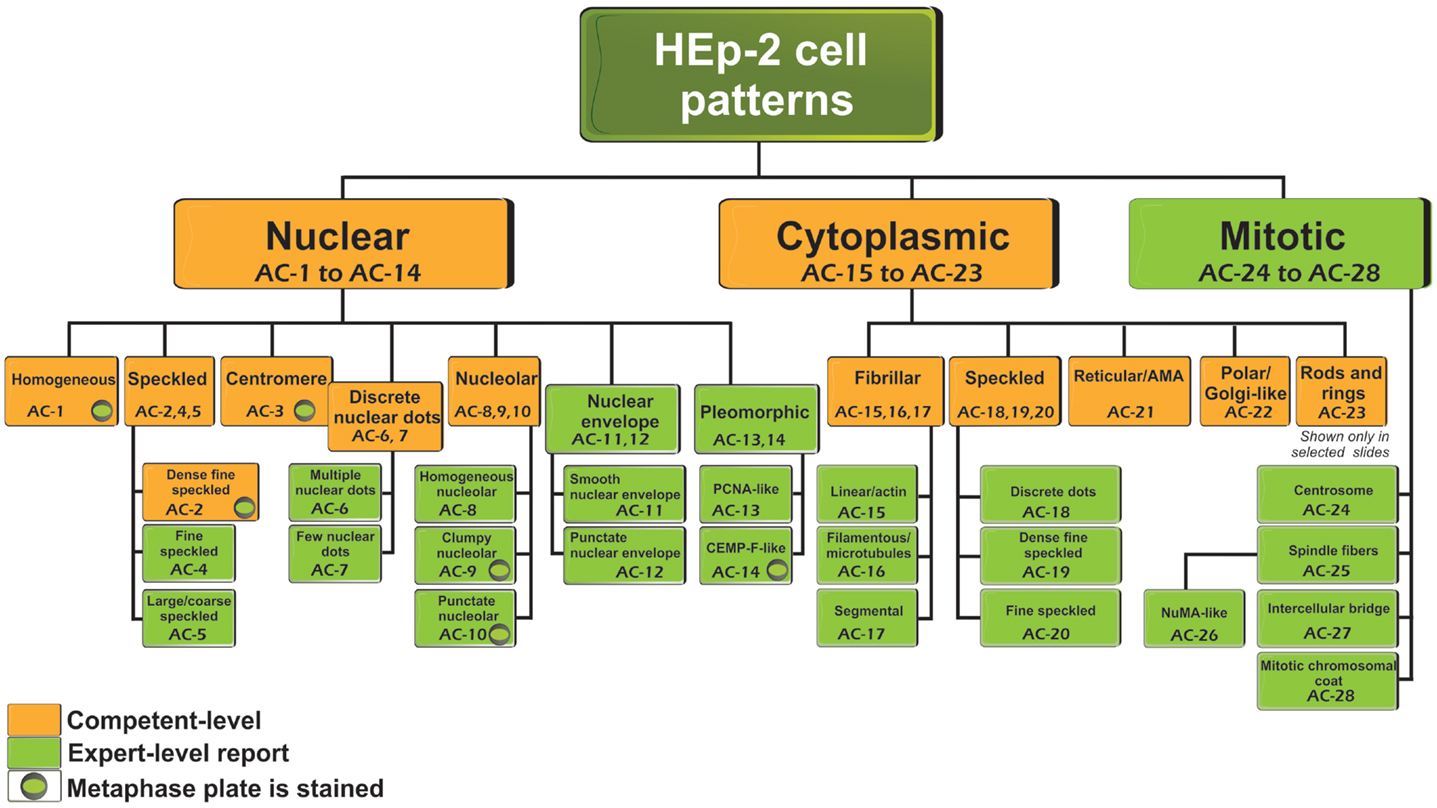
Hep2 Cell Patterns - International consensus on ana patterns. Web deep mutational scanning reveals that conserved proline codons at the 3′ end of the hepatitis b virus polymerase open reading frame stall ribosomes. The dichotomous outcome, negative or positive, is. Web patterns are categorized in three major groups (nuclear, cytoplasmic, and mitotic patterns) and each pattern has been defined and described in detail. Web icap was initiated as a workshop aiming to thoroughly discuss and to promote consensus regarding the richness and nuances of morphological patterns observed in the indirect. Negative (n = 1), nuclear (n = 15), cytoplasmic (n = 9),. Web patterns are categorized in three major groups (nuclear, cytoplasmic, and mitotic patterns) and each pattern has been defined and described in detail. Web icap was initiated as a workshop aiming to thoroughly discuss and to promote consensus regarding the richness and nuances of morphological patterns observed in the indirect. International consensus on ana patterns. Negative (n = 1), nuclear. The dichotomous outcome, negative or positive, is. Web patterns are categorized in three major groups (nuclear, cytoplasmic, and mitotic patterns) and each pattern has been defined and described in detail. International consensus on ana patterns. Web deep mutational scanning reveals that conserved proline codons at the 3′ end of the hepatitis b virus polymerase open reading frame stall ribosomes. Negative. The dichotomous outcome, negative or positive, is. International consensus on ana patterns. Web deep mutational scanning reveals that conserved proline codons at the 3′ end of the hepatitis b virus polymerase open reading frame stall ribosomes. Web patterns are categorized in three major groups (nuclear, cytoplasmic, and mitotic patterns) and each pattern has been defined and described in detail. Negative. Negative (n = 1), nuclear (n = 15), cytoplasmic (n = 9),. Web icap was initiated as a workshop aiming to thoroughly discuss and to promote consensus regarding the richness and nuances of morphological patterns observed in the indirect. International consensus on ana patterns. Web deep mutational scanning reveals that conserved proline codons at the 3′ end of the hepatitis. The dichotomous outcome, negative or positive, is. Negative (n = 1), nuclear (n = 15), cytoplasmic (n = 9),. Web patterns are categorized in three major groups (nuclear, cytoplasmic, and mitotic patterns) and each pattern has been defined and described in detail. Web icap was initiated as a workshop aiming to thoroughly discuss and to promote consensus regarding the richness. The dichotomous outcome, negative or positive, is. Web icap was initiated as a workshop aiming to thoroughly discuss and to promote consensus regarding the richness and nuances of morphological patterns observed in the indirect. Negative (n = 1), nuclear (n = 15), cytoplasmic (n = 9),. Web deep mutational scanning reveals that conserved proline codons at the 3′ end of. Negative (n = 1), nuclear (n = 15), cytoplasmic (n = 9),. Web patterns are categorized in three major groups (nuclear, cytoplasmic, and mitotic patterns) and each pattern has been defined and described in detail. International consensus on ana patterns. Web icap was initiated as a workshop aiming to thoroughly discuss and to promote consensus regarding the richness and nuances. Web deep mutational scanning reveals that conserved proline codons at the 3′ end of the hepatitis b virus polymerase open reading frame stall ribosomes. Negative (n = 1), nuclear (n = 15), cytoplasmic (n = 9),. International consensus on ana patterns. The dichotomous outcome, negative or positive, is. Web icap was initiated as a workshop aiming to thoroughly discuss and. Web deep mutational scanning reveals that conserved proline codons at the 3′ end of the hepatitis b virus polymerase open reading frame stall ribosomes. Web patterns are categorized in three major groups (nuclear, cytoplasmic, and mitotic patterns) and each pattern has been defined and described in detail. Negative (n = 1), nuclear (n = 15), cytoplasmic (n = 9),. International. International consensus on ana patterns. Web patterns are categorized in three major groups (nuclear, cytoplasmic, and mitotic patterns) and each pattern has been defined and described in detail. Negative (n = 1), nuclear (n = 15), cytoplasmic (n = 9),. Web deep mutational scanning reveals that conserved proline codons at the 3′ end of the hepatitis b virus polymerase open. Negative (n = 1), nuclear (n = 15), cytoplasmic (n = 9),. Web patterns are categorized in three major groups (nuclear, cytoplasmic, and mitotic patterns) and each pattern has been defined and described in detail. International consensus on ana patterns. Web deep mutational scanning reveals that conserved proline codons at the 3′ end of the hepatitis b virus polymerase open reading frame stall ribosomes.
The surface of six Hep2 cell patterns. Download Scientific Diagram
ANA HEp2 Fluorescent Test System Immuno Concepts

2. IFA Pattern recognition & HEp2 cell components YouTube

Representative images of selected major HEp2 cell patterns. (A

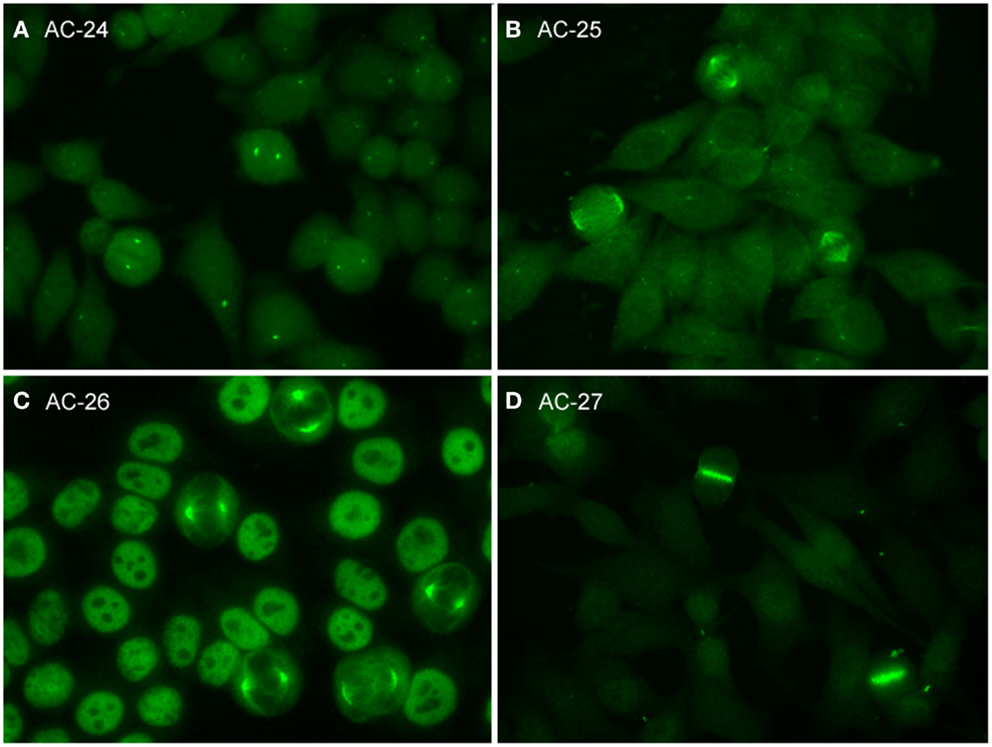
HEp2 cell classification in indirect immunofluorescence images
Frontiers Report of the First International Consensus on Standardized

Figure 1 from The Clinical Significance of the Dense Fine Speckled
Frontiers Report of the First International Consensus on Standardized

Rheumatology Diagnostics Indirect Immunofluorescence Tests (IIF assays

Portrait of the HEp2 cell, the pet of immunofluorescence professionals
Web Icap Was Initiated As A Workshop Aiming To Thoroughly Discuss And To Promote Consensus Regarding The Richness And Nuances Of Morphological Patterns Observed In The Indirect.
The Dichotomous Outcome, Negative Or Positive, Is.
Related Post: