Hemophilia Hereditary Pattern
Hemophilia Hereditary Pattern - Clotting factors are proteins in your blood. Web hemophilia is a rare, inherited blood disorder that causes your blood to clot less, which results in an increased risk of bleeding or bruising. Sometimes, there are carrier females in the family, but no affected boys, just by chance. Congenital hemophilia is classified by the type of clotting factor that's low. Web hemophilia is usually inherited, meaning a person is born with the disorder (congenital). The xs and ys of hemophilia. It results from one of over 1000 known pathogenic variants in the fix gene, f9; These gene variations do not typically produce enough blood. Both hemophilia a and b are inherited in the same way, because both the genes for factor viii and factor ix are located on the x chromosome (chromosomes are structures within the body’s cells that contain the genes). A person’s sex binary (male or female) is determined by the pairing of two sex chromosomes (x and y) inherited from their parents. Hemophilia is a condition that affects the blood’s ability to coagulate, or. People who have severe hemophilia have spontaneous bleeding into the joints and muscles. Congenital hemophilia is classified by the type of clotting factor that's low. Both hemophilia a and b result from factor viii and factor ix protein deficiency or dysfunction, respectively, and is characterized by prolonged and. People who have hemophilia often have longer bleeding after an injury or surgery. Web hemophilia encompasses a group of inherited ailments that alter the body's normal blood coagulation. These gene variations do not typically produce enough blood. Hemophilias are common hereditary bleeding disorders caused by deficiencies of either clotting factor viii or ix. Hemophilia happens because your body doesn’t make. The extent of factor deficiency determines the probability and severity of bleeding. A hereditary hemorrhagic disorder resulting from a congenital deficit or scarcity of factor viii, hemophilia a, which is known as classical hemophilia, manifests as protracted and excessive bleeding either spontaneously or. In males (who have only one x chromosome), one altered copy of the gene in each cell. Hemophilia happens because your body doesn’t make enough protein (clotting factors) to help your blood form clots. Web hemophilia a, also called factor viii deficiency, and hemophilia b, also called factor ix deficiency, are inherited on the x chromosome in an autosomal recessive pattern. Both hemophilia a and b result from factor viii and factor ix protein deficiency or dysfunction,. Web hemophilia is a rare, inherited blood disorder that causes your blood to clot less, which results in an increased risk of bleeding or bruising. Hemophilia is a condition that affects the blood’s ability to coagulate, or. Web since the f8 and f9 genes are on the x chromosome, hemophilia is inherited differently in males and females (see inheritance, below).. People with this disorder experience prolonged bleeding following an injury, surgery, or having a tooth pulled. People who have severe hemophilia have spontaneous bleeding into the joints and muscles. The age of diagnosis and frequency of bleeding episodes are related to the level of factor viii clotting activity. The most common type is hemophilia a, associated with a low level. Both hemophilia a and b result from factor viii and factor ix protein deficiency or dysfunction, respectively, and is characterized by prolonged and excessive bleeding after minor trauma or sometimes even spontaneously. People who have severe hemophilia have spontaneous bleeding into the joints and muscles. People who have hemophilia often have longer bleeding after an injury or surgery. This is. In males (who have only one x chromosome), one altered copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition. In the majority of cases, the bleeding disorder is inherited from a parent to a child. Web hemophilia, which means love (philia) of blood (hemo), is the most common severe hereditary hemorrhagic disorder. Hemophilias are common hereditary. People with hemophilia can live full lives and enjoy most of the activities that other people do. In males (who have only one x chromosome), one altered copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition. Web hemophilia a is characterized by deficiency in factor viii clotting activity that results in prolonged bleeding after injuries, tooth. Web learn more about the inheritance pattern for hemophilia. Web hemophilia encompasses a group of inherited ailments that alter the body's normal blood coagulation. It results from one of over 1000 known pathogenic variants in the fix gene, f9; 2 such a male is termed hemizygous and has the full phenotype of the disease. Web another form of the disorder,. It results from one of over 1000 known pathogenic variants in the fix gene, f9; Bleeding into deep tissues or joints usually develops within hours of trauma. A person’s sex binary (male or female) is determined by the pairing of two sex chromosomes (x and y) inherited from their parents. Web hemophilia is usually an inherited bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot properly. Web hemophilia encompasses a group of inherited ailments that alter the body's normal blood coagulation. These gene variations do not typically produce enough blood. Web hemophilia is usually inherited, meaning a person is born with the disorder (congenital). Web hemophilia a is characterized by deficiency in factor viii clotting activity that results in prolonged bleeding after injuries, tooth extractions, or surgery, and delayed or recurrent bleeding prior to complete wound healing. Web hemophilia a, also called factor viii deficiency, and hemophilia b, also called factor ix deficiency, are inherited on the x chromosome in an autosomal recessive pattern. Even though hemophilia runs in families, some families have no prior history of family members with hemophilia. People who have severe hemophilia have spontaneous bleeding into the joints and muscles. A hereditary hemorrhagic disorder resulting from a congenital deficit or scarcity of factor viii, hemophilia a, which is known as classical hemophilia, manifests as protracted and excessive bleeding either spontaneously or. Web hemophilia, which means love (philia) of blood (hemo), is the most common severe hereditary hemorrhagic disorder. Hemophilia is a bleeding disorder that slows down the blood clotting process. People with hemophilia can live full lives and enjoy most of the activities that other people do. The age of diagnosis and frequency of bleeding episodes are related to the level of factor viii clotting activity.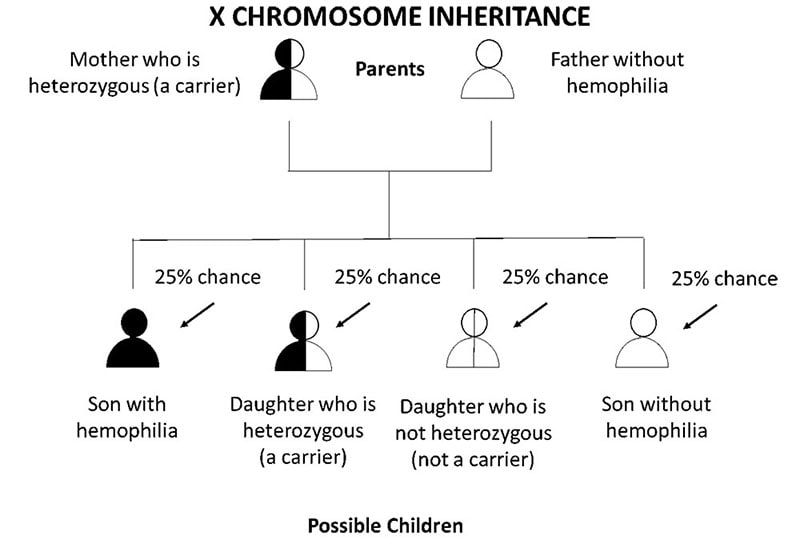
How Hemophilia is Inherited CDC
Hemophilia Causes, symptoms & treatment Live Science
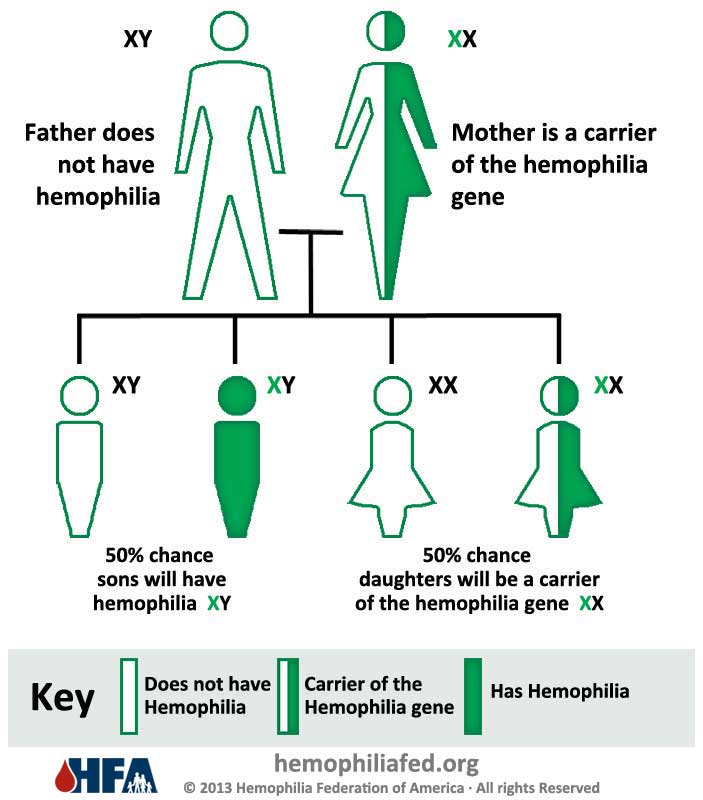
Inheritance Pattern of Hemophilia Hemophilia Federation of America

Hemophilia Causes, Signs, Symptoms, Types, Inheritance, Treatment

Hemophilia Causes, Signs, Symptoms, Types, Inheritance, Treatment

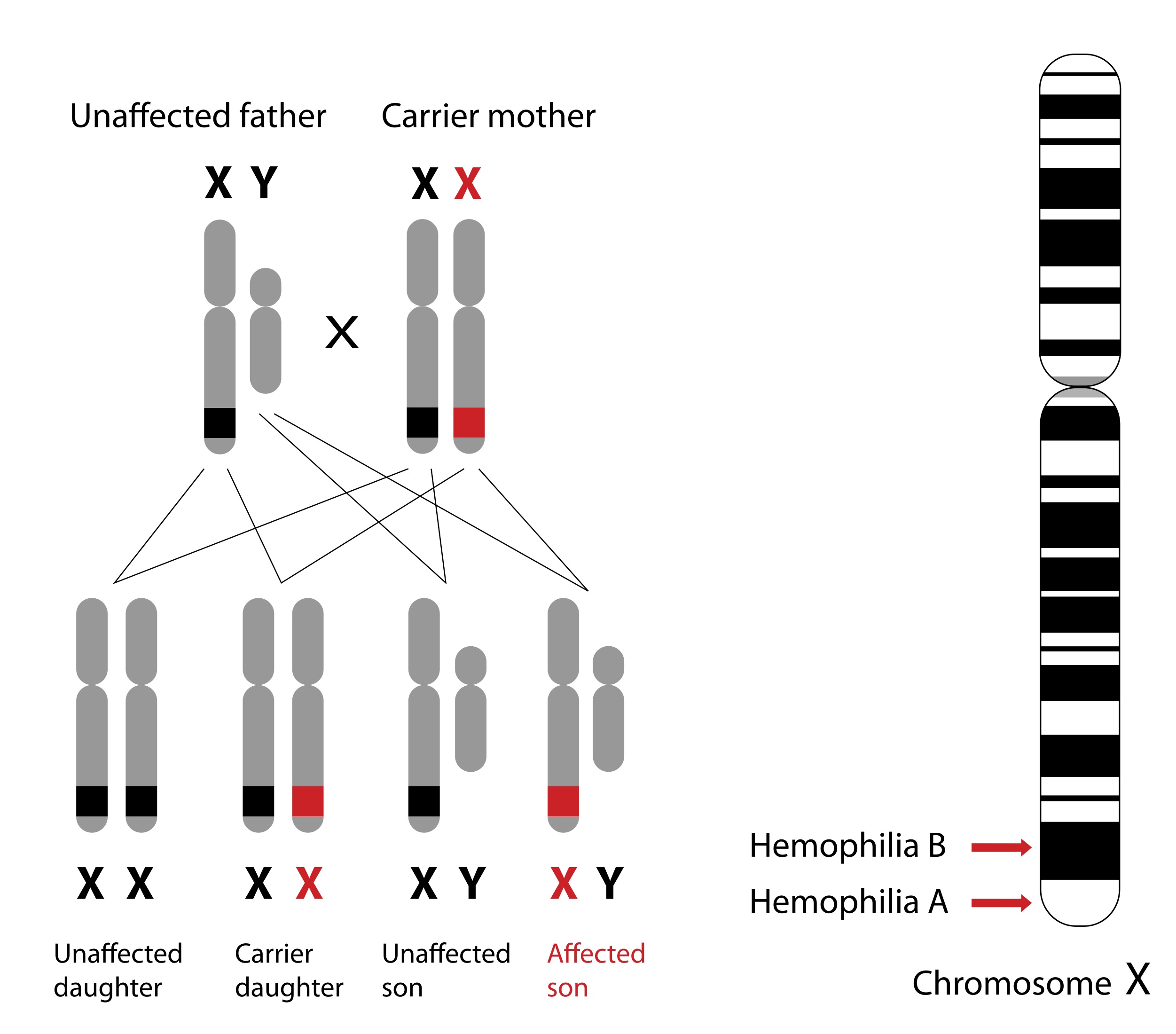
Hemophilia Inheritance Patterns X Chromosomes Mutation
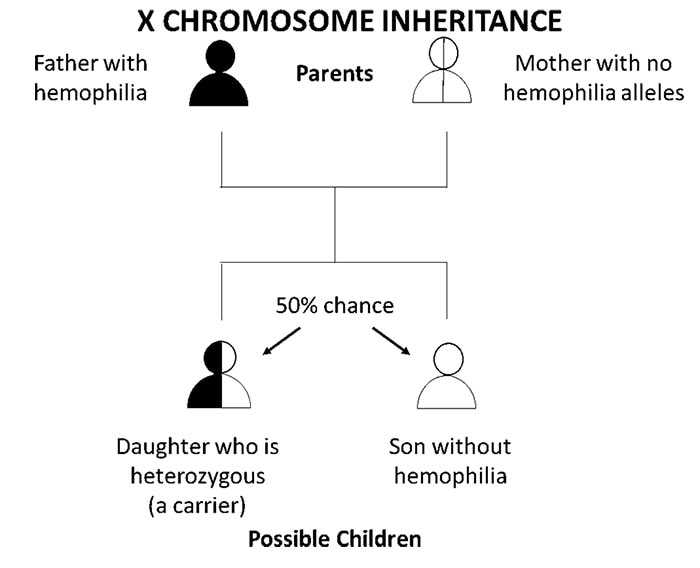
How Hemophilia is Inherited CDC

Hemophilia Inheritance Patterns X Chromosomes Mutation
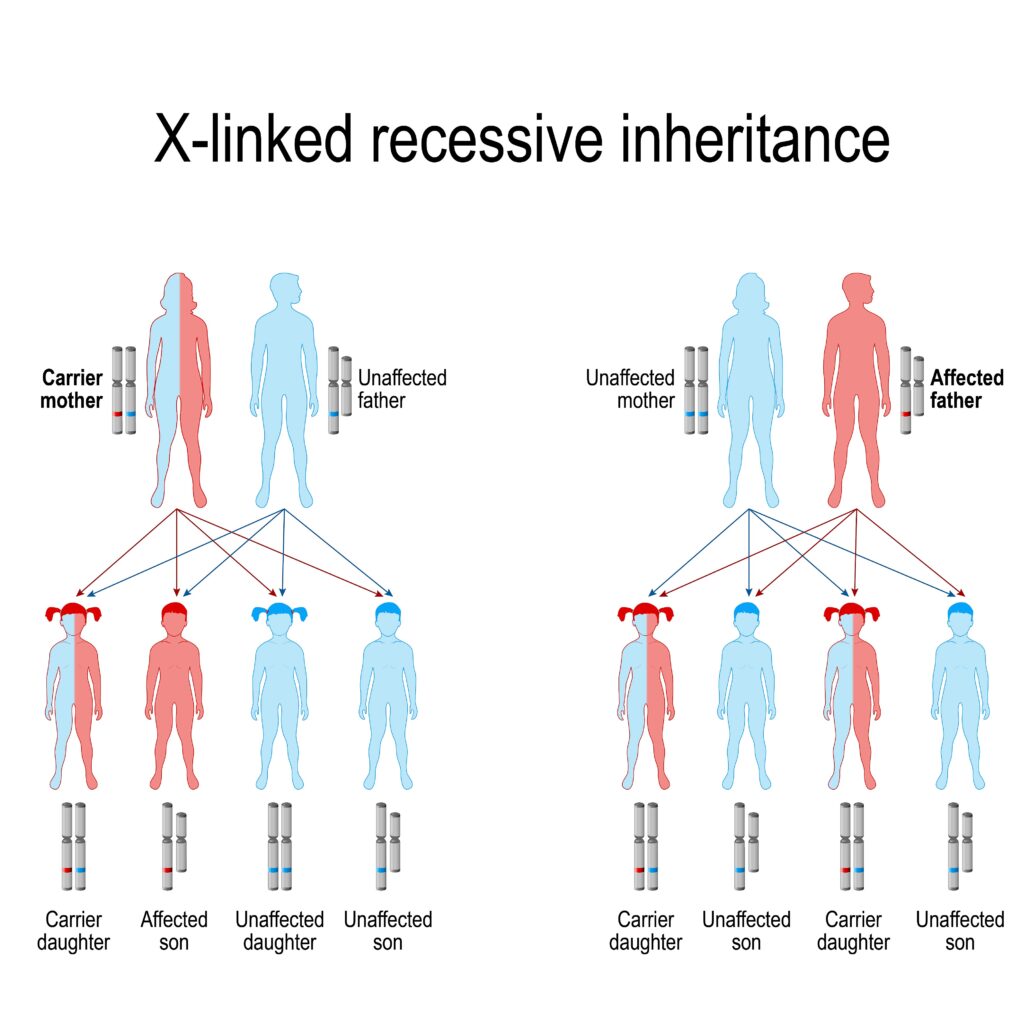
What causes Haemophilia? The Haemophilia Society
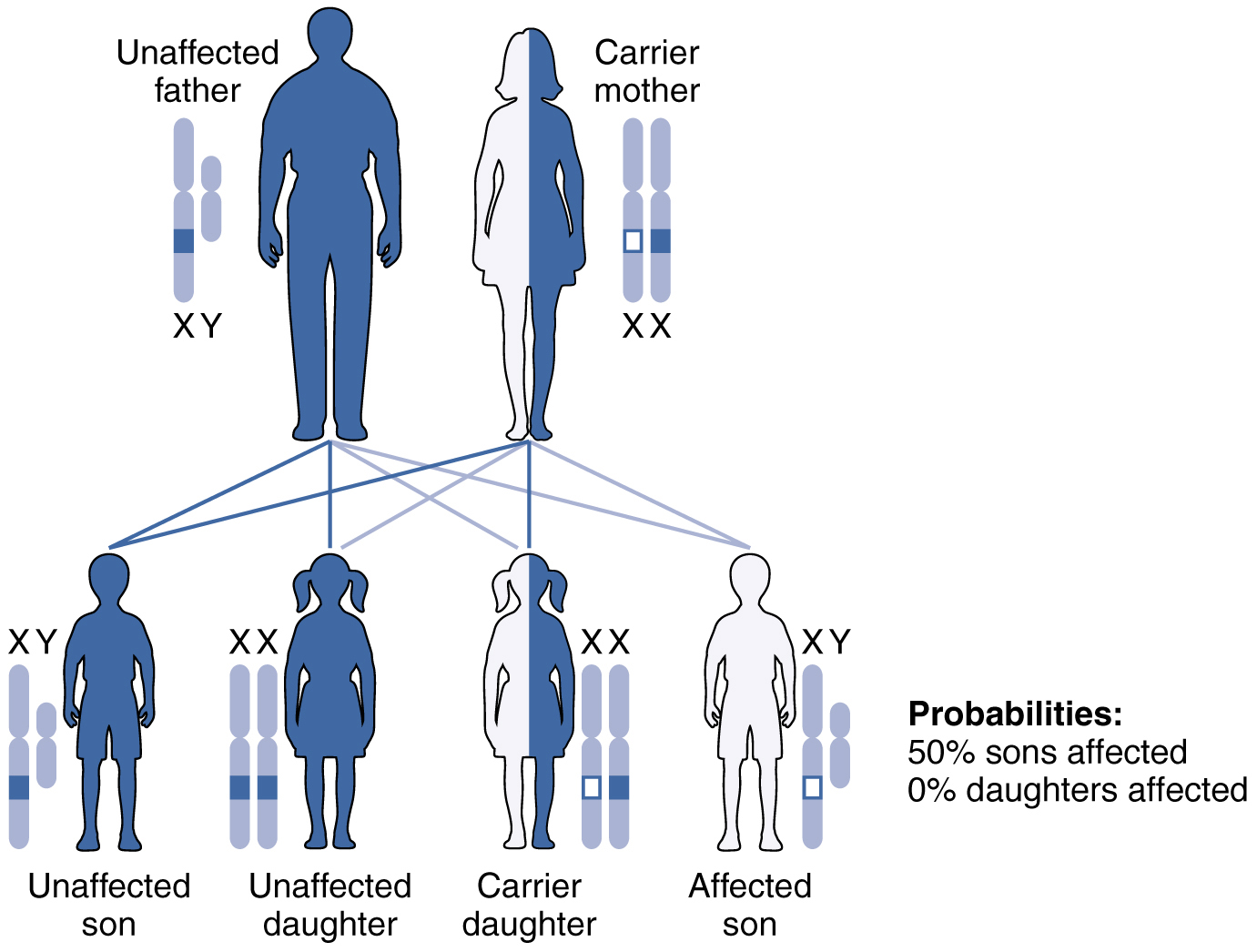
Hemophilia a sexlinked disorder Principles of Biology
Hemophilia Is A Bleeding Disorder That Slows The Blood Clotting Process.
Hemophilia Is A Condition That Affects The Blood’s Ability To Coagulate, Or.
People With This Disorder Experience Prolonged Bleeding Following An Injury, Surgery, Or Having A Tooth Pulled.
Web It Almost Always Is Inherited (Passed Down) From A Parent To A Child.
Related Post: