Fanned Pattern Residual Plot
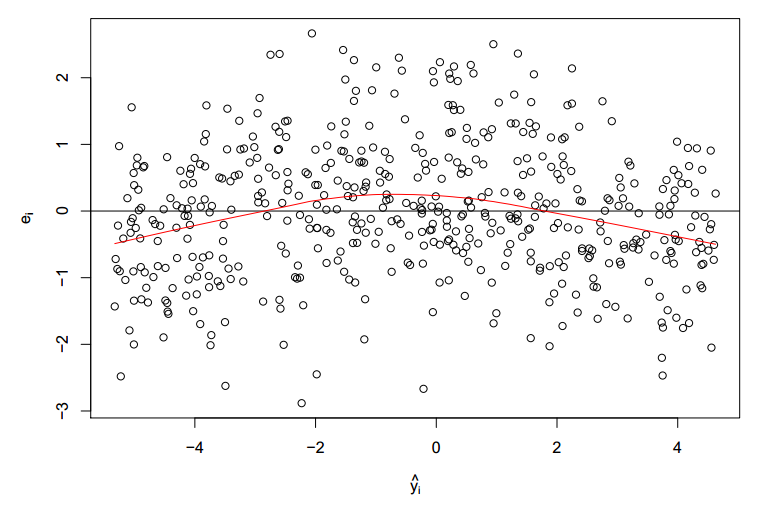
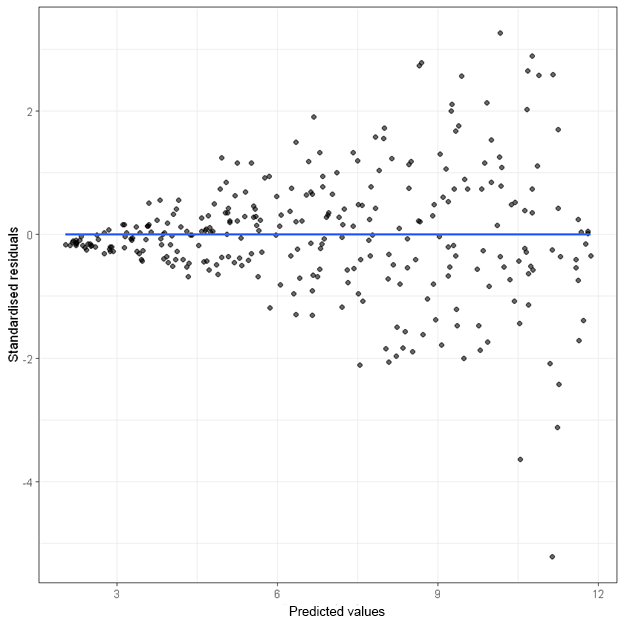
Fanned Pattern Residual Plot - It is a scatter plot of residuals on the y axis and fitted values (estimated. Web obviously there are some bad signs in this plot: Web when some outcome data are censored, standard residual plots become less appropriate. The fanned pattern indicates that the linear model is not appropriate. Web in this section, we learn how to use residuals versus fits (or predictor) plots to detect problems with our formulated regression model. A residual plot is a scatterplot that displays the residuals on the vertical axis and the independent variable on the horizontal axis. Web use the residuals versus fits plot to verify the assumption that the residuals are randomly distributed and have constant variance. Learn how to use residuals vs. In a “bad” residual plot, the. Web in statistics, resids (short for residuals) are the differences between the predicted values and the actual values of the response variable. Web the fanned pattern indicates that the linear model is not appropriate. Web when some outcome data are censored, standard residual plots become less appropriate. Web obviously there are some bad signs in this plot: The following are examples of residual plots when (1) the assumptions are met, (2) the homoscedasticity assumption is violated and (3) the linearity assumption. The. The following are examples of residual plots when (1) the assumptions. Web when conducting a residual analysis, a residuals versus fits plot is the most frequently created plot. Ideally, the points should fall randomly on both. In a “bad” residual plot, the. Web use the residuals versus fits plot to verify the assumption that the residuals are randomly distributed and. The fanned pattern indicates that the linear model is not appropriate. Web when some outcome data are censored, standard residual plots become less appropriate. In a “bad” residual plot, the. The scattered residuals plot indicates an appropriate linear model. Here, we develop a new procedure for producing residual plots for. In a “bad” residual plot, the. Web when conducting a residual analysis, a residuals versus fits plot is the most frequently created plot. Web in this section, we learn how to use residuals versus fits (or predictor) plots to detect problems with our formulated regression model. Web in statistics, resids (short for residuals) are the differences between the predicted values. The scattered residuals plot indicates an appropriate linear model. Web use the residuals versus fits plot to verify the assumption that the residuals are randomly distributed and have constant variance. It is a scatter plot of residuals on the y axis and fitted values (estimated. Web a residual plot is an essential tool for checking the assumption of linearity and. Many points fall outside the confidence bands and there is a distinctive pattern to the residuals. The fanned pattern indicates that the linear model is not appropriate. The following are examples of residual plots when (1) the assumptions are met, (2) the homoscedasticity assumption is violated and (3) the linearity assumption. In a “bad” residual plot, the. It is a. Web the fanned pattern indicates that the linear model is not appropriate. Web in a “good” residual plot, the residuals are randomly scattered about zero with no systematic increase or decrease in variance. The fanned pattern indicates that the linear model is not appropriate. Residual plots help us to determine. Web when conducting a residual analysis, a residuals versus fits. Web use the residuals versus fits plot to verify the assumption that the residuals are randomly distributed and have constant variance. In a “bad” residual plot, the. Web the fanned pattern indicates that the linear model is not appropriate. Web when conducting a residual analysis, a residuals versus fits plot is the most frequently created plot. Web in statistics, resids. Web when conducting a residual analysis, a residuals versus fits plot is the most frequently created plot. Learn how to use residuals vs. A residual plot is a scatterplot that displays the residuals on the vertical axis and the independent variable on the horizontal axis. Web in this section, we learn how to use residuals versus fits (or predictor) plots. The following are examples of residual plots when (1) the assumptions. Web use the residuals versus fits plot to verify the assumption that the residuals are randomly distributed and have constant variance. Web the fanned pattern indicates that the linear model is not appropriate. Learn how to use residuals vs. The following are examples of residual plots when (1) the. Web in this section, we learn how to use residuals versus fits (or predictor) plots to detect problems with our formulated regression model. Web a residual plot is an essential tool for checking the assumption of linearity and homoscedasticity. Here, we develop a new procedure for producing residual plots for. In a “bad” residual plot, the. Web obviously there are some bad signs in this plot: Learn how to use residuals vs. Many points fall outside the confidence bands and there is a distinctive pattern to the residuals. The fanned pattern indicates that the linear model is not appropriate. The model's predicting power increases as the values of the explanatory variable increases. A residual plot is a scatterplot that displays the residuals on the vertical axis and the independent variable on the horizontal axis. Web in statistics, resids (short for residuals) are the differences between the predicted values and the actual values of the response variable. Ideally, the points should fall randomly on both. Web in a “good” residual plot, the residuals are randomly scattered about zero with no systematic increase or decrease in variance. Web the fanned pattern indicates that the linear model is not appropriate. The following are examples of residual plots when (1) the assumptions. Web when conducting a residual analysis, a residuals versus fits plot is the most frequently created plot.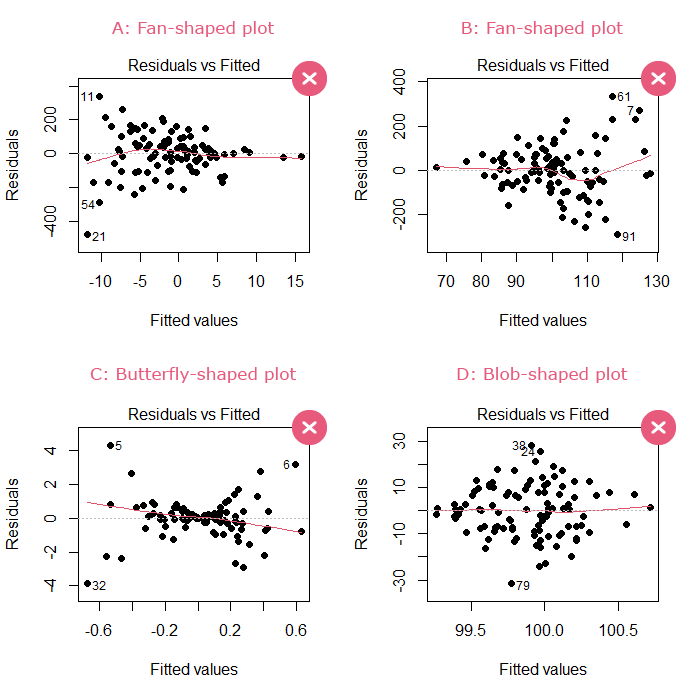
Understand Linear Regression Assumptions QUANTIFYING HEALTH
Several types of residual plots — residual_plots • metan
Residual Diagnostics Residual Plot Linear Regression

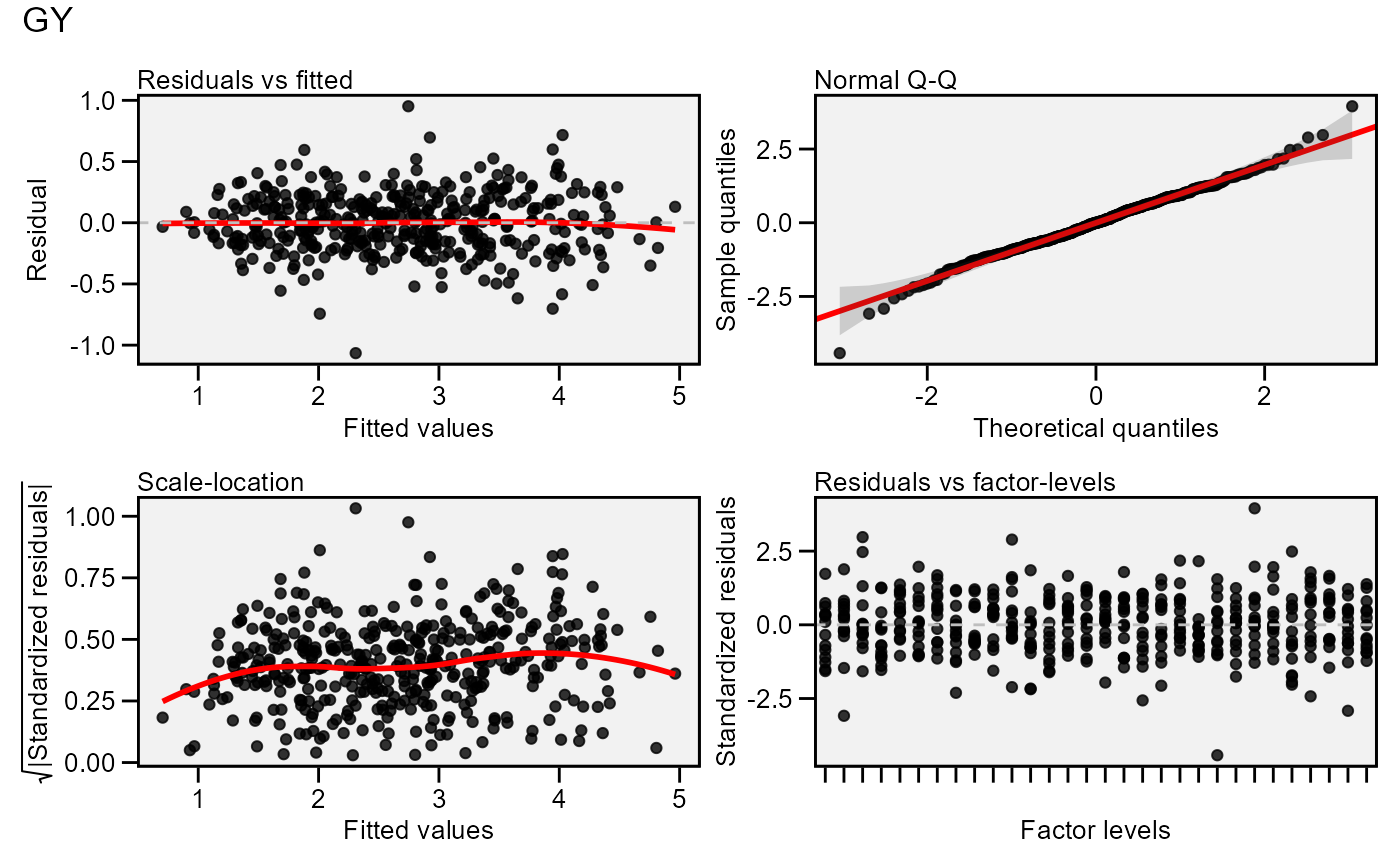
Residual plots under the final model. Top plot is a plot of residuals

Residual Plot Patterns

The best way to Develop a Residual Plot in R StatsIdea Learning
Residual Plots and Assumption Checking StatsNotebook Simple

How to Create a Residual Plot in R Statology
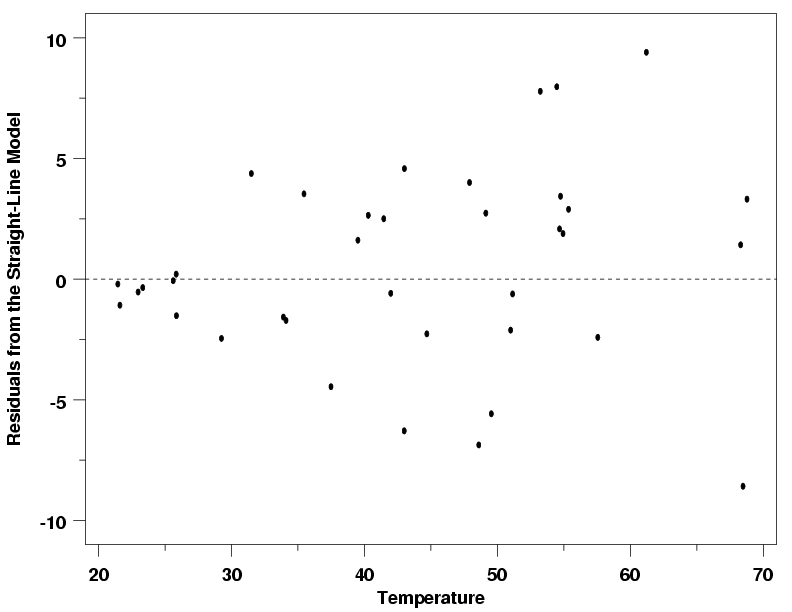
How To Make A Residual Plot Slide Course

Residual plots for VMS Four in one residual plots are drawn to check
Residual Plots Help Us To Determine.
Web When Some Outcome Data Are Censored, Standard Residual Plots Become Less Appropriate.
Web Use The Residuals Versus Fits Plot To Verify The Assumption That The Residuals Are Randomly Distributed And Have Constant Variance.
The Following Are Examples Of Residual Plots When (1) The Assumptions Are Met, (2) The Homoscedasticity Assumption Is Violated And (3) The Linearity Assumption.
Related Post: